ARP Poisoning Attack and Mitigation Techniques ARP欺骗 中间人攻击 Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack 嗅探 防范 Can one MAC address have two different IP addresses within the network?
小结:
1、
ARP缓存投毒,窃听中毒者之间的通信;
2、
ARP Poisoning Attack and Mitigation Techniques - Cisco
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/products/collateral/switches/catalyst-6500-series-switches/white_paper_c11_603839.html
ARP Poisoning (Man-in-the-Middle) Attack and Mitigation Techniques
A CSSTG SE Residency Program White Paper
Jeff King, CCIE 11873, CCSP, CISSP 80875
Kevin Lauerman, CCSP, CISSP 80877
Abstract
Security is at the forefront of most networks, and many companies implement a comprehensive security policy encompassing many of the OSI layers, from application layer all the way down to IP security. However, one area that is often left untouched is hardening Layer 2 and this can open the network to a variety of attacks and compromises.
This document will have a focus on understanding and preventing the ARP Poisoning (also known as the Man-In-The-Middle [MITM]) Layer 2 attack on the Cisco® Catalyst® 6500 switching series switch running Cisco IOS® Software. The Ettercap attack tool will be used to initiate Layer 2 attacks that you might encounter. Mitigation techniques to stop this attack are also covered.
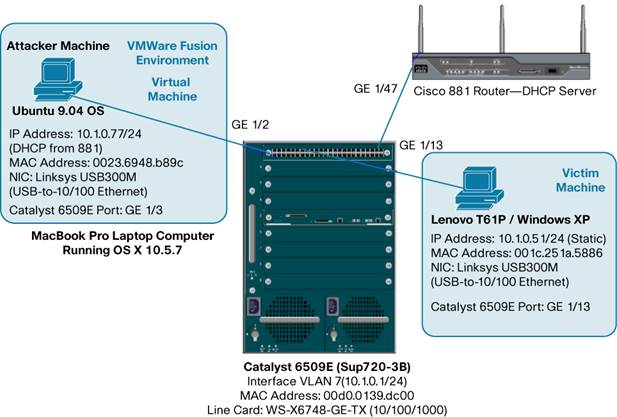
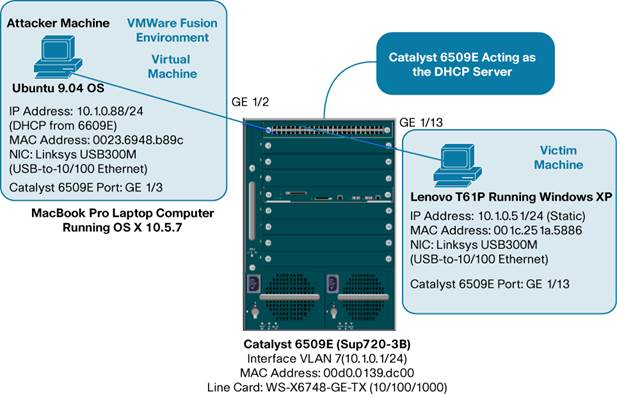
A MacBook Pro and a Lenovo T61P (laptops) was used for these test and acted as the attacker in some cases and the victim in others. Both computers also ran VMware.
Note that the attacks performed in this white paper were done in a controlled lab environment. We do not recommend that you perform this attack on your enterprise network.
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) Poisoning (MITM) Attack
A Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack is achieved when an attacker poisons the ARP cache of two devices with the (48-bit) MAC address of their Ethernet NIC (Network Interface Card). Once the ARP cache has been successfully poisoned, each of the victim devices send all their packets to the attacker when communicating to the other device. This puts the attacker in the middle of the communications path between the two victim devices; hence the name Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack. It allows an attacker to easily monitor all communication between victim devices.
The objective of this MITM attack is to take over a session. The intent is to intercept and view the information being passed between the two victim devices.
Three (3) scenarios were used for the MITM attack. They were as follows:
|
Scenario |
Description |
|
1 |
Static IP Address on Attacker machine |
|
2 |
DHCP from 881 Router (DHCP Server) on Attacker machine |
|
3 |
DHCP from Cisco Catalyst 6509E DHCP Server on Attacker machine |
These (3) scenarios were chosen because they were all valid configurations that one might see in a customer's network; although scenario 2 and 3 are more likely in an enterprise network.
攻击步骤

Steps for the MITM (ARP Poisoning) Attack:
1. View initial ARP cache on the Victim PC (Windows XP)
2. View initial ARP cache on the Attacker PC (Ubuntu 9.04)
3. View initial MAC Address-Table on the Cisco Catalyst 6509E (Sup 720-3B)
4. Start Ettercap attack application on the Attacker PC (Ubuntu 9.04)
5. Configure Ettercap for “Unified Sniffing”
6. Select Interface (eth2) to sniff on Ubuntu 9.04 Attacker PC
7. Scan for host on wire
8. List hosts discovered and select targets for attack
9. Start sniffing
10. Start the MITM (ARP Poisoning) attack
11. Activate the “repoison_arp” plugin in Ettercap
12. Activate the “remote_browser” plugin in Ettercap
13. Open a Telnet session from the Victim to 10.1.0.1 (Int Vlan 7 on 6509E)
14. View “connections” in Ettercap for “active” connections (telnet session)
15. Select “active” session and then “view details”
16. View login and password between Victims (Windows XP and 6509E)
17. Perform “character injection” from Ettercap toward the 6509E (CLI)
18. Perform “character injection” from Ettercap toward Windows XP (Victim)
19. Open up web browser to from Windows XP Victim to CVDM on 6509E
20. Spawn browser on Attacker PC to view Victim's web pages being viewed
21. Scenario 2: DHCP from 881 Router (DHCP Server) on Attacker machine
22. Scenario 3: DHCP from Cisco Catalyst 6509E DHCP Server on Attacker machine
23. Mitigation of the MITM (ARP Poisoning) Attack
24. Summary
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ARP_spoofing
ARP Poisoning Attack and Mitigation Techniques ARP欺骗 中间人攻击 Man-In-The-Middle (MITM) attack 嗅探 防范 Can one MAC address have two different IP addresses within the network?的更多相关文章
- 中间人攻击之arp欺骗 科普ARP欺骗
中间人攻击之arp欺骗 科普ARP欺骗 A <-> B A中有个ARP Table,每次发包都会在此Table中查找,若找不到,发APR Request包询问.此时若hacker冒充B的M ...
- ARP欺骗与中间人攻击
前言: 上一篇WPA/WAP2wifi 密码破解笔记说到如何探测附近开放的AP并且破解进入,那么进入别人据局域网我们能干些什么呢?换句话说如果别人进入了我们内部网络,会有什么影响?本文简要介绍了ARP ...
- ARP欺骗与MITM(中间人攻击)实例
ARP协议(address resolution protocol):地址解析协议 一台主机和另一台主机通信,要知道目标的IP地址,但是在局域网中传输数据的网卡却不能直接识别IP地址,所以用ARP解析 ...
- 关于ARP欺骗与MITM(中间人攻击)的一些笔记( 二 )
一直没有折腾啥东西,直到最近kali Linux发布,才回想起应该更新博客了….. 再次说明,这些技术并不是本人原创的,而是以前记录在Evernote的旧内容(排版不是很好,请谅解),本文是继关于AR ...
- 中间人攻击——ARP欺骗的原理、实战及防御
1.1 什么是网关 首先来简单解释一下什么是网关,网关工作在OSI七层模型中的传输层或者应用层,用于高层协议的不同网络之间的连接,简单地说,网关就好比是一个房间通向另一个房间的一扇门. 1.2 A ...
- 从Linux内核角度看中间人攻击(ARP欺骗)并利用Python scapy实现
邻居子系统与ARP协议 邻居子系统的作用就是将IP地址,转换为MAC地址,类似操作系统中的MMU(内存管理单元),将虚拟地址,转换为物理地址. 其中邻居子系统相当于地址解析协议(IPv4的ARP协议, ...
- 【网络编程4】网络编程基础-ARP响应(ARP欺骗之中间人攻击)
arp欺骗->arp响应 ARP 缓存中毒(ARP欺骗) arp传送原理在于主机发送信息时将包含目标IP地址的ARP请求广播到网络上的所有主机,并接收返回消息,以此确定目标的物理地址:收到返回消 ...
- arp协议分析&python编程实现arp欺骗抓图片
arp协议分析&python编程实现arp欺骗抓图片 序 学校tcp/ip协议分析课程老师布置的任务,要求分析一种网络协议并且研究安全问题并编程实现,于是我选择了研究arp协议,并且利用pyt ...
- 图解ARP协议(四)代理ARP原理与实践(“善意的欺骗”)
一.代理ARP概述 我:当电脑要访问互联网上的服务器,目标MAC是什么? 很多小伙伴在刚学习网络协议的时候,经常这样直接回应:不就是服务器的MAC嘛! 这时我会反问:那电脑怎么拿到这个服务器的MAC地 ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu下双显示器设定
自8.10后的版本,系统自带了xrandr工具,可以很好的实现双显示器.配置与使用如下: 介绍 X Windows 中有一个显示分辨率的概念,在默认情况下,这个显示分辨率为 max*max ,m ...
- 使用.bat 批量将部分文件迁移到新的路径下
1.建一个11.bat ,里面写 : dir /b /s >1111.txt 保存后运行 即将所有的文件路径保存到1111.txt中 2.可以将获取的路径复制到execl中,找到自己需 ...
- 第一章 Django之学习Django所需知识(3)
所需编程知识 本书读者需要理解基本的面向过程和面向对象编程:流程控制(if, while 和 for),数据结构(列表,哈希表/字典),变量,类和对象. Web 开发经验,正如你所想的,也是非常有帮助 ...
- 关于HA(双机冗余接口)
HA是双机接口,即说明这款防火墙支持双机冗余并行运行模式,可以用同型号的两台机器同时接上联和下联线路,并用线路将两台机器的HA口连接起来,达到协同工作,并行运行的功能. 高可用性H.A.(High A ...
- 从win到多系统
相信有不少电脑爱好者喜欢折腾系统,尤其还是一个小白(感觉多系统强的不要不要的,各种崇拜),然后就走上了深渊. 首先,我一开始也是个win系统的忠实用户,没用过其他系统的我几乎不知道其他系统的存在,反正 ...
- Java&Selenium自动化测试调用JS实现单击
Java&Selenium自动化测试调用JS实现单击 /* * the method of invoking js to do something * * @author davieyang ...
- Lucene简单了解和使用
一,Lucene简介 1 . Lucene 是什么? Lucene 是一个开放源代码的全文检索引擎工具包,但它不是一个完整的全文检索引擎,而是一个全文检索引擎的架构,提供了完整的查询引擎和索引引擎, ...
- 0012SpringBoot访问首页
有三种方式可以实现访问首页: 第一种: 定义一个Controller,定义请求方法和返回内容,方法内容如下: @RequestMapping({"/","/index&q ...
- BZOJ 3052/Luogu P4074 [wc2013]糖果公园 (树上带修莫队)
题面 中文题面,难得解释了 BZOJ传送门 Luogu传送门 分析 树上带修莫队板子题... 开始没给分块大小赋初值T了好一会... CODE #include <bits/stdc++.h&g ...
- [Google Guava] 6-字符串处理:分割,连接,填充
原文链接 译文链接 译者:沈义扬,校对:丁一 连接器[Joiner] 用分隔符把字符串序列连接起来也可能会遇上不必要的麻烦.如果字符串序列中含有null,那连接操作会更难.Fluent风格的Joine ...
