第07节-开源蓝牙协议BTStack框架代码阅读(上)
首先来看一下,对于硬件操作,它是如何来进行处理的。在上篇文章中曾说过,在main函数里面它会调用硬件相关的代码,调用操作系统相关的代码。在BTStack中,可以搜索一下main.c,将会发现有很多main.c,都是为于port目录下面。
Main.c (port\esp32\components\btstack)
Main.c (port\ez430-rf2560\src)
Main.c (port\libusb)
Main.c (port\libusb-intel)
Main.c (port\max32630-fthr\src)
Main.c (port\msp-exp430f5438-cc2564b\src)
Main.c (port\msp430f5229lp-cc2564b\src)
Main.c (port\nrf5-zephyr)
Main.c (port\nrf5x)
Main.c (port\pic32-harmony\src)
Main.c (port\posix-h4)
Main.c (port\posix-h4-atwilc3000)
Main.c (port\posix-h4-da14581)
Main.c (port\posix-h4-da14585)
Main.c (port\posix-h4-zephyr)
Main.c (port\posix-h5)
Main.c (port\posix-h5-bcm)
Main.c (port\raspi)
Main.c (port\samv71-xplained-atwilc3000)
Main.c (port\stm32-f103rb-nucleo)
Main.c (port\stm32-f4discovery-cc256x\eclipse-template\src)
Main.c (port\stm32-l053r8-em9304\cubemx-l053r8-em9304\src)
Main.c (port\wiced-h4)
Main.c (port\wiced-h5)
Main.c (port\windows-h4)
Main.c (port\windows-h4-zephyr)
Main.c (port\windows-winusb)
Main.c (port\windows-winusb-intel)
看一下windows,有Main.c (port\windows-h4)、Main.c (port\windows-winusb),使用的是usb口的蓝牙模块。注意后h4表示5线串口的蓝牙模块。
分析Main.c 中的main函数,按照上一篇文章中总结出来的框架,首先找到硬件操作的相关代码,然后再看操作系统先关的代码
1. 硬件相关的代码:
a.使用usb口
分析Main.c (port\windows-winusb)
// setup USB Transport
transport = hci_transport_usb_instance();
const hci_transport_t * hci_transport_usb_instance(void) {
return &hci_transport_usb; //返回hci_transport_usb的结构体
}
hci_transport_usb的结构体定义如下:
// get usb singleton
static const hci_transport_t hci_transport_usb = {
/* const char * name; */ "H2_WINUSB",
/* void (*init) (const void *transport_config); */ &usb_init,
/* int (*open)(void); */ &usb_open,
/* int (*close)(void); */ &usb_close,
/* void (*register_packet_handler)(void (*handler)(...); */ &usb_register_packet_handler,
/* int (*can_send_packet_now)(uint8_t packet_type); */ &usb_can_send_packet_now,
/* int (*send_packet)(...); */ &usb_send_packet,
/* int (*set_baudrate)(uint32_t baudrate); */ NULL,
/* void (*reset_link)(void); */ NULL,
#ifdef ENABLE_SCO_OVER_HCI
/* void (*set_sco_config)(uint16_t voice_setting, int num_connections); */ usb_set_sco_config,
#else
/* void (*set_sco_config)(uint16_t voice_setting, int num_connections); */ NULL,
#endif
};
在hci_transport_usb结构体中,有初始化函数、有open函数、有注册函数、有发送包的函数等等,这些函数应该就是用来操作硬件的。
在main函数中,返回了一个结构体,以后将使用transport 这个结构体去操作硬件——从硬件里面得到数据或把数据发给硬件。
以上使用的是USB口,如果我使用的是串口呢?硬件操作的相关代码又是怎样的?
b. 使用串口
分析Main.c (port\windows-h4)
main
const btstack_uart_block_t * uart_driver = btstack_uart_block_windows_instance();
const hci_transport_t * transport = hci_transport_h4_instance(uart_driver); //同样是返回一个transport结构体
// configure and return h4 singleton
const hci_transport_t * hci_transport_h4_instance(const btstack_uart_block_t * uart_driver) {
btstack_uart = uart_driver;
return &hci_transport_h4;//返回hci_transport_h4的结构体
}
hci_transport_h4结构体是什么样的呢?定义如下:
static const hci_transport_t hci_transport_h4 = {
/* const char * name; */ "H4",
/* void (*init) (const void *transport_config); */ &hci_transport_h4_init,
/* int (*open)(void); */ &hci_transport_h4_open,
/* int (*close)(void); */ &hci_transport_h4_close,
/* void (*register_packet_handler)(void (*handler)(...); */ &hci_transport_h4_register_packet_handler,
/* int (*can_send_packet_now)(uint8_t packet_type); */ &hci_transport_h4_can_send_now,
/* int (*send_packet)(...); */ &hci_transport_h4_send_packet,
/* int (*set_baudrate)(uint32_t baudrate); */ &hci_transport_h4_set_baudrate,
/* void (*reset_link)(void); */ NULL,
/* void (*set_sco_config)(uint16_t voice_setting, int num_connections); */ NULL,
};
注意:btstack_uart这个参数是用来干嘛的呢?
BTStack支持多种接口的蓝牙模块,比如USB口、3线串口、5线串口。对于3线串口和5线串口,它们之间有什么差别呢?
对于3线串口,它只有三条线:TxD、RxD、GND。5线串口比三线串口多了两条线:CTS、RTS,用来控制流量。
使用三线串口和无线串口传输同一个数据时,它们使用的协议不一样。

假设图中红色的部分就是要发送的数据,当使用三线串口时可能给它加上头部、尾部后再发送给硬件,当使用五线串口时可能将数据直接发给硬件。
从这个地方可以产出,无论是三线串口还是五线串口,它们的底层硬件操作都是一样的。因此在硬件的这一层,又抽象出了一个结构体:uart_driver。使用该结构体来操作硬件。
H5协议只是将数据加上各种头部和各种尾部,H4协议也只是对数据进行了某种处理。
因此在main函数中,首先得到了uart_driver,然后再将该结构体作为hci_transport_h4_instance的参数传进去。
看一下hci_transport_h4_open()函数:
hci_transport_h4_open
btstack_uart->open();//直接调用了btstack_uart的open函数。
从中可以看出,H4、H5协议通过 btstack_uart_block_t结构体来操作硬件。
2. 操作系统相关的代码
a.windows操作系统
分析Main.c (port\windows-winusb)
main
btstack_run_loop_init(btstack_run_loop_windows_get_instance());
通过btstack_run_loop_windows_get_instance()来获取一个结构体,
/**
* Provide btstack_run_loop_windows instance
*/
const btstack_run_loop_t * btstack_run_loop_windows_get_instance(void){
return &btstack_run_loop_windows;
}
btstack_run_loop_windows结构体定义如下:定义了操作系统先关的循环函数。
static const btstack_run_loop_t btstack_run_loop_windows = {
&btstack_run_loop_windows_init,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_add_data_source,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_remove_data_source,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_enable_data_source_callbacks,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_disable_data_source_callbacks,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_set_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_add_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_remove_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_execute,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_dump_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_windows_get_time_ms,
};
b. linux操作系统
Main.c (port\posix-h4)
main
btstack_run_loop_init(btstack_run_loop_posix_get_instance());
通过btstack_run_loop_posix_get_instance()来获取一个结构体
/**
* Provide btstack_run_loop_posix instance
*/
const btstack_run_loop_t * btstack_run_loop_posix_get_instance(void){
return &btstack_run_loop_posix;
}
btstack_run_loop_posix结构体定义如下:定义了操作系统先关的循环函数。
static const btstack_run_loop_t btstack_run_loop_posix = {
&btstack_run_loop_posix_init,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_add_data_source,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_remove_data_source,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_enable_data_source_callbacks,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_disable_data_source_callbacks,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_set_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_add_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_remove_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_execute,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_dump_timer,
&btstack_run_loop_posix_get_time_ms,
};
3. 在主循环中读取数据、处理数据,它是如何用代码来实现的呢?
例如:如果我使用H5协议的话,从硬件中得到数据,需要将这个数据的头部去掉,才能得到真正的数据。如果我使用H4协议的话,从硬件中得到的数据就是真正的数据。
如果我使用usb协议的话,得到的数据又需要作另一种处理。从这个地方就可以看出某种端倪来,什么端倪呢?得到数据和处理数据应该绑定在一起。
即使用A协议得到数据,就使用process_A来处理;使用B协议来得到数据,就使用process_B来处理。在BTStack中,又抽象处理另外一个结构体,该结构体就是btstack_data_source。

上面已经提到操作系统相关的代码时,在结构体btstack_run_loop中它有一个函数指针void (*add_data_source)(btstack_data_source_t * data_source),就是给这个循环添加一个数据来源。这个数据来源里面有文件句柄或handle、process函数。以后在循环里面,它可以通过文件句柄或handle中获取数据,得到数据后马上调用它里面的process函数。问题来了,btstack_data_source结构体是在什么时候创建的?显然应该在打开硬件设备时,就会创建这个结构体,并且把这格结构体添加到btstack_run_loop中。
4.数据如何进行处理的呢?
process函数就是数据处理的起点,前面已经说过,对数据的处理分为两部分:一部分是蓝牙协议栈中各个层次的处理,另一个部分是APP的处理。
data_source结构体中有process函数,process函数就是数据处理的起点,在这里会干什么事情呢?它会调用各个层的处理函数,也会调用APP的处理函数。
看一下函数usb_process_event_in,在里面会做什么事情呢?
usb_process_event_in
// notify uppper 通知更上面的层次
packet_handler(HCI_EVENT_PACKET, hci_event_in_buffer, bytes_read);
packet_handler是一个函数指针,static void (*packet_handler)(uint8_t packet_type, uint8_t *packet, uint16_t size) = &usb_dummy_handler;
该函数指针在哪里被设置呢?
static void usb_register_packet_handler(void (*handler)(uint8_t packet_type, uint8_t *packet, uint16_t size)){
log_info("registering packet handler");
packet_handler = handler;
}
在硬件相关的结构体hci_transport_usb里面,有一个注册函数usb_register_packet_handler。
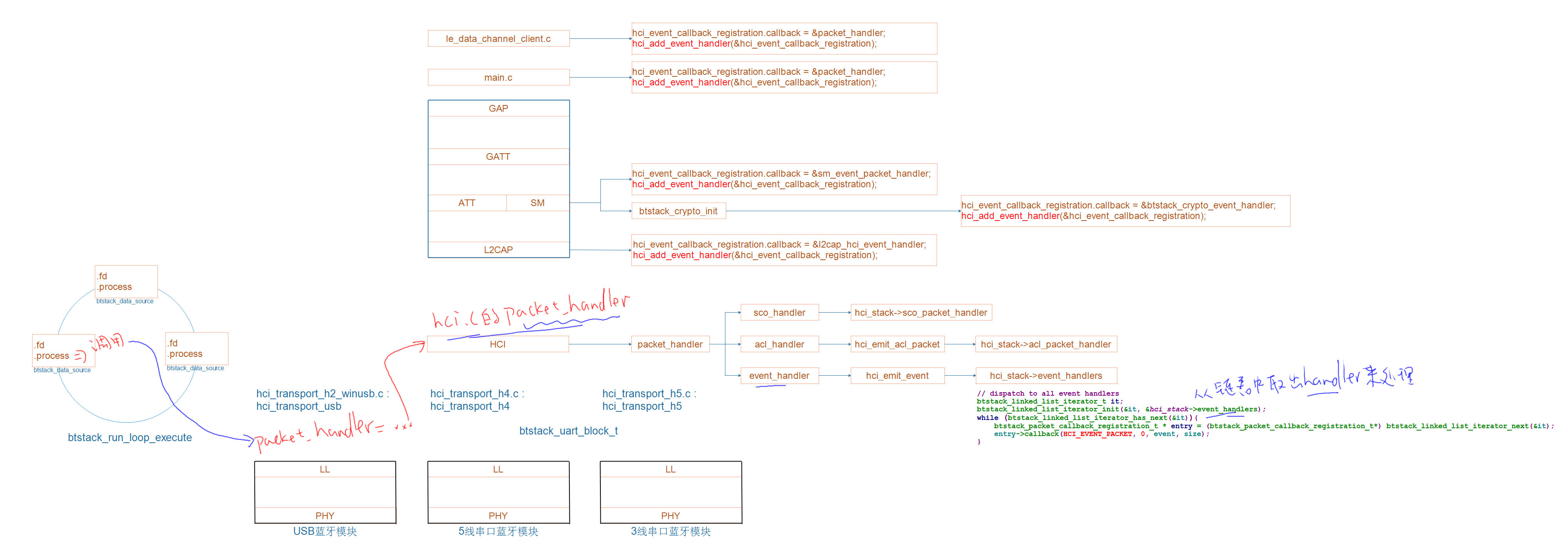
对于usb蓝牙模块,它使用hci_transport_h2_winusb.c文件中抽象出来的hci_transport_usb结构体,在这个结构体里面有usb_register_packet_handler函数,
static void usb_register_packet_handler(void (*handler)(uint8_t packet_type, uint8_t *packet, uint16_t size)){
log_info("registering packet handler");
packet_handler = handler; 对函数指针packet_handler进行赋值。
}
此处的handler是什么?就需要看看谁调用了register_packet_handler函数指针,调用了register_packet_handler函数指针,就相当于调用了usb_register_packet_handler函数
在hci.c文件中的hci_init函数中调用了register_packet_handler函数指针。
hci_init
// register packet handlers with transport
transport->register_packet_handler(&packet_handler); 从这个地方可以看出,上面的handler就是hci.c文件中的packet_handler
再看一下参数packet_handler
static void packet_handler(uint8_t packet_type, uint8_t *packet, uint16_t size){
hci_dump_packet(packet_type, 1, packet, size);
switch (packet_type) {
case HCI_EVENT_PACKET:
event_handler(packet, size);
break;
case HCI_ACL_DATA_PACKET:
acl_handler(packet, size);
break;
#ifdef ENABLE_CLASSIC
case HCI_SCO_DATA_PACKET:
sco_handler(packet, size);
break;
#endif
default:
break;
}
}
在主循环中,得到数据之后,会调用btstack_data_source中的process函数,在process函数中最终会进行packet_handler = handler这样的赋值操作。最终会调用到hci.c中的packet_handler函数。在该函数中将数据分为了三类:HCI_EVENT_PACKET、HCI_ACL_DATA_PACKET、HCI_SCO_DATA_PACKET。根据类别的不同调用不同的处理函数。
event_handler(packet, size);
hci_emit_event
// dispatch to all event handlers 分发给所有的事件处理器,那么这些event handler保存在event_handlers链表中。
btstack_linked_list_iterator_t it;
btstack_linked_list_iterator_init(&it, &hci_stack->event_handlers);从链表中将handler一个个取出来,调用那些结构体中的callback函数来处理那些数据。
while (btstack_linked_list_iterator_has_next(&it)){
btstack_packet_callback_registration_t * entry = (btstack_packet_callback_registration_t*) btstack_linked_list_iterator_next(&it);
entry->callback(HCI_EVENT_PACKET, 0, event, size);
}
问题:谁向hci_stack->event_handlers链表中放入handler的呢?
从图中可以看出,上面的各个层都调用了hci_add_event_handler,上面的各层如果对数据感兴趣的话就调用hci_add_event_handler函数在链表中添加自己的处理函数。
void hci_add_event_handler(btstack_packet_callback_registration_t * callback_handler){
btstack_linked_list_add_tail(&hci_stack->event_handlers, (btstack_linked_item_t*) callback_handler); 向event_handler链表中添加了btstack_packet_callback_registration_t结构体,这个结构体是什么样的呢?
}
typedef struct {
btstack_linked_item_t item;
btstack_packet_handler_t callback; 有callback函数,刚好与上面对应起来。
} btstack_packet_callback_registration_t;
5. 谁来启动数据传输?
hci_power_control会启动蓝牙模块,向蓝牙模块发送第一个数据,以后所有的数据都会在主循环中进行的,收到数据后将调用process函数。
第07节-开源蓝牙协议BTStack框架代码阅读(上)的更多相关文章
- 第07节-开源蓝牙协议BTStack框架代码阅读(下)
上篇博客中已经对BTStack框架进行了较为详细的说明,本篇博客将进一步总结一下(由韦大仙笔记所得). 可以从5个方面来理解BTStack的框架: 1.硬件操作:hci_transport_t BTS ...
- 第06节-开源蓝牙协议BTStack框架分析
本篇博客根据韦东山的视频,整理所得. 本篇博客讲解BTStack的框架,首先来看一下硬件的结构: 蓝牙模块接在电脑上,或是接在开发板上.不论接在哪,我们都需要编写程序来控制这个蓝牙模块. . 我们需要 ...
- 第08节-开源蓝牙协议栈BTStack数据处理
本篇博客根据韦东山的视频整理所得. 在上篇博客,通过阅读BTStack的源码,大体了解了其框架,对于任何一个BTStack的应用程序都有一个main函数,这个main函数是统一的.这个main函数做了 ...
- [转]FFMpeg框架代码阅读
简介 FFmpeg是一个集录制.转换.音/视频编码解码功能为一体的完整的开源解决方案. FFmpeg的开发是基于Linux操作系统,但是可以在大多数操作系统中编译和使用.FFmpeg支持MPEG.Di ...
- FFMpeg框架代码阅读
http://blog.csdn.net/wstarx/article/details/1572393 FFMPEG源码分析(二) http://www.cnblogs.com/qingquan/ar ...
- Deepctr框架代码阅读
DeepCtr是一个简易的CTR模型框架,集成了深度学习流行的所有模型,适合学推荐系统模型的人参考. 我在参加比赛中用到了这个框架,但是效果一般,为了搞清楚原因从算法和框架两方面入手.在读代码的过程中 ...
- 痞子衡嵌入式:开源软件协议(MIT/BSD/Apache/LGPL/MPL/GPL)
大家好,我是痞子衡,是正经搞技术的痞子.今天痞子衡给大家讲的是关于开源软件协议基本知识. 牛顿曾说过:"如果我比别人看得更远,那是因为我站在巨人的肩上".在软件开发中如果说也存在巨 ...
- 蓝牙协议分析(5)_BLE广播通信相关的技术分析
1. 前言 大家都知道,相比传统蓝牙,蓝牙低功耗(BLE)最大的突破就是加大了对广播通信(Advertising)的支持和利用.关于广播通信,通过“玩转BLE(1)_Eddystone beacon” ...
- 蓝牙协议(bluetooth spec)
1.概述: 蓝牙协议规范遵循开放系统互连参考模型(OSI/RM),从低到高地定义了蓝牙协议堆栈的各个层次. SIG(Session Initiation Protocol)所定义的蓝牙技术规范的目 ...
随机推荐
- MySQL实战45讲学习笔记:第三十讲
一.复习一下加锁规则 在第20和21篇文章中,我和你介绍了 InnoDB 的间隙锁.next-key lock,以及加锁规则.在这两篇文章的评论区,出现了很多高质量的留言.我觉得通过分析这些问题,可以 ...
- 3 datax mysql和hive之间相互导入
mysql-->hive 0 参考文档: https://github.com/alibaba/D ...
- vscode java
https://devblogs.microsoft.com/visualstudio/announcing-visual-studio-code-java-installer/ public cla ...
- (一)golang--初识go语言
学习来源:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av35928275/?p=1 尚硅谷的(我学spring.springmvc和mybatis就是他们的课) 使用1.9.2的 ...
- kafka的安装和初步使用
简介 最近开发的项目中,kafka用的比较多,为了方便梳理,从今天起准备记录一些关于kafka的文章,首先,当然是如何安装kafka了. Apache Kafka是分布式发布-订阅消息系统. Apac ...
- Unity Shader 序列帧动画
shader中的序列帧动画属于纹理动画中的一种,主要原理是将给定的纹理进行等分,再根据时间的变化循环播放等分中的一部分. Unity Shader 内置时间变量 名称 类型 描述 _Time floa ...
- python笔记 面向对象编程从入门到高级
目录: 一.概念 二.方法 2.1组合 2.2继承 2.3多态 2.4封装 2.5归一化设计 三.面向对象高级 3.1 反射(自省) 3.2 内置方法__getatter__, __ ...
- CentOS7. 6 上部署MongoDB
*安装步骤** 配置yum源 vim /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org-4.0.repo #添加以下内容: [mongodb-org-4.0] name=MongoDB Rep ...
- golang 学习笔记 ---JSON
JSON解析到结构体 在介绍这部分之前先简要介绍一下Json语法 JSON 语法是 JavaScript 语法的子集.JSON 语法是 JavaScript 对象表示法语法的子集. 数据在名称/值对中 ...
- 【01】Jenkins:安装配置
写在前面的话 从我的工作经历来看,刚出来的时候的第一家公司我们上线采用的是脚本上线.就是那种开发合并完代码以后,在一个固定的时间点,我们上服务器执行更新脚本打包更新.这种方法有一个很大的问题,就是对于 ...
