C11简洁之道:函数绑定
1、 可调用对象
在C++中,有“可调用对象”这么个概念,那么什么是调用对象呢?有哪些情况?我们来看看:
- 函数指针;
- 具有operator()成员函数的类对象(仿函数);
- 可以被转换为函数指针的类对象;
- 类成员(函数)指针。
我们来看代码:
//函数指针 void func(void)
{
//...
} struct Foo
{
void operator()(void)
{
//...
}
}; struct Bar
{
using fr_t = void(*)(void);
static void func(void)
{
//...
} operator fr_t(void)
{
return func;
}
}; struct A
{
int mia; void mem_func(void)
{
//...
}
}; int main(void)
{
//函数指针
void(* func_ptr)(void) = &func;
func_ptr(); //仿函数
Foo foo;
foo(); //被转为指针的类对象
Bar bar;
bar(); //类成员函数指针
void (A::*mem_func_ptr)(void) = &A::mem_func; //类成员指针
int A::*mem_obj_ptr = &A::mia; A aa;
(aa.*mem_func_ptr)();
aa.*mem_obj_ptr = ; return ;
}
上述的对象都是可调用对象,这些对象的类型统称为“可调用类型”。这些可调用对象都具有统一的操作形式,除了类成员指针之外,都是通过括号的方式来进行调用,但是定义的方法比较多,在C++11中增加了std::function来进行函数对象的调用。
2、 std::function
std::function是一个可调用对象的包装器,他是一个类模板,可以容纳除了类成员(函数)指针之外的所用可调用对象,通过指定他的模板参数,可以以统一的方式处理函数、函数对象、函数指针,并允许保存或者延迟执行。
当我们给std::function填入合适的函数签名(即一个函数类型,只需要包括返回值和参数列表)之后,它就变成了一个可以容纳所有这一类调用方式的“函数包装器”。
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> void func(void)
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << std::endl;
} class Foo
{
public:
static int foo_func(int a)
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << "(" << a << ")->: ";
return a;
}
}; class Bar
{
public: int operator()(int a)
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << "(" << a << ")->: ";
return a;
}
}; int main(void)
{
//绑定一个普通函数
std::function<void(void)> fr1 = func;
fr1(); //绑定一个静态成员函数
std::function<int(int)> fr2 = Foo::foo_func;
std::cout << fr2() << std::endl; //绑定一个仿函数
Bar bar;
fr2 = bar;
std::cout << fr2() << std::endl; return ;
}
执行结果:
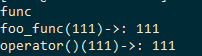
std::function还可以取代函数指针的作用,因为它可以保存函数延迟执行,所以也适合做回调函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> class A
{
std::function<void()> callback;
public:
A(const std::function<void()> &f) : callback(f){} void notify(void)
{
callback();
}
}; class Foo
{
public:
void operator()(void)
{
std::cout << __FUNCTION__ << std::endl;
}
}; int main(void)
{
Foo foo;
A aa(foo);
aa.notify(); return ;
}
std::function还可以作为函数入参,比普通函数指针更加灵活和便利。
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> void call_when_event(int x, const std::function<void(int)>& f)
{
if(!(x & )) //x % 2 == 0
{
f(x);
}
} void output(int x)
{
std::cout << x << " ";
} int main(void)
{
for(int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
call_when_event(i, output);
} std::cout << std::endl; return ;
}
3、 std::bind绑定器
3.1 std::bind绑定器
std::bind用来将可调用对象与起参数一起进行绑定,绑定的结果使用std::function进行保存,并在我们需要调用的时候调用。它主要有两大作用:
- 将可调用对象和参数绑定成为一个仿函数;
- 将多元(参数个数为n,n-1)可调用对象转换成一元或者(n-1)元可调用对象,即只绑定部分对象。
我们来看实际使用:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> void call_when_event(int x, const std::function<void(int)>& f)
{
if(!(x & )) //x % 2 == 0
{
f(x);
}
} void output(int x)
{
std::cout << x << " ";
} void output2(int x)
{
std::cout << x + << " ";
} int main(void)
{
{
auto fr = std::bind(output, std::placeholders::_1);
for(int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
call_when_event(i, fr);
} std::cout << std::endl;
}
{
auto fr = std::bind(output2, std::placeholders::_1);
for(int i = ; i < ; i++)
{
call_when_event(i, fr);
} std::cout << std::endl;
} return ;
}
通过代码我们可以知道std::bind在函数外部通过绑定不同的函数,控制执行结果。这里我们还使用了std::placeholders占位符来绑定函数参数。
3.2 std::placeholders
通过std::placeholders占位符绑定函数参数,使得std::bind的使用非常灵活。std::placeholders决定函数占用位置取用输入参数的第几个参数。
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> void output(int x, int y)
{
std::cout << x << " " << y << std::endl;
} int main(void)
{
std::bind(output, , )(); //输出:1 2
std::bind(output, std::placeholders::_1, )(); //输出:1 2
std::bind(output, , std::placeholders::_1)(); //输出:2 1
//std::bind(output, 2, std::placeholders::_2)(1); //error,没有第二个参数
std::bind(output, , std::placeholders::_2)(,); //输出:2 2,第一个参数被抛弃
std::bind(output, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2)(,); //输出:1 2
std::bind(output, std::placeholders::_2, std::placeholders::_1)(,); //输出:2 1 return ;
}
3.3 std::bind+std::function
我们先看一组例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> class A
{
public:
int mi = ; void output(int x, int y)
{
std::cout << x << " " << y << std::endl;
}
}; int main(void)
{
A a;
std::function<void(int, int)> fr = std::bind(&A::output, &a, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2);
fr(, ); std::function<int &(void)> fr_i = std::bind(&A::mi, &a);
fr_i() = ;
std::cout << a.mi << std::endl; return ;
}
fr的类型是std::function<void(int, int)>,我们通过std::bind将A的成员函数output的指针和a绑定,并转换为一个仿函数存储在fr中。
通过std::bind将A的成员mi的指针和a绑定,返回的结果放入类型为std::function<int &(void)>的fr_i中,可以在需要的时候修改这个成员的值。
3.4 改善标准函数
假如我们有一个这样的需求,对某个集合里面的元素进行统计,假设元素类型为int,那么我们需要对类型做比较,必须有一个阀值,即大于或者小于这个数。这里我们可以通过标准库的函数来实现。
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> int main()
{
std::vector<int> coll;
for (int i = ; i <= ; ++i)
{
coll.push_back(i);
} // 查找元素值大于10的元素的个数
// 也就是使得10 < elem成立的元素个数
int res = count_if(coll.begin(), coll.end(), std::bind1st(less<int>(), ));
cout << res << endl; // 查找元素值小于10的元素的个数
// 也就是使得elem < 10成立的元素个数
res = count_if(coll.begin(), coll.end(), std::bind2nd(less<int>(), ));
cout << res << endl; bool b = less<int>(, ); // 返回true return ;
}
本质上是对一个二元函数less<int>的调用,但是要分别调用bind1st,bind2nd,用起来比较繁杂,现在我们有bind,可以用统一的方式去实现。并不用关心是bind1st还是bind2nd,用bind即可。
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> int main()
{
using std::placeholders::_1;
std::vector<int> coll; //查找元素值大于10的元素个数
int count = std::count_if(coll.begin(), coll.end(), std::bind(less<int>(), , _1)); //查找元素值小于10的元素个数
count = std::count_if(coll.begin(), coll.end(), std::bind(less<int>(), _1, )); return ;
}
3.5 组合使用
bind可以绑定多个函数,假设我们要对某个集合在大于5小于10的元素个数进行统计,我们该怎么封装呢?
首先封装一个判断是否大于5的函数,使其输入只有一个参数,直接和5比较,大于5返回true。
std::bind(std::greater<int>(), std::placeholders::_1, );
同样,我们需要封装一个判断是否小于10的函数,使其输入一个参数,小于10则返回true。
std::bind(std::less_equal<int>(), std::placeholders::_1, );
然后组合,即可调用:
using std::placeholders::_1; auto f = std::bind(std::logical_and<bool>(), std::bind(std::greater<int>(), std::placeholders::_1, ), std::bind(std::less_equal<int>(), std::placeholders::_1, )); int count = std::count_if(coll.begin(), coll.end(), f);
C11简洁之道:函数绑定的更多相关文章
- C11简洁之道:类型推导
1. 概述 C++11里面引入了auto和decltype关键字来实现类型推导,通过这两个关键字不仅能方便的获取复杂的类型,还能简化书写,提高编码效率. 2. auto 2.1 auto关键字的新 ...
- C11简洁之道:lambda表达式
1. 定义 lambda表达式是C++11非常重要也是很常用的特性之一,来源于函数式编程的概念,也是现代编程语言的一个特点.它有如下特点: 声明式编程风格:就地匿名定义目标函数或者函数,不需要额外写 ...
- C11简洁之道:初始化改进
1. C++98/03初始化 我们先来总结一下C++98/03的各种不同的初始化情况: //普通数组 ] = {, , }; //POD(plain old data) struct A { int ...
- C11简洁之道:模板改进
1. 右尖括号 我们在C++98/03中使用泛型编程的时候,经常遇到“>>”被当作右移操作符,而不是模板参数的结尾.假如我们有如下代码: template <typename T& ...
- C11简洁之道:tupe元祖
tuple元组是一个固定大小不同类型的值的集合,是泛化的std::pair.我们也可以把它当作一个通用的结构体来使用,不需要创建结构体有获取结构体特征,在某些情况可以取代结构体,使程序更简洁.直观. ...
- C11简洁之道:循环的改善
1. for循环的新用法 在C++98/03中,通过for循环对一个容器进行遍历,一般有两种方法,常规的for循环,或者使用<algorithm>中的for_each方法. for循环遍 ...
- JS代码简洁之道--函数
函数的参数越少越好 有一个准则是:如果你的函数参数超过两个,就应该改为对象传入. 这样做是合理的,因为当函数参数超过两个时,参数顺序开始变得难以记忆,而且容易出现一种很尴尬的情况:比如我只需要传入第三 ...
- 《javascript dom编程艺术》笔记(一)——优雅降级、向后兼容、多个函数绑定onload函数
刚刚开始自学前端,如果不对请指正:欢迎各位技术大牛指点. 开始学习<javascript dom编程艺术>,整理一下学习到的知识.今天刚刚看到第六章,记下get到的几个知识点. 优雅降级 ...
- 《Clean Code》 代码简洁之道
作者介绍 原文作者: Robert C. Martin, Object Mentor公司总裁,面向对象设计.模式.UML.敏捷方法学和极限编程领域的资深顾问,是<敏捷软件开发:原则.模式.与实践 ...
随机推荐
- 哈希表 STL map
计数排序时我们使用一个数组来记录出现的数字的次数,而当数据范围太大时,无法建立一个那么大地数组(而且可能空间利用率很低,太浪费),此时可以改用hash table . binary search tr ...
- Spring中Controller和RequestMapping的详解
先看一个简单的实例: @Controller @RequestMapping("/hello") public class anyTypeController{ @RequestM ...
- flash builder 4.6在debug调试时需要系统安装flashplayer debug版本
http://blog.csdn.net/cupid0051/article/details/46684295
- C#中堆和栈的区别?
http://www.jb51.net/article/55306.htm http://www.cnblogs.com/JimmyZhang/archive/2008/01/31/1059383.h ...
- 在线api查询网站
1.包含各种常用的语言 http://tool.oschina.net/apidocs
- TCP协议详解7层和4层解析(美团,阿里) 尤其是三次握手,四次挥手 具体发送的报文和状态都要掌握
如果想了解HTTP的协议结构,原理,post,get的区别(阿里面试题目),请参考:HTTP协议 结构,get post 区别(阿里面试) 这里有个大白话的解说,可以参考:TCP/IP协议三次握手和四 ...
- concurrenthashmap jdk1.8
参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/c0642afe03e0 CAS的思想很简单:三个参数,一个当前内存值V.旧的预期值A.即将更新的值B,当且仅当预期值A和内存值V相同时,将内 ...
- Spring MVC之@RequestBody@ResponseBody详解
引言: 接上一篇文章讲述处理@RequestMapping的方法参数绑定之后,详细介绍下@RequestBody.@ResponseBody的具体用法和使用时机: 简介: @RequestBody 作 ...
- [剑指Offer] 48.不用加减乘除做加法
题目描述 写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用+.-.*./四则运算符号. [思路] 首先看十进制是如何做的: 5+7=12,三步走第一步:相加各位的值,不算进位,得到2.第二步:计算进 ...
- 能选择日期范围js控件
html页面中使用日期控件是常有的事,好控件能使用开发变的快捷,下面是在开发过程中发现的几款日期控件,比较不错,收藏 1.基于bootstrap的jQuery日期范围选择插件 2.jQuery多功能日 ...
