MATLAB 颜色图函数(imagesc/scatter/polarPcolor/pcolor)
2维的热度图 imagesc
imagesc(x, y, z),x和y分别是横纵坐标,z为值,表示颜色
imagesc(theta,phi,slc); colorbar
xlabel('theta(°)','fontname','Times New Roman','FontSize',);
ylabel('phi(°)','fontname','Times New Roman','FontSize',);
sta = '3 objects at (θ,φ,r) : (-30,30,1) (0,0,2) (60,-60,0.5)';
str=sprintf(strcat('3D Imaging Slice at :', num2str(d_max*D/N), '(m)', '\n',sta));
title(str, 'fontname','Times New Roman','Color','k','FontSize',);
grid on
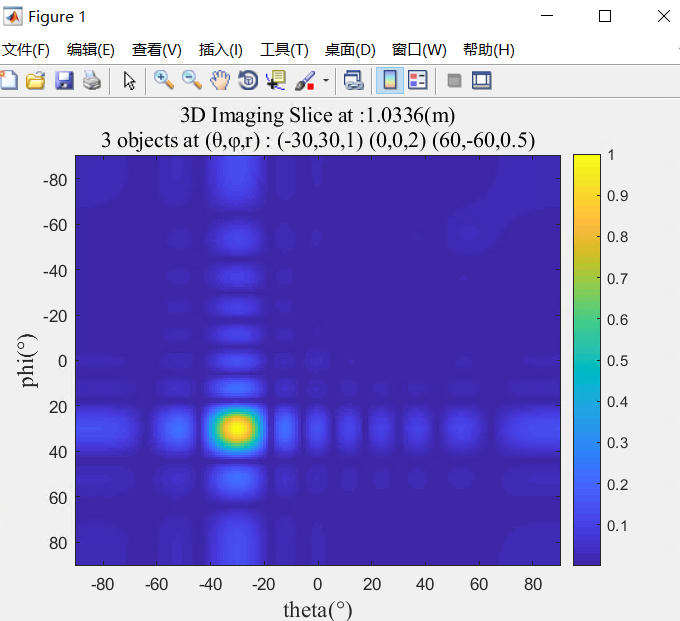
其中,colorbar的坐标值调整:caxis([0 1]);
colormap的色系调整:colormap hot
3维散点图 scatter
scatter3(x,y,z,,c,'filled');
% axis([-(R+) (R+) -(R+) (R+) (h+)]);
colorbar
2维 极坐标热度图 polarPcolor
polarPcolor(R_axis, theta, value),前两个为半径方向坐标轴和圆心角坐标轴,value为值,用颜色表示
[fig, clr] = polarPcolor(R_axis, theta, x_d_th, 'labelR','range (m)','Ncircles', ,'Nspokes',);
colormap hot
% caxis([ ]);

其中polarPcolor代码如下:
function [varargout] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,varargin)
% [h,c] = polarPcolor1(R,theta,Z,varargin) is a pseudocolor plot of matrix
% Z for a vector radius R and a vector angle theta.
% The elements of Z specify the color in each cell of the
% plot. The goal is to apply pcolor function with a polar grid, which
% provides a better visualization than a cartesian grid.
%
%% Syntax
%
% [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z)
% [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,'Ncircles',)
% [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,'Nspokes',)
% [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,'Nspokes',,'colBar',)
% [h,c] = polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,'Nspokes',,'labelR','r (km)')
%
% INPUT
% * R :
% - type: float
% - size: [ x Nrr ] where Nrr = numel(R).
% - dimension: radial distance.
% * theta :
% - type: float
% - size: [ x Ntheta ] where Ntheta = numel(theta).
% - dimension: azimuth or elevation angle (deg).
% - N.B.: The zero is defined with respect to the North.
% * Z :
% - type: float
% - size: [Ntheta x Nrr]
% - dimension: user's defined .
% * varargin:
% - Ncircles: number of circles for the grid definition.
% - Nspokes: number of spokes for the grid definition.
% - colBar: display the colorbar or not.
% - labelR: legend for R.
%
%
% OUTPUT
% h: returns a handle to a SURFACE object.
% c: returns a handle to a COLORBAR object.
%
%% Examples
% R = linspace(,,);
% theta = linspace(,,);
% Z = linspace(,,)'*linspace(0,10,100);
% figure
% polarPcolor(R,theta,Z,'Ncircles',)
%
%% Author
% Etienne Cheynet, University of Stavanger, Norway. //
% see also pcolor
% %% InputParseer
p = inputParser();
p.CaseSensitive = false;
p.addOptional('Ncircles',);
p.addOptional('Nspokes',);
p.addOptional('labelR','');
p.addOptional('colBar',);
p.parse(varargin{:}); Ncircles = p.Results.Ncircles ;
Nspokes = p.Results.Nspokes ;
labelR = p.Results.labelR ;
colBar = p.Results.colBar ;
%% Preliminary checks
% case where dimension is reversed
Nrr = numel(R);
Noo = numel(theta);
if isequal(size(Z),[Noo,Nrr]),
Z=Z';
end % case where dimension of Z is not compatible with theta and R
if ~isequal(size(Z),[Nrr,Noo])
fprintf('\n')
fprintf([ 'Size of Z is : [',num2str(size(Z)),'] \n']);
fprintf([ 'Size of R is : [',num2str(size(R)),'] \n']);
fprintf([ 'Size of theta is : [',num2str(size(theta)),'] \n\n']);
error(' dimension of Z does not agree with dimension of R and Theta')
end
%% data plot
rMin = min(R);
rMax = max(R);
thetaMin=min(theta);
thetaMax =max(theta);
% Definition of the mesh
Rrange = rMax - rMin; % get the range for the radius
rNorm = R/Rrange; %normalized radius [,]
% get hold state
cax = newplot;
% transform data in polar coordinates to Cartesian coordinates.
YY = (rNorm)'*cosd(theta);
XX = (rNorm)'*sind(theta);
% plot data on top of grid
h = pcolor(XX,YY,Z,'parent',cax);
shading flat
set(cax,'dataaspectratio',[ ]);axis off;
if ~ishold(cax);
% make a radial grid
hold(cax,'on')
% Draw circles and spokes
createSpokes(thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes);
createCircles(rMin,rMax,thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes)
end %% PLot colorbar if specified
if colBar==,
c =colorbar('location','WestOutside');
caxis([quantile(Z(:),0.01),quantile(Z(:),0.99)])
else
c = [];
end %% Outputs
nargoutchk(,)
if nargout==,
varargout{}=h;
elseif nargout==,
varargout{}=h;
varargout{}=c;
end %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% Nested functions
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
function createSpokes(thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes) circleMesh = linspace(rMin,rMax,Ncircles);
spokeMesh = linspace(thetaMin,thetaMax,Nspokes);
contour = abs((circleMesh - circleMesh())/Rrange+R()/Rrange);
cost = cosd(-spokeMesh); % the zero angle is aligned with North
sint = sind(-spokeMesh); % the zero angle is aligned with North
for kk = :Nspokes
plot(cost(kk)*contour,sint(kk)*contour,'k:',...
'handlevisibility','off');
% plot graduations of angles
% avoid superimposition of and
if and(thetaMin==,thetaMax == ),
if spokeMesh(kk)<, text(1.05.*contour(end).*cost(kk),...
1.05.*contour(end).*sint(kk),...
[num2str(spokeMesh(kk),),char()],...
'horiz', 'center', 'vert', 'middle');
end
else
text(1.05.*contour(end).*cost(kk),...
1.05.*contour(end).*sint(kk),...
[num2str(spokeMesh(kk),),char()],...
'horiz', 'center', 'vert', 'middle');
end end
end
function createCircles(rMin,rMax,thetaMin,thetaMax,Ncircles,Nspokes) % define the grid in polar coordinates
angleGrid = linspace(-thetaMin,-thetaMax,);
xGrid = cosd(angleGrid);
yGrid = sind(angleGrid);
circleMesh = linspace(rMin,rMax,Ncircles);
spokeMesh = linspace(thetaMin,thetaMax,Nspokes);
contour = abs((circleMesh - circleMesh())/Rrange+R()/Rrange);
% plot circles
for kk=:length(contour)
plot(xGrid*contour(kk), yGrid*contour(kk),'k:');
end
% radius tick label
for kk=:Ncircles position = 0.51.*(spokeMesh(min(Nspokes,round(Ncircles/)))+...
spokeMesh(min(Nspokes,+round(Ncircles/)))); if abs(round(position)) ==,
% radial graduations
text((contour(kk)).*cosd(-position),...
(0.1+contour(kk)).*sind(-position),...
num2str(circleMesh(kk),),'verticalalignment','BaseLine',...
'horizontalAlignment', 'center',...
'handlevisibility','off','parent',cax); % annotate spokes
text(contour(end).*0.6.*cosd(-position),...
0.07+contour(end).*0.6.*sind(-position),...
[labelR],'verticalalignment','bottom',...
'horizontalAlignment', 'right',...
'handlevisibility','off','parent',cax);
else
% radial graduations
text((contour(kk)).*cosd(-position),...
(contour(kk)).*sind(-position),...
num2str(circleMesh(kk),),'verticalalignment','BaseLine',...
'horizontalAlignment', 'right',...
'handlevisibility','off','parent',cax); % annotate spokes
text(contour(end).*0.6.*cosd(-position),...
contour(end).*0.6.*sind(-position),...
[labelR],'verticalalignment','bottom',...
'horizontalAlignment', 'right',...
'handlevisibility','off','parent',cax);
end
end end
end
再贴一个示例代码:
%% Examples
% The following examples illustrate the application of the function
% polarPcolor
clearvars;close all;clc; %% Minimalist example
% Assuming that a remote sensor is measuring the wind field for a radial
% distance ranging from to m. The scanning azimuth is oriented from
% North ( deg) to North-North-East ( deg):
R = linspace(,,)./; % (distance in km)
Az = linspace(,,); % in degrees
[~,~,windSpeed] = peaks(); % radial wind speed
figure()
[h,c]=polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed); %% Example with options
% We want to have circles and spokes, and to give a label to the
% radial coordinate figure()
[~,c]=polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed,'labelR','r (km)','Ncircles',,'Nspokes',);
ylabel(c,' radial wind speed (m/s)');
set(gcf,'color','w')
%% Dealing with outliers
% We introduce outliers in the wind velocity data. These outliers
% are represented as wind speed sample with a value of m/s. These
% corresponds to unrealistic data that need to be ignored. To avoid bad
% scaling of the colorbar, the function polarPcolor uses the function caxis
% combined to the function quantile to keep the colorbar properly scaled:
% caxis([quantile(Z(:),0.01),quantile(Z(:),0.99)]) windSpeed(::end,::end)=; figure()
[~,c]=polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed);
ylabel(c,' radial wind speed (m/s)');
set(gcf,'color','w') %% polarPcolor without colorbar
% The colorbar is activated by default. It is possible to remove it by
% using the option 'colBar'. When the colorbar is desactivated, the
% outliers are not "removed" and bad scaling is clearly visible: figure()
polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed,'colBar',) ; %% Different geometry
N = ;
R = linspace(,,N)./; % (distance in km)
Az = linspace(,,N); % in degrees
[~,~,windSpeed] = peaks(N); % radial wind speed
figure()
[~,c]= polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed);
ylabel(c,' radial wind speed (m/s)');
set(gcf,'color','w')
%% Different geometry
N = ;
R = linspace(,,N)./; % (distance in km)
Az = linspace(,,N); % in degrees
[~,~,windSpeed] = peaks(N); % radial wind speed
figure()
[~,c]= polarPcolor(R,Az,windSpeed,'Ncircles',);
location = 'NorthOutside';
ylabel(c,' radial wind speed (m/s)');
set(c,'location',location);
set(gcf,'color','w')
MATLAB 颜色图函数(imagesc/scatter/polarPcolor/pcolor)的更多相关文章
- matlab读图函数
最基本的读图函数:imread imread函数的语法并不难,I=imread('D:\fyc-00_1-005.png');其中括号内写图片所在的完整路径(注意路径要用单引号括起来).I代表这个图片 ...
- Matlab脚本和函数
脚本和函数 脚本: 特点:按照文件中所输入的指令执行,一段matlab指令集合.运行后,运算过程产生的所有变量保存在基本工作区.可以进行图形输出,如plot()函数. 举例: 脚本文件ex4_15.m ...
- matlab中patch函数的用法
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_707b64550100z1nz.html matlab中patch函数的用法——emily (2011-11-18 17:20:33) ...
- 【原创】Matlab.NET混合编程技巧之直接调用Matlab内置函数
本博客所有文章分类的总目录:[总目录]本博客博文总目录-实时更新 Matlab和C#混合编程文章目录 :[目录]Matlab和C#混合编程文章目录 在我的上一篇文章[ ...
- matlab画图形函数 semilogx
matlab画图形函数 semilogx loglog 主要是学习semilogx函数,其中常用的是semilogy函数,即后标为x的是在x轴取对数,为y的是y轴坐标取对数.loglog是x y轴都取 ...
- matlab中subplot函数的功能
转载自http://wenku.baidu.com/link?url=UkbSbQd3cxpT7sFrDw7_BO8zJDCUvPKrmsrbITk-7n7fP8g0Vhvq3QTC0DrwwrXfa ...
- 【原创】Matlab中plot函数全功能解析
[原创]Matlab中plot函数全功能解析 该帖由Matlab技术论(http://www.matlabsky.com)坛原创,更多精彩内容参见http://www.matlabsky.com 功能 ...
- Matlab.NET混合编程技巧之——直接调用Matlab内置函数(附源码)
原文:[原创]Matlab.NET混合编程技巧之--直接调用Matlab内置函数(附源码) 在我的上一篇文章[原创]Matlab.NET混编技巧之——找出Matlab内置函数中,已经大概的介绍了mat ...
- Matlab中plot函数全功能解析
Matlab中plot函数全功能解析 功能 二维曲线绘图 语法 plot(Y)plot(X1,Y1,...)plot(X1,Y1,LineSpec,...)plot(...,'PropertyName ...
随机推荐
- 一致性哈希算法(consistent hashing)PHP实现
一致性哈希算法在1997年由麻省理工学院提出的一种分布式哈希(DHT)实现算法,设计目标是为了解决因特网中的热点(Hot spot)问题,初衷和CARP十分类似.一致性哈希修正了CARP使用的简单哈希 ...
- Flutter Widgets 之 SnackBar
注意:无特殊说明,Flutter版本及Dart版本如下: Flutter版本: 1.12.13+hotfix.5 Dart版本: 2.7.0 基础用法 应用程序有时候需要弹出消息提示用户,比如'网络连 ...
- vs2017 tfs服务器迁移更换服务器IP地址方法
今天公司服务器换了IP地址,然后发现tfs的服务器删除不了,也添加不了.最后参考了其他vs版本提供的方法,找到了解决的方法. 一共需要修改两个地方: 1.找到项目的sln文件,使用其他文本编辑器打开, ...
- PKI详解
预备: 一.密码基元 二.密钥管理 三.PKI本质是把非对称密钥管理标准化 PKI 是 Public Key Infrastructure 的缩写,其主要功能是绑定证书持有者的身份和相关的密钥对(通过 ...
- 有点长的博客:Redis不是只有get set那么简单
我以前还没接触Redis的时候,听到大数据组的小伙伴在讨论Redis,觉得这东西好高端,要是哪天我们组也可以使用下Redis就好了,好长一段时间后,我们项目中终于引入了Redis这个技术,我用了几下, ...
- Taro_Mall 是一款多端开源在线商城小程序.
介绍 Taro_Mall是一款多端开源在线商城应用程序,后台是基于litemall基础上进行开发,前端采用Taro框架编写,现已全部完成小程序和h5移动端,后续会对APP,淘宝,头条,百度小程序进行适 ...
- 绕过Referer和Host检查
1.我们在尝试抓取其他网站的数据接口时,某些接口需要经过请求头中的Host和Referer的检查,不是指定的host或referer将不予返回数据,且前端无法绕过这种检查 此时通过后端代理解决 在vu ...
- 一篇文章彻底说清JS的深拷贝/浅拷贝
一篇文章彻底说清JS的深拷贝and浅拷贝 这篇文章的受众 第一类,业务需要,急需知道如何深拷贝JS对象的开发者. 第二类,希望扎实JS基础,将来好去面试官前秀操作的好学者. 写给第一类读者 你只需要一 ...
- a标签嵌套href默认行为与子元素click事件存在影响
2018-08-07 Question about work 开发过程中遇到问题,简单写个demo 运行环境为Chrome 68 描述一下这个问题,当<a>标签内部存在嵌套时, 父元素&l ...
- 前端ps中常用的操作
昨天,ui给了个psd图,让写成网页.额,要自己切图.很久之前,操作的还凑乎.但是,好久了,都忘了.所以,打算自己记个笔记,方便以后查看. 首先,打开ps就先来设置一下ps的单位啦点击最上面的一行的编 ...
