PAT Advanced 1034 Head of a Gang (30) [图的遍历,BFS,DFS,并查集]
题目
One way that the police finds the head of a gang is to check people’s phone calls. If there is a phone call between A and B, we say that A and B is related. The weight of a relation is defined to be the total time length of all the phone calls made between the two persons. A “Gang” is a cluster of more than 2 persons who are related to each other with total relation weight being greater than a given threshold K. In each gang, the one with maximum total weight is the head. Now given a list of phone calls, you are supposed to find the gangs and the heads.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains two positive numbers N and K (both less than or equal to 1000), the number of phone calls and the weight threthold, respectively. Then N lines follow, each in the following format:
Name1 Name2 Time
where Name1 and Name2 are the names of people at the two ends of the call, and Time is the length of the call. A name is a string of three capital letters chosen from A-Z. A time length is a positive integer which is no more than 1000 minutes.
Output Specification:
For each test case, first print in a line the total number of gangs. Then for each gang, print in a line the name of the head and the total number of the members. It is guaranteed that the head is unique for each gang. The output must be sorted according to the alphabetical order of the names of the heads.
Sample Input 1:
8 59
AAA BBB 10
BBB AAA 20
AAA CCC 40
DDD EEE 5
EEE DDD 70
FFF GGG 30
GGG HHH 20
HHH FFF 10
Sample Output 1:
2
AAA 3
GGG 3
Sample Input 2:
8 70
AAA BBB 10
BBB AAA 20
AAA CCC 40
DDD EEE 5
EEE DDD 70
FFF GGG 30
GGG HHH 20
HHH FFF 10
Sample Output 2:
0
题意
警察通过电话记录分析犯罪团伙,有通话记录的人视为有一个关系网,若关系网的总通话时长超过阈值视为犯罪团伙,每个犯罪组织中通话时长最多的视为犯罪头目,求犯罪团伙数目和每个犯罪团伙的头目
已知所有人员、电话记录、阈值
求犯罪团伙数目、每个犯罪团伙的头目名称和成员数
题目分析
- A和B有电话记录即为有关联---边
- A和B的关系权重为所有AB相互通话记录(A->B,B->A)的总时长---边权
- 多个有关联的人员组成一个组,组的权重为所有人员关系权重和---连通分量总边权和
- 判断一个组是否是犯罪团伙的标准:人数大于2,权重大于已知阈值k
- 判断一个犯罪团伙的头目标准:点权最大(点权等于所有关联权重和)
已知一个图,求所有连通分量的边权和awt,总人数anum,最大点权wt。判断边权和>k,并且总人数anum>2的连通分量
解题思路
1 存储节点名称,点权,边权
注:可以不使用边权,因为最终统计的是连通分量的总权重,每条边的权重都保存在两边顶点的点权中,最终计算的连通分量总权重是所有边权的两倍
思路 01
注意点:题目已知通话记录为n,若每个通话记录的A,B都不同,最多有2*n个名称(即2*n个顶点),所以maxn=2*n
- 需要将顶点字符串名称转换为整数,方便操作,使用map<string,int> si存储<名称,id>,使用map<int,string> is存储<id,名称>
- 点权存储,使用整型数组int wt[maxn]存储
- 边权存储,使用二维矩阵int g[maxn][maxn]存储
思路 02
- map<string,vector<string>> g; //存储边
- map<string,int> wt; //存储点权
- map<string,int> vis; //标识顶点是否被访问过
- map<string,int> res; //存储最终结果,map默认key字典序排序
- int k,num,sum; //k-判断连通分量总权重是否满足条件的阈值;num-连通分量顶点数;sum-连通分量总权重
- string head; //满足条件的连通分量点权最大的顶点
2 寻找连通分量,并统计各个连通分量的总边权,总人数,最大点权
思路 01:深度优先遍历DFS
思路 02:广度优先遍历BFS
思路 03:并查集(+路径压缩)
- 输入测试样例时,将所有关联边进行并查集操作,全部输入完成后,所有连通分量都已划分好并用各自的唯一根id作为连通分量标识
- 再次遍历所有顶点,并使用并查集的find函数查找其所在连通分量的根节点,记录权重,人数,和最大权重顶点名称
问题 01:若连通分量中有环,BFS和DFS过程中累加边权时,可能会重复记录
并查集-解决方案 01
并查集过程中不做任何处理,最后比较判断时,将阈值2,若连通分量的总边权>2阈值即为犯罪团伙
DFS/BFS-解决方案 01
访问完A点累计AC边权后,将AC边权g[A][C]和CA边权g[C][A]都置为0,再次访问到CA时不再累加
DFS/BFS-解决方案 02
使用二维矩阵int evis[maxn][maxn]记录每条边的访问情况,初始为0,访问后置为1
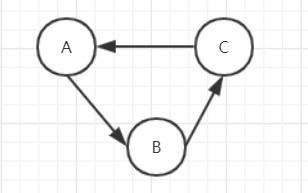
如图1所示,A->B->C,访问A时累加了A与C边权,访问C时累加了A与C边权
问题 02:各个连通分量的总边权,总人数,最大点权如何记录?
DFS/BFS-解决方案 01
定义三个整型变量,记录每个连通分量总边权,最大点权对应id,连通分量总人数
并查集-解决方案 01
使用三个整型数组,数组的下标对应顶点id,并查集处理时,将总边权和最大点权和集合人数统计到根节点id对应的下标处
并查集-解决方案 02
定义连通分量结构体数组node gang[maxn](下标对应顶点id),结构体中定义总边权,最大点权对应id,连通分量总人数。并查集处理时,将总边权和最大点权和集合人数统计到根节点id对应的下标处
易错点
- 最终打印的多个连通分量,需要按照最大点权对应的顶点名称的字典序排序(测试点2,5)
Code
Code 01(邻接表 DFS)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <map>using namespace std;const int maxn=2010;map<string,vector<string>> g;map<string,int> wt;map<string,int> vis;map<string,int> res;int k,num,sum;string head;void dfs(string s) {vis[s]=1;num++;sum+=wt[s];if(wt[s]>wt[head])head=s;for(int i=0; i<g[s].size(); i++) {if(vis[g[s][i]]==0)dfs(g[s][i]);}}void dfs_travel() {for(auto &it:vis) {if(it.second==1)continue;num=sum=0;head=it.first;dfs(it.first);if(num>2&&sum/2>k)res[head]=num;}}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int n,t;string a,b;scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {cin>>a>>b>>t;wt[a]+=t;wt[b]+=t;g[a].push_back(b);g[b].push_back(a);vis[a]=vis[b]=0;}dfs_travel();printf("%d\n",res.size());for(map<string,int>::iterator it=res.begin(); it!=res.end(); it++) {printf("%s %d\n",it->first.c_str(),it->second);}return 0;}
Code 02(邻接矩阵 DFS)
#include <iostream>#include <map>using namespace std;const int maxn = 2010;map<string,int> si;map<int,string> is;map<string,int> ans;int id,k,wt[maxn],g[maxn][maxn],vis[maxn];//wt点权,g边权int sti(string s) {if(si[s]==0) {si[s]=++id; //从1开始is[id]=s;}return si[s];}void dfs(int i,int &head,int &num,int &tv) {num++;vis[i]=true;if(wt[i]>wt[head])head=i;for(int j=1; j<=id; j++) {if(g[i][j]==0)continue;tv+=g[i][j];g[i][j]=g[j][i]=0;if(vis[j]==false)dfs(j,head,num,tv);}}void dfs_travel() {for(int i=1; i<=id; i++) {if(vis[i]==true)continue;int head=i,num=0,tv=0;dfs(i,head,num,tv);if(num>2&&tv>k)ans[is[head]]=num;}}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int n,w;string s1,s2;scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {cin>>s1>>s2>>w;int id1=sti(s1);int id2=sti(s2);wt[id1]+=w;wt[id2]+=w;g[id1][id2]+=w;g[id2][id1]+=w;}dfs_travel(); //深度优先遍历printf("%d\n",ans.size());for(auto it=ans.begin();it!=ans.end();it++){printf("%s %d\n",it->first.c_str(),it->second);}return 0;}
Code 03(邻接矩阵 BFS)
#include <iostream>#include <map>#include <queue>const int maxn=2010;using namespace std;map<string,int> si;map<int,string> is;map<string,int> ans;int id,k,wt[maxn],g[maxn][maxn],vis[maxn],evis[maxn][maxn];//wt点权,g边权int sti(string s) {if(si[s]==0) {si[s]=++id; //从1开始is[id]=s;}return si[s];}void bfs(int now, int &head, int &num, int &tv) {queue<int> q;q.push(now);vis[now]=true;while(!q.empty()) {int i = q.front();q.pop();num++;if(wt[i]>wt[head])head=i;for(int j=1; j<=id; j++) {if(evis[i][j]==1||g[i][j]==0)continue;tv+=g[i][j];evis[i][j]=evis[j][i]=1;if(vis[j]==false) {q.push(j);vis[j]=true;}}}}void bfs_travel() {for(int i=1; i<=id; i++) {if(vis[i]==true)continue;int head=i,num=0,tv=0;bfs(i,head,num,tv);if(num>2&&tv>k)ans[is[head]]=num;}}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {int n,w;string s1,s2;scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {cin>>s1>>s2>>w;int id1=sti(s1);int id2=sti(s2);wt[id1]+=w;wt[id2]+=w;g[id1][id2]+=w;g[id2][id1]+=w;}bfs_travel(); //深度优先遍历printf("%d\n",ans.size());for(auto it=ans.begin(); it!=ans.end(); it++) {printf("%s %d\n",it->first.c_str(),it->second);}return 0;}
Code 04(邻接矩阵 并查集 结构体记录连通分量属性)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <map>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int maxn=2010;map<string,int> si;map<int,string> is;int id=1,k,father[maxn],wt[maxn];//wt点权,g边权struct node { //定义每个连通块的属性int anum,awt,head; //总人数,总权重,队首整数编号} gang[maxn];int sti(string s) {if(si[s]==0) {si[s]=id; //从1开始is[id]=s;id++;}return si[s];}/* 并查集 初始化 */void init() {for(int i=0; i<maxn; i++) father[i]=i;}/* 并查集 查 */int find(int x) {int a = x;while(x!=father[x])x=father[x];while(a!=father[a]) {int temp=a;a=father[a];father[temp]=x;}return x;}/* 并查集 并 */void Union(int a, int b) {int x = find(a);int y = find(b);if(x<=y)father[y]=x;else father[x]=y;}bool cmp(node &n1,node &n2){return is[n1.head]<is[n2.head];}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {init();int n,w;string s1,s2;scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {cin>>s1>>s2>>w;int id1=sti(s1);int id2=sti(s2);Union(id1,id2);wt[id1]+=w;wt[id2]+=w;}for(int i=1; i<id; i++) {int r = find(i);gang[r].anum++; //人数增加1gang[r].awt += wt[i]; //总权重增加if(wt[gang[r].head]<wt[i]) {gang[r].head=i;}}sort(gang+1,gang+id,cmp);vector<int> v;for(int i=1; i<=id; i++) {if(gang[i].awt>2*k&&gang[i].anum>2)v.push_back(i);}printf("%d\n",v.size());for(int i=0; i<v.size(); i++) {printf("%s %d\n",is[gang[v[i]].head].c_str(),gang[v[i]].anum);}return 0;}
Code 05(邻接矩阵 并查集 整型数组记录连通分量属性)
#include <iostream>#include <vector>#include <map>#include <algorithm>using namespace std;const int maxn=2010;map<string,int> si;map<int,string> is;int id=1,k,father[maxn],wt[maxn],awt[maxn],anum[maxn],head[maxn];//wt点权,g边权int sti(string s) {if(si[s]==0) {si[s]=id; //从1开始is[id]=s;id++;}return si[s];}/* 并查集 初始化 */void init() {for(int i=0; i<maxn; i++) father[i]=i;}/* 并查集 查 */int find(int x) {int a = x;while(x!=father[x])x=father[x];while(a!=father[a]) {int temp=a;a=father[a];father[temp]=x;}return x;}/* 并查集 并 */int Union(int a, int b) {int x = find(a);int y = find(b);if(x<=y)father[y]=x;else father[x]=y;}bool cmp(int a, int b) {return is[head[a]]<is[head[b]];}int main(int argc,char * argv[]) {init();int n,w;string s1,s2;scanf("%d %d",&n,&k);for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {cin>>s1>>s2>>w;int id1=sti(s1);int id2=sti(s2);Union(id1,id2);wt[id1]+=w;wt[id2]+=w;}for(int i=1; i<id; i++) {int r = find(i);awt[r]+=wt[i]; //累计权重anum[r]++; //累计人数if(wt[head[r]]<wt[i]) {head[r]=i;}}vector<int> v;for(int i=1; i<id; i++) {if(awt[i]>2*k&&anum[i]>2)v.push_back(i);}sort(v.begin(),v.end(),cmp); //不排序不符合条件,有两个测试点错误printf("%d\n",v.size());for(int i=0; i<v.size(); i++) {printf("%s %d\n",is[head[v[i]]].c_str(),anum[v[i]]);}return 0;}
PAT Advanced 1034 Head of a Gang (30) [图的遍历,BFS,DFS,并查集]的更多相关文章
- pat 甲级 1034. Head of a Gang (30)
1034. Head of a Gang (30) 时间限制 100 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue One wa ...
- PAT 甲级 1034 Head of a Gang (30 分)(bfs,map,强连通)
1034 Head of a Gang (30 分) One way that the police finds the head of a gang is to check people's p ...
- PAT Advanced 1053 Path of Equal Weight (30) [树的遍历]
题目 Given a non-empty tree with root R, and with weight Wi assigned to each tree node Ti. The weight ...
- PAT甲级1034. Head of a Gang
PAT甲级1034. Head of a Gang 题意: 警方找到一个帮派的头的一种方式是检查人民的电话.如果A和B之间有电话,我们说A和B是相关的.关系的权重被定义为两人之间所有电话的总时间长度. ...
- PAT 1034. Head of a Gang (30)
题目地址:http://pat.zju.edu.cn/contests/pat-a-practise/1034 此题考查并查集的应用,要熟悉在合并的时候存储信息: #include <iostr ...
- PAT甲题题解-1034. Head of a Gang (30)-并查集
给出n和k接下来n行,每行给出a,b,c,表示a和b之间的关系度,表明他们属于同一个帮派一个帮派由>2个人组成,且总关系度必须大于k.帮派的头目为帮派里关系度最高的人.(注意,这里关系度是看帮派 ...
- pat 甲级 1034 ( Head of a Gang )
1034 Head of a Gang (30 分) One way that the police finds the head of a gang is to check people's pho ...
- 1034. Head of a Gang (30) -string离散化 -map应用 -并查集
题目如下: One way that the police finds the head of a gang is to check people's phone calls. If there is ...
- 1034. Head of a Gang (30)
分析: 考察并查集,注意中间合并时的时间的合并和人数的合并. #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #include <algor ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu基于Apache为自己的网站开启HTTPS
暂时放这里链接,之后整理 https://www.deanhan.cn/ubuntu-apache-https.html
- 【转载】Jmeter关联-正则表达式提取器
今天研发同事提供了一个验证token的接口,要验证token的正确性,现在将整个过程做如下记录: 场景:验证token的正确性 原理:首先用户登录成功后,会在Response head ...
- MQTT 协议学习:006-订阅主题 与 对应报文(SUBSCRIBE、SUBACK、UNSUBSCRIBE、UNSUBACK)
背景 之前我们提到了怎么发布消息对应的报文:现在我们来看,订阅一个主题的报文是怎么样的. SUBSCRIBE - 订阅主题 客户端向服务端发送SUBSCRIBE报文用于创建一个或多个订阅.每个订阅注册 ...
- decompiler of java
运维了两个java项目,但是没有源代码,整天都是各种问题,各方面都不配合.我也只是个小小的兵,但是工作还是要做. 转机 偶然想试一试decomplier,就找到了gd-gui,感觉用着挺好的,到把项目 ...
- Delphi 10.3.3 THTTPClient Post问题
如果对于Post提交,需要对参数进行urlEncode处理的需要注意. 对于Post参数,可以用TString或者TStringStream两者.如果你采用的是用TStringStream,那么必须按 ...
- javascript中call与this的初见
call定义 语法:call([thisObj[,arg1[, arg2[, [,.argN]]]]]) 定义:调用一个对象的一个方法,以另一个对象替换当前对象. 说明:call 方法可以用来代替另一 ...
- 吴裕雄 Bootstrap 前端框架开发——Bootstrap 字体图标(Glyphicons):glyphicon glyphicon-repeat
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name ...
- 在ubuntu中使用ipython
python自带的shell实在是不怎么好用 大家可以用一下ipython这个软件,它可以自动缩进,补齐,语法高亮等 安装办法: sudo apt install ipython #这个是安装2.7的 ...
- windows中的运行命令
首先按“开始”-“运行”,或按WIN键+R,进入『运行』窗口. 下面是常用的运行命令 (按英文字符顺序排列) appwize.cpl----添加.删除程序 access.cpl-----辅助功能选项 ...
- Linux系统下的/etc/nsswitch.conf文件
一.什么是nsswithch.conf(服务搜索顺序)文件呢? nsswitch.conf(name service switch configuration,名字服务切换配置)文件位于/etc目录下 ...