Springboot一些常用注解
Springboot启动注解
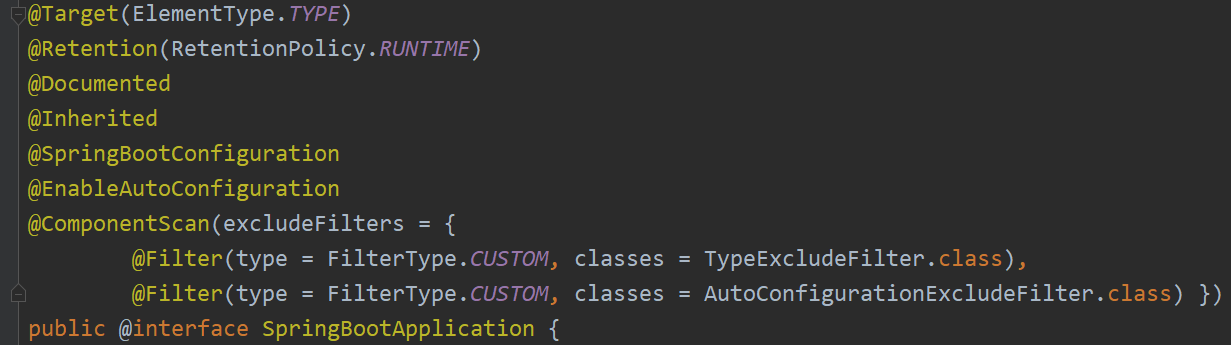
@SpringbootApplication
这个注解是Springboot最核心的注解,用在Springboot的主类上,标识这是一个Springboot应用,用来开启Springboot的各项能力。实际上这个注解 @SpringbootApplication = @SpringBootConfiguration + @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan。
@EnableAutoConfiguration
允许Springboot自动配置,帮助Springboot将所有符合条件的@Configuration配置都加载到Spring容器中。
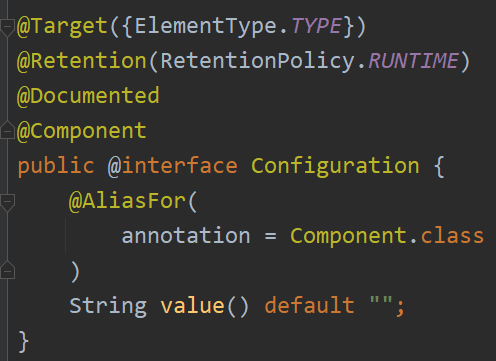
@Configuration
@Configuration注解用于定义配置类,替换xml配置文件,被注解的类内部包含一个或多个被@Bean注解的方法。这些方法会被
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext或AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext类进行扫描,并用于构建bean定义,初始化Spring容器。
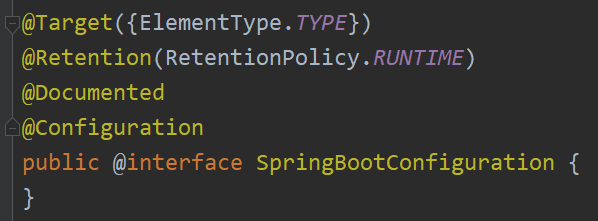
@SpringBootConfiguration
@SpringBootConfiguration继承自@Configuration,二者功能一致,标注当前类是配置类,并将类内声明的一个或多个@Bean注解标记的方法对应的实例加载到Spring容器中。
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan注解默认会装配标识了@Controller,@Service,@Repository,@Component注解的类到Spring容器中。扫描路径可以通过value属性或basePackages属性配置。如果不指定扫描路径则默认从声明@ComponetScan所在类的包进行扫描。
Spring Bean相关注解
@Component, @Controller, @Service, @Repository
@Component: 通用的注解,可标注任意类为Spring组件
@Controller: 对应SpringMVC控制层,主要用于接受用户请求,并调用Service层返回数据给前端
@Service: 对应Service层,主要是一些逻辑功能的实现,并调用DAO层接口
@Repository: 对应DAO层,主要用于操作数据库
@RestController
@RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody,表示这是一个控制器Bean,并返回JSON或XML格式数据(对应前后端分离的情况)。
@Bean
@Bean明确地指示了方法产生一个bean实例,并交给Spring容器管理。
@Bean
@Scope("singleton")
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Scope
@Scope用于声明Spring Bean的作用域。
- singletion: 单例(默认情况)
- prototype: 每次请求创建一个新的实例
- request: 每一次HTTP请求产生一个新的实例,该实例仅在当前HTTP request内有效
- session: 每一个HTTP Session会产生一个新的实例,该实例仅在当前HTTP Session内有效
@Autowired
@Autowired自动注入对象到类中。
注入方式:
- 构造器注入(推荐)
优点:保证依赖不为空,强依赖处理(编译阶段即可发现);避免了循环依赖;提升代码可复用性
缺点:注入参数较多时,代码臃肿不友好 - Field注入
优点:代码少,简洁明了
缺点:容易出现空指针异常,Field注入允许构建对象实例的时候依赖的实例对象为空,直到调用该实例才能发现 - Setter注入
优点:相比构造注入,Setter注入类似于选择注入;允许在类构造完成后重新注入
# Field注入
public class UmsAdminController {
@Autowired
private UmsAdminService umsAdminService;
}
# 构造器注入
public class UmsAdminController {
private UmsAdminService umsAdminService;
@Autowired
public UmsAdminController(UmsAdminService umsAdminService) {
this.umsAdminService = umsAdminService;
}
}
# Setter注入
public class UmsAdminController {
private UmsAdminService umsAdminService;
@Autowired
public void setAdminController(UmsAdminService umsAdminService) {
this.umsAdminService = umsAdminService;
}
}
HTTP请求相关注解
HTTP的请求类型:
- GET: 从服务器获取资源
- POST: 在服务器创建一个新的资源
- PUT: 更新服务器上的资源(全量更新,由客户端提供更新后的整个资源)
- DELETE: 从服务器删除资源
- PATCH: 更新服务器上的资源(增量更新,客户端提供更改的属性,使用较少)
@GetMapping
@GetMapping = @RequestMappig(method=RequestMethod.GET)
@PostMapping
@PostMapping= @RequestMappig(method=RequestMethod.POST)
@PutMapping
@PutMapping= @RequestMappig(method=RequestMethod.PUT)
@DeleteMapping
@DeleteMapping= @RequestMappig(method=RequestMethod.DELETE)
@PathVariable
获取路径参数。
@RequestMapping(value = "/permission/{adminId}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult<List<UmsPermission>> getPermissionList(@PathVariable Long adminId) {
List<UmsPermission> permissionList = umsAdminService.getAllPermission(adminId);
return CommonResult.success(permissionList);
}
可以从请求的url中获取adminId。
@RequestParam
获取请求参数。
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete/batch", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult<Object> delete(@RequestParam("ids") List<Long> ids) {
esProductService.delete(ids);
return CommonResult.success(null);
}
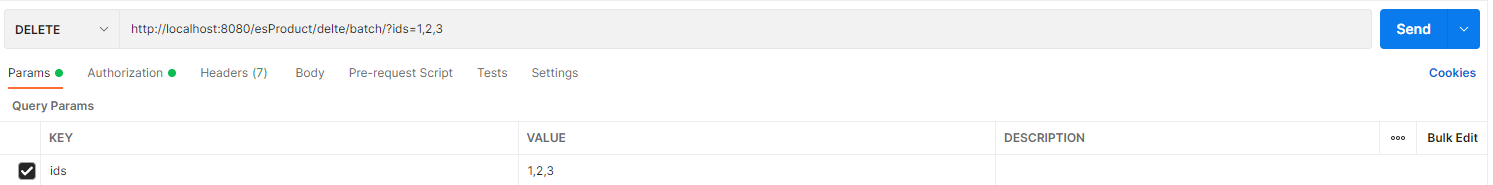
RequestParam会跟在url的 ? 之后。
@RequestBody
读取Request请求的body部分,并且Content-Type为application/json格式,接收到数据之后会自动将数据绑定到Java对象。
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public CommonResult login(@RequestBody UmsAdminLoginParam umsAdminLoginParam, BindingResult result) {
String token = umsAdminService.login(umsAdminLoginParam.getUsername(), umsAdminLoginParam.getPassword());
if (token == null) {
return CommonResult.validateFailed("用户名或密码错误");
}
Map<String, String> tokenMap = new HashMap<>();
tokenMap.put("tokenHead", tokenHead);
tokenMap.put("token", token);
return CommonResult.success(tokenMap);
}
public class UmsAdminLoginParam {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}
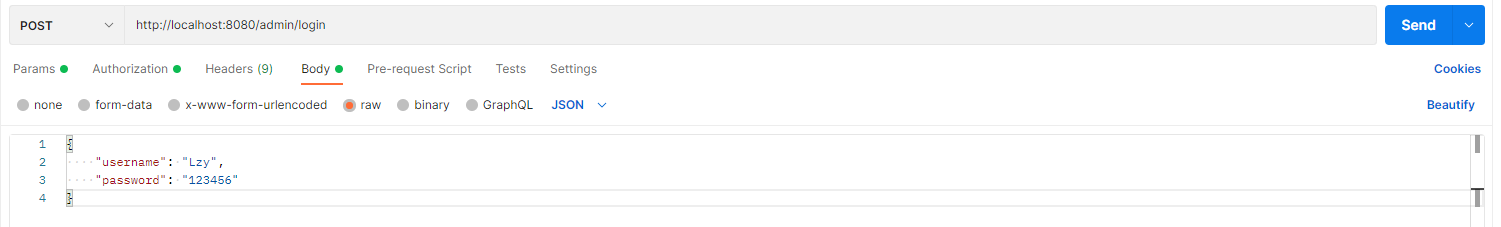
在RequestBody中发送JSON数据,后端可以把JSON数据映射到UmsAdminLoginParam类实例上。
总结:一个请求方法只能有一个@RequestBody,可以有多个@RequestParam和@PathVariable。
读取配置信息相关注解
@Value
读取简单配置信息。
# application.yml
jwt:
field: Authorization
secret: mySecret
expiration: 604800
tokenHead: Bearer
@Component
public class JwtTokenUtil {
@Value("${jwt.secret}")
private String secret;
@Value("${jwt.expiration}")
private Long expiration;
}
@ConfigurationProperties
@ConfigurationProperties有一个
prefix属性,通过指定前缀来绑定配置文件中的配置信息。
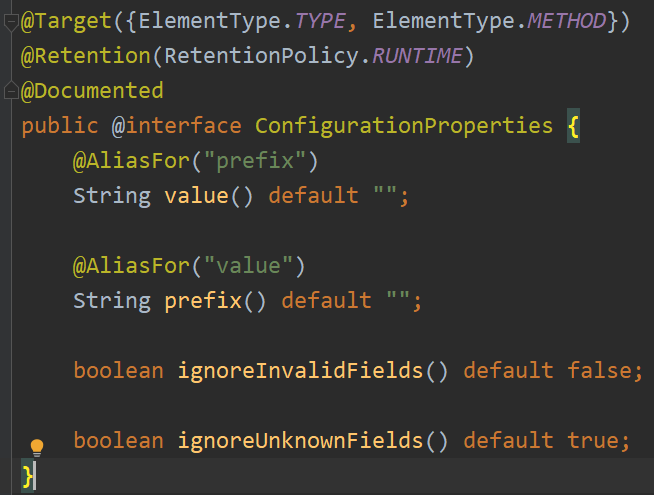
使用方式:
- 作用于类上
- 作用于方法上:该方法需要有@Bean注解且所属类有@Configuration注解
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mall-learning?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
username: root
password: "0926"
// 作用于类上
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Component
@Getter
@Setter
public class Datasource {
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
}
// 作用于方法上
@Configuration
public class DatasourceConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
@Bean
public Datasource datasource() {
return new Datasource();
}
}
public class ConfigurationPropertiesController {
@Autowired
private Datasource datasource;
}
这种绑定对象的方式是隐式绑定的,即配置文件中的字段除 prefix 后的名称需要与类中对应相同。
@PropertySource
@PropertySource读取指定 properties 文件。
# jwt.properties
jwt.field: Authorization
jwt.secret: mySecret
jwt.expiration: 604800
jwt.tokenHead: Bearer
@Component
@PeopertySource(name = "classpath:jwt.properties")
public class JwtTokenUtil {
@Value("${jwt.secret}")
private String secret;
@Value("${jwt.expiration}")
private Long expiration;
}
Springboot一些常用注解的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot 中常用注解
本篇博文将介绍几种SpringBoot 中常用注解 其中,各注解的作用为: @PathVaribale 获取url中的数据 @RequestParam 获取请求参数的值 @GetMapping 组合注 ...
- SpringBoot 中常用注解@PathVaribale/@RequestParam/@GetMapping介绍
SpringBoot 中常用注解@PathVaribale/@RequestParam/@GetMapping介绍 本篇博文将介绍几种如何处理url中的参数的注解@PathVaribale/@Requ ...
- SpringBoot 中常用注解@Controller/@RestController/@RequestMapping的区别
SpringBoot中常用注解@Controller/@RestController/@RequestMapping的区别 @Controller 处理http请求 @Controller //@Re ...
- SpringBoot 中常用注解@Controller/@RestController/@RequestMapping介绍
原文 SpringBoot 中常用注解 @Controller/@RestController/@RequestMapping介绍 @Controller 处理http请求 @Controller / ...
- SpringBoot+Spring常用注解总结
为什么要写这篇文章? 最近看到网上有一篇关于 SpringBoot 常用注解的文章被转载的比较多,我看了文章内容之后属实觉得质量有点低,并且有点会误导没有太多实际使用经验的人(这些人又占据了大多数). ...
- SpringBoot中常用注解@Controller/@RestController/@RequestMapping的区别
@Controller 处理http请求 @Controller //@ResponseBody public class HelloController { @RequestMapping(valu ...
- springboot部分常用注解
目录:[持续更新.....] spring 部分常用注解 spring boot 学习之路1(简单入门) spring boot 学习之路2(注解介绍) spring boot 学习之路3( 集成my ...
- springboot系列总结(二)---springboot的常用注解
上一篇文章我们简单讲了一下@SpringBootApplication这个注解,申明让spring boot自动给程序进行必要的配置,他是一个组合注解,包含了@ComponentScan.@Confi ...
- SpringBoot之常用注解
在spring boot中,摒弃了spring以往项目中大量繁琐的配置,遵循约定大于配置的原则,通过自身默认配置,极大的降低了项目搭建的复杂度.同样在spring boot中,大量注解的使用,使得代码 ...
- 【SpringBoot】常用注解
@EnableAutoConfiguration 启动自动装载:使用了这个注解之后,所有引入的jar的starters都会被自动注入.这个类的设计就是为starter工作的. @RestControl ...
随机推荐
- Java8中Stream的用法
Java8中Stream的用法 1.概述 Stream APl ( java.util.stream)把真正的函数式编程风格引入到Java中.这是目前为止对Java类库最好的补充,因为Stream A ...
- oracle导入dmp
通过impdp导入 1.sqlplus (连接oracle数据库) 2.输入用户名密码3.create user abc identified by 123456; (创建用户名为ab ...
- C语言初级阶段8——预处理
C语言初级阶段8--预处理 预定义符号 1.概念:预处理是编译之前做的一些事. 2.常用的预定义符号: 注意:: (1)-(4)的格式占位符都用%是,如:printf("%s",D ...
- STM32任意引脚模拟IIC
关于模拟I2C,任意接口都可模拟(未全部测试,可能存在特殊情况). 关于SDA_IN与SDAOUT:如下定义: 举例:#define MPU_SDA_IN() {GPIOA->CRL&= ...
- OSIDP-并发:死锁和饥饿-06
死锁原理 死锁:一组相互竞争系统资源或者进行通信的进程间"永久"阻塞的现象. 资源分为两类:可重用资源和可消耗资源. 可重用资源:一次只能被一个进程使用且不会被耗尽的资源.如处理器 ...
- Tomcat后端无法返回数据
以前使用的是Tomcat8和9,这次使用的10怎么就无法返回数据呢? 一开始以为是因为这个错误:Using CATALINA_OPTS: "" 但是后来发现怎么尝试都无法取出这 ...
- 采用4-20mA电流的模拟量传输
工业上常用的总线协议RS232,RS485等,都是传输数字信号的方式.工业上普遍需要测量各类非电物理量,例如温度.压力.速度.角度等,这些都需要转换成模拟量电信号才能传输到几百米外的控制室或显示设备上 ...
- python读书笔记-网页制作
socket()函数 Python 中,我们用 socket()函数来创建套接字,语法格式如下: Socket 对象(内建)方法 Python Internet 模块:
- ffmpeg设置超时时间
使用 -rw_timeout 参数 注意:1.参数单位是微秒,而不是秒.1秒(s)=1000000微秒(μs) 2.参数要放在开流前,否则不会生效 参考资料: FFmpeg命令读取RTMP流如何设 ...
- Oracle 取Group By 第一条
select *from (select emp.*,row_number() over(partition by deptno order by rownum) cn from emp)where ...
