PCL学习(三) SAC-IA 估记object pose
SAC-IA是基于RANSAC算法的对齐算法
通过降采样提高法向计算、FPFH特征的计算
最后通过SAC-IA计算得到对齐的旋转和平移
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/point_cloud.h>
#include <pcl/common/time.h>
#include <pcl/console/print.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d_omp.h>
#include <pcl/features/fpfh_omp.h>
#include <pcl/filters/filter.h>
#include <pcl/filters/voxel_grid.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/registration/icp.h>
#include <pcl/registration/sample_consensus_prerejective.h>
#include <pcl/segmentation/sac_segmentation.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Types
typedef pcl::PointNormal PointNT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<PointNT> PointCloudT;
typedef pcl::FPFHSignature33 FeatureT;
typedef pcl::FPFHEstimationOMP<PointNT, PointNT, FeatureT> FeatureEstimationT;
typedef pcl::PointCloud<FeatureT> FeatureCloudT;
typedef pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<PointNT> ColorHandlerT; //handle the param of the align in the txt to save the fucking time of complie
int parseConfigFile(
const std::string &filepath,
char *objFile,
char *sceFile,
float *downLeaf
); // Align a rigid object to a scene with clutter and occlusions
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// Point clouds
PointCloudT::Ptr object(new PointCloudT);
PointCloudT::Ptr object_aligned(new PointCloudT);
PointCloudT::Ptr scene(new PointCloudT);
FeatureCloudT::Ptr object_features(new FeatureCloudT);
FeatureCloudT::Ptr scene_features(new FeatureCloudT); // Get input object and scene
/*if (argc != 3)
{
pcl::console::print_error("Syntax is: %s object.pcd scene.pcd\n", argv[0]);
return (1);
}*/
/*std::string paramFilePath = "data/param.txt";
char *obj_filepath = { '\0' };
char *sce_filepath = { '\0' };
float *downsample_leaf = nullptr;
parseConfigFile(
paramFilePath,
obj_filepath,
sce_filepath,
downsample_leaf
);*/ // Load object and scene
pcl::console::print_highlight("Loading point clouds...\n");
if (pcl::io::loadPCDFile<PointNT>("data/obj_seg.pcd", *object) < 0 ||//"data/obj_seg.pcd"
pcl::io::loadPCDFile<PointNT>("data/sce_seg.pcd", *scene) < 0) //"data/sce_seg.pcd"
{
pcl::console::print_error("Error loading object/scene file!\n");
return (1);
} // Downsample
pcl::console::print_highlight("Downsampling...\n");
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointNT> grid;
const float leaf = 0.08f;//0.005f == resolution of 5mm
grid.setLeafSize(leaf, leaf, leaf);
grid.setInputCloud(object);
grid.filter(*object);
grid.setInputCloud(scene);
grid.filter(*scene); // Estimate normals for scene
pcl::console::print_highlight("Estimating scene normals...\n");
pcl::NormalEstimationOMP<PointNT, PointNT> nest;
nest.setRadiusSearch(0.01);
nest.setInputCloud(scene);
nest.compute(*scene); // Estimate features
pcl::console::print_highlight("Estimating features...\n");
FeatureEstimationT fest;
fest.setRadiusSearch(0.025);
fest.setInputCloud(object);
fest.setInputNormals(object);
fest.compute(*object_features);
fest.setInputCloud(scene);
fest.setInputNormals(scene);
fest.compute(*scene_features); // Perform alignment
pcl::console::print_highlight("Starting alignment...\n");
pcl::SampleConsensusPrerejective<PointNT, PointNT, FeatureT> align;
align.setInputSource(object);
align.setSourceFeatures(object_features);
align.setInputTarget(scene);
align.setTargetFeatures(scene_features);
align.setMaximumIterations(100000); // Number of RANSAC iterations 50000
align.setNumberOfSamples(3); // Number of points to sample for generating/prerejecting a pose
align.setCorrespondenceRandomness(5); // Number of nearest features to use
align.setSimilarityThreshold(0.9f); // Polygonal edge length similarity threshold
align.setMaxCorrespondenceDistance(2.5f * leaf); // Inlier threshold
align.setInlierFraction(0.25f); // Required inlier fraction for accepting a pose hypothesis
{
pcl::ScopeTime t("Alignment");
align.align(*object_aligned);
} if (align.hasConverged())
{
// Print results
printf("\n");
Eigen::Matrix4f transformation = align.getFinalTransformation();
pcl::console::print_info(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", transformation(0, 0), transformation(0, 1), transformation(0, 2));
pcl::console::print_info("R = | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", transformation(1, 0), transformation(1, 1), transformation(1, 2));
pcl::console::print_info(" | %6.3f %6.3f %6.3f | \n", transformation(2, 0), transformation(2, 1), transformation(2, 2));
pcl::console::print_info("\n");
pcl::console::print_info("t = < %0.3f, %0.3f, %0.3f >\n", transformation(0, 3), transformation(1, 3), transformation(2, 3));
pcl::console::print_info("\n");
pcl::console::print_info("Inliers: %i/%i\n", align.getInliers().size(), object->size()); // Show alignment
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer visu("Alignment");
visu.addPointCloud(scene, ColorHandlerT(scene, 0.0, 255.0, 0.0), "scene");
visu.addPointCloud(object_aligned, ColorHandlerT(object_aligned, 0.0, 0.0, 255.0), "object_aligned");
visu.spin();
system("PAUSE");
}
else
{
pcl::console::print_error("Alignment failed!\n");
system("PAUSE");
return (1);
} return (0);
} int parseConfigFile(
const std::string &filepath,
char *objFile,
char *sceFile,
float *downLeaf
)
{
// open the configuration file
FILE *file = fopen(filepath.c_str(), "r");
//FILE *stream;//test
if (!file)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot parse configuration file \"%s\".\n",
filepath.c_str());
exit(1);
}
//read parameters
char buf[256];
while (fscanf(file, "%s", buf) != EOF) {
switch (buf[0]) {
case '#':
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), file);
break;
case'o':
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), file);
memcpy(objFile, buf + 1, strlen(buf) - 2);
//printf("%s", objFile);
break;
case's':
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), file);
memcpy(sceFile, buf + 1, strlen(buf) - 2);
break;
case'l':
fscanf(file, "%f", downLeaf);
}
}
return 0; }
对齐前的点云数据(采集于两帧kinect的扫描深度图)

对齐后的结果
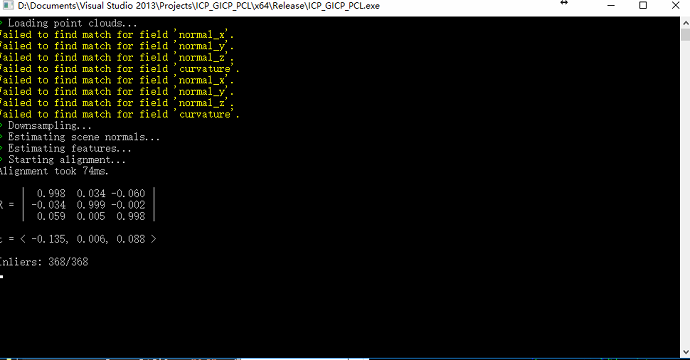
对齐的旋转和平移,以及对齐速度
PCL学习(三) SAC-IA 估记object pose的更多相关文章
- day 82 Vue学习三之vue组件
Vue学习三之vue组件 本节目录 一 什么是组件 二 v-model双向数据绑定 三 组件基础 四 父子组件传值 五 平行组件传值 六 xxx 七 xxx 八 xxx 一 什么是组件 首先给 ...
- Android JNI学习(三)——Java与Native相互调用
本系列文章如下: Android JNI(一)——NDK与JNI基础 Android JNI学习(二)——实战JNI之“hello world” Android JNI学习(三)——Java与Nati ...
- Spring Boot 项目学习 (三) Spring Boot + Redis 搭建
0 引言 本文主要介绍 Spring Boot 中 Redis 的配置和基本使用. 1 配置 Redis 1. 修改pom.xml,添加Redis依赖 <!-- Spring Boot Redi ...
- HTTP学习三:HTTPS
HTTP学习三:HTTPS 1 HTTP安全问题 HTTP1.0/1.1在网络中是明文传输的,因此会被黑客进行攻击. 1.1 窃取数据 因为HTTP1.0/1.1是明文的,黑客很容易获得用户的重要数据 ...
- TweenMax动画库学习(三)
目录 TweenMax动画库学习(一) TweenMax动画库学习(二) TweenMax动画库学习(三) ...
- Struts2框架学习(三) 数据处理
Struts2框架学习(三) 数据处理 Struts2框架框架使用OGNL语言和值栈技术实现数据的流转处理. 值栈就相当于一个容器,用来存放数据,而OGNL是一种快速查询数据的语言. 值栈:Value ...
- 4.机器学习——统计学习三要素与最大似然估计、最大后验概率估计及L1、L2正则化
1.前言 之前我一直对于“最大似然估计”犯迷糊,今天在看了陶轻松.忆臻.nebulaf91等人的博客以及李航老师的<统计学习方法>后,豁然开朗,于是在此记下一些心得体会. “最大似然估计” ...
- DjangoRestFramework学习三之认证组件、权限组件、频率组件、url注册器、响应器、分页组件
DjangoRestFramework学习三之认证组件.权限组件.频率组件.url注册器.响应器.分页组件 本节目录 一 认证组件 二 权限组件 三 频率组件 四 URL注册器 五 响应器 六 分 ...
- [ZZ] 深度学习三巨头之一来清华演讲了,你只需要知道这7点
深度学习三巨头之一来清华演讲了,你只需要知道这7点 http://wemedia.ifeng.com/10939074/wemedia.shtml Yann LeCun还提到了一项FAIR开发的,用于 ...
随机推荐
- Spring Cloud Gateway(九):网关过滤器 GatewayFilter
本文基于 spring cloud gateway 2.0.1 1.简介 GatewayFilter 网关过滤器用于拦截并链式处理web请求,可以实现横切的与应用无关的需求,比如:安全.访问超时的设置 ...
- 前端代码规范-CSS
CSS规范 一.命名规范BEM(Block Element Modifier) 1.Block name -- 实体名称中的单词之间用连字符分隔(-) HTML <div class=" ...
- hello world&Restart the Journey
一个女OIer. 总结,游记,集训日志在博客园:题解大多在洛谷. 洛谷博客点这里. $\texttt{ You can go on,just take me with you.}$ 可以叫我Har ...
- SpringCloud学习整理
参考文档 [1]: Spring Cloud Ribbon负载均衡
- Sollin算法的C++实现 BY gremount
Sollin算法可以看作是Kruskal算法和Prim算法的综合 基本思想是: 1. 从所有节点都孤立的森林开始,通过合并树来得到最小生成树 2. 每次合并树的边都是用最小权重的割边 程序具体实现思路 ...
- 2018-2019-2 《网络对抗技术》Exp9 Web安全基础 20165114
Exp9 Web安全基础 目录 一.实验内容 二.基础问题回答 (1)SQL注入攻击原理,如何防御 (2)XSS攻击的原理,如何防御 (3)CSRF攻击原理,如何防御 三.实践过程记录 3.1 注入缺 ...
- mysql 触发器语法详解
1.创建Mysql触发器: 语法: CREATE TRIGGER trigger_name trigger_time trigger_event ON tbl_name FOR EACH ROW BE ...
- zsh: no matches found
具体原因: 因为zsh缺省情况下始终自己解释这个 *.h,而不会传递给 find 来解释. 解决办法: 在~/.zshrc中加入: setopt no_nomatch, 然后进行source .zsh ...
- opencv常见示例
1.批量转换灰度图并保存 #include <iostream> #include <opencv2/opencv.hpp> #include <string> u ...
- 简易的CRM系统案例之SpringMVC+JSP+MySQL+myBatis框架版本
主要对上一版DAO框架的替换hibernate变成myBatis 简易的CRM系统案例之SpringMVC+JSP+MySQL+hibernate框架版本 src/mybatis.xml <?x ...
