深入解析Kubernetes admission webhooks
BACKGROUND
admission controllers的特点:
- 可定制性:准入功能可针对不同的场景进行调整。
- 可预防性:审计则是为了检测问题,而准入控制器可以预防问题发生
- 可扩展性:在kubernetes自有的验证机制外,增加了另外的防线,弥补了RBAC仅能对资源提供安全保证。
下图,显示了用户操作资源的流程,可以看出 admission controllers 作用是在通过身份验证资源持久化之前起到拦截作用。在准入控制器的加入会使kubernetes增加了更高级的安全功能。
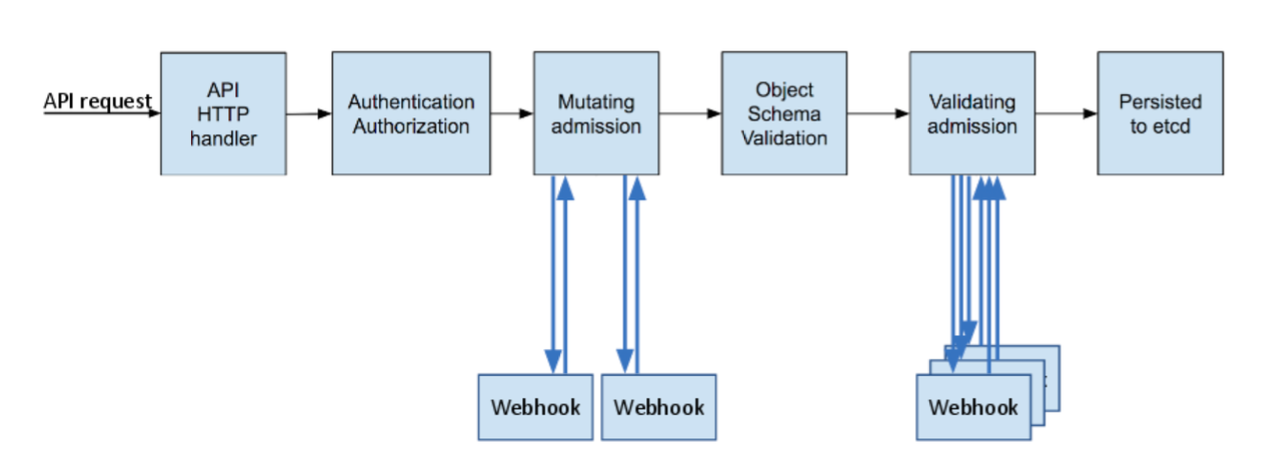
图:Kubernetes API 请求的请求处理步骤图
Source:https://kubernetes.io/blog/2019/03/21/a-guide-to-kubernetes-admission-controllers/
这里找到一个大佬博客画的图,通过两张图可以很清晰的了解到admission webhook流程,与官方给出的不一样的地方在于,这里清楚地定位了kubernetes admission webhook 处于准入控制中,RBAC之后,push 之前。
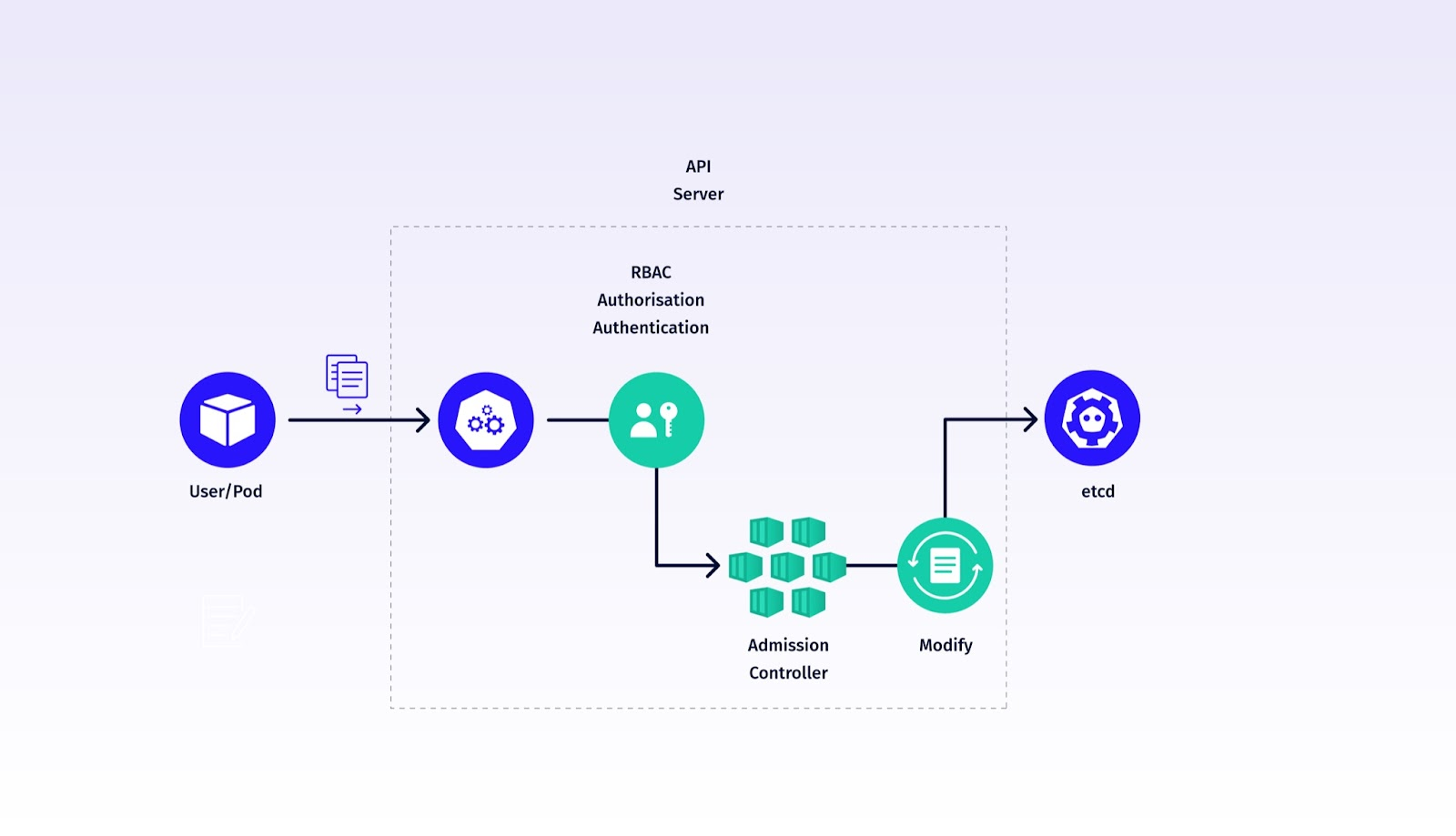
图:Kubernetes API 请求的请求处理步骤图(详细)
Source:https://www.armosec.io/blog/kubernetes-admission-controller/
两种控制器有什么区别?
根据官方提供的说法是
Mutating controllers may modify related objects to the requests they admit; validating controllers may not
从结构图中也可以看出,validating 是在持久化之前,而 Mutating 是在结构验证前,根据这些特性我们可以使用 Mutating 修改这个资源对象内容(如增加验证的信息),在 validating 中验证是否合法。
composition of admission controllers
kubernetes中的 admission controllers 由两部分组成:
- 内置在APIServer中的准入控制器 build-in list
- 特殊的控制器;也是内置在APIServer中,但提供一些自定义的功能
- MutatingAdmission
- ValidatingAdmission
Mutating 控制器可以修改他们处理的资源对象,Validating 控制器不会。当在任何一个阶段中的任何控制器拒绝这个了请求,则会立即拒绝整个请求,并将错误返回。
admission webhook
由于准入控制器是内置在 kube-apiserver 中的,这种情况下就限制了admission controller的可扩展性。在这种背景下,kubernetes提供了一种可扩展的准入控制器 extensible admission controllers,这种行为叫做动态准入控制 Dynamic Admission Control,而提供这个功能的就是 admission webhook 。
admission webhook 通俗来讲就是 HTTP 回调,通过定义一个http server,接收准入请求并处理。用户可以通过kubernetes提供的两种类型的 admission webhook,validating admission webhook 和 mutating admission webhook。来完成自定义的准入策略的处理。
webhook 就是
注:从上面的流程图也可以看出,admission webhook 也是有顺序的。首先调用mutating webhook,然后会调用validating webhook。
如何使用准入控制器
使用条件:kubernetes v1.16 使用 admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1 ;kubernetes v1.9 使用 admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1。
如何在集群中开启准入控制器? :查看kube-apiserver 的启动参数 --enable-admission-plugins ;通过该参数来配置要启动的准入控制器,如 --enable-admission-plugins=NodeRestriction 多个准入控制器以 , 分割,顺序无关紧要。 反之使用 --disable-admission-plugins 参数可以关闭相应的准入控制器(Refer to apiserver opts)。
通过 kubectl 命令可以看到,当前kubernetes集群所支持准入控制器的版本
$ kubectl api-versions | grep admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1beta1
webhook工作原理
通过上面的学习,已经了解到了两种webhook的工作原理如下所示:
mutating webhook,会在持久化前拦截在 MutatingWebhookConfiguration 中定义的规则匹配的请求。MutatingAdmissionWebhook 通过向 mutating webhook 服务器发送准入请求来执行验证。
validaing webhook,会在持久化前拦截在
ValidatingWebhookConfiguration中定义的规则匹配的请求。ValidatingAdmissionWebhook 通过将准入请求发送到 validating webhook server来执行验证。
那么接下来将从源码中看这个在这个工作流程中,究竟做了些什么?
资源类型
对于 1.9 版本之后,也就是 v1 版本 ,admission 被定义在 k8s.io\api\admissionregistration\v1\types.go ,大同小异,因为本地只有1.18集群,所以以这个讲解。
对于 Validating Webhook 来讲实现主要都在webhook中
type ValidatingWebhookConfiguration struct {
// 每个api必须包含下列的metadata,这个是kubernetes规范,可以在注释中的url看到相关文档
metav1.TypeMeta `json:",inline"`
metav1.ObjectMeta `json:"metadata,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=metadata"`
// Webhooks在这里被表示为[]ValidatingWebhook,表示我们可以注册多个
// +optional
// +patchMergeKey=name
// +patchStrategy=merge
Webhooks []ValidatingWebhook `json:"webhooks,omitempty" patchStrategy:"merge" patchMergeKey:"name" protobuf:"bytes,2,rep,name=Webhooks"`
}
webhook,则是对这种类型的webhook提供的操作、资源等。对于这部分不做过多的注释了,因为这里本身为kubernetes API资源,官网有很详细的例子与说明。这里更多字段的意思的可以参考官方 doc
type ValidatingWebhook struct {
// admission webhook的名词,Required
Name string `json:"name" protobuf:"bytes,1,opt,name=name"`
// ClientConfig 定义了与webhook通讯的方式 Required
ClientConfig WebhookClientConfig `json:"clientConfig" protobuf:"bytes,2,opt,name=clientConfig"`
// rule表示了webhook对于哪些资源及子资源的操作进行关注
Rules []RuleWithOperations `json:"rules,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,3,rep,name=rules"`
// FailurePolicy 对于无法识别的value将如何处理,allowed/Ignore optional
FailurePolicy *FailurePolicyType `json:"failurePolicy,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,4,opt,name=failurePolicy,casttype=FailurePolicyType"`
// matchPolicy 定义了如何使用“rules”列表来匹配传入的请求。
MatchPolicy *MatchPolicyType `json:"matchPolicy,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,9,opt,name=matchPolicy,casttype=MatchPolicyType"`
NamespaceSelector *metav1.LabelSelector `json:"namespaceSelector,omitempty" protobuf:"bytes,5,opt,name=namespaceSelector"`
SideEffects *SideEffectClass `json:"sideEffects" protobuf:"bytes,6,opt,name=sideEffects,casttype=SideEffectClass"`
AdmissionReviewVersions []string `json:"admissionReviewVersions" protobuf:"bytes,8,rep,name=admissionReviewVersions"`
}
到这里了解了一个webhook资源的定义,那么这个如何使用呢?通过 Find Usages 找到一个 k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/admission/plugin/webhook/accessors.go 在使用它。这里没有注释,但在结构上可以看出,包含客户端与一系列选择器组成
type mutatingWebhookAccessor struct {
*v1.MutatingWebhook
uid string
configurationName string
initObjectSelector sync.Once
objectSelector labels.Selector
objectSelectorErr error
initNamespaceSelector sync.Once
namespaceSelector labels.Selector
namespaceSelectorErr error
initClient sync.Once
client *rest.RESTClient
clientErr error
}
accessor 因为包含了整个webhookconfig定义的一些动作(这里个人这么觉得)。
accessor.go 下面 有一个 GetRESTClient 方法 ,通过这里可以看出,这里做的就是使用根据 accessor 构造一个客户端。
func (m *mutatingWebhookAccessor) GetRESTClient(clientManager *webhookutil.ClientManager) (*rest.RESTClient, error) {
m.initClient.Do(func() {
m.client, m.clientErr = clientManager.HookClient(hookClientConfigForWebhook(m))
})
return m.client, m.clientErr
}
到这步骤已经没必要往下看了,因已经知道这里是请求webhook前的步骤了,下面就是何时请求了。
k8s.io\apiserver\pkg\admission\plugin\webhook\validating\dispatcher.go 下面有两个方法,Dispatch去请求我们自己定义的webhook
func (d *validatingDispatcher) Dispatch(ctx context.Context, attr admission.Attributes, o admission.ObjectInterfaces, hooks []webhook.WebhookAccessor) error {
var relevantHooks []*generic.WebhookInvocation
// Construct all the versions we need to call our webhooks
versionedAttrs := map[schema.GroupVersionKind]*generic.VersionedAttributes{}
for _, hook := range hooks {
invocation, statusError := d.plugin.ShouldCallHook(hook, attr, o)
if statusError != nil {
return statusError
}
if invocation == nil {
continue
}
relevantHooks = append(relevantHooks, invocation)
// If we already have this version, continue
if _, ok := versionedAttrs[invocation.Kind]; ok {
continue
}
versionedAttr, err := generic.NewVersionedAttributes(attr, invocation.Kind, o)
if err != nil {
return apierrors.NewInternalError(err)
}
versionedAttrs[invocation.Kind] = versionedAttr
}
if len(relevantHooks) == 0 {
// no matching hooks
return nil
}
// Check if the request has already timed out before spawning remote calls
select {
case <-ctx.Done():
// parent context is canceled or timed out, no point in continuing
return apierrors.NewTimeoutError("request did not complete within requested timeout", 0)
default:
}
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
errCh := make(chan error, len(relevantHooks))
wg.Add(len(relevantHooks))
// 循环所有相关的注册的hook
for i := range relevantHooks {
go func(invocation *generic.WebhookInvocation) {
defer wg.Done()
// invacation 中有一个 Accessor,Accessor注册了一个相关的webhookconfig
// 也就是我们 kubectl -f 注册进来的那个webhook的相关配置
hook, ok := invocation.Webhook.GetValidatingWebhook()
if !ok {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("validating webhook dispatch requires v1.ValidatingWebhook, but got %T", hook))
return
}
versionedAttr := versionedAttrs[invocation.Kind]
t := time.Now()
// 调用了callHook去请求我们自定义的webhook
err := d.callHook(ctx, hook, invocation, versionedAttr)
ignoreClientCallFailures := hook.FailurePolicy != nil && *hook.FailurePolicy == v1.Ignore
rejected := false
if err != nil {
switch err := err.(type) {
case *webhookutil.ErrCallingWebhook:
if !ignoreClientCallFailures {
rejected = true
admissionmetrics.Metrics.ObserveWebhookRejection(hook.Name, "validating", string(versionedAttr.Attributes.GetOperation()), admissionmetrics.WebhookRejectionCallingWebhookError, 0)
}
case *webhookutil.ErrWebhookRejection:
rejected = true
admissionmetrics.Metrics.ObserveWebhookRejection(hook.Name, "validating", string(versionedAttr.Attributes.GetOperation()), admissionmetrics.WebhookRejectionNoError, int(err.Status.ErrStatus.Code))
default:
rejected = true
admissionmetrics.Metrics.ObserveWebhookRejection(hook.Name, "validating", string(versionedAttr.Attributes.GetOperation()), admissionmetrics.WebhookRejectionAPIServerInternalError, 0)
}
}
admissionmetrics.Metrics.ObserveWebhook(time.Since(t), rejected, versionedAttr.Attributes, "validating", hook.Name)
if err == nil {
return
}
if callErr, ok := err.(*webhookutil.ErrCallingWebhook); ok {
if ignoreClientCallFailures {
klog.Warningf("Failed calling webhook, failing open %v: %v", hook.Name, callErr)
utilruntime.HandleError(callErr)
return
}
klog.Warningf("Failed calling webhook, failing closed %v: %v", hook.Name, err)
errCh <- apierrors.NewInternalError(err)
return
}
if rejectionErr, ok := err.(*webhookutil.ErrWebhookRejection); ok {
err = rejectionErr.Status
}
klog.Warningf("rejected by webhook %q: %#v", hook.Name, err)
errCh <- err
}(relevantHooks[i])
}
wg.Wait()
close(errCh)
var errs []error
for e := range errCh {
errs = append(errs, e)
}
if len(errs) == 0 {
return nil
}
if len(errs) > 1 {
for i := 1; i < len(errs); i++ {
// TODO: merge status errors; until then, just return the first one.
utilruntime.HandleError(errs[i])
}
}
return errs[0]
}
callHook 可以理解为真正去请求我们自定义的webhook服务的动作
func (d *validatingDispatcher) callHook(ctx context.Context, h *v1.ValidatingWebhook, invocation *generic.WebhookInvocation, attr *generic.VersionedAttributes) error {
if attr.Attributes.IsDryRun() {
if h.SideEffects == nil {
return &webhookutil.ErrCallingWebhook{WebhookName: h.Name, Reason: fmt.Errorf("Webhook SideEffects is nil")}
}
if !(*h.SideEffects == v1.SideEffectClassNone || *h.SideEffects == v1.SideEffectClassNoneOnDryRun) {
return webhookerrors.NewDryRunUnsupportedErr(h.Name)
}
}
uid, request, response, err := webhookrequest.CreateAdmissionObjects(attr, invocation)
if err != nil {
return &webhookutil.ErrCallingWebhook{WebhookName: h.Name, Reason: err}
}
// 发生请求,可以看到,这里从上面的讲到的地方获取了一个客户端
client, err := invocation.Webhook.GetRESTClient(d.cm)
if err != nil {
return &webhookutil.ErrCallingWebhook{WebhookName: h.Name, Reason: err}
}
trace := utiltrace.New("Call validating webhook",
utiltrace.Field{"configuration", invocation.Webhook.GetConfigurationName()},
utiltrace.Field{"webhook", h.Name},
utiltrace.Field{"resource", attr.GetResource()},
utiltrace.Field{"subresource", attr.GetSubresource()},
utiltrace.Field{"operation", attr.GetOperation()},
utiltrace.Field{"UID", uid})
defer trace.LogIfLong(500 * time.Millisecond)
// 这里设置超时,超时时长就是在yaml资源清单中设置的那个值
if h.TimeoutSeconds != nil {
var cancel context.CancelFunc
ctx, cancel = context.WithTimeout(ctx, time.Duration(*h.TimeoutSeconds)*time.Second)
defer cancel()
}
// 直接用post请求我们自己定义的webhook接口
r := client.Post().Body(request)
// if the context has a deadline, set it as a parameter to inform the backend
if deadline, hasDeadline := ctx.Deadline(); hasDeadline {
// compute the timeout
if timeout := time.Until(deadline); timeout > 0 {
// if it's not an even number of seconds, round up to the nearest second
if truncated := timeout.Truncate(time.Second); truncated != timeout {
timeout = truncated + time.Second
}
// set the timeout
r.Timeout(timeout)
}
}
if err := r.Do(ctx).Into(response); err != nil {
return &webhookutil.ErrCallingWebhook{WebhookName: h.Name, Reason: err}
}
trace.Step("Request completed")
result, err := webhookrequest.VerifyAdmissionResponse(uid, false, response)
if err != nil {
return &webhookutil.ErrCallingWebhook{WebhookName: h.Name, Reason: err}
}
for k, v := range result.AuditAnnotations {
key := h.Name + "/" + k
if err := attr.Attributes.AddAnnotation(key, v); err != nil {
klog.Warningf("Failed to set admission audit annotation %s to %s for validating webhook %s: %v", key, v, h.Name, err)
}
}
if result.Allowed {
return nil
}
return &webhookutil.ErrWebhookRejection{Status: webhookerrors.ToStatusErr(h.Name, result.Result)}
}
走到这里基本上对 admission webhook 有了大致的了解,可以知道这个操作是由 apiserver 完成的。下面就实际操作下自定义一个webhook。
这里还有两个概念,就是请求参数 AdmissionRequest 和相应参数 AdmissionResponse,这些可以在 callHook 中看到,这两个参数被定义在 k8s.io\api\admission\v1\types.go ;这两个参数也就是我们在自定义 webhook时需要处理接收到的请求的内容。
如何编写一个自定义的admission webhook
通过上面的学习了解到了,自定义的webhook就是做为kubernetes提供给用户两种admission controller来验证自定义业务的一个中间件 admission webhook。本质上他是一个HTTP Server,用户可以使用任何语言来完成这部分功能。当然,如果涉及到需要对kubernetes集群资源操作的话,还是建议使用kubernetes官方提供了SDK的编程语言来完成自定义的webhook。
那么完成一个自定义admission webhook需要两个步骤:
- 将相关的webhook config注册给kubernetes,也就是让kubernetes知道你的webhook
- 准备一个http server来处理 apiserver发过来验证的信息
向kubernetes注册webhook对象
kubernetes提供的两种类型可自定义的准入控制器,和其他资源一样,可以利用资源清单,动态配置那些资源要被adminssion webhook处理。 kubernetes将这种形式抽象为两种资源:
ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
MutatingWebhookConfiguration
ValidatingAdmission
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: "pod-policy.example.com"
webhooks:
- name: "pod-policy.example.com"
rules:
- apiGroups: [""] # 拦截资源的Group "" 表示 core。"*" 表示所有。
apiVersions: ["v1"] # 拦截资源的版本
operations: ["CREATE"] # 什么请求下拦截
resources: ["pods"] # 拦截什么资源
scope: "Namespaced" # 生效的范围,cluster还是namespace "*"表示没有范围限制。
clientConfig: # 我们部署的webhook服务,
service: # service是在cluster-in模式下
namespace: "example-namespace"
name: "example-service"
port: 443 # 服务的端口
path: "/validate" # path是对应用于验证的接口
# caBundle是提供给 admission webhook CA证书
caBundle: "Ci0tLS0tQk...<base64-encoded PEM bundle containing the CA that signed the webhook's serving certificate>...tLS0K"
admissionReviewVersions: ["v1", "v1beta1"]
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 5 # 1-30s直接,表示请求api的超时时间
MutatingAdmission
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: "valipod-policy.example.com"
webhooks:
- name: "valipod-policy.example.com"
rules:
- apiGroups: ["apps"] # 拦截资源的Group "" 表示 core。"*" 表示所有。
apiVersions: ["v1"] # 拦截资源的版本
operations: ["CREATE"] # 什么请求下拦截
resources: ["deployments"] # 拦截什么资源
scope: "Namespaced" # 生效的范围,cluster还是namespace "*"表示没有范围限制。
clientConfig: # 我们部署的webhook服务,
url: "https://10.0.0.1:81/validate" # 这里是外部模式
# service: # service是在cluster-in模式下
# namespace: "default"
# name: "admission-webhook"
# port: 81 # 服务的端口
# path: "/mutate" # path是对应用于验证的接口
# caBundle是提供给 admission webhook CA证书
caBundle: "Ci0tLS0tQk...<base64-encoded PEM bundle containing the CA that signed the webhook's serving certificate>...tLS0K"
admissionReviewVersions: ["v1"]
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 5 # 1-30s直接,表示请求api的超时时间
注:对于webhook,也可以引入外部的服务,并非必须部署到集群内部
对于外部服务来讲,需要 clientConfig 中的 service , 更换为 url ; 通过 url 参数可以将一个外部的服务引入
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
...
webhooks:
- name: my-webhook.example.com
clientConfig:
url: "https://my-webhook.example.com:9443/my-webhook-path"
...
注:这里的url规则必须准守下列形式:
scheme://host:port/path- 使用了url 时,这里不应填写集群内的服务
scheme必须是 https,不能为http,这就意味着,引入外部时也需要- 配置时使用了,
?xx=xx的参数也是不被允许的(官方说法是这样的,通过源码学习了解到因为会发送特定的请求体,所以无需管参数)
更多的配置可以参考kubernetes官方提供的 doc
准备一个webhook
让我们编写我们的 webhook server。将创建两个钩子,/mutate 与 /validate;
/mutate将在创建deployment资源时,基于版本,给资源加上注释webhook.example.com/allow: true/validate将对/mutate增加的allow:true那么则继续,否则拒绝。
这里为了方便,全部写在一起了,实际上不符合软件的设计。在kubernetes代码库中也提供了一个webhook server,可以参考他这个webhook server来学习具体要做什么
package main
import (
"context"
"crypto/tls"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"os/signal"
"strings"
"syscall"
v1admission "k8s.io/api/admission/v1"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/runtime/serializer"
appv1 "k8s.io/api/apps/v1"
metav1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/klog"
)
type patch struct {
Op string `json:"op"`
Path string `json:"path"`
Value map[string]string `json:"value"`
}
func serve(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
var body []byte
if data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(r.Body); err == nil {
body = data
}
klog.Infof(fmt.Sprintf("receive request: %v....", string(body)[:130]))
if len(body) == 0 {
klog.Error(fmt.Sprintf("admission request body is empty"))
http.Error(w, fmt.Errorf("admission request body is empty").Error(), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
var admission v1admission.AdmissionReview
codefc := serializer.NewCodecFactory(runtime.NewScheme())
decoder := codefc.UniversalDeserializer()
_, _, err := decoder.Decode(body, nil, &admission)
if err != nil {
msg := fmt.Sprintf("Request could not be decoded: %v", err)
klog.Error(msg)
http.Error(w, msg, http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
if admission.Request == nil {
klog.Error(fmt.Sprintf("admission review can't be used: Request field is nil"))
http.Error(w, fmt.Errorf("admission review can't be used: Request field is nil").Error(), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
switch strings.Split(r.RequestURI, "?")[0] {
case "/mutate":
req := admission.Request
var admissionResp v1admission.AdmissionReview
admissionResp.APIVersion = admission.APIVersion
admissionResp.Kind = admission.Kind
klog.Infof("AdmissionReview for Kind=%v, Namespace=%v Name=%v UID=%v Operation=%v",
req.Kind.Kind, req.Namespace, req.Name, req.UID, req.Operation)
switch req.Kind.Kind {
case "Deployment":
var (
respstr []byte
err error
deploy appv1.Deployment
)
if err = json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &deploy); err != nil {
respStructure := v1admission.AdmissionResponse{Result: &metav1.Status{
Message: fmt.Sprintf("could not unmarshal resouces review request: %v", err),
Code: http.StatusInternalServerError,
}}
klog.Error(fmt.Sprintf("could not unmarshal resouces review request: %v", err))
if respstr, err = json.Marshal(respStructure); err != nil {
klog.Error(fmt.Errorf("could not unmarshal resouces review response: %v", err))
http.Error(w, fmt.Errorf("could not unmarshal resouces review response: %v", err).Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
http.Error(w, string(respstr), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
current_annotations := deploy.GetAnnotations()
pl := []patch{}
for k, v := range current_annotations {
pl = append(pl, patch{
Op: "add",
Path: "/metadata/annotations",
Value: map[string]string{
k: v,
},
})
}
pl = append(pl, patch{
Op: "add",
Path: "/metadata/annotations",
Value: map[string]string{
deploy.Name + "/Allow": "true",
},
})
annotationbyte, err := json.Marshal(pl)
if err != nil {
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
respStructure := &v1admission.AdmissionResponse{
UID: req.UID,
Allowed: true,
Patch: annotationbyte,
PatchType: func() *v1admission.PatchType {
t := v1admission.PatchTypeJSONPatch
return &t
}(),
Result: &metav1.Status{
Message: fmt.Sprintf("could not unmarshal resouces review request: %v", err),
Code: http.StatusOK,
},
}
admissionResp.Response = respStructure
klog.Infof("sending response: %s....", admissionResp.Response.String()[:130])
respByte, err := json.Marshal(admissionResp)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Can't encode response messages: %v", err)
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
klog.Infof("prepare to write response...")
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
if _, err := w.Write(respByte); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Can't write response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not write response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
default:
klog.Error(fmt.Sprintf("unsupport resouces review request type"))
http.Error(w, "unsupport resouces review request type", http.StatusBadRequest)
}
case "/validate":
req := admission.Request
var admissionResp v1admission.AdmissionReview
admissionResp.APIVersion = admission.APIVersion
admissionResp.Kind = admission.Kind
klog.Infof("AdmissionReview for Kind=%v, Namespace=%v Name=%v UID=%v Operation=%v",
req.Kind.Kind, req.Namespace, req.Name, req.UID, req.Operation)
var (
deploy appv1.Deployment
respstr []byte
)
switch req.Kind.Kind {
case "Deployment":
if err = json.Unmarshal(req.Object.Raw, &deploy); err != nil {
respStructure := v1admission.AdmissionResponse{Result: &metav1.Status{
Message: fmt.Sprintf("could not unmarshal resouces review request: %v", err),
Code: http.StatusInternalServerError,
}}
klog.Error(fmt.Sprintf("could not unmarshal resouces review request: %v", err))
if respstr, err = json.Marshal(respStructure); err != nil {
klog.Error(fmt.Errorf("could not unmarshal resouces review response: %v", err))
http.Error(w, fmt.Errorf("could not unmarshal resouces review response: %v", err).Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
return
}
http.Error(w, string(respstr), http.StatusBadRequest)
return
}
}
al := deploy.GetAnnotations()
respStructure := v1admission.AdmissionResponse{
UID: req.UID,
}
if al[fmt.Sprintf("%s/Allow", deploy.Name)] == "true" {
respStructure.Allowed = true
respStructure.Result = &metav1.Status{
Code: http.StatusOK,
}
} else {
respStructure.Allowed = false
respStructure.Result = &metav1.Status{
Code: http.StatusForbidden,
Reason: func() metav1.StatusReason {
return metav1.StatusReasonForbidden
}(),
Message: fmt.Sprintf("the resource %s couldn't to allow entry.", deploy.Kind),
}
}
admissionResp.Response = &respStructure
klog.Infof("sending response: %s....", admissionResp.Response.String()[:130])
respByte, err := json.Marshal(admissionResp)
if err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Can't encode response messages: %v", err)
http.Error(w, err.Error(), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
klog.Infof("prepare to write response...")
w.Header().Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
if _, err := w.Write(respByte); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Can't write response: %v", err)
http.Error(w, fmt.Sprintf("could not write response: %v", err), http.StatusInternalServerError)
}
}
}
func main() {
var (
cert, key string
)
if cert = os.Getenv("TLS_CERT"); len(cert) == 0 {
cert = "./tls/tls.crt"
}
if key = os.Getenv("TLS_KEY"); len(key) == 0 {
key = "./tls/tls.key"
}
ca, err := tls.LoadX509KeyPair(cert, key)
if err != nil {
klog.Error(err.Error())
return
}
server := &http.Server{
Addr: ":81",
TLSConfig: &tls.Config{
Certificates: []tls.Certificate{
ca,
},
},
}
httpserver := http.NewServeMux()
httpserver.HandleFunc("/validate", serve)
httpserver.HandleFunc("/mutate", serve)
httpserver.HandleFunc("/ping", func(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
klog.Info(fmt.Sprintf("%s %s", r.RequestURI, "pong"))
fmt.Fprint(w, "pong")
})
server.Handler = httpserver
go func() {
if err := server.ListenAndServeTLS("", ""); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("Failed to listen and serve webhook server: %v", err)
}
}()
klog.Info("starting serve.")
signalChan := make(chan os.Signal, 1)
signal.Notify(signalChan, syscall.SIGINT, syscall.SIGTERM)
<-signalChan
klog.Infof("Got shut signal, shutting...")
if err := server.Shutdown(context.Background()); err != nil {
klog.Errorf("HTTP server Shutdown: %v", err)
}
}
对应的Dockerfile
FROM golang:alpine AS builder
MAINTAINER cylon
WORKDIR /admission
COPY ./ /admission
ENV GOPROXY https://goproxy.cn,direct
RUN \
sed -i 's/dl-cdn.alpinelinux.org/mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/g' /etc/apk/repositories && \
apk add upx && \
GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 CGO_ENABLED=0 go build -ldflags "-s -w" -o webhook main.go && \
upx -1 webhook && \
chmod +x webhook
FROM alpine AS runner
WORKDIR /go/admission
COPY --from=builder /admission/webhook .
VOLUME ["/admission"]
集群内部部署所需的资源清单
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: admission-webhook
labels:
app: admission-webhook
spec:
ports:
- port: 81
targetPort: 81
selector:
app: simple-webhook
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
labels:
app: simple-webhook
name: simple-webhook
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: simple-webhook
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: simple-webhook
spec:
containers:
- image: cylonchau/simple-webhook:v0.0.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: webhook
command: ["./webhook"]
env:
- name: "TLS_CERT"
value: "./tls/tls.crt"
- name: "TLS_KEY"
value: "./tls/tls.key"
- name: NS_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
ports:
- containerPort: 81
volumeMounts:
- name: tlsdir
mountPath: /go/admission/tls
readOnly: true
volumes:
- name: tlsdir
secret:
secretName: webhook
---
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: MutatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: "pod-policy.example.com"
webhooks:
- name: "pod-policy.example.com"
rules:
- apiGroups: ["apps"] # 拦截资源的Group "" 表示 core。"*" 表示所有。
apiVersions: ["v1"] # 拦截资源的版本
operations: ["CREATE"] # 什么请求下拦截
resources: ["deployments"] # 拦截什么资源
scope: "Namespaced" # 生效的范围,cluster还是namespace "*"表示没有范围限制。
clientConfig: # 我们部署的webhook服务,
url: "https://10.0.0.1:81/mutate"
# service: # service是在cluster-in模式下
# namespace: "default"
# name: "admission-webhook"
# port: 81 # 服务的端口
# path: "/mutate" # path是对应用于验证的接口
# caBundle是提供给 admission webhook CA证书
caBundle: Put you CA (base64 encode) in here
admissionReviewVersions: ["v1"]
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 5 # 1-30s直接,表示请求api的超时时间
---
apiVersion: admissionregistration.k8s.io/v1
kind: ValidatingWebhookConfiguration
metadata:
name: "valipod-policy.example.com"
webhooks:
- name: "valipod-policy.example.com"
rules:
- apiGroups: ["apps"] # 拦截资源的Group "" 表示 core。"*" 表示所有。
apiVersions: ["v1"] # 拦截资源的版本
operations: ["CREATE"] # 什么请求下拦截
resources: ["deployments"] # 拦截什么资源
scope: "Namespaced" # 生效的范围,cluster还是namespace "*"表示没有范围限制。
clientConfig: # 我们部署的webhook服务,
# service: # service是在cluster-in模式下
# namespace: "default"
# name: "admission-webhook"
# port: 81 # 服务的端口
# path: "/mutate" # path是对应用于验证的接口
# caBundle是提供给 admission webhook CA证书
caBundle: Put you CA (base64 encode) in here
admissionReviewVersions: ["v1"]
sideEffects: None
timeoutSeconds: 5 # 1-30s直接,表示请求api的超时时间
这里需要主义的问题
证书问题
如果需要 cluster-in ,那么则需要对对应webhookconfig资源配置 service ;如果使用的是外部部署,则需要配置对应访问地址,如:"https://xxxx:port/method"
这两种方式的证书均需要对应的 subjectAltName ,cluster-in 模式 需要对应service名称,如,至少包含serviceName.NS.svc 这一个域名。
下面就是证书类问题的错误
Failed calling webhook, failing closed pod-policy.example.com: failed calling webhook "pod-policy.example.com": Post https://admission-webhook.default.svc:81/mutate?timeout=5s: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority (possibly because of "crypto/rsa: verification error" while trying to verify candidate authority certificate "admission-webhook-ca")
相应信息问题
上面我们了解到的APIServer是去发出 v1admission.AdmissionReview 也就是 Request 和 Response类型的,所以,为了更清晰的表示出问题所在,需要对响应格式中的 Reason 与 Message 配置,这也就是我们在客户端看到的报错信息。
&metav1.Status{
Code: http.StatusForbidden,
Reason: func() metav1.StatusReason {
return metav1.StatusReasonForbidden
}(),
Message: fmt.Sprintf("the resource %s couldn't to allow entry.", deploy.Kind),
}
通过上面的设置用户可以看到下列错误
$ kubectl apply -f nginx.yaml
Error from server (Forbidden): error when creating "nginx.yaml": admission webhook "valipod-policy.example.com" denied the request: the resource Deployment couldn't to allow entry.
注:必须的参数还包含,UID,allowed,这两个是必须的,上面阐述的只是对用户友好的提示信息
下面的报错就是对相应格式设置错误
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "nginx.yaml": Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "pod-policy.example.com": the server rejected our request for an unknown reason
相应信息版本问题
相应信息也需要指定一个版本,这个与请求来的结构中拿即可
admissionResp.APIVersion = admission.APIVersion
admissionResp.Kind = admission.Kind
下面是没有为对应相应信息配置对应KV的值出现的报错
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "nginx.yaml": Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "pod-policy.example.com": expected webhook response of admission.k8s.io/v1, Kind=AdmissionReview, got /, Kind=
关于patch
kubernetes中patch使用的是特定的规范,如 jsonpatch
kubernetes当前唯一支持的
patchType是JSONPatch。 有关更多详细信息,请参见 JSON patch对于
jsonpatch是一个固定的类型,在go中必须定义其结构体{
"op": "add", // 做什么操作
"path": "/spec/replicas", // 操作的路径
"value": 3 // 对应添加的key value
}
下面就是字符串类型设置为布尔型产生的报错
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "nginx.yaml": Internal error occurred: v1.Deployment.ObjectMeta: v1.ObjectMeta.Annotations: ReadString: expects " or n, but found t, error found in #10 byte of ...|t/Allow":true},"crea|..., bigger context ...|tadata":{"annotations":{"nginx-deployment/Allow":true},"creationTimestamp":null,"managedFields":[{"m|..
准备证书
Ubuntu
touch ./demoCAindex.txt
touch ./demoCA/serial
touch ./demoCA/crlnumber
echo 01 > ./demoCA/serial
mkdir ./demoCA/newcerts
openssl genrsa -out cakey.pem 2048
openssl req -new \
-x509 \
-key cakey.pem \
-out cacert.pem \
-days 3650 \
-subj "/CN=admission webhook ca"
openssl genrsa -out tls.key 2048
openssl req -new \
-key tls.key \
-subj "/CN=admission webhook client" \
-reqexts webhook \
-config <(cat /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf \
<(printf "[webhook]\nsubjectAltName=DNS: admission-webhook, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc.cluster.local, IP:10.0.0.1, IP:10.0.0.4")) \
-out tls.csr
sed -i 's/= match/= optional/g' /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf
openssl ca \
-in tls.csr \
-cert cacert.pem \
-keyfile cakey.pem \
-out tls.crt \
-days 300 \
-extensions webhook \
-extfile <(cat /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf \
<(printf "[webhook]\nsubjectAltName=DNS: admission-webhook, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc.cluster.local, IP:10.0.0.1, IP:10.0.0.4"))
CentOS
touch /etc/pki/CA/index.txt
touch /etc/pki/CA/serial # 下一个要颁发的编号 16进制
touch /etc/pki/CA/crlnumber
echo 01 > /etc/pki/CA/serial
openssl req -new \
-x509 \
-key cakey.pem \
-out cacert.pem \
-days 3650 \
-subj "/CN=admission webhook ca"
openssl genrsa -out tls.key 2048
openssl req -new \
-key tls.key \
-subj "/CN=admission webhook client" \
-reqexts webhook \
-config <(cat /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf \
<(printf "[webhook]\nsubjectAltName=DNS: admission-webhook, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc.cluster.local, IP:10.0.0.1, IP:10.0.0.4")) \
-out tls.csr
sed -i 's/= match/= optional/g' /etc/ssl/openssl.cnf
openssl ca \
-in tls.csr \
-cert cacert.pem \
-keyfile cakey.pem \
-out tls.crt \
-days 300 \
-extensions webhook \
-extfile <(cat /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf \
<(printf "[webhook]\nsubjectAltName=DNS: admission-webhook, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc, DNS: admission-webhook.default.svc.cluster.local, IP:10.0.0.1, IP:10.0.0.4"))
通过部署测试结果
可以看到我们自己注入的 annotation nginx-deployment/Allow: true,在该示例中,仅为演示过程,而不是真的策略,实际环境中可以根据情况进行定制自己的策略。
结果可以看出,当在 mutating 中不通过,即缺少对应的 annotation 标签 , 则 validating 会不允许准入
$ kubectl describe deploy nginx-deployment
Name: nginx-deployment
Namespace: default
CreationTimestamp: Mon, 11 Jul 2022 20:25:16 +0800
Labels: <none>
Annotations: deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: 1
nginx-deployment/Allow: true
Selector: app=nginx
Replicas: 1 desired | 1 updated | 1 total | 1 available | 0 unavailable
StrategyType: RollingUpdate
MinReadySeconds: 0
RollingUpdateStrategy: 25% max unavailable, 25% max surge
Pod Template:
Labels: app=nginx
Containers:
nginx:
Image: nginx:1.14.2
Reference
extensible admission controllers
深入解析Kubernetes admission webhooks的更多相关文章
- 深入解析kubernetes controller-runtime
Overview controller-runtime 是 Kubernetes 社区提供可供快速搭建一套 实现了controller 功能的工具,无需自行实现Controller的功能了:在 Kub ...
- 解析kubernetes架构
一. 简介: kubernetes是一个开源的容器管理工具,是基于GO语言开实现的,轻量级和便携式的应用,可以把kubernetes cluster在linux主机上部署.管理和扩容docker容器的 ...
- 深入解析kubernetes中的选举机制
Overview 在 Kubernetes的 kube-controller-manager , kube-scheduler, 以及使用 Operator 的底层实现 controller-rumt ...
- 使用minukube部署kubernetes admission webhook实现etcd pod安全删除
本需求来自于一道面试题
- Kubernetes 两步验证 - 使用 Serverless 实现动态准入控制
作者:CODING - 王炜 1. 背景 如果对 Kubernetes 集群安全特别关注,那么我们可能想要实现这些需求: 如何实现 Kubernetes 集群的两步验证,除了集群凭据,还需要提供一次性 ...
- image management in kubernet
Image How can I edit an existing docker image metadata? docker-copyedit Registry Disk kubevirtis a g ...
- kubernetes高级之动态准入控制
系列目录 动态准入控制器文档介绍了如何使用标准的,插件式的准入控制器.但是,但是由于以下原因,插件式的准入控制器在一些场景下并不灵活: 它们需要编译到kube-apiserver里 它们仅在apise ...
- 深入解析 Kubebuilder:让编写 CRD 变得更简单
作者 | 刘洋(炎寻) 阿里云高级开发工程师 导读:自定义资源 CRD(Custom Resource Definition)可以扩展 Kubernetes API,掌握 CRD 是成为 Kubern ...
- 使用 Admission Webhook 机制实现多集群资源配额控制
1 要解决的问题 集群分配给多个用户使用时,需要使用配额以限制用户的资源使用,包括 CPU 核数.内存大小.GPU 卡数等,以防止资源被某些用户耗尽,造成不公平的资源分配. 大多数情况下,集群原生的 ...
随机推荐
- jmeter元件分析
jmeter元件分析 一.脚本通用性 1.性能测试脚本改动一下,加入断言等元件,就可以作为接口测试脚本来使用 2.但是接口测试的脚本不可以作为性能测试脚本来使用 3.原因:因为性能测试考虑更多的性能, ...
- 一次IOS通知推送问题排查全过程
原创:打码日记(微信公众号ID:codelogs),欢迎分享,转载请保留出处. 发现问题 在上周一个将要下班的夜晚,测试突然和我打招呼,说IOS推送的修复更新上线后存在问题,后台报错. 连忙跑到测试那 ...
- 攻防世界web进阶题—bug
攻防世界web进阶题-bug 1.打开题目看一下源码,没有问题 2.扫一下目录,没有问题 3.查一下网站的组成:php+Apache+Ubuntu 只有登录界面 这里可以可以想到:爆破.万能密码.进行 ...
- vue - Vue脚手架(终结篇)/ vue动画
几天的内容不是很多,因为我们脚手架的学习告一段落了,也是为了跟明天开始的内容有一个区分. 明天将会有一个非常重要的内容来了,各位,vue中的ajax他来了,这个绝对是重量级,有点兴奋! 十一.TODO ...
- 一个关于 useState 的误解
一个关于 useState 的误解 本文写于 2020 年 11 月 17 日 前两天有人问了我一个问题,他有一段这样的代码: function App() { const [n, setN] = u ...
- 106_Power Pivot之HR入离调转、在职、离职率相关指标
博客:www.jiaopengzi.com 焦棚子的文章目录 请点击下载附件 一.背景 之前有帮公司HR做了些员工入离调转.在职.人工成本分析等(体量:4000人左右).在和其他朋友交流的时候得知,貌 ...
- 安装Speedtest到Python
Speedtest模块可以测试主机的网络带宽大小. 运行环境 系统版本:CentOS Linux release 7.3.1611 (Core) 软件版本:无 硬件要求:无 安装过程 1.安装Spee ...
- drools中的条件 when
目录 1.介绍 2.语法结构 3.模式例子 3.1 单个对象匹配 3.2 匹配任何对象 3.3 带条件匹配 3.3.1 注意事项 3.4 嵌套属性的匹配 3.4.1 访问单个嵌套属性 3.4.2 访问 ...
- 第06组 Beta冲刺 (5/5)
目录 1.1 基本情况 1.2 冲刺概况汇报 1.郝雷明 2. 方梓涵 3.曾丽莉 4.黄少丹 5. 董翔云 6.鲍凌函 7.杜筱 8.詹鑫冰 9.曹兰英 10.吴沅静 1.3 冲刺成果展示 1.1 ...
- Lucene开发实例:Lucene中文分词(转载)
1.准备工作下载lucene 3.6.1 : http://lucene.apache.org/下载中文分词IK Analyzer: http://code.google.com/p/ik-analy ...
