Trie树(c++实现)——转载自jihite的博客
Trie树(c++实现)
原理
先看个例子,存储字符串abc、ab、abm、abcde、pm可以利用以下方式存储
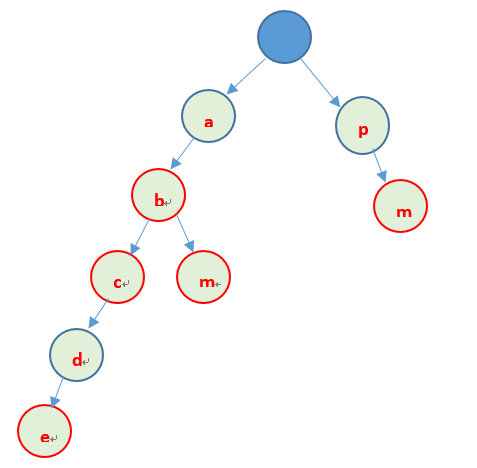
上边就是Trie树的基本原理:利用字串的公共前缀来节省存储空间,最大限度的减少无谓的字串比较。
应用
Trie树又称单词查找树,典型的应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(不仅用于字符串),所以经常被搜索引擎系统用于文本词频的统计。
设计
trie,又称前缀树或字典树,是一种有序树,用于保存关联数组,其中的键通常是字符串。与二叉查找树不同,键不是直接保存在节点中,而是由节点在树中的位置决定。一个节点的所有子孙都有相同的前缀,也就是这个节点对应的字符串,而根节点对应空字符串。一般情况下,不是所有的节点都有对应的值,只有叶子节点和部分内部节点所对应的键才有相关的值。
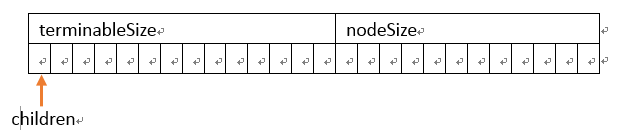
结点可以设计成这样:
class trieNode
{
public:
trieNode() : terminableSize(), nodeSize() { for(int i = ; i < Size; ++i) children[i] = NULL; }
~trieNode()
{
for(int i = ; i < Size; ++i)
{
delete children[i];
children[i] = NULL;
}
}
public:
int terminableSize; //存储以此结点为结尾的字串的个数
int nodeSize; //记录此结点孩子的个数
trieNode* children[Size]; //该数组记录指向孩子的指针
};
图示
树设计成这样:
template<int Size, class Type>
class trie
{
public:
typedef trieNode<Size> Node;
typedef trieNode<Size>* pNode;
trie() : root(new Node) {} template<class Iterator>
void insert(Iterator beg, Iterator end);
void insert(const char *str); template<class Iterator>
bool find(Iterator beg, Iterator end);
bool find(const char *str); template<class Iterator>
bool downNodeAlone(Iterator beg); template<class Iterator>
bool erase(Iterator beg, Iterator end);
bool erase(const char *str); int sizeAll(pNode);
int sizeNoneRedundant(pNode);
public:
pNode root;
private:
Type index;
};
index字串索引利用(char % 26) 得到,这样'a' % 26 = 19, 'b' % 26 = 20
实现
插入
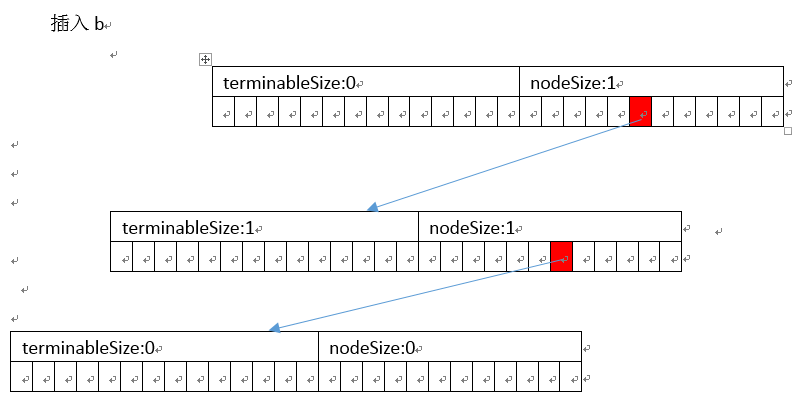
以插入abc、ab为例
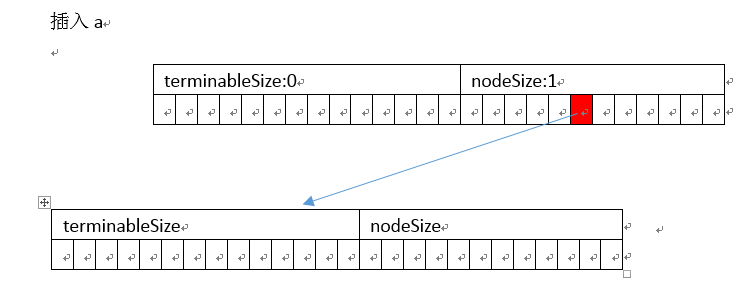 ]
]
删除
删除结点,首先查找此字串是否在树中,如果在树中,再查找此结点以下的部分是不是都是只有一个孩子,并且每个结点只有叶子结点是结束结点,如果不是继续往下重复上边过程。
统计字串个数
分两种情况
- 计算重复的字串的个数:是结束结点,此时加的是terminabel的个数
- 计算不重复的字串的个数:是结束结点,此时加的是1(当terminabel>0)的个数
参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std; template<int Size>
class trieNode
{
public:
trieNode() : terminableSize(), nodeSize() { for(int i = ; i < Size; ++i) children[i] = NULL; }
~trieNode()
{
for(int i = ; i < Size; ++i)
{
delete children[i];
children[i] = NULL;
}
}
public:
int terminableSize;
int nodeSize;
trieNode* children[Size];
}; template<int Size, class Type>
class trie
{
public:
typedef trieNode<Size> Node;
typedef trieNode<Size>* pNode;
trie() : root(new Node) {} template<class Iterator>
void insert(Iterator beg, Iterator end);
void insert(const char *str); template<class Iterator>
bool find(Iterator beg, Iterator end);
bool find(const char *str); template<class Iterator>
bool downNodeAlone(Iterator beg); template<class Iterator>
bool erase(Iterator beg, Iterator end);
bool erase(const char *str); int sizeAll(pNode);
int sizeNoneRedundant(pNode);
public:
pNode root;
private:
Type index;
}; template<int Size, class Type>
template<class Iterator>
void trie<Size, Type>::insert(Iterator beg, Iterator end)
{
pNode cur = root;
pNode pre;
for(; beg != end; ++beg)
{
if(!cur->children[index[*beg]])
{
cur->children[index[*beg]] = new(Node);
++cur->nodeSize;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->children[index[*beg]];
}
++pre->terminableSize;
}
template<int Size, class Type>
void trie<Size, Type>::insert(const char *str)
{
return insert(str, str + strlen(str));
} template<int Size, class Type>
template<class Iterator>
bool trie<Size, Type>::find(Iterator beg, Iterator end)
{
pNode cur = root;
pNode pre;
for(; beg != end; ++beg)
{
if(!cur->children[index[*beg]])
{
return false;
break;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->children[index[*beg]];
}
if(pre->terminableSize > )
return true;
return false;
} template<int Size, class Type>
bool trie<Size, Type>::find(const char *str)
{
return find(str, str + strlen(str));
} template<int Size, class Type>
template<class Iterator>
bool trie<Size, Type>::downNodeAlone(Iterator beg)
{
pNode cur = root;
int terminableSum = ;
while(cur->nodeSize != )
{
terminableSum += cur->terminableSize;
if(cur->nodeSize > )
return false;
else //cur->nodeSize = 1
{
for(int i = ; i < Size; ++i)
{
if(cur->children[i])
cur = cur->children[i];
}
}
}
if(terminableSum == )
return true;
return false;
}
template<int Size, class Type>
template<class Iterator>
bool trie<Size, Type>::erase(Iterator beg, Iterator end)
{
if(find(beg, end))
{
pNode cur = root;
pNode pre;
for(; beg != end; ++beg)
{
if(downNodeAlone(cur))
{
delete cur;
return true;
}
pre = cur;
cur = cur->children[index[*beg]];
}
if(pre->terminableSize > )
--pre->terminableSize;
return true;
}
return false;
} template<int Size, class Type>
bool trie<Size, Type>::erase(const char *str)
{
if(find(str))
{
erase(str, str + strlen(str));
return true;
}
return false;
} template<int Size, class Type>
int trie<Size, Type>::sizeAll(pNode ptr)
{
if(ptr == NULL)
return ;
int rev = ptr->terminableSize;
for(int i = ; i < Size; ++i)
rev += sizeAll(ptr->children[i]);
return rev;
} template<int Size, class Type>
int trie<Size, Type>::sizeNoneRedundant(pNode ptr)
{
if(ptr == NULL)
return ;
int rev = ;
if(ptr->terminableSize > )
rev = ;
if(ptr->nodeSize != )
{
for(int i = ; i < Size; ++i)
rev += sizeNoneRedundant(ptr->children[i]);
}
return rev;
} template<int Size>
class Index
{
public:
int operator[](char vchar)
{ return vchar % Size; }
}; int main()
{
trie<, Index<> > t;
t.insert("hello");
t.insert("hello");
t.insert("h");
t.insert("h");
t.insert("he");
t.insert("hel");
cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeAll(t.root) << endl;
cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeNoneRedundant(t.root) << endl;
t.erase("h");
cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeAll(t.root) << endl;
cout << "SizeALL:" << t.sizeNoneRedundant(t.root) << endl;
}
结果

技术实现细节
1. 对树的删除,并不是树销毁结点,而是通过结点自身的析构函数实现
2. 模版类、模版函数、非类型模版可以参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/kaituorensheng/p/3601495.html
3. 字母的存储并不是存储的字母,而是存储的位置,如果该位置的指针为空,则说明此处没有字母;反之有字母。
4. terminableNum存储以此结点为结束结点的个数,这样可以避免删除时,不知道是否有多个相同字符串的情况。
Trie树(c++实现)——转载自jihite的博客的更多相关文章
- 【转载】国内网站博客数据统计选免费Google Analytics还是百度统计
[转载]国内网站博客数据统计选免费Google Analytics还是百度统计 Google Analytics谷歌统计是我用的第一个网站统计工具,当然现在也一直在用.Google Analytics ...
- 转载来自朱小厮博客的 一文看懂Kafka消息格式的演变
转载来自朱小厮博客的 一文看懂Kafka消息格式的演变 ✎摘要 对于一个成熟的消息中间件而言,消息格式不仅关系到功能维度的扩展,还牵涉到性能维度的优化.随着Kafka的迅猛发展,其消息格式也在 ...
- 如何快速转载CSDN中的博客
看到一篇<如何快速转载CSDN中的博客>,介绍通过检查元素→复制html来实现快速转载博客的方法.不过,不知道是我没有领会其精神还是其他原因,测试结果为失败.
- [转]如何快速转载CSDN中的博客
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/bolu1234/article/details/51867099 前言 对于喜欢逛CSDN的人来说,看别人的博客确实能够对自己有不小的提高,有时 ...
- 【转载】如何快速转载CSDN中的博客
前言 对于喜欢逛CSDN的人来说,看别人的博客确实能够对自己有不小的提高,有时候看到特别好的博客想转载下载,但是不能一个字一个字的敲了,这时候我们就想快速转载别人的博客,把别人的博客移到自己的空间 ...
- JavaScript资源大全中文版(Awesome最新版--转载自张果老师博客)
JavaScript资源大全中文版(Awesome最新版) 目录 前端MVC 框架和库 包管理器 加载器 打包工具 测试框架 框架 断言 覆盖率 运行器 QA 工具 基于 Node 的 CMS 框 ...
- 转载自jguangyou的博客,XML基本属性大全
android:layout_width 指定组件布局宽度 android:layout_height 指定组件布局高度 android:alpha 设置组件透明度 android:backgroun ...
- 在mac系统安装Apache Tomcat的详细步骤(转载自himi的博客,修改了错误添加了图片)
链接地址:http://blog.csdn.net/liuyuyefz/article/details/8072485 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 对于Apache Tomcat 估计很多童鞋都会, ...
- 一个最最简易的RPC框架雏形---转载自梁飞的博客
查阅RPC与HTTP区别的时候, 无意间发现一篇博客,内容是一个简易的RPC服务框架, 仔细一看, 不得了,博主竟然就是阿里dubbo的作者. 原文链接在此: http://javatar.iteye ...
随机推荐
- k8s-高可用架构设计
docker的私有仓库harbor.容器化kubernetes部分组建.使用阿里云日志服务收集日志. 部署完成后,你将理解系统各组件的交互原理,进而能快速解决实际问题,所以本文档主要适合于那些有一定k ...
- JavaScript-checkbox标签-隐藏、显示、全选、取消和反选等操作
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- pthread 笔记
1.创建线程 res = pthread_create(&a_thread, NULL, thread_function1, NULL); if (res != 0) { perror(&qu ...
- Laravel 查询数据按照时间分组
首先取消严格模式: // config/database.php // 'strict' => true, // 严谨模式注释掉 查询构造器代码: //查询构造器部分代码 })->with ...
- Kendall tau距离(即两个内容相同的数组中逆序数对的数量)(算法》P220 第2.5.3.2小节)
一组排列就是一组N个整数的数组,其中0~N-1的每个数都只出现一次.两个排列之间的 Kendall tau距离就是在两组排列中相对顺序不同的数对的数目.例如,0 3 1 6 2 5 4和1 0 3 6 ...
- 帝国cms 修改分页样式
帝国cms 修改分页样式(路径) /e/class/t_functions.php
- mysql一些语句
<!-- 报警量排行按创建时间每月来排行 --> <select id="alarmDaySort" resultType="alarm"&g ...
- java代码备份mysql数据库
编写bat文件 @echo off set "date_string=%date:~0,4%-%date:~5,2%-%date:~8,2%" set "time_str ...
- 阿里Java开发规约【摘录】
1.命名规约 [强制]类名使用UpperCamelCase风格,必须遵从驼峰形式,但以下情形例外:(领域模型的相关命名)DO / BO / DTO / VO等. 正例:MarcoPolo / User ...
- python中的负数取模问题(一个大坑)
先来看一段代码 这是什么情况?为什么会出现这种结果.我们再来看看其它语言的执行结果 我们用golang.js.c分别算了一下,结果得到的结果都是一致的,但是python为啥不一样呢? 其实之所以这么做 ...
