go路由httprouter中的压缩字典树算法图解及c++实现
go路由httprouter中的压缩字典树算法图解及c++实现
@
前言
准备从嵌入式往go后端转,今年准备学习一下gin框架,决定先从这个轻量级的路由请求器着手,本文讲讲它用到的压缩字典树算法。
httprouter简介
HttpRouter是一个Go编写的轻量级的高性能Http请求路由器(也可称为多路选择器multiplexer简称mux)
与Go的net/http包的默认mux不同,该路由器支持路由中的变量与请求方法进行匹配,同时具有很好的伸缩性。
该路由具有高性能的同时,也优化了内存的占用,即是是很长的路径和大量的路径,他都能很好的扩展,采用压缩字典树(基数树)结构实现高效的匹配。
压缩字典树
概念
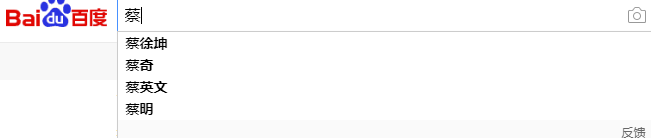
压缩字典树,是trie树的一种,也称单词查找树、前缀树,善于进行字符串的检索、取字符串最长公共前缀、以及排序,常应用在搜索引擎中例如百度输入蔡可能自动弹出能匹配到的单词出来.
压缩tire和标准trie最大的不同点就节点的数量与插入字符串的个数成正比,而不是与字符串的长度成正比,所以当字符串数量越来越多,越密集且相似度极高的情况下,会退化成标准trie树。
下面分别是/,/bear,/bell,/bid,/bull,/buy,/sell,/stock,/stop 的标准tire 和压缩 tire


插入操作
下面图解一串子串插入压缩trie过程,/,/serach,/support,/blog , 在httprouter上截的一段例子,我们只插到/blog

插入/

插入/serach

插入/support

插入/blog

查询操作
查询比较简单,后面看代码也比较快。
1、先找共同前缀。
2、再找目录。
3、循环上面两步,知道当前path相等。
c+++实现
这里注册了4个路径的回调函数,addRoute 即是插入操作,handler即是查询。
// httprouter.hpp
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
namespace httprouter{
typedef std::function<void(void)> handler_t;
typedef struct _tree_node {
std::string path;
std::string indices;
std::vector<std::shared_ptr<struct _tree_node>> children;
handler_t handle;
}tree_node_t;
class node
{
public:
//! ctor
node();
//! dtor
~node(void);
//! copy ctor
node(const node&) = delete;
//! assignment operator
node& operator=(const node&) = delete;
//! addRouter adds a node with the given handle to the path
//! Not concurrency-safe!
void addRoute(std::string path, handler_t handle);
//! get path handler
handler_t handler(std::string path);
private:
void insertChild(tree_node_t* node, std::string& path, handler_t handle);
private:
std::shared_ptr<tree_node_t> node_;
};
}
// httprouter.cpp
#include <algorithm>
#include "httprouter.hpp"
using namespace httprouter;
node::node()
:node_(new tree_node_t{
path: "",
indices: "",
children: {},
handle: nullptr,
})
{
}
node::~node(){
}
void node::addRoute(std::string path, handler_t handle) {
std::string fullPath = path;
auto node = node_;
// no-empty tree
if (node->path.size() > 0 || node->children.size() > 0) {
while (true) {
bool have_indices = false;
//find the longest common prefix.
std::size_t i = 0;
auto max = std::min(node->path.size(), path.size());
for (; i < max && path[i] == node->path[i];) {
i++;
}
// Split edge
if (i < node->path.size()) {
auto child = std::shared_ptr<tree_node_t>(new tree_node_t{
path : std::string(node->path.c_str() + i),
indices : node->indices,
children : std::move(node->children),
handle : node->handle,
});
node->children = std::vector<std::shared_ptr<tree_node_t>>{ child };
node->indices = std::string(node->path.c_str() + i, 1);
node->path = std::string(path.c_str(), i);
node->handle = nullptr;
}
// make new node a child of this node
if (i < path.size()) {
path = std::string(path.c_str() + i);
char ch = path[0];
// Check if a child with the next path byte exists
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < node->indices.size(); i++) {
if (ch == node->indices[i]) {
//i = node.incrementChildPrio(i);
node = node->children[i];
have_indices = true;
break;
}
}
if (have_indices) {
continue;
}
//otherwise insert it
if (ch != ':' && ch != '*') {
node->indices += ch;
auto child = std::shared_ptr<tree_node_t>(new tree_node_t{
path : "",
indices : "",
children : {},
handle : nullptr,
});
node->children.push_back(child);
node = child;
}
insertChild(node.get(), path, handle);
return;
}
else if (i == path.size()) {
if (node->handle) {
printf("error ! handle already exists.");
exit(1);
}
node->handle = handle;
}
return;
}
}
else { // Empty tree
insertChild(node.get(), path, handle);
}
}
void node::insertChild(tree_node_t* node, std::string& path, handler_t handle) {
node->path = std::string(path.c_str());
node->handle = handle;
}
handler_t node::handler(std::string path) {
auto node = node_;
while (true) {
if (path.size() > node->path.size()) {
if (std::string(path.c_str(), node->path.size()) == node->path) {
path = std::string(path.c_str() + node->path.size());
}
char ch = path[0];
for (std::size_t i = 0; i < node->indices.size(); i++) {
if (ch == node->indices[i]) {
node = node->children[i];
continue;
}
}
// handle wildcard child
// fix me
}
else if (path == node->path) {
return node->handle;
}
}
}
//main.cpp
#include "httprouter.hpp"
#include <iostream>
void hello1() {
std::cout << "hello1" << std::endl;
}
void hello2() {
std::cout << "hello2" << std::endl;
}
void hello3() {
std::cout << "hello3" << std::endl;
}
void hello4() {
std::cout << "hello4" << std::endl;
}
void hello5() {
std::cout << "hello5" << std::endl;
}
int main() {
httprouter::node no;
no.addRoute("/", hello1);
no.addRoute("/serach/", hello2);
no.addRoute("/support/", hello3);
no.addRoute("/blog/", hello4);
no.handler("/")();
no.handler("/serach/")();
no.handler("/support/")();
no.handler("/blog/")();
}
结果:

节点信息:

go路由httprouter中的压缩字典树算法图解及c++实现的更多相关文章
- Android 中图片压缩分析(上)
作者: shawnzhao,QQ音乐技术团队一员 一.前言 在 Android 中进行图片压缩是非常常见的开发场景,主要的压缩方法有两种:其一是质量压缩,其二是下采样压缩. 前者是在不改变图片尺寸的情 ...
- Django的视图函数和路由系统中一些没有用过的小点
1.request对象 print("返回用户访问的url,但是不包括域名",request.path_info) print("返回请求的方法,全大写",re ...
- 【Redis源代码剖析】 - Redis内置数据结构之压缩字典zipmap
原创作品,转载请标明:http://blog.csdn.net/Xiejingfa/article/details/51111230 今天为大家带来Redis中zipmap数据结构的分析,该结构定义在 ...
- python中列表和字典常用方法和函数
Python列表函数&方法 Python包含以下函数: 序号 函数 1 cmp(list1, list2)比较两个列表的元素 2 len(list)列表元素个数 3 max(list)返回列表 ...
- 在ASP.NET中实现压缩多个文件为.zip文件,实现批量下载功能 (转载并优化处理篇)
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/yanlele424/article/details/6895986 这段时间一直在做一个网站,其中遇到了一个问题,就是在服务器端压缩多个服务器端的文件 ...
- OC中如何把字典中的数据拼接成url字符串
在使用objective-c语言开发iOS应用中,会向服务器通过URL请求一些数据,因此对URL的拼接肯定少不了.而在iOS中,我们一般是通过将字典中的数据拼接成我们要请求的URL字符串,那这个是怎么 ...
- 使用secureCRT和Telnet将文件压缩导出到Ubuntu中,到Ubuntu中加压缩发现:tar解压包的时候出现错误gzip: stdin: not in gzip format tar: Child returned status 1 tar: Error is not recoverable: exiting now
细节描述: 问题如题所示:查找博客园和CSDN上查找问题,得到问题解决方法大致如下: 1 修改解压缩命令: 由 tar zxvf software_package.tar.gz变为tar xvf so ...
- Linux中常用压缩打包工具
Linux中常用压缩打包工具 压缩打包是常用的功能,在linux中目前常用的压缩工具有gzip,bzip2以及后起之秀xz.本文将介绍如下的工具常见压缩.解压缩工具以及打包工具tar. gzip2 直 ...
- iOS开发中的压缩以及解压
事实上,在iOS开发中,压缩与解压,我都是采用第三方框架SSZipArchive实现的 gitHub地址: https://github.com/ZipArchive/ZipArchive 上面有 ...
随机推荐
- 走近深度学习,认识MoXing:初识华为云ModelArts的王牌利器 — MoXing
[摘要] 本文为MoXing系列文章第一篇,主要介绍什么是MoXing,MoXing API的优势以及MoXing程序的基本结构. MoXing的概念 MoXing是华为云深度学习服务提供的网络模型开 ...
- Too many open files的四种解决办法
[摘要] Too many open files有四种可能:一 单个进程打开文件句柄数过多,二 操作系统打开的文件句柄数过多,三 systemd对该进程进行了限制,四 inotify达到上限. 领导见 ...
- go-channel处理高并发请求
目录 go-channel处理高并发请求 一.Channel简介 二.处理包并发请求 三.测试 1.测试工具 2.测试结果 go-channel处理高并发请求 最近看了一篇文章讲解怎样使用go-cha ...
- [TimLinux] 系统配置 CentOS7配置Samba
1. 安装软件 yum install -y samba samba-client samba-common 2. 配置用户 useradd tim passwd tim # 设置用户登录密码 smb ...
- k8s 开船记-触礁:四涡轮发动机撞坏3个引发502故障
(图片来自网络) 非常抱歉,这次开船触礁故障给您带来麻烦了,请您谅解. 在我们昨天发布 k8s 开船记首航博文后,有园友在评论中发来贺词——“泰坦尼克号出发了[狗头]”,借此吉言,今天船就触礁了,还好 ...
- Spring Boot 外部化配置(一)- Environment、ConfigFileApplicationListener
目录 前言 1.起源 2.外部化配置的资源类型 3.外部化配置的核心 3.1 Environment 3.1.1.ConfigFileApplicationListener 3.1.2.关联 Spri ...
- selenium处理弹窗
处理登录弹窗:https://www.cnblogs.com/TD1900/p/11938573.html #定位弹窗 ale = driver.switch_to.alert #处理方式 ale.a ...
- C语言每日一练——第7题
一.题目要求 已知数据文件in.dat中存有200个四位数,把这些数存到数组a中,编写函数jsVal(),其功能是:把千位数字和十位数字重新组成一个新的含有两位数字的数ab(新数的十位数字是原四位数的 ...
- 简单学习【1】——使用webpack
使用webpack webpack命令 webpack配置 第三方脚手架 1.webpack命令 webpack - h (webpack 所有的选项) webpack -v (查看webpack的版 ...
- CCF-CSP题解 201903-4 消息传递接口
求并行的各个进程,且进程内部顺序执行的情况下,会不会出现"死锁". 首先用\(%[^\n]\)将每个进程读入.最后过不了居然是因为\(str[\ ]\)开小了(悲喜交加.存储在\( ...
