Rendering Transparent 3D Surfaces in WPF with C#(转载)
Rendering Transparent 3D Surfaces in WPF with C#
The primary problems that arise when rendering semi-transparent 3d objects in Windows Presentation Foundation have to do with false z-buffer occlusions. Specifically, when a transparent surface or polygon is rendered, it sets the z-buffer depth values to block objects that are behind it from being rendered, even though they should show through the transparent layer.
In WPF with C#, the z-buffer is not accessible. So, it can not be disabled during transparent rendering. Instead, we must render the transparent objects last so that they are layered over the rest of the scene and the objects behind them show through.
Below, I have a program for the single code file that I used to generate the spinning, transparent tetrahedron shown above. The C# project that I used is a simple Console Application project with the libraries PresentationCore,PresentationFramework, and WindowsBase references added to it as I showed in a prior post: Using WPF in a C# Console Application. The Main() function creates the Window for the program and calls TransparentScene() to do all of the rendering.
Inside the function TransparentScene(), I create the camera, the light, the animated rotation transformation, the tetrahedron geometry, and then use that geometry to specify three tetrahedrons. The first tetrahedron is called the Inner Tetrahedronbecause it is scaled to fit inside the others. The second tetrahedron is called the Outer Tetrahedron and is semi-transparent. The third tetrahedron is also part of the Outer Tetrahedron, but consists of the opaque back faces. Note that it only makes sense to render the back faces because the front faces are semi-transparent. Otherwise, the back would not be visible.
At the end the code, I use the following lines to add the tetrahedrons to the scene:
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qBackGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qInnerGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qOuterGeometry);
Notice that the transparent “Outer Geometry” layer is added last. This is necessary to avoid false occlusions.
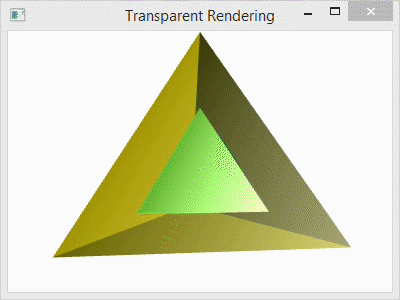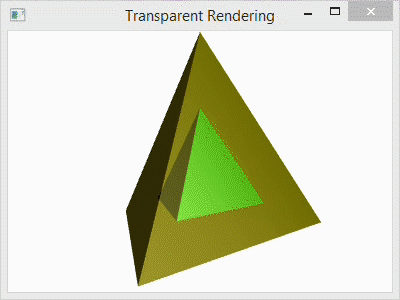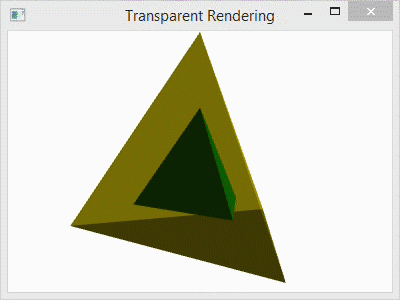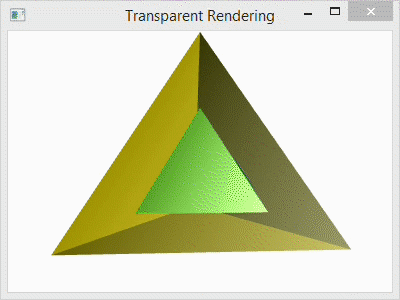
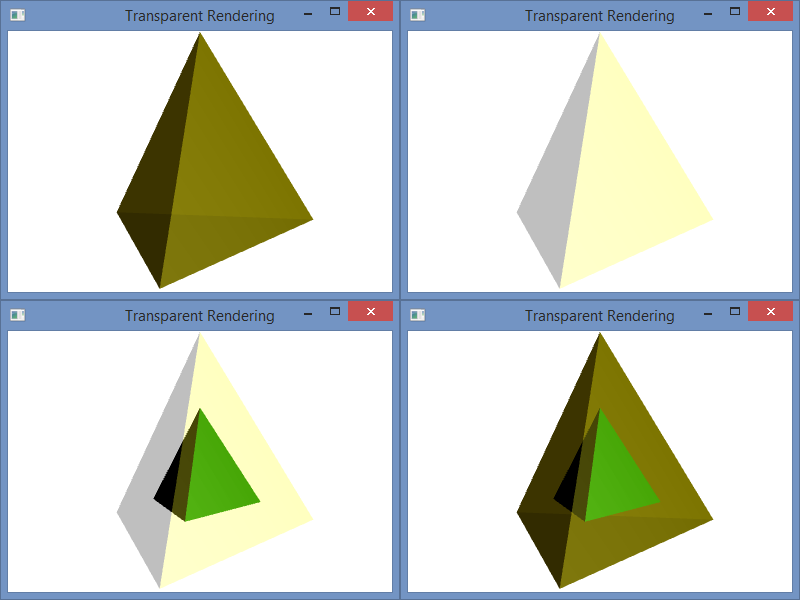
For comparison, I have included the image below with four different arrangements. The first (top-left) shows the scene with the transparent outer layer added before the inner and after the back. The second (top-right) shows the transparent outer layer added before both the inner and the back layers. The third (bottom-left) shows the transparent layer added before the back and after the inner layer. The last (bottom-right) shows the scene with the transparent layer added last as it is in the code.
Program.cs
using System;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Media;
using System.Windows.Media.Media3D;
using System.Windows.Media.Animation; namespace WpfTransparent {
class Program {
[STAThread]
static void Main(string[] args) {
Window qWindow = new Window();
qWindow.Title = "Transparent Rendering";
qWindow.Width = 400;
qWindow.Height = 300;
qWindow.Content = TransparentScene();
qWindow.ShowDialog();
} static Viewport3D TransparentScene() {
// Define the camera
PerspectiveCamera qCamera = new PerspectiveCamera();
qCamera.Position = new Point3D(0, .25, 2.25);
qCamera.LookDirection = new Vector3D(0, -.05, -1);
qCamera.UpDirection = new Vector3D(0, 1, 0);
qCamera.FieldOfView = 60; // Define a lighting model
DirectionalLight qLight = new DirectionalLight();
qLight.Color = Colors.White;
qLight.Direction = new Vector3D(-0.5, -0.25, -0.5); // Define the animated rotation transformation
RotateTransform3D qRotation =
new RotateTransform3D(new AxisAngleRotation3D(new Vector3D(0, 1, 0), 1));
DoubleAnimation qAnimation = new DoubleAnimation();
qAnimation.From = 1;
qAnimation.To = 361;
qAnimation.Duration = new Duration(TimeSpan.FromMilliseconds(5000));
qAnimation.RepeatBehavior = RepeatBehavior.Forever;
qRotation.Rotation.BeginAnimation(AxisAngleRotation3D.AngleProperty, qAnimation); // Define the geometry
const double kdSqrt2 = 1.4142135623730950488016887242097;
const double kdSqrt6 = 2.4494897427831780981972840747059;
// Create a collection of vertex positions
Point3D[] qaV = new Point3D[4]{
new Point3D(0.0, 1.0, 0.0),
new Point3D(2.0 * kdSqrt2 / 3.0, -1.0 / 3.0, 0.0),
new Point3D(-kdSqrt2 / 3.0, -1.0 / 3.0, -kdSqrt6 / 3.0),
new Point3D(-kdSqrt2 / 3.0, -1.0 / 3.0, kdSqrt6 / 3.0)};
Point3DCollection qPoints = new Point3DCollection();
// Designate Vertices
// My Scheme (0, 1, 2), (1, 0, 3), (2, 3, 0), (3, 2, 1)
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i) {
if ((i/3) % 2 == 0) {
qPoints.Add(qaV[i%4]);
} else {
qPoints.Add(qaV[(i*3)%4]);
}
}
// Designate Triangles
Int32Collection qTriangles = new Int32Collection();
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i ) {
qTriangles.Add(i);
}
Int32Collection qBackTriangles = new Int32Collection();
// Designate Back Triangles in the opposite orientation
for (int i = 0; i < 12; ++i) {
qBackTriangles.Add(3 * (i / 3) + (2 * (i % 3) % 3));
} // Inner Tetrahedron: Define the mesh, material and transformation.
MeshGeometry3D qFrontMesh = new MeshGeometry3D();
qFrontMesh.Positions = qPoints;
qFrontMesh.TriangleIndices = qTriangles;
GeometryModel3D qInnerGeometry = new GeometryModel3D();
qInnerGeometry.Geometry = qFrontMesh;
// *** Material ***
DiffuseMaterial qDiffGreen =
new DiffuseMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(255, 0, 128, 0)));
SpecularMaterial qSpecWhite = new
SpecularMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(255, 255, 255, 255)), 30.0);
MaterialGroup qInnerMaterial = new MaterialGroup();
qInnerMaterial.Children.Add(qDiffGreen);
qInnerMaterial.Children.Add(qSpecWhite);
qInnerGeometry.Material = qInnerMaterial;
// *** Transformation ***
ScaleTransform3D qScale = new ScaleTransform3D(new Vector3D(.5, .5, .5));
Transform3DGroup myTransformGroup = new Transform3DGroup();
myTransformGroup.Children.Add(qRotation);
myTransformGroup.Children.Add(qScale);
qInnerGeometry.Transform = myTransformGroup; // Outer Tetrahedron (semi-transparent) : Define the mesh, material and transformation.
GeometryModel3D qOuterGeometry = new GeometryModel3D();
qOuterGeometry.Geometry = qFrontMesh;
// *** Material ***
DiffuseMaterial qDiffTransYellow =
new DiffuseMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(64, 255, 255, 0)));
SpecularMaterial qSpecTransWhite =
new SpecularMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(128, 255, 255, 255)), 30.0);
MaterialGroup qOuterMaterial = new MaterialGroup();
qOuterMaterial.Children.Add(qDiffTransYellow);
qOuterMaterial.Children.Add(qSpecTransWhite);
qOuterGeometry.Material = qOuterMaterial;
// *** Transformation ***
qOuterGeometry.Transform = qRotation; // Outer Tetrahedron (solid back) : Define the mesh, material and transformation.
MeshGeometry3D qBackMesh = new MeshGeometry3D();
qBackMesh.Positions = qPoints;
qBackMesh.TriangleIndices = qBackTriangles;
GeometryModel3D qBackGeometry = new GeometryModel3D();
qBackGeometry.Geometry = qBackMesh;
// *** Material ***
DiffuseMaterial qDiffBrown =
new DiffuseMaterial(new SolidColorBrush(Color.FromArgb(255, 200, 175, 0)));
qBackGeometry.Material = qDiffBrown;
// *** Transformation ***
qBackGeometry.Transform = qRotation; // Collect the components
Model3DGroup qModelGroup = new Model3DGroup();
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qLight);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qBackGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qInnerGeometry);
qModelGroup.Children.Add(qOuterGeometry);
ModelVisual3D qVisual = new ModelVisual3D();
qVisual.Content = qModelGroup;
Viewport3D qViewport = new Viewport3D();
qViewport.Children.Add(qVisual);
qViewport.Camera = qCamera; return qViewport;
}
}
}
Rendering Transparent 3D Surfaces in WPF with C#(转载)的更多相关文章
- WPF拖动总结[转载]
WPF拖动总结 这篇博文总结下WPF中的拖动,文章内容主要包括: 1.拖动窗口 2.拖动控件 Using Visual Studio 2.1thumb控件 2.2Drag.Drop(不连续,没有中 ...
- WPF阴影效果(DropShadowEffect)(转载)
<TextBlock Text="阴影效果" FontSize="32"> <TextBlock.Effect> <DropSha ...
- WPF 3D 知识点大全以及实例
引言 现在物联网概念这么火,如果监控的信息能够实时在手机的客服端中以3D形式展示给我们,那种体验大家可以发挥自己的想象. 那生活中我们还有很多地方用到这些,如上图所示的Kinect 在医疗上的应用,当 ...
- 3D开发基础知识和简单示例
引言 现在物联网概念这么火,如果监控的信息能够实时在手机的客服端中以3D形式展示给我们,那种体验大家可以发挥自己的想象. 那生活中我们还有很多地方用到这些,如上图所示的Kinect 在医疗上的应用,当 ...
- 优化WPF 3D性能
Maximize WPF 3D Performance .NET Framework 4.5 As you use the Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF ...
- WPF 3D 常用类(1)
原文:WPF 3D 常用类(1) 几何数据相关类 Geometry3D 抽象类, 用于定义物体的几何数据, 可用于计算HitTest和BoundingBox MeshGeometry3D Geomet ...
- WPF中反转3D列表项
原文:WPF中反转3D列表项 WPF中反转3D列表项 周银辉记得在苹果电脑中有一个很酷的 ...
- WPF 3D 小小小小引擎 - ·WPF 3D变换应用
原文:WPF 3D 小小小小引擎 - ·WPF 3D变换应用 WPF可以提供的3D模型使我们可以轻松地创建3D实体,虽然目前来看还很有一些性能上的问题,不过对于一些简单的3D应用应该是可取的,毕竟其开 ...
- WPF换肤之八:创建3D浏览效果
原文:WPF换肤之八:创建3D浏览效果 上节中,我们展示了WPF中的异步以及界面线程交互的方式,使得应用程序的显示更加的流畅.这节我们主要讲解如何设计一个具有3D浏览效果的天气信息浏览器. 效果显示 ...
随机推荐
- 批量Linux 网络安装环境建立工具cobbler/kickstart
批量Linux 网络安装环境建立工具网络安装服务器套件: Cobbler(Red Hat 2008年发布的项目) Kickstart(Red Hat08年前项目,相关脚本令人望而却步,现 ...
- Jquery Mobile左右滑动效果
首先在一个页面里面定义两个< div data-role="page">,这里为了突出重点,就没有写出footer和header.定义的页面如下: <body&g ...
- HDU4283:You Are the One(区间DP)
Problem Description The TV shows such as You Are the One has been very popular. In order to meet the ...
- indexOf()不区分大小写用法
str.toLowerCase().indexOf(str.toLowerCase())>=0; 对字符串进行统一小写转换. indexOf()查找到返回索引值大于=0; 未找到,返回-1; i ...
- nginx配置中文域名解析
当nginx配置文件中的default如果遇到解析指向问题的时候 ,配置了中文 没有用 后来找了找这个网址 http://tools.jb51.net/punycode/ 然后进去转换了一下 把 评估 ...
- 泛型类、Map集合
————泛型: JDK1.5之后出现的新特性:用于解决安全问题,是一个类型安全机制. 好处: 1.将运行时期出现的问题ClassCastException ,转移到了编译时期,方便于程序员解决问题,让 ...
- C# 动态创建出来的窗体间的通讯 delegate3
附件1:http://files.cnblogs.com/xe2011/CSharp_WindowsForms_delegate03.rar 一个RTF文件管理器 描述 Form2,Form3,For ...
- DS18B20测温
项目需要实现分布式大规模测温,需要52个测温点,采样DS18B20进行设计. 30cm一个点,一共8个点串联.采用国标单芯单股纯铜硬线BV0.5做导线,测试一会儿正常,一会儿不正常.后面换线了,测试正 ...
- 谷歌google搜索打不开、谷歌gmail邮箱及相关服务无法登录的解决的方法
歌打不开 google打不开,与中国大陆封杀有关,可是主要是由于近期googleserver在全球范围内又一次进行了布局调整. 解决的方法是仅仅要改动用户本地计算机hosts文件就能够了. 一.Win ...
- careercup-链表 2.2
2.2 实现一个算法,找到单链表中倒数第k个节点. 这道题的考点在于我们怎么在一个单链表中找到倒数第n个元素? 由于是单链表,所以我们没办法从最后一个元素数起,然后数n个得到答案. 但这种最直观的思路 ...
