Linux ALSA声卡驱动之二:声卡的创建
1. struct snd_card
1.1. snd_card是什么
snd_card可以说是整个ALSA音频驱动最顶层的一个结构,整个声卡的软件逻辑结构开始于该结构,几乎所有与声音相关的逻辑设备都是在snd_card的管理之下,声卡驱动的第一个动作通常就是创建一个snd_card结构体。正因为如此,本节中,我们也从 struct cnd_card开始吧。
1.2. snd_card的定义
snd_card的定义位于改头文件中:include/sound/core.h
- /* main structure for soundcard */
- struct snd_card {
- int number; /* number of soundcard (index to
- snd_cards) */
- char id[16]; /* id string of this card */
- char driver[16]; /* driver name */
- char shortname[32]; /* short name of this soundcard */
- char longname[80]; /* name of this soundcard */
- char mixername[80]; /* mixer name */
- char components[128]; /* card components delimited with
- space */
- struct module *module; /* top-level module */
- void *private_data; /* private data for soundcard */
- void (*private_free) (struct snd_card *card); /* callback for freeing of
- private data */
- struct list_head devices; /* devices */
- unsigned int last_numid; /* last used numeric ID */
- struct rw_semaphore controls_rwsem; /* controls list lock */
- rwlock_t ctl_files_rwlock; /* ctl_files list lock */
- int controls_count; /* count of all controls */
- int user_ctl_count; /* count of all user controls */
- struct list_head controls; /* all controls for this card */
- struct list_head ctl_files; /* active control files */
- struct snd_info_entry *proc_root; /* root for soundcard specific files */
- struct snd_info_entry *proc_id; /* the card id */
- struct proc_dir_entry *proc_root_link; /* number link to real id */
- struct list_head files_list; /* all files associated to this card */
- struct snd_shutdown_f_ops *s_f_ops; /* file operations in the shutdown
- state */
- spinlock_t files_lock; /* lock the files for this card */
- int shutdown; /* this card is going down */
- int free_on_last_close; /* free in context of file_release */
- wait_queue_head_t shutdown_sleep;
- struct device *dev; /* device assigned to this card */
- #ifndef CONFIG_SYSFS_DEPRECATED
- struct device *card_dev; /* cardX object for sysfs */
- #endif
- #ifdef CONFIG_PM
- unsigned int power_state; /* power state */
- struct mutex power_lock; /* power lock */
- wait_queue_head_t power_sleep;
- #endif
- #if defined(CONFIG_SND_MIXER_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_MIXER_OSS_MODULE)
- struct snd_mixer_oss *mixer_oss;
- int mixer_oss_change_count;
- #endif
- };
- struct list_head devices 记录该声卡下所有逻辑设备的链表
- struct list_head controls 记录该声卡下所有的控制单元的链表
- void *private_data 声卡的私有数据,可以在创建声卡时通过参数指定数据的大小
2. 声卡的建立流程
2.1.1. 第一步,创建snd_card的一个实例
- struct snd_card *card;
- int err;
- ....
- err = snd_card_create(index, id, THIS_MODULE, 0, &card);
- index 一个整数值,该声卡的编号
- id 字符串,声卡的标识符
- 第四个参数 该参数决定在创建snd_card实例时,需要同时额外分配的私有数据的大小,该数据的指针最终会赋值给snd_card的private_data数据成员
- card 返回所创建的snd_card实例的指针
2.1.2. 第二步,创建声卡的芯片专用数据
声卡的专用数据主要用于存放该声卡的一些资源信息,例如中断资源、io资源、dma资源等。可以有两种创建方法:
- 通过上一步中snd_card_create()中的第四个参数,让snd_card_create自己创建
- // struct mychip 用于保存专用数据
- err = snd_card_create(index, id, THIS_MODULE,
- sizeof(struct mychip), &card);
- // 从private_data中取出
- struct mychip *chip = card->private_data;
- 自己创建:
- struct mychip {
- struct snd_card *card;
- ....
- };
- struct snd_card *card;
- struct mychip *chip;
- chip = kzalloc(sizeof(*chip), GFP_KERNEL);
- ......
- err = snd_card_create(index[dev], id[dev], THIS_MODULE, 0, &card);
- // 专用数据记录snd_card实例
- chip->card = card;
- .....
然后,把芯片的专有数据注册为声卡的一个低阶设备:
- static int snd_mychip_dev_free(struct snd_device *device)
- {
- return snd_mychip_free(device->device_data);
- }
- static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
- .dev_free = snd_mychip_dev_free,
- };
- ....
- snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_LOWLEVEL, chip, &ops);
注册为低阶设备主要是为了当声卡被注销时,芯片专用数据所占用的内存可以被自动地释放。
2.1.3. 第三步,设置Driver的ID和名字
- strcpy(card->driver, "My Chip");
- strcpy(card->shortname, "My Own Chip 123");
- sprintf(card->longname, "%s at 0x%lx irq %i",
- card->shortname, chip->ioport, chip->irq);
snd_card的driver字段保存着芯片的ID字符串,user空间的alsa-lib会使用到该字符串,所以必须要保证该ID的唯一性。shortname字段更多地用于打印信息,longname字段则会出现在/proc/asound/cards中。
2.1.4. 第四步,创建声卡的功能部件(逻辑设备),例如PCM,Mixer,MIDI等
这时候可以创建声卡的各种功能部件了,还记得开头的snd_card结构体的devices字段吗?每一种部件的创建最终会调用snd_device_new()来生成一个snd_device实例,并把该实例链接到snd_card的devices链表中。
通常,alsa-driver的已经提供了一些常用的部件的创建函数,而不必直接调用snd_device_new(),比如:
PCM ---- snd_pcm_new()
RAWMIDI -- snd_rawmidi_new()
CONTROL -- snd_ctl_create()
TIMER -- snd_timer_new()
INFO -- snd_card_proc_new()
JACK -- snd_jack_new()
2.1.5. 第五步,注册声卡
- err = snd_card_register(card);
- if (err < 0) {
- snd_card_free(card);
- return err;
- }
2.2. 一个实际的例子
我把/sound/arm/pxa2xx-ac97.c的部分代码贴上来:
- static int __devinit pxa2xx_ac97_probe(struct platform_device *dev)
- {
- struct snd_card *card;
- struct snd_ac97_bus *ac97_bus;
- struct snd_ac97_template ac97_template;
- int ret;
- pxa2xx_audio_ops_t *pdata = dev->dev.platform_data;
- if (dev->id >= 0) {
- dev_err(&dev->dev, "PXA2xx has only one AC97 port./n");
- ret = -ENXIO;
- goto err_dev;
- }
- ////(1)////
- ret = snd_card_create(SNDRV_DEFAULT_IDX1, SNDRV_DEFAULT_STR1,
- THIS_MODULE, 0, &card);
- if (ret < 0)
- goto err;
- card->dev = &dev->dev;
- ////(3)////
- strncpy(card->driver, dev->dev.driver->name, sizeof(card->driver));
- ////(4)////
- ret = pxa2xx_pcm_new(card, &pxa2xx_ac97_pcm_client, &pxa2xx_ac97_pcm);
- if (ret)
- goto err;
- ////(2)////
- ret = pxa2xx_ac97_hw_probe(dev);
- if (ret)
- goto err;
- ////(4)////
- ret = snd_ac97_bus(card, 0, &pxa2xx_ac97_ops, NULL, &ac97_bus);
- if (ret)
- goto err_remove;
- memset(&ac97_template, 0, sizeof(ac97_template));
- ret = snd_ac97_mixer(ac97_bus, &ac97_template, &pxa2xx_ac97_ac97);
- if (ret)
- goto err_remove;
- ////(3)////
- snprintf(card->shortname, sizeof(card->shortname),
- "%s", snd_ac97_get_short_name(pxa2xx_ac97_ac97));
- snprintf(card->longname, sizeof(card->longname),
- "%s (%s)", dev->dev.driver->name, card->mixername);
- if (pdata && pdata->codec_pdata[0])
- snd_ac97_dev_add_pdata(ac97_bus->codec[0], pdata->codec_pdata[0]);
- snd_card_set_dev(card, &dev->dev);
- ////(5)////
- ret = snd_card_register(card);
- if (ret == 0) {
- platform_set_drvdata(dev, card);
- return 0;
- }
- err_remove:
- pxa2xx_ac97_hw_remove(dev);
- err:
- if (card)
- snd_card_free(card);
- err_dev:
- return ret;
- }
- static int __devexit pxa2xx_ac97_remove(struct platform_device *dev)
- {
- struct snd_card *card = platform_get_drvdata(dev);
- if (card) {
- snd_card_free(card);
- platform_set_drvdata(dev, NULL);
- pxa2xx_ac97_hw_remove(dev);
- }
- return 0;
- }
- static struct platform_driver pxa2xx_ac97_driver = {
- .probe = pxa2xx_ac97_probe,
- .remove = __devexit_p(pxa2xx_ac97_remove),
- .driver = {
- .name = "pxa2xx-ac97",
- .owner = THIS_MODULE,
- #ifdef CONFIG_PM
- .pm = &pxa2xx_ac97_pm_ops,
- #endif
- },
- };
- static int __init pxa2xx_ac97_init(void)
- {
- return platform_driver_register(&pxa2xx_ac97_driver);
- }
- static void __exit pxa2xx_ac97_exit(void)
- {
- platform_driver_unregister(&pxa2xx_ac97_driver);
- }
- module_init(pxa2xx_ac97_init);
- module_exit(pxa2xx_ac97_exit);
- MODULE_AUTHOR("Nicolas Pitre");
- MODULE_DESCRIPTION("AC97 driver for the Intel PXA2xx chip");
驱动程序通常由probe回调函数开始,对一下2.1中的步骤,是否有相似之处?
经过以上的创建步骤之后,声卡的逻辑结构如下图所示:
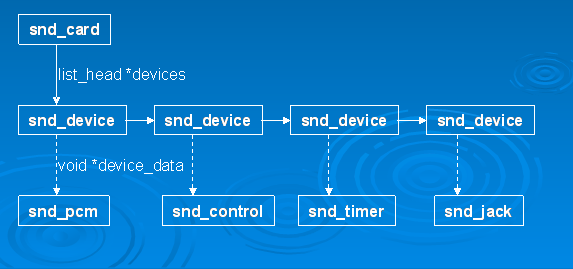
图 2.2.1 声卡的软件逻辑结构
下面的章节里我们分别讨论一下snd_card_create()和snd_card_register()这两个函数。
3. snd_card_create()
snd_card_create()在/sound/core/init.c中定义。
- /**
- * snd_card_create - create and initialize a soundcard structure
- * @idx: card index (address) [0 ... (SNDRV_CARDS-1)]
- * @xid: card identification (ASCII string)
- * @module: top level module for locking
- * @extra_size: allocate this extra size after the main soundcard structure
- * @card_ret: the pointer to store the created card instance
- *
- * Creates and initializes a soundcard structure.
- *
- * The function allocates snd_card instance via kzalloc with the given
- * space for the driver to use freely. The allocated struct is stored
- * in the given card_ret pointer.
- *
- * Returns zero if successful or a negative error code.
- */
- int snd_card_create(int idx, const char *xid,
- struct module *module, int extra_size,
- struct snd_card **card_ret)
首先,根据extra_size参数的大小分配内存,该内存区可以作为芯片的专有数据使用(见前面的介绍):
- card = kzalloc(sizeof(*card) + extra_size, GFP_KERNEL);
- if (!card)
- return -ENOMEM;
拷贝声卡的ID字符串:
- if (xid)
- strlcpy(card->id, xid, sizeof(card->id));
如果传入的声卡编号为-1,自动分配一个索引编号:
- if (idx < 0) {
- for (idx2 = 0; idx2 < SNDRV_CARDS; idx2++)
- /* idx == -1 == 0xffff means: take any free slot */
- if (~snd_cards_lock & idx & 1<<idx2) {
- if (module_slot_match(module, idx2)) {
- idx = idx2;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- if (idx < 0) {
- for (idx2 = 0; idx2 < SNDRV_CARDS; idx2++)
- /* idx == -1 == 0xffff means: take any free slot */
- if (~snd_cards_lock & idx & 1<<idx2) {
- if (!slots[idx2] || !*slots[idx2]) {
- idx = idx2;
- break;
- }
- }
- }
初始化snd_card结构中必要的字段:
- card->number = idx;
- card->module = module;
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->devices);
- init_rwsem(&card->controls_rwsem);
- rwlock_init(&card->ctl_files_rwlock);
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->controls);
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->ctl_files);
- spin_lock_init(&card->files_lock);
- INIT_LIST_HEAD(&card->files_list);
- init_waitqueue_head(&card->shutdown_sleep);
- #ifdef CONFIG_PM
- mutex_init(&card->power_lock);
- init_waitqueue_head(&card->power_sleep);
- #endif
建立逻辑设备:Control
- /* the control interface cannot be accessed from the user space until */
- /* snd_cards_bitmask and snd_cards are set with snd_card_register */
- err = snd_ctl_create(card);
建立proc文件中的info节点:通常就是/proc/asound/card0
- err = snd_info_card_create(card);
把第一步分配的内存指针放入private_data字段中:
- if (extra_size > 0)
- card->private_data = (char *)card + sizeof(struct snd_card);
4. snd_card_register()
snd_card_create()在/sound/core/init.c中定义。
- /**
- * snd_card_register - register the soundcard
- * @card: soundcard structure
- *
- * This function registers all the devices assigned to the soundcard.
- * Until calling this, the ALSA control interface is blocked from the
- * external accesses. Thus, you should call this function at the end
- * of the initialization of the card.
- *
- * Returns zero otherwise a negative error code if the registrain failed.
- */
- int snd_card_register(struct snd_card *card)
首先,创建sysfs下的设备:
- if (!card->card_dev) {
- card->card_dev = device_create(sound_class, card->dev,
- MKDEV(0, 0), card,
- "card%i", card->number);
- if (IS_ERR(card->card_dev))
- card->card_dev = NULL;
- }
其中,sound_class是在/sound/sound_core.c中创建的:
- static char *sound_devnode(struct device *dev, mode_t *mode)
- {
- if (MAJOR(dev->devt) == SOUND_MAJOR)
- return NULL;
- return kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "snd/%s", dev_name(dev));
- }
- static int __init init_soundcore(void)
- {
- int rc;
- rc = init_oss_soundcore();
- if (rc)
- return rc;
- sound_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "sound");
- if (IS_ERR(sound_class)) {
- cleanup_oss_soundcore();
- return PTR_ERR(sound_class);
- }
- sound_class->devnode = sound_devnode;
- return 0;
- }
由此可见,声卡的class将会出现在文件系统的/sys/class/sound/下面,并且,sound_devnode()也决定了相应的设备节点也将会出现在/dev/snd/下面。
接下来的步骤,通过snd_device_register_all()注册所有挂在该声卡下的逻辑设备,snd_device_register_all()实际上是通过snd_card的devices链表,遍历所有的snd_device,并且调用snd_device的ops->dev_register()来实现各自设备的注册的。
- if ((err = snd_device_register_all(card)) < 0)
- return err;
最后就是建立一些相应的proc和sysfs下的文件或属性节点,代码就不贴了。
至此,整个声卡完成了建立过程。
Linux ALSA声卡驱动之二:声卡的创建的更多相关文章
- 基于Linux ALSA音频驱动的wav文件解析及播放程序 2012
本设计思路:先打开一个普通wav音频文件,从定义的文件头前面的44个字节中,取出文件头的定义消息,置于一个文件头的结构体中.然后打开alsa音频驱动,从文件头结构体取出采样精度,声道数,采样频率三个重 ...
- 【VS开发】【DSP开发】浅谈Linux PCI设备驱动(二)
我们在 浅谈Linux PCI设备驱动(一)中(以下简称 浅谈(一) )介绍了PCI的配置寄存器组,而Linux PCI初始化就是使用了这些寄存器来进行的.后面我们会举个例子来说明Linux PCI设 ...
- 嵌入式驱动开发之---Linux ALSA音频驱动(一)
本文的部分内容参考来自DroidPhone的博客(http://blog.csdn.net/droidphone/article/details/6271122),关于ALSA写得很不错的文章,只是少 ...
- 调试exynos4412—ARM嵌入式Linux—LEDS/GPIO驱动之二
/** ****************************************************************************** * @author 暴走的小 ...
- Linux 块设备驱动 (二)
linux下Ramdisk驱动 1 什么是Ramdisk Ramdisk是一种模拟磁盘,其数据实际上是存储在RAM中,它使用一部分内存空间来模拟出一个磁盘设备,并以块设备的方式来组织和访问这片内存.对 ...
- linux lcd设备驱动剖析二
上一节中,分析了s3c2410fb,c的入口出口函数,以及一些重要结构体的分析,初步知道了这是一个平台驱动的架构. 上一节文章链接:http://blog.csdn.net/lwj103862095/ ...
- linux 块设备驱动(二)——块设备数据结构
本文来源于: 1. http://www.cnblogs.com/dyllove98/archive/2013/07/01/3165567.html 块设备相关的数据结构以及接口: 块设备接口则相对复 ...
- Linux下GPIO驱动(二) ----s3c_gpio_cfgpin();gpio_set_value();
首先来看s3c_gpio_cfgpin(); int s3c_gpio_cfgpin(unsigned int pin, unsigned int config) { struct s3c_gpio_ ...
- Linux 网络编程详解二(socket创建流程、多进程版)
netstat -na | grep " --查看TCP/IP协议连接状态 //socket编程提高版--服务器 #include <stdio.h> #include < ...
随机推荐
- Properties集合
Map |--Hashtable |--Properties Properties集合特点: 1.该集合中的键和值都是字符串类型 2.集合中的数据可以保存在IO流中或者从IO流中获取数据. 通常该集合 ...
- URAL 2099 Space Invader题解 (计算几何)
啥也不说了,直接看图吧…… 代码如下: #include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<math.h> using na ...
- java 设计模式之工厂模式与反射的结合
工厂模式: /** * @author Rollen-Holt 设计模式之 工厂模式 */ interface fruit{ public abstract void eat(); } ...
- Day05_JAVAEE系列:XML
XML概述 1)什么是xml? xml, eXtend Markup Language, 可扩展标记语言 2) html vs xml 都由w3c组织制定的. html语法特征:语法比较松散 ...
- 单片AT89C2051 + SD卡 + 3310LCD = 音乐播放器
http://www.amobbs.com/thread-4503884-1-1.html 这个小玩意,采用 ATMEL 的传统51MCU作主控制芯片,加上SD卡和显示屏,就可以作简单的音乐播放器了, ...
- css居中
<html><head lang="en"> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>< ...
- 触发器(基本的SR触发器、同步触发器、D触发器)
一.能够存储1位二值信号的基本单元电路统称为触发器(Filp-Flop) 触发器是构成时序逻辑电路的基本逻辑部件.它有两个稳定状态:“0”和“1”.在不同的输入情况下,它可以被置0状态或1状态,当输入 ...
- php正则表达式手册
(http://deerchao.net/tutorials/regex/regex.htm)转载:作者:deerchao php的正则表达式很强大,学好了的确有很大的用处,但是正则表达式的规则很繁琐 ...
- 套接字和域名系统DNS
套接字产生的原因: 当应用进程通过传输层进行通信时 ,TCP和 UDP将面临同时为多个应用进程提供并行通信的问题.多个TCP连接或多个应用程序进程可能需要通过同一个TCP协议端口传输数据. 为了区别每 ...
- 前端UI
一个非常好的前端UI,值得研究下 http://semantic-ui.com/
