ThreadLocal ——android消息机制handler在非主线程创建not called Looper.prepare() 错误的原因
引用自:https://www.jianshu.com/p/a8fa72e708d3
引出:
使用Handler的时候,其必须要跟一个Looper绑定。在UI线程可直接初始化Handler来使用。但是在非主线程中直接new Handler() 会报错: E/AndroidRuntime( 6173): Uncaught handler: thread Thread-8 exiting due to uncaught exception E/AndroidRuntime( 6173): java.lang.RuntimeException: Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()
原因是非主线程中默认没有创建Looper对象,需要先调用Looper.prepare()启用Looper。 当初始化Handler的时候,其会通过Looper来获取当前的Looper,代码如下:
public Handler(Callback callback, boolean async) {
//省略
mLooper = Looper.myLooper();
if (mLooper == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Can't create handler inside thread that has not called Looper.prepare()");
}
//省略
}
那么,问题来了,为什么在子线程中,通过Looper.myLooper()方法获取的就是为空呢?如果有人回答了Looper是线程相绑定的,那它是如何做到绑定的? 如果还知道答案的话,那就可以跳过本篇文章了。
代码分析
1. Looper的myLooper方法
public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {
return sThreadLocal.get();
}
此方法只是通过从变量sThreadLocal中取出一个值。那么它的值是哪里来的呢?
2. Looper的prepare方法
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}
可以看出的是调用了这个方法之后,会在sThreadLocal中存在一个新建的Looper对象。那么看看这个sThreadLocal是什么东西呢?
ThreadLocal分析:
1. 定义 (本地线程副本变量工具类)
先看一下官方的解释:
Implements a thread-local storage, that is, a variable for which each thread
has its own value. All threads share the same {@code ThreadLocal} object,
but each sees a different value when accessing it, and changes made by one
thread do not affect the other threads. The implementation supports
{@code null} values.
这段话的意思是实现了一个线程相关的存储,即每个线程都有自己独立的变量。所有的线程都共享着这一个ThreadLocal对象,
并且当一个线程的值发生改变之后,不会影响其他的线程的值。
threadlocal是一个范型类,这标志着threadlocal可以存储所有数据,作为存储数据来说,我们首先想到的是会对外提供set(),get(),remove(),等方法,顺着我们的想法来看源码,果然如此。
2. 核心机制
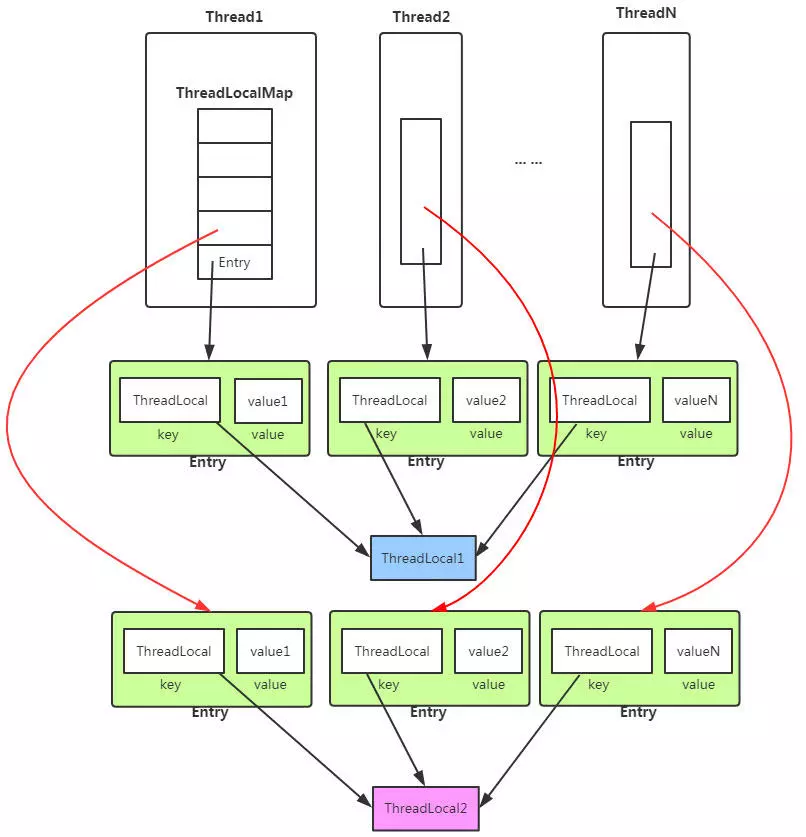
ThreadLocal的核心机制:
- 每个Thread线程内部都有一个Map。
- Map里面存储线程本地对象(key)和线程的变量副本(value)
- 但是,Thread内部的Map是由ThreadLocal维护的,由ThreadLocal负责向map获取和设置线程的变量值。
3. 实现
ThreadLocal的类定义使用了泛型ThreadLocal<T>,其中T指代的是在线程中存取值的类型。(对应Android中使用的ThreadLocal, T则存放的类型为Looper)
- set方法
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
} ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
} void createMap(Thread t, T firstValue) {
t.threadLocals = new ThreadLocalMap(this, firstValue);
}
步骤:
1.获取当前线程的成员变量map
2.map非空,则重新将ThreadLocal和新的value副本放入到map中。
3.map空,则对线程的成员变量ThreadLocalMap进行初始化创建,并将ThreadLocal和value副本放入map中。
- get方法
/**
* Returns the value in the current thread's copy of this
* thread-local variable. If the variable has no value for the
* current thread, it is first initialized to the value returned
* by an invocation of the {@link #initialValue} method.
*
* @return the current thread's value of this thread-local
*/
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null)
return (T)e.value;
}
return setInitialValue();
} ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
} private T setInitialValue() {
T value = initialValue();
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
return value;
} protected T initialValue() {
return null;
}
1.获取当前线程的ThreadLocalMap对象threadLocals
2.从map中获取线程存储的K-V Entry节点。
3.从Entry节点获取存储的Value副本值返回。
4.map为空的话返回初始值null,即线程变量副本为null,在使用时需要注意判断NullPointerException。
remove()方法
public void remove() {
ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread());
if (m != null)
m.remove(this);
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
---------------------
Thread线程内部的Map在类中描述如下:
public class Thread implements Runnable {
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
}
总结
举例:
package test;
import test.*;
public class Test {
static final ThreadLocal<ThreadValue> mThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<ThreadValue>();
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ThreadValue threadValue = new ThreadValue("主线程");
mThreadLocal.set(threadValue);
System.out.print("in main thread : mThreadLocal:" + mThreadLocal +"\n");
System.out.print("in main thread : 名字:" + mThreadLocal.get().name +"\n");
mThreadLocal.get().print();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ThreadValue childThreadValue = new ThreadValue("子线程");
mThreadLocal.set(childThreadValue);
System.out.print("in child thread : mThreadLocal:" + mThreadLocal +"\n");
System.out.print("in child thread : 名字:" + mThreadLocal.get().name +"\n");
mThreadLocal.get().print();
}
}).start();
}
}
package test;
public class ThreadValue {
String name;
public ThreadValue() {
}
public ThreadValue(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public void print()
{
System.out.print("this = " + this+" \n");
}
}
结果:
然后编译:javac test/*.java
运行:java test.Test
输出:
in main thread : mThreadLocal:java.lang.ThreadLocal@788bf135
in main thread : 名字:主线程
this = test.ThreadValue@2b890c67
in child thread : mThreadLocal:java.lang.ThreadLocal@788bf135
in child thread : 名字:子线程
this = test.ThreadValue@4f93b604
可以看出由于mThreadLocal定义为静态最终变量,所以在主线程和子线程中,mThreadLocal都是同一个实例。
但是在两个线程中调用mThreadLocal.get(),得到的ThreadValue对象却并不相同。
这是因为mThreadLocal.get(),取到的对象是线程内的局部变量,相互之间并不干扰。
---------------------
作者:??-D-Luffy
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/zyfzhangyafei/article/details/64927617
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!
ThreadLocal ——android消息机制handler在非主线程创建not called Looper.prepare() 错误的原因的更多相关文章
- Android消息机制——Handler
/**android的消息处理有三个核心类:Looper,Handler和Message.其实还有一个MessageQueue(消息队列), * 但是MessageQueue被封装到Looper里 ...
- Android消息机制
每一个Android应用在启动的时候都会创建一个线程,这个线程被称为主线程或者UI线程,Android应用的所有操作默认都会运行在这个线程中. 但是当我们想要进行数据请求,图片下载,或者其他耗时操作时 ...
- 在非主线程里面使用NSTimer创建和取消定时任务
为什么要在非主线程创建NSTimer 将 timer 添加到主线程的Runloop里面本身会增加线程负荷 如果主线程因为某些原因阻塞卡顿了,timer 定时任务触发的时间精度肯定也会受到影响 有些定时 ...
- Android消息机制:Looper,MessageQueue,Message与handler
Android消息机制好多人都讲过,但是自己去翻源码的时候才能明白. 今天试着讲一下,因为目标是讲清楚整体逻辑,所以不追究细节. Message是消息机制的核心,所以从Message讲起. 1.Mes ...
- Android开发之漫漫长途 ⅥI——Android消息机制(Looper Handler MessageQueue Message)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- Android开发之漫漫长途 Ⅶ——Android消息机制(Looper Handler MessageQueue Message)
该文章是一个系列文章,是本人在Android开发的漫漫长途上的一点感想和记录,我会尽量按照先易后难的顺序进行编写该系列.该系列引用了<Android开发艺术探索>以及<深入理解And ...
- Android消息机制之ThreadLocal的工作原理
来源: http://blog.csdn.net/singwhatiwanna/article/details/48350919 很多人认为Handler的作用是更新UI,这说的的确没错,但是更新UI ...
- Android 进阶14:源码解读 Android 消息机制( Message MessageQueue Handler Looper)
不要心急,一点一点的进步才是最靠谱的. 读完本文你将了解: 前言 Message 如何获取一个消息 Messageobtain 消息的回收利用 MessageQueue MessageQueue 的属 ...
- Android消息机制探索(Handler,Looper,Message,MessageQueue)
概览 Android消息机制是Android操作系统中比较重要的一块.具体使用方法在这里不再阐述,可以参考Android的官方开发文档. 消息机制的主要用途有两方面: 1.线程之间的通信.比如在子线程 ...
随机推荐
- win7下iis的配置问题
开始asp的学习时,首先得配置iis服务,中途遇到各种问题也谷歌了不少,但是答案都很凌乱,折腾了两天才彻底解决这个问题.下面是我坎坷的配置过程,希望对你有所帮助: 第一步:打开Internet信息服务 ...
- vue:绑定数据的vue页面加载会闪烁问题
1:在挂在数据的容器加上属性 v-cloak 2:在css中添加如下代码 但有时候还是会不起作用,可能原因有两个 2.1:display属性被更高权限的display属性覆盖了,我们增加权限就好了 2 ...
- data型怎么转换格式
data型如何转换格式01-1月 -03 如何转成 YYYY-MM-DD 的格式 本来就是date了 ------解决方案--------------------to_char ...
- How to Pronounce We’ll Contraction
How to Pronounce We’ll Contraction Share Tweet Share Tagged With: WILL Contractions There are severa ...
- Haskell语言学习笔记(80)req
req req 是一个好用,类型安全,可扩展,上层的HTTP客户端的库. $ cabal install req Installed req-1.1.0 Prelude> :m +Network ...
- python 装饰器的缺点以及解决方法
1.python装饰器的缺点 装饰器可以允许我们在不改变函数或犯方法的调用方式的情况下,添加额外的功能; 如下所示,我们要在中的方法之前增加装饰器check_is_admin,用来判断执行类的方法的用 ...
- Win8系统本地连接显示为网络2
Win8系统中,当改变了网络环境,本地连接就会被识别为网络2,网络3等: 如果在一个固定的网络环境中,需要修改此名称,可以打开注册表: [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Mic ...
- ubuntu下搭建node server的几个坑
[ubuntu下搭建node server的几个坑] 1.环境变量 process.env.PORT需要使用 export PORT=80设置 windows下是set PORT=80 2.命令连结 ...
- 基于oslo_messaging的RPC通信
oslo_messaging源于Openstack的一个经典的模块,用以实现服务间的RPC通信.Client端将数据放入rabbitmq中,server端从消息队列中获取传送数据. oslo.mess ...
- Application类
using System.Collections; using System.Collections.Generic; using UnityEngine; using System.IO; usin ...
