[SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]004 - SSD设备的发现
源代码及NVMe协议版本
- SPDK : spdk-17.07.1
- DPDK : dpdk-17.08
- NVMe Spec: 1.2.1
基本分析方法
- 01 - 到官网http://www.spdk.io/下载spdk-17.07.1.tar.gz
- 02 - 到官网http://www.dpdk.org/下载dpdk-17.08.tar.xz
- 03 - 创建目录nvme/src, 将spdk-17.07.1.tar.gz和dpdk-17.08.tar.xz解压缩到nvme/src中,然后用OpenGrok创建网页版的源代码树
- 04 - 阅读SPDK/NVMe驱动源代码, 同时参考NVMeDirect和Linux内核NVMe驱动
1. 识别NVMe固态硬盘的方法
NVMe SSD是一个PCIe设备, 那么怎么识别这种类型的设备? 有两种方法。
方法1: 通过Device ID + Vendor ID
方法2: 通过Class Code
在Linux内核NVMe驱动中,使用的是第一种方法。而在SPDK中,使用的是第二种方法。 上代码:
- src/spdk-17.07.1/include/spdk/pci_ids.h
52 /**
53 * PCI class code for NVMe devices.
54 *
55 * Base class code 01h: mass storage
56 * Subclass code 08h: non-volatile memory
57 * Programming interface 02h: NVM Express
58 */
59 #define SPDK_PCI_CLASS_NVME 0x010802
而Class Code (0x010802) 在NVMe Specification中的定义如下:

2. Hello World
开始学习一门新的语言或者开发套件的时候,总是离不开"Hello World"。 SPDK也不例外, 让我们从hello_world.c开始, 看一下main()是如何使用SPDK/NVMe驱动的API的,从而帮助我们发现使用NVMe SSDs的主逻辑,
- src/spdk-17.07.1/examples/nvme/hello_world/hello_world.c
306 int main(int argc, char **argv)
307 {
308 int rc;
309 struct spdk_env_opts opts;
310
311 /*
312 * SPDK relies on an abstraction around the local environment
313 * named env that handles memory allocation and PCI device operations.
314 * This library must be initialized first.
315 *
316 */
317 spdk_env_opts_init(&opts);
318 opts.name = "hello_world";
319 opts.shm_id = 0;
320 spdk_env_init(&opts);
321
322 printf("Initializing NVMe Controllers\n");
323
324 /*
325 * Start the SPDK NVMe enumeration process. probe_cb will be called
326 * for each NVMe controller found, giving our application a choice on
327 * whether to attach to each controller. attach_cb will then be
328 * called for each controller after the SPDK NVMe driver has completed
329 * initializing the controller we chose to attach.
330 */
331 rc = spdk_nvme_probe(NULL, NULL, probe_cb, attach_cb, NULL);
332 if (rc != 0) {
333 fprintf(stderr, "spdk_nvme_probe() failed\n");
334 cleanup();
335 return 1;
336 }
337
338 if (g_controllers == NULL) {
339 fprintf(stderr, "no NVMe controllers found\n");
340 cleanup();
341 return 1;
342 }
343
344 printf("Initialization complete.\n");
345 hello_world();
346 cleanup();
347 return 0;
348 }
main()的处理流程为:
001 - 317 spdk_env_opts_init(&opts);
002 - 320 spdk_env_init(&opts);
003 - 331 rc = spdk_nvme_probe(NULL, NULL, probe_cb, attach_cb, NULL);
004 - 345 hello_world();
005 - 346 cleanup();
- 001-002,spdk运行环境初始化
- 003,调用函数spdk_nvme_probe()主动发现NVMe SSDs设备。 显然, 接下来我们要分析的关键函数就是spdk_nvme_probe()。
- 004,调用函数hello_world()做简单的读写操作
- 005,调用函数cleanup()以释放内存资源,detach NVMe SSD设备等。
在分析关键函数spdk_nvme_probe()之前,让我们先搞清楚两个问题:
- 问题1: 每一块NVMe固态硬盘里都一个控制器(Controller), 那么发现的所有NVMe固态硬盘(也就是NVMe Controllers)以什么方式组织在一起?
- 问题2: 每一块NVMe固态硬盘都可以划分为多个NameSpace (类似逻辑分区的概念), 那么这些NameSpace以什么方式组织在一起?
对有经验的C程序员来说,回答这两个问题很easy,那就是链表。我们的hello_world.c也是这么干的。看代码:
39 struct ctrlr_entry {
40 struct spdk_nvme_ctrlr *ctrlr;
41 struct ctrlr_entry *next;
42 char name[1024];
43 };
44
45 struct ns_entry {
46 struct spdk_nvme_ctrlr *ctrlr;
47 struct spdk_nvme_ns *ns;
48 struct ns_entry *next;
49 struct spdk_nvme_qpair *qpair;
50 };
51
52 static struct ctrlr_entry *g_controllers = NULL;
53 static struct ns_entry *g_namespaces = NULL;
其中,
- g_controllers是管理所有NVMe固态硬盘(i.e. NVMe Controllers)的全局链表头。
- g_namespaces是管理所有的namespaces的全局链表头。
那么,回到main()的L338-342, 就很好理解了。 因为g_controllers指针为NULL, 所以没有找到NVMe SSD盘啊,于是cleanup后退出。
338 if (g_controllers == NULL) {
339 fprintf(stderr, "no NVMe controllers found\n");
340 cleanup();
341 return 1;
342 }
现在看看hello_world.c是如何使用spdk_nvme_probe()的,
331 rc = spdk_nvme_probe(NULL, NULL, probe_cb, attach_cb, NULL);
显然,probe_cb和attach_cb是两个callback函数, (其实还有remove_cb, L331未使用)
- probe_cb: 当枚举到一个NVMe设备的时候被调用
- attach_cb: 当一个NVMe设备已经被attach(挂接?)到一个用户态的NVMe 驱动的时候被调用
probe_cb, attach_cb以及remove_cb的相关定义如下:
- src/spdk-17.07.1/include/spdk/nvme.h
268 /**
269 * Callback for spdk_nvme_probe() enumeration.
270 *
271 * \param opts NVMe controller initialization options. This structure will be populated with the
272 * default values on entry, and the user callback may update any options to request a different
273 * value. The controller may not support all requested parameters, so the final values will be
274 * provided during the attach callback.
275 * \return true to attach to this device.
276 */
277 typedef bool (*spdk_nvme_probe_cb)(void *cb_ctx, const struct spdk_nvme_transport_id *trid,
278 struct spdk_nvme_ctrlr_opts *opts);
279
280 /**
281 * Callback for spdk_nvme_probe() to report a device that has been attached to the userspace NVMe driver.
282 *
283 * \param opts NVMe controller initialization options that were actually used. Options may differ
284 * from the requested options from the probe call depending on what the controller supports.
285 */
286 typedef void (*spdk_nvme_attach_cb)(void *cb_ctx, const struct spdk_nvme_transport_id *trid,
287 struct spdk_nvme_ctrlr *ctrlr,
288 const struct spdk_nvme_ctrlr_opts *opts);
289
290 /**
291 * Callback for spdk_nvme_probe() to report that a device attached to the userspace NVMe driver
292 * has been removed from the system.
293 *
294 * The controller will remain in a failed state (any new I/O submitted will fail).
295 *
296 * The controller must be detached from the userspace driver by calling spdk_nvme_detach()
297 * once the controller is no longer in use. It is up to the library user to ensure that
298 * no other threads are using the controller before calling spdk_nvme_detach().
299 *
300 * \param ctrlr NVMe controller instance that was removed.
301 */
302 typedef void (*spdk_nvme_remove_cb)(void *cb_ctx, struct spdk_nvme_ctrlr *ctrlr);
303
304 /**
305 * \brief Enumerate the bus indicated by the transport ID and attach the userspace NVMe driver
306 * to each device found if desired.
307 *
308 * \param trid The transport ID indicating which bus to enumerate. If the trtype is PCIe or trid is NULL,
309 * this will scan the local PCIe bus. If the trtype is RDMA, the traddr and trsvcid must point at the
310 * location of an NVMe-oF discovery service.
311 * \param cb_ctx Opaque value which will be passed back in cb_ctx parameter of the callbacks.
312 * \param probe_cb will be called once per NVMe device found in the system.
313 * \param attach_cb will be called for devices for which probe_cb returned true once that NVMe
314 * controller has been attached to the userspace driver.
315 * \param remove_cb will be called for devices that were attached in a previous spdk_nvme_probe()
316 * call but are no longer attached to the system. Optional; specify NULL if removal notices are not
317 * desired.
318 *
319 * This function is not thread safe and should only be called from one thread at a time while no
320 * other threads are actively using any NVMe devices.
321 *
322 * If called from a secondary process, only devices that have been attached to the userspace driver
323 * in the primary process will be probed.
324 *
325 * If called more than once, only devices that are not already attached to the SPDK NVMe driver
326 * will be reported.
327 *
328 * To stop using the the controller and release its associated resources,
329 * call \ref spdk_nvme_detach with the spdk_nvme_ctrlr instance returned by this function.
330 */
331 int spdk_nvme_probe(const struct spdk_nvme_transport_id *trid,
332 void *cb_ctx,
333 spdk_nvme_probe_cb probe_cb,
334 spdk_nvme_attach_cb attach_cb,
335 spdk_nvme_remove_cb remove_cb);
为了不被proce_cb, attach_cb, remove_cb带跑偏了,我们接下来看看结构体struct spdk_nvme_transport_id和spdk_nvme_probe()函数的主逻辑。
- src/spdk-17.07.1/include/spdk/nvme.h
142 /**
143 * NVMe transport identifier.
144 *
145 * This identifies a unique endpoint on an NVMe fabric.
146 *
147 * A string representation of a transport ID may be converted to this type using
148 * spdk_nvme_transport_id_parse().
149 */
150 struct spdk_nvme_transport_id {
151 /**
152 * NVMe transport type.
153 */
154 enum spdk_nvme_transport_type trtype;
155
156 /**
157 * Address family of the transport address.
158 *
159 * For PCIe, this value is ignored.
160 */
161 enum spdk_nvmf_adrfam adrfam;
162
163 /**
164 * Transport address of the NVMe-oF endpoint. For transports which use IP
165 * addressing (e.g. RDMA), this should be an IP address. For PCIe, this
166 * can either be a zero length string (the whole bus) or a PCI address
167 * in the format DDDD:BB:DD.FF or DDDD.BB.DD.FF
168 */
169 char traddr[SPDK_NVMF_TRADDR_MAX_LEN + 1];
170
171 /**
172 * Transport service id of the NVMe-oF endpoint. For transports which use
173 * IP addressing (e.g. RDMA), this field shoud be the port number. For PCIe,
174 * this is always a zero length string.
175 */
176 char trsvcid[SPDK_NVMF_TRSVCID_MAX_LEN + 1];
177
178 /**
179 * Subsystem NQN of the NVMe over Fabrics endpoint. May be a zero length string.
180 */
181 char subnqn[SPDK_NVMF_NQN_MAX_LEN + 1];
182 };
对于NVMe over PCIe, 我们只需要关注"NVMe transport type"这一项:
154 enum spdk_nvme_transport_type trtype;
而目前,支持两种传输类型, PCIe和RDMA。
130 enum spdk_nvme_transport_type {
131 /**
132 * PCIe Transport (locally attached devices)
133 */
134 SPDK_NVME_TRANSPORT_PCIE = 256,
135
136 /**
137 * RDMA Transport (RoCE, iWARP, etc.)
138 */
139 SPDK_NVME_TRANSPORT_RDMA = SPDK_NVMF_TRTYPE_RDMA,
140 };
有关RDMA的问题,我们后面暂时不做讨论,因为我们目前主要关心NVMe over PCIe。
接下来看函数spdk_nvme_probe()的代码,
- src/spdk-17.07.1/lib/nvme/nvme.c
396 int
397 spdk_nvme_probe(const struct spdk_nvme_transport_id *trid, void *cb_ctx,
398 spdk_nvme_probe_cb probe_cb, spdk_nvme_attach_cb attach_cb,
399 spdk_nvme_remove_cb remove_cb)
400 {
401 int rc;
402 struct spdk_nvme_ctrlr *ctrlr;
403 struct spdk_nvme_transport_id trid_pcie;
404
405 rc = nvme_driver_init();
406 if (rc != 0) {
407 return rc;
408 }
409
410 if (trid == NULL) {
411 memset(&trid_pcie, 0, sizeof(trid_pcie));
412 trid_pcie.trtype = SPDK_NVME_TRANSPORT_PCIE;
413 trid = &trid_pcie;
414 }
415
416 if (!spdk_nvme_transport_available(trid->trtype)) {
417 SPDK_ERRLOG("NVMe trtype %u not available\n", trid->trtype);
418 return -1;
419 }
420
421 nvme_robust_mutex_lock(&g_spdk_nvme_driver->lock);
422
423 nvme_transport_ctrlr_scan(trid, cb_ctx, probe_cb, remove_cb);
424
425 if (!spdk_process_is_primary()) {
426 TAILQ_FOREACH(ctrlr, &g_spdk_nvme_driver->attached_ctrlrs, tailq) {
427 nvme_ctrlr_proc_get_ref(ctrlr);
428
429 /*
430 * Unlock while calling attach_cb() so the user can call other functions
431 * that may take the driver lock, like nvme_detach().
432 */
433 nvme_robust_mutex_unlock(&g_spdk_nvme_driver->lock);
434 attach_cb(cb_ctx, &ctrlr->trid, ctrlr, &ctrlr->opts);
435 nvme_robust_mutex_lock(&g_spdk_nvme_driver->lock);
436 }
437
438 nvme_robust_mutex_unlock(&g_spdk_nvme_driver->lock);
439 return 0;
440 }
441
442 nvme_robust_mutex_unlock(&g_spdk_nvme_driver->lock);
443 /*
444 * Keep going even if one or more nvme_attach() calls failed,
445 * but maintain the value of rc to signal errors when we return.
446 */
447
448 rc = nvme_init_controllers(cb_ctx, attach_cb);
449
450 return rc;
451 }
spdk_nvme_probe()的处理流程为:
001 405: rc = nvme_driver_init();
002 410-414: set trid if it is NULL
003 416: check NVMe trtype via spdk_nvme_transport_available(trid->trtype)
004 423: nvme_transport_ctrlr_scan(trid, cb_ctx, probe_cb, remove_cb);
005 425: check spdk process is primary, if not, do something at L426-440
006 448: rc = nvme_init_controllers(cb_ctx, attach_cb);
接下来,让我们看看函数nvme_transport_ctrlr_scan(),
423 nvme_transport_ctrlr_scan(trid, cb_ctx, probe_cb, remove_cb);
/* src/spdk-17.07.1/lib/nvme/nvme_transport.c#92 */ 91 int
92 nvme_transport_ctrlr_scan(const struct spdk_nvme_transport_id *trid,
93 void *cb_ctx,
94 spdk_nvme_probe_cb probe_cb,
95 spdk_nvme_remove_cb remove_cb)
96 {
97 NVME_TRANSPORT_CALL(trid->trtype, ctrlr_scan, (trid, cb_ctx, probe_cb, remove_cb));
98 }
而宏NVME_TRANSPORT_CALL的定义是:
/* src/spdk-17.07.1/lib/nvme/nvme_transport.c#60 */
52 #define TRANSPORT_PCIE(func_name, args) case SPDK_NVME_TRANSPORT_PCIE: return nvme_pcie_ ## func_name args;
..
60 #define NVME_TRANSPORT_CALL(trtype, func_name, args) \
61 do { \
62 switch (trtype) { \
63 TRANSPORT_PCIE(func_name, args) \
64 TRANSPORT_FABRICS_RDMA(func_name, args) \
65 TRANSPORT_DEFAULT(trtype) \
66 } \
67 SPDK_UNREACHABLE(); \
68 } while (0)
..
于是, nvme_transport_ctrlr_scan()被转化为nvme_pcie_ctrlr_scan()调用(对NVMe over PCIe)来说,
/* src/spdk-17.07.1/lib/nvme/nvme_pcie.c#620 */
619 int
620 nvme_pcie_ctrlr_scan(const struct spdk_nvme_transport_id *trid,
621 void *cb_ctx,
622 spdk_nvme_probe_cb probe_cb,
623 spdk_nvme_remove_cb remove_cb)
624 {
625 struct nvme_pcie_enum_ctx enum_ctx = {};
626
627 enum_ctx.probe_cb = probe_cb;
628 enum_ctx.cb_ctx = cb_ctx;
629
630 if (strlen(trid->traddr) != 0) {
631 if (spdk_pci_addr_parse(&enum_ctx.pci_addr, trid->traddr)) {
632 return -1;
633 }
634 enum_ctx.has_pci_addr = true;
635 }
636
637 if (hotplug_fd < 0) {
638 hotplug_fd = spdk_uevent_connect();
639 if (hotplug_fd < 0) {
640 SPDK_TRACELOG(SPDK_TRACE_NVME, "Failed to open uevent netlink socket\n");
641 }
642 } else {
643 _nvme_pcie_hotplug_monitor(cb_ctx, probe_cb, remove_cb);
644 }
645
646 if (enum_ctx.has_pci_addr == false) {
647 return spdk_pci_nvme_enumerate(pcie_nvme_enum_cb, &enum_ctx);
648 } else {
649 return spdk_pci_nvme_device_attach(pcie_nvme_enum_cb, &enum_ctx, &enum_ctx.pci_addr);
650 }
651 }
接下来重点看看L647对应的函数spck_pci_nvme_enumerate()就好,因为我们的目标是看明白是如何利用Class Code发现SSD设备的。
647 return spdk_pci_nvme_enumerate(pcie_nvme_enum_cb, &enum_ctx);
/* src/spdk-17.07.1/lib/env_dpdk/pci_nvme.c */ 81 int
82 spdk_pci_nvme_enumerate(spdk_pci_enum_cb enum_cb, void *enum_ctx)
83 {
84 return spdk_pci_enumerate(&g_nvme_pci_drv, enum_cb, enum_ctx);
85 }
注意: L84第一个参数为一个全局变量g_nvme_pci_drv的地址, ( 看到一个全局结构体变量总是令人兴奋的:-) )
/* src/spdk-17.07.1/lib/env_dpdk/pci_nvme.c */
38 static struct rte_pci_id nvme_pci_driver_id[] = {
39 #if RTE_VERSION >= RTE_VERSION_NUM(16, 7, 0, 1)
40 {
41 .class_id = SPDK_PCI_CLASS_NVME,
42 .vendor_id = PCI_ANY_ID,
43 .device_id = PCI_ANY_ID,
44 .subsystem_vendor_id = PCI_ANY_ID,
45 .subsystem_device_id = PCI_ANY_ID,
46 },
47 #else
48 {RTE_PCI_DEVICE(0x8086, 0x0953)},
49 #endif
50 { .vendor_id = 0, /* sentinel */ },
51 };
..
53 static struct spdk_pci_enum_ctx g_nvme_pci_drv = {
54 .driver = {
55 .drv_flags = RTE_PCI_DRV_NEED_MAPPING,
56 .id_table = nvme_pci_driver_id,
..
66 },
67
68 .cb_fn = NULL,
69 .cb_arg = NULL,
70 .mtx = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER,
71 .is_registered = false,
72 };
啊哈! 终于跟Class Code (SPDK_PCI_CLASS_NVME=0x010802)扯上了关系。 全局变量g_nvme_pci_drv就是在L53行定义的,而g_nvme_pci_drv.driver.id_table则是在L38行定义的。
38 static struct rte_pci_id nvme_pci_driver_id[] = {
..
41 .class_id = SPDK_PCI_CLASS_NVME,
..
53 static struct spdk_pci_enum_ctx g_nvme_pci_drv = {
54 .driver = {
..
56 .id_table = nvme_pci_driver_id,
..
那么,我们只需要进一步深挖spdk_pci_enumerate()就可以找到SSD设备是如何被发现的了...
/* src/spdk-17.07.1/lib/env_dpdk/pci.c#150 */ 149 int
150 spdk_pci_enumerate(struct spdk_pci_enum_ctx *ctx,
151 spdk_pci_enum_cb enum_cb,
152 void *enum_ctx)
153 {
...
168
169 #if RTE_VERSION >= RTE_VERSION_NUM(17, 05, 0, 4)
170 if (rte_pci_probe() != 0) {
171 #else
172 if (rte_eal_pci_probe() != 0) {
173 #endif
...
184 return 0;
185 }
省略了一些代码,我们接下来重点关注L170,
170 if (rte_pci_probe() != 0) {
从rte_pci_probe()函数的实现开始,我们就深入到DPDK的内部了,代码如下,
/* src/dpdk-17.08/lib/librte_eal/common/eal_common_pci.c#413 */ 407 /*
408 * Scan the content of the PCI bus, and call the probe() function for
409 * all registered drivers that have a matching entry in its id_table
410 * for discovered devices.
411 */
412 int
413 rte_pci_probe(void)
414 {
415 struct rte_pci_device *dev = NULL;
416 size_t probed = 0, failed = 0;
417 struct rte_devargs *devargs;
418 int probe_all = 0;
419 int ret = 0;
420
421 if (rte_pci_bus.bus.conf.scan_mode != RTE_BUS_SCAN_WHITELIST)
422 probe_all = 1;
423
424 FOREACH_DEVICE_ON_PCIBUS(dev) {
425 probed++;
426
427 devargs = dev->device.devargs;
428 /* probe all or only whitelisted devices */
429 if (probe_all)
430 ret = pci_probe_all_drivers(dev);
431 else if (devargs != NULL &&
432 devargs->policy == RTE_DEV_WHITELISTED)
433 ret = pci_probe_all_drivers(dev);
434 if (ret < 0) {
435 RTE_LOG(ERR, EAL, "Requested device " PCI_PRI_FMT
436 " cannot be used\n", dev->addr.domain, dev->addr.bus,
437 dev->addr.devid, dev->addr.function);
438 rte_errno = errno;
439 failed++;
440 ret = 0;
441 }
442 }
443
444 return (probed && probed == failed) ? -1 : 0;
445 }
L430是我们关注的重点,
430 ret = pci_probe_all_drivers(dev);
函数pci_probe_all_drivers()的实现如下:
/* src/dpdk-17.08/lib/librte_eal/common/eal_common_pci.c#307 */ 301 /*
302 * If vendor/device ID match, call the probe() function of all
303 * registered driver for the given device. Return -1 if initialization
304 * failed, return 1 if no driver is found for this device.
305 */
306 static int
307 pci_probe_all_drivers(struct rte_pci_device *dev)
308 {
309 struct rte_pci_driver *dr = NULL;
310 int rc = 0;
311
312 if (dev == NULL)
313 return -1;
314
315 /* Check if a driver is already loaded */
316 if (dev->driver != NULL)
317 return 0;
318
319 FOREACH_DRIVER_ON_PCIBUS(dr) {
320 rc = rte_pci_probe_one_driver(dr, dev);
321 if (rc < 0)
322 /* negative value is an error */
323 return -1;
324 if (rc > 0)
325 /* positive value means driver doesn't support it */
326 continue;
327 return 0;
328 }
329 return 1;
330 }
L320是我们关注的重点,
320 rc = rte_pci_probe_one_driver(dr, dev);
/* src/dpdk-17.08/lib/librte_eal/common/eal_common_pci.c#200 */ 195 /*
196 * If vendor/device ID match, call the probe() function of the
197 * driver.
198 */
199 static int
200 rte_pci_probe_one_driver(struct rte_pci_driver *dr,
201 struct rte_pci_device *dev)
202 {
203 int ret;
204 struct rte_pci_addr *loc;
205
206 if ((dr == NULL) || (dev == NULL))
207 return -EINVAL;
208
209 loc = &dev->addr;
210
211 /* The device is not blacklisted; Check if driver supports it */
212 if (!rte_pci_match(dr, dev))
213 /* Match of device and driver failed */
214 return 1;
215
216 RTE_LOG(INFO, EAL, "PCI device "PCI_PRI_FMT" on NUMA socket %i\n",
217 loc->domain, loc->bus, loc->devid, loc->function,
218 dev->device.numa_node);
219
220 /* no initialization when blacklisted, return without error */
221 if (dev->device.devargs != NULL &&
222 dev->device.devargs->policy ==
223 RTE_DEV_BLACKLISTED) {
224 RTE_LOG(INFO, EAL, " Device is blacklisted, not"
225 " initializing\n");
226 return 1;
227 }
228
229 if (dev->device.numa_node < 0) {
230 RTE_LOG(WARNING, EAL, " Invalid NUMA socket, default to 0\n");
231 dev->device.numa_node = 0;
232 }
233
234 RTE_LOG(INFO, EAL, " probe driver: %x:%x %s\n", dev->id.vendor_id,
235 dev->id.device_id, dr->driver.name);
236
237 if (dr->drv_flags & RTE_PCI_DRV_NEED_MAPPING) {
238 /* map resources for devices that use igb_uio */
239 ret = rte_pci_map_device(dev);
240 if (ret != 0)
241 return ret;
242 }
243
244 /* reference driver structure */
245 dev->driver = dr;
246 dev->device.driver = &dr->driver;
247
248 /* call the driver probe() function */
249 ret = dr->probe(dr, dev);
250 if (ret) {
251 dev->driver = NULL;
252 dev->device.driver = NULL;
253 if ((dr->drv_flags & RTE_PCI_DRV_NEED_MAPPING) &&
254 /* Don't unmap if device is unsupported and
255 * driver needs mapped resources.
256 */
257 !(ret > 0 &&
258 (dr->drv_flags & RTE_PCI_DRV_KEEP_MAPPED_RES)))
259 rte_pci_unmap_device(dev);
260 }
261
262 return ret;
263 }
L212是我们关注的重点,
212 if (!rte_pci_match(dr, dev))
而rte_pci_match()的实现如下,
/* src/dpdk-17.08/lib/librte_eal/common/eal_common_pci.c#163 */ 151 /*
152 * Match the PCI Driver and Device using the ID Table
153 *
154 * @param pci_drv
155 * PCI driver from which ID table would be extracted
156 * @param pci_dev
157 * PCI device to match against the driver
158 * @return
159 * 1 for successful match
160 * 0 for unsuccessful match
161 */
162 static int
163 rte_pci_match(const struct rte_pci_driver *pci_drv,
164 const struct rte_pci_device *pci_dev)
165 {
166 const struct rte_pci_id *id_table;
167
168 for (id_table = pci_drv->id_table; id_table->vendor_id != 0;
169 id_table++) {
170 /* check if device's identifiers match the driver's ones */
171 if (id_table->vendor_id != pci_dev->id.vendor_id &&
172 id_table->vendor_id != PCI_ANY_ID)
173 continue;
174 if (id_table->device_id != pci_dev->id.device_id &&
175 id_table->device_id != PCI_ANY_ID)
176 continue;
177 if (id_table->subsystem_vendor_id !=
178 pci_dev->id.subsystem_vendor_id &&
179 id_table->subsystem_vendor_id != PCI_ANY_ID)
180 continue;
181 if (id_table->subsystem_device_id !=
182 pci_dev->id.subsystem_device_id &&
183 id_table->subsystem_device_id != PCI_ANY_ID)
184 continue;
185 if (id_table->class_id != pci_dev->id.class_id &&
186 id_table->class_id != RTE_CLASS_ANY_ID)
187 continue;
188
189 return 1;
190 }
191
192 return 0;
193 }
看到这里,我们终于找到了SSD设备是如何被发现的, L185-187是我们最希望看到的三行代码:
185 if (id_table->class_id != pci_dev->id.class_id &&
186 id_table->class_id != RTE_CLASS_ANY_ID)
187 continue;
而结构体struct rte_pci_driver和struct rte_pci_device的定义为:
/* src/dpdk-17.08/lib/librte_eal/common/include/rte_pci.h#100 */ 96 /**
97 * A structure describing an ID for a PCI driver. Each driver provides a
98 * table of these IDs for each device that it supports.
99 */
100 struct rte_pci_id {
101 uint32_t class_id; /**< Class ID (class, subclass, pi) or RTE_CLASS_ANY_ID. */
102 uint16_t vendor_id; /**< Vendor ID or PCI_ANY_ID. */
103 uint16_t device_id; /**< Device ID or PCI_ANY_ID. */
104 uint16_t subsystem_vendor_id; /**< Subsystem vendor ID or PCI_ANY_ID. */
105 uint16_t subsystem_device_id; /**< Subsystem device ID or PCI_ANY_ID. */
106 }; /* src/dpdk-17.08/lib/librte_eal/common/include/rte_pci.h#120 */ 120 /**
121 * A structure describing a PCI device.
122 */
123 struct rte_pci_device {
124 TAILQ_ENTRY(rte_pci_device) next; /**< Next probed PCI device. */
125 struct rte_device device; /**< Inherit core device */
126 struct rte_pci_addr addr; /**< PCI location. */
127 struct rte_pci_id id; /**< PCI ID. */
128 struct rte_mem_resource mem_resource[PCI_MAX_RESOURCE];
129 /**< PCI Memory Resource */
130 struct rte_intr_handle intr_handle; /**< Interrupt handle */
131 struct rte_pci_driver *driver; /**< Associated driver */
132 uint16_t max_vfs; /**< sriov enable if not zero */
133 enum rte_kernel_driver kdrv; /**< Kernel driver passthrough */
134 char name[PCI_PRI_STR_SIZE+1]; /**< PCI location (ASCII) */
135 }; /* src/dpdk-17.08/lib/librte_eal/common/include/rte_pci.h#178 */ 175 /**
176 * A structure describing a PCI driver.
177 */
178 struct rte_pci_driver {
179 TAILQ_ENTRY(rte_pci_driver) next; /**< Next in list. */
180 struct rte_driver driver; /**< Inherit core driver. */
181 struct rte_pci_bus *bus; /**< PCI bus reference. */
182 pci_probe_t *probe; /**< Device Probe function. */
183 pci_remove_t *remove; /**< Device Remove function. */
184 const struct rte_pci_id *id_table; /**< ID table, NULL terminated. */
185 uint32_t drv_flags; /**< Flags contolling handling of device. */
186 };
到此为止,我们可以对SSD设备发现做如下总结:
- 01 - 使用Class Code (0x010802)作为SSD设备发现的依据
- 02 - 发现SSD设备的时候,从SPDK进入到DPDK中,函数调用栈为:
00 hello_word.c
01 -> main()
02 --> spdk_nvme_probe()
03 ---> nvme_transport_ctrlr_scan()
04 ----> nvme_pcie_ctrlr_scan()
05 -----> spdk_pci_nvme_enumerate()
06 ------> spdk_pci_enumerate(&g_nvme_pci_drv, ...) | SPDK |
=========================================================================
07 -------> rte_pci_probe() | DPDK |
08 --------> pci_probe_all_drivers()
09 ---------> rte_pci_probe_one_driver()
10 ----------> rte_pci_match()
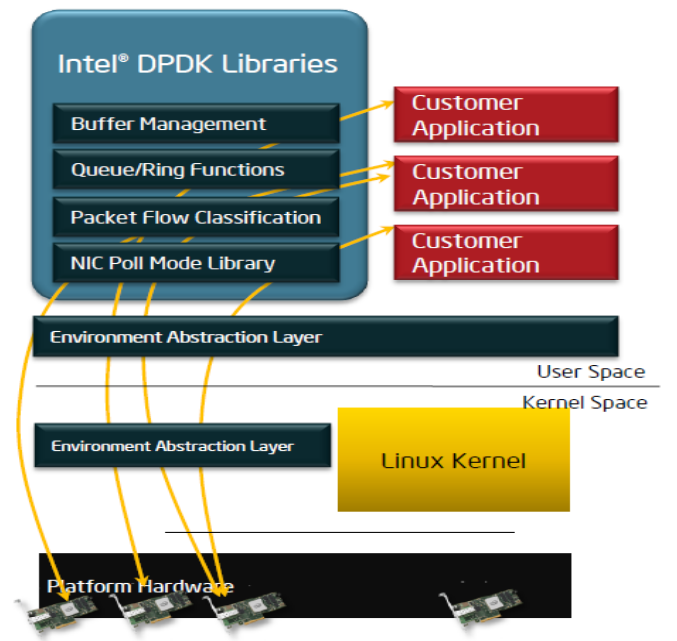
- 03 - DPDK中环境抽象层(EAL: Environment Abstraction Layer)的函数rte_pci_match()是发现SSD设备的关键。
- 04 - DPDK的EAL在DPDK架构中所处的位置,如下图所示:
Your greatness is measured by your horizons. | 你的成就是由你的眼界来衡量的。
[SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]004 - SSD设备的发现的更多相关文章
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]003 - NVMeDirect论文
说明: 之所以要翻译这篇论文,是因为参考此论文可以很好地理解SPDK/NVMe的设计思想. NVMeDirect: A User-space I/O Framework for Application ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]002 - SPDK官方介绍
Introduction to the Storage Performance Development Kit (SPDK) | SPDK概述 By Jonathan S. (Intel), Upda ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]001 - SPDK/NVMe概述
1. NVMe概述 NVMe是一个针对基于PCIe的固态硬盘的高性能的.可扩展的主机控制器接口. NVMe的显著特征是提供多个队列来处理I/O命令.单个NVMe设备支持多达64K个I/O 队列,每个I ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]008 - RDMA概述
毫无疑问地,用来取代iSCSI/iSER(iSCSI Extensions for RDMA)技术的NVMe over Fabrics着实让RDMA又火了一把.在介绍NVMe over Fabrics ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]005 - DPDK概述
注: 之所以要中英文对照翻译下面的文章,是因为SPDK严重依赖于DPDK的实现. Introduction to DPDK: Architecture and PrinciplesDPDK概论:体系结 ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]012 - 用户态ibv_post_send()源码分析
OFA定义了一组标准的Verbs,并提供了一个标准库libibvers.在用户态实现NVMe over RDMA的Host(i.e. Initiator)和Target, 少不了要跟OFA定义的Ver ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]007 - 初识UIO
注: 要进一步搞清楚SSD盘对应的PCI的BAR寄存器的映射,有必要先了解一下UIO(Userspace I/O). UIO(Userspace I/O)是运行在用户空间的I/O技术.在Linux系统 ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]015 - 理解内存注册(Memory Registration)
使用RDMA, 必然关系到内存区域(Memory Region)的注册问题.在本文中,我们将以mlx5 HCA卡为例回答如下几个问题: 为什么需要注册内存区域? 注册内存区域有嘛好处? 注册内存区域的 ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]014 - (NVMe over PCIe)Host端的命令处理流程
NVMe over PCIe最新的NVMe协议是1.3. 在7.2.1讲了Command Processing流程.有图有真相. This section describes command subm ...
随机推荐
- [翻译]Introduction to JSON Web Tokens
JWT: Json Web Tokens JWT是一种开放标准(RFC 7519),它定义了一种紧凑且独立的方式,用于将各方之间的信息安全地传输为JSON对象.因为它是经过数字签名的,所以该信息可以进 ...
- java Excel 简单工具
我就简单的分享一下我常用的工具 这次由于个人问题工具注释全部乱码差点无法还原,也是为了防止数据丢失后期找不到再次保留方法把. 调用工具个别方法 <dependency> <group ...
- 我们一起来学Shell - shell的函数
文章目录 定义函数 执行不带参数的函数 执行带参数的函数 函数的执行总结 我们一起来学Shell - 初识shell 我们一起来学Shell - shell的变量 我们一起来学Shell - shel ...
- Ultra Math Preview : VSCode上的LaTeX公式实时预览插件
一直觉着 VS Code 的 TeX 公式(包括 markdown 和 LaTeX)只能在定界符上hover预览,或者开一个预览面板看,没有那种像 Typora 一样紧跟在公式后面的预览面板,多少有些 ...
- scrapy爬取《坏蛋是怎样练成的4》
scrapy具体介绍就不用说了,自己百度一下.或者参考以下文档 https://blog.csdn.net/u011054333/article/details/70165401 直接在cmd里运行 ...
- containerd与kubernetes集成部署
概念介绍 cri (Container runtime interface) cri is a containerd plugin implementation of Kubernetes conta ...
- vs2022 如何让.net库文件参与程序调试【可以.net库文件的源代码中设置断点,单步跟踪】
由于.net core 是开源的.所以可以让.net库文件参与程序调试.具体vs2022配置如下 1.设置VS2022 加载程序数据文件(.pdb俗称符号文件) 1)选择工具>选项>调试& ...
- (一) operator、explicit与implicit 操作符重载
原文地址: Click Here 操作符重载必须用public static 应为操作符是用来操作实例的. operator operator ...
- Qt:QThread
0.说明 QThread提供了一种与平台无关的线程管理方法. 一个QThread对象管理一个线程.QThread通过run()方法启动线程.默认情况下,run()方法通过exec()启动一个事件循环, ...
- jq获取不包含某些属性的元素
最近写项目,有个功能实现checkbox全选,但是被禁用的checkbox不能选中 点击全选后发现禁用checkbox的也被选中了,不符合需求. 但是想了半天,属性选择器都是判断某个属性值的,没有判断 ...
