ResNet网络的Pytorch实现
1.文章原文地址
Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
2.文章摘要
神经网络的层次越深越难训练。我们提出了一个残差学习框架来简化网络的训练,这些网络比之前使用的网络都要深的多。我们明确地将层变为学习关于层输入的残差函数,而不是学习未参考的函数。我们提供了综合的实验证据来表明这个残差网络更容易优化,以及通过极大提升网络深度可以获得更好的准确率。在ImageNet数据集上,我们评估了残差网络,该网络有152层,层数是VGG网络的8倍,但是有更低的复杂度。几个残差网络的集成在ImageNet数据集上取得了3.57%错误率。这个结果在ILSVRC2015分类任务上取得第一名的成绩。我们也使用了100和1000层网络用在了数据集CIFAR-10上加以分析。
在许多视觉识别任务中,表征的深度是至关重要的。仅仅通过极端深的表征,我们在COCO目标检测数据集上得到了28%的相对提高。深度残差网络是我们提交到ILSVRC & COCO2015竞赛的网络基础,在这里我们获得了ImageNet检测任务、ImageNet定位任务,COCO检测任务和COCO分割任务的第一名。
3.网络结构
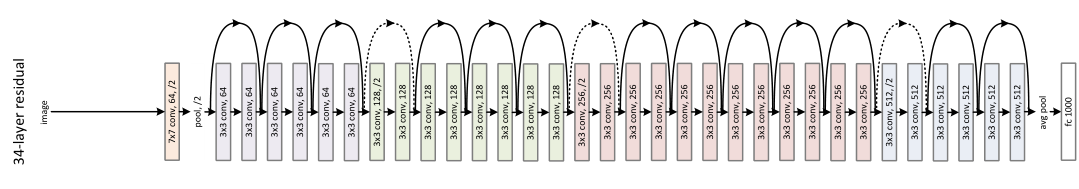
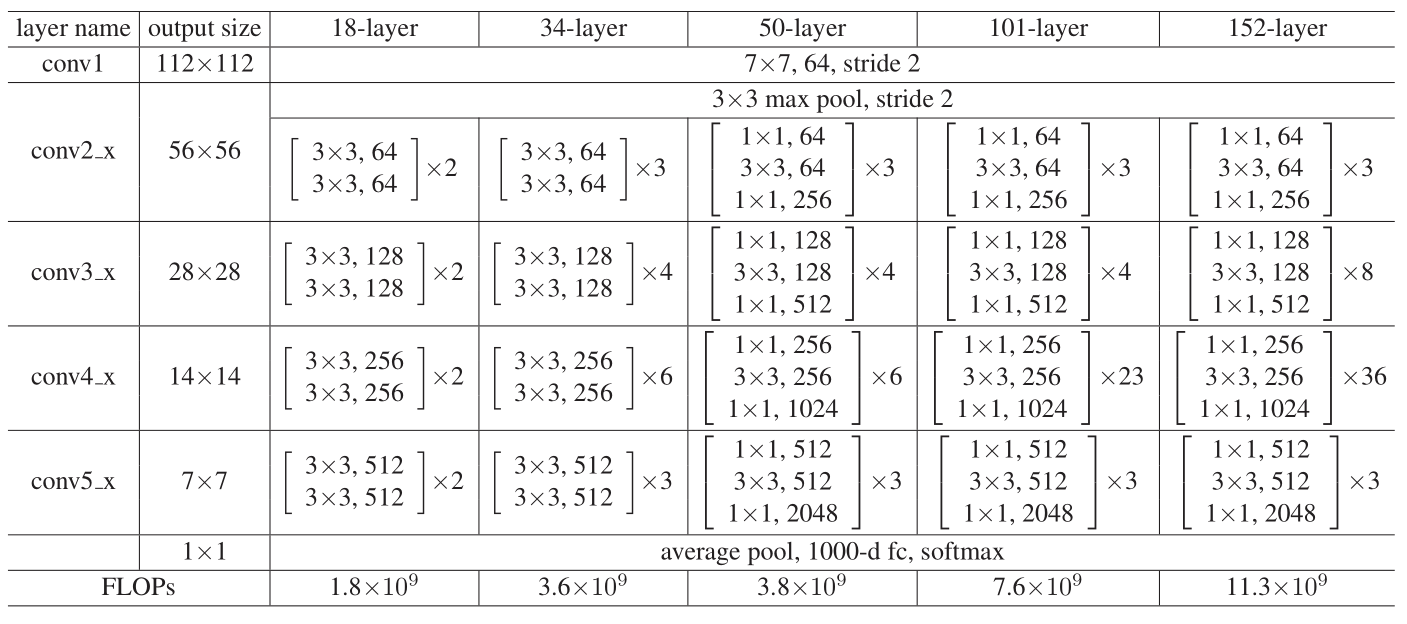
4.Pytorch实现
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.utils.model_zoo import load_url as load_state_dict_from_url __all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnet101',
'resnet152', 'resnext50_32x4d', 'resnext101_32x8d'] model_urls = {
'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth',
'resnet34': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth',
'resnet50': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth',
'resnet101': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth',
'resnet152': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth',
} def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, groups=1, dilation=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation, groups=groups, bias=False, dilation=dilation) def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False) class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
if groups != 1 or base_width != 64:
raise ValueError('BasicBlock only supports groups=1 and base_width=64')
if dilation > 1:
raise NotImplementedError("Dilation > 1 not supported in BasicBlock")
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(planes)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride def forward(self, x):
identity = x out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out) if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x) out += identity
out = self.relu(out) return out class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None, groups=1,
base_width=64, dilation=1, norm_layer=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
width = int(planes * (base_width / 64.)) * groups
# Both self.conv2 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, width)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(width, width, stride, groups, dilation)
self.bn2 = norm_layer(width)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(width, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = norm_layer(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride def forward(self, x):
identity = x out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out) if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x) out += identity
out = self.relu(out) return out class ResNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000, zero_init_residual=False,
groups=1, width_per_group=64, replace_stride_with_dilation=None,
norm_layer=None):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if norm_layer is None:
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
self._norm_layer = norm_layer self.inplanes = 64
self.dilation = 1
if replace_stride_with_dilation is None:
# each element in the tuple indicates if we should replace
# the 2x2 stride with a dilated convolution instead
replace_stride_with_dilation = [False, False, False]
if len(replace_stride_with_dilation) != 3:
raise ValueError("replace_stride_with_dilation should be None "
"or a 3-element tuple, got {}".format(replace_stride_with_dilation))
self.groups = groups
self.base_width = width_per_group
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = norm_layer(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2,
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[0])
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2,
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[1])
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2,
dilate=replace_stride_with_dilation[2])
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0) # Zero-initialize the last BN in each residual branch,
# so that the residual branch starts with zeros, and each residual block behaves like an identity.
# This improves the model by 0.2~0.3% according to https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.02677
if zero_init_residual:
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, Bottleneck):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn3.weight, 0)
elif isinstance(m, BasicBlock):
nn.init.constant_(m.bn2.weight, 0) def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilate=False):
norm_layer = self._norm_layer
downsample = None
previous_dilation = self.dilation
if dilate:
self.dilation *= stride
stride = 1
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
norm_layer(planes * block.expansion),
) layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample, self.groups,
self.base_width, previous_dilation, norm_layer))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, groups=self.groups,
base_width=self.base_width, dilation=self.dilation,
norm_layer=norm_layer)) return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x) x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x) x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.reshape(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x) return x def _resnet(arch, inplanes, planes, pretrained, progress, **kwargs):
model = ResNet(inplanes, planes, **kwargs)
if pretrained:
state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_urls[arch],
progress=progress)
model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
return model def resnet18(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-18 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet18', BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs) def resnet34(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-34 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet34', BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs) def resnet50(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-50 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet50', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs) def resnet101(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet101', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs) def resnet152(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):
"""Constructs a ResNet-152 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
progress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr
"""
return _resnet('resnet152', Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], pretrained, progress,
**kwargs) def resnext50_32x4d(**kwargs):
kwargs['groups'] = 32
kwargs['width_per_group'] = 4
return _resnet('resnext50_32x4d', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3],
pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs) def resnext101_32x8d(**kwargs):
kwargs['groups'] = 32
kwargs['width_per_group'] = 8
return _resnet('resnext101_32x8d', Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3],
pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs)
参考
https://github.com/pytorch/vision/tree/master/torchvision/models
ResNet网络的Pytorch实现的更多相关文章
- PyTorch对ResNet网络的实现解析
PyTorch对ResNet网络的实现解析 1.首先导入需要使用的包 import torch.nn as nn import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo # ...
- 学习笔记-ResNet网络
ResNet网络 ResNet原理和实现 总结 一.ResNet原理和实现 神经网络第一次出现在1998年,当时用5层的全连接网络LetNet实现了手写数字识别,现在这个模型已经是神经网络界的“hel ...
- 0609-搭建ResNet网络
0609-搭建ResNet网络 目录 一.ResNet 网络概述 二.利用 torch 实现 ResNet34 网络 三.torchvision 中的 resnet34网络调用 四.第六章总结 pyt ...
- Resnet网络详细结构(针对Cifar10)
Resnet网络详细结构(针对Cifar10) 结构 具体结构(Pytorch) conv1 (conv1): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, ...
- ResNet网络再剖析
随着2018年秋季的到来,提前批和内推大军已经开始了,自己也成功得当了几次炮灰,不过在总结的过程中,越是了解到自己的不足,还是需要加油. 最近重新复习了resnet网络,又能发现一些新的理念,感觉很f ...
- 深度学习之ResNet网络
介绍 Resnet分类网络是当前应用最为广泛的CNN特征提取网络. 我们的一般印象当中,深度学习愈是深(复杂,参数多)愈是有着更强的表达能力.凭着这一基本准则CNN分类网络自Alexnet的7层发展到 ...
- ResNet网络的训练和预测
ResNet网络的训练和预测 简介 Introduction 图像分类与CNN 图像分类 是指将图像信息中所反映的不同特征,把不同类别的目标区分开来的图像处理方法,是计算机视觉中其他任务,比如目标检测 ...
- 残差网络resnet理解与pytorch代码实现
写在前面 深度残差网络(Deep residual network, ResNet)自提出起,一次次刷新CNN模型在ImageNet中的成绩,解决了CNN模型难训练的问题.何凯明大神的工作令人佩服 ...
- 深度残差网络(DRN)ResNet网络原理
一说起“深度学习”,自然就联想到它非常显著的特点“深.深.深”(重要的事说三遍),通过很深层次的网络实现准确率非常高的图像识别.语音识别等能力.因此,我们自然很容易就想到:深的网络一般会比浅的网络效果 ...
随机推荐
- linux系统 重启盘符错乱问题
linux磁盘重启乱序问题处理 最近到客户那去巡检时,客户提到一个问题,他们的rac在重启的时候,原来的sda1.sdb1.sdc1会对应变成sdd1.sde1.sdf1,由于他们使用的是盘符来绑定裸 ...
- Winsock.简单UDP
PS:vs2017 编译C++代码 支持 XP:项目属性-->链接器-->系统-->需要的最小版本--> 输入 "5.1" 1.ZC:测试:c向s 发送长度 ...
- 记录一下vue slot
使用步骤: 1.在组件(panda)当中建立一个slot,定义好name.(<slot name='myname'></slot>) 2.引用组件的时候如果需要补充内容, ...
- confluence6.14.1linux安装破解
一.简介 Confluence为团队提供一个协作环境.在这里,团队成员齐心协力,各擅其能,协同地编写文档和管理项目.从此打破不同团队.不同部门以及个人之间信息孤岛的僵局,Confluence真正实现了 ...
- springboot之Redis
1.springboot之Redis配置 在学习springboot配置Redis之前先了解Redis. 1.了解Redis Redis简介: redis是一个key-value存储系统.和Memca ...
- Zuul【入门】
1.创建eureka-server注册中心工程,配置跟之前讲eureka文章中一样,这里不再赘述 1.1.端口8888 2.创建一个demo-client工程 2.1.demo-client启动类跟之 ...
- Java基础笔试练习(五)
1.以下关于Integer与int的区别错误的是? A.int是java提供的8种原始数据类型之一 B.Integer是java为int提供的封装类 C.int的默认值为0 D.Integer的默认值 ...
- 【dfs】Sequence Decoding
Sequence Decoding 题目描述 The amino acids in proteins are classified into two types of elements, hydrop ...
- redis原理及集群主从配置
一.简介 存储系统背景 存储系统有三类: RDBMS oracle,dh2,postgresql,mysql,sql server NoSQL: KV NoSQL:redis,memcached 列式 ...
- GRIT VIEW删除事件
1.点选表格后找到事件 RowCommand 2.輸入gvGroupUser_RowCommand后双击 ------注分 ...
