SVN搭建以及客户端使用
第1章 CentOS下搭建SVN服务器
1.1 SVN简介
SVN是Subversion的简称,是一个开放源代码的版本控制系统,相较于RCS、CVS,它采用了分支管理系统,它的设计目标就是取代CVS。互联网上很多版本控制服务已从CVS迁移到Subversion。说得简单一点SVN就是用于多个人共同开发同一个项目,共用资源的目的
1.2 SVN安装
官网下载: http://subversion.apache.org/packages.html
SVN客户端TortoiseSVN :https://tortoisesvn.net/downloads.html
1.2.1 系统环境
[root@Alex ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release
CentOS Linux release 7.1.1503 (Core)
[root@Alex ~]# uname -r
3.10.0-229.el7.x86_64
[root@Alex ~]# systemctl status firewalld
firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon
Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled)
Active: inactive (dead) Oct 30 22:13:43 Alex systemd[1]: Starting firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...
Oct 30 22:13:48 Alex systemd[1]: Started firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.
Oct 30 22:44:11 Alex systemd[1]: Stopping firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon...
Oct 30 22:44:12 Alex systemd[1]: Stopped firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon.
[root@Alex ~]# getenforce
Permissive
1.2.2 安装
使用yum命令安装svn
$ yum install subversion -y
新建svn存储目录
$ mkdir /svn
新建一个测试仓库
$ svnadmin create /svn/test/
$ ll /svn/test/
total 16
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 51 Oct 31 12:45 conf
drwxr-sr-x. 6 root root 4096 Oct 31 12:45 db
-r--r--r--. 1 root root 2 Oct 31 12:45 format
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 4096 Oct 31 12:45 hooks
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 39 Oct 31 12:45 locks
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 229 Oct 31 12:45 README.txt
以下关于目录的说明:
hooks目录:放置hook脚步文件的目录
locks目录:用来放置subversion的db锁文件和db_logs锁文件的目录,用来追踪存取文件库的客户端
format目录:是一个文本文件,里边只放了一个整数,表示当前文件库配置的版本号
conf目录:是这个仓库配置文件(仓库用户访问账户,权限)
1.2.3 配置SVN配置文件
$ cd /svn/test/conf
$ vim svnserve.conf
### This file controls the configuration of the svnserve daemon, if you
### use it to allow access to this repository. (If you only allow
### access through http: and/or file: URLs, then this file is
### irrelevant.)
### Visit http://subversion.tigris.org/ for more information.
[general]
### These options control access to the repository for unauthenticated
### and authenticated users. Valid values are "write", "read",
### and "none". The sample settings below are the defaults.
anon-access = read ##注意前边不要有空格,要顶齐
auth-access = write ##注意前边不要有空格,要顶齐
### The password-db option controls the location of the password
### database file. Unless you specify a path starting with a /,
### the file's location is relative to the directory containing
### this configuration file.
### If SASL is enabled (see below), this file will NOT be used.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default password file.
password-db = passwd ##注意前边不要有空格,要顶齐
### The authz-db option controls the location of the authorization
### rules for path-based access control. Unless you specify a path
### starting with a /, the file's location is relative to the the
### directory containing this file. If you don't specify an
### authz-db, no path-based access control is done.
### Uncomment the line below to use the default authorization file.
authz-db = authz #授权文件
### This option specifies the authentication realm of the repository.
### If two repositories have the same authentication realm, they should
### have the same password database, and vice versa. The default realm
### is repository's uuid.
realm = This is My First Test Repository ##这个是提示信息
[sasl]
### This option specifies whether you want to use the Cyrus SASL
### library for authentication. Default is false.
### This section will be ignored if svnserve is not built with Cyrus
### SASL support; to check, run 'svnserve --version' and look for a line
### reading 'Cyrus SASL authentication is available.'
# use-sasl = true
### These options specify the desired strength of the security layer
### that you want SASL to provide. 0 means no encryption, 1 means
### integrity-checking only, values larger than 1 are correlated
### to the effective key length for encryption (e.g. 128 means 128-bit
### encryption). The values below are the defaults.
# min-encryption = 0
# max-encryption = 256
1.2.4 配置访问用户及密码
$ cd /svn/test/conf
$ vim passwd
### This file is an example password file for svnserve.
### Its format is similar to that of svnserve.conf. As shown in the
### example below it contains one section labelled [users].
### The name and password for each user follow, one account per line. [users]
# harry = harryssecret
# sally = sallyssecret
dev = 123456
test1 = 123456
test2 = 123456
1.2.5 配置新用户的授权文件
$ cd /svn/test/conf
### This file is an example authorization file for svnserve.
### Its format is identical to that of mod_authz_svn authorization
### files.
### As shown below each section defines authorizations for the path and
### (optional) repository specified by the section name.
### The authorizations follow. An authorization line can refer to:
### - a single user,
### - a group of users defined in a special [groups] section,
### - an alias defined in a special [aliases] section,
### - all authenticated users, using the '$authenticated' token,
### - only anonymous users, using the '$anonymous' token,
### - anyone, using the '*' wildcard.
###
### A match can be inverted by prefixing the rule with '~'. Rules can
### grant read ('r') access, read-write ('rw') access, or no access
### (''). [aliases]
# joe = /C=XZ/ST=Dessert/L=Snake City/O=Snake Oil, Ltd./OU=Research Institute/CN=Joe Average [groups]
# harry_and_sally = harry,sally
# harry_sally_and_joe = harry,sally,&joe # [/foo/bar]
# harry = rw
# &joe = r
# * = # [repository:/baz/fuz]
# @harry_and_sally = rw
# * = r
admin = dev,test1
user = test2
[/svn/test/]
@admin = rw
@user = r
* = r
说明:
[repo0:/] 代表对repo0所有版本库设置权限权限
[repo0:/21yunwei] 代表对repo0版本库下的21yunwei项目设置权限
[repo0:/21yunwei/demo] 代表对repo0版本库下的21yunwei项目的demo目录设置权限
admin = lqb,test2 创建admin组,组成员为:lqb,test2
user = test1 创建用户组,用户成员:test1
[test:/] 赋予根权限,为了便于管理和权限的控制,可以把权限细化到版本库中相应的目录,如[test:/test]这就是test项目下的一个目录
@admin = rw admin组有读写的权限
@user = r user组只有读的权限
*= 表示除了上面设置的权限用户组以外,其他所有用户都设置空权限,空权限表示禁止访问本目录,这很重要一定要加上
1.2.6 启动svn
$ svnserve -d -r /svn
注意:更改svnserver.conf时需要重启SVN服务,更改authz,passwd文件时则不需要重启服务
第2章 通过客户端进行连接
2.1 下载客户端并安装
首先安装SVN客户端,windows一般选择乌龟客户端https://tortoisesvn.net/downloads.html。
根据系统位数选择相应客户端进行安装
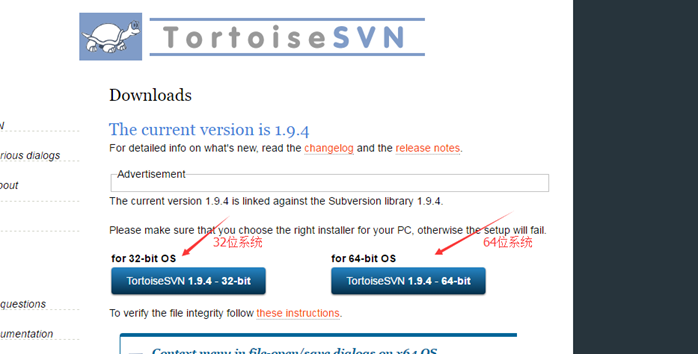
如果你喜欢用命令行操作,请务必记得勾选command line client tool为will be install on local hard driver,不用命令行的跳过这一步
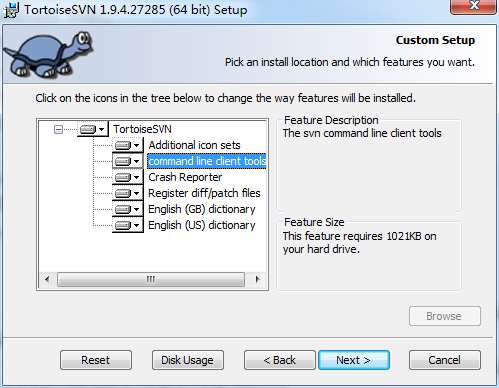
然后一路next即可安装。安装完毕后,在任意地方右键查看快捷菜单。发现TortoiseSVN即表示安装成功。
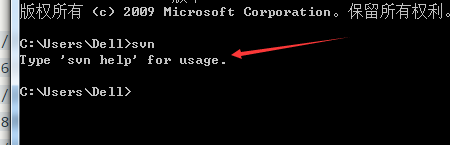
如果勾选了安装命令行工具,那么输入命令SVN,有如下提示也表示安装成功
2.2 中文设置
但是此时菜单全是英文的,如果你不习惯英文,可以去下载语言包,记得下对系统位数
官网下载,上面有地址
安装完语言包之后,可以右键进入setting设置
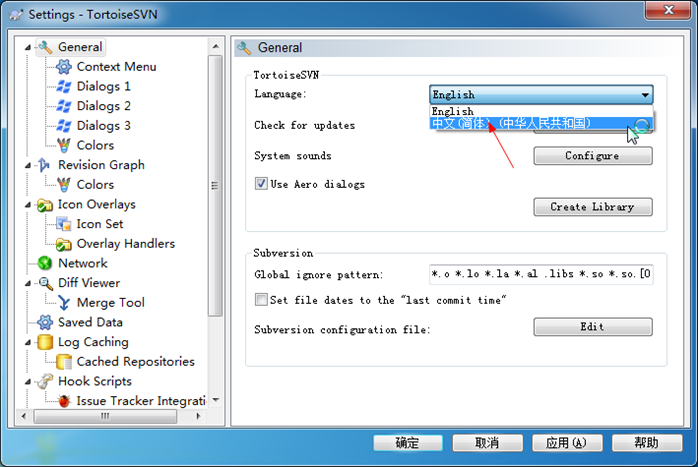
选择你喜欢的语言(比如中文),然后确定,不出意外,现在的语言已经切换到中文了

安装教程到此结束,下面开始介绍SVN的使用
2.3 使用说明
2.3.1 检出项目
假如项目已经在服务器的仓库里,那么现在你要做的就是把它检出到本地。
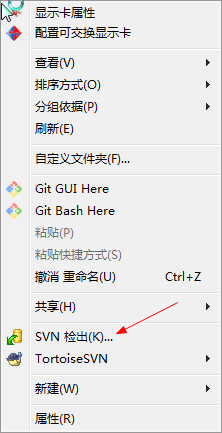
首先创建一个空文件夹。在空文件夹内右键,选择SVN检出
现在你看到应该是这个界面,填入版本库地址,选择确定
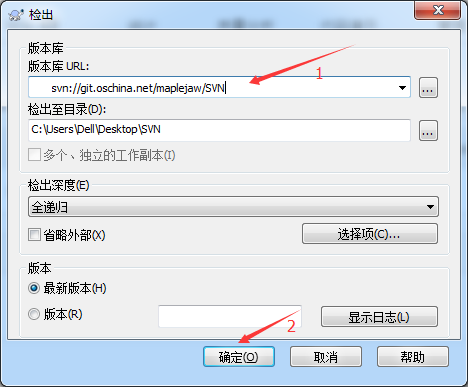
此时会弹出一个对话框让你输入账号密码,输入你的账号密码即可。记得勾选保存认证,不然每次操作都会让你输入。

等几分钟就可以检出完毕
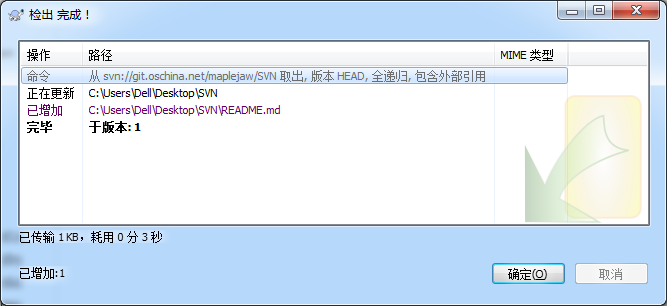
此时在你的目录下就能看到你的项目,现在可以开始愉快的工作了
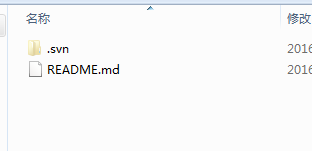
2.3.2 导入项目
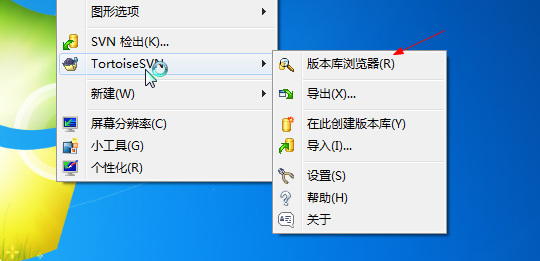
但是有时候你已经在本地建立好了项目,需要把你项目推到SVN上,此时应怎么做呢?
右键选择版本库浏览器。
在相应目录下,右键,加入文件/加入文件夹,选择相应目录即可
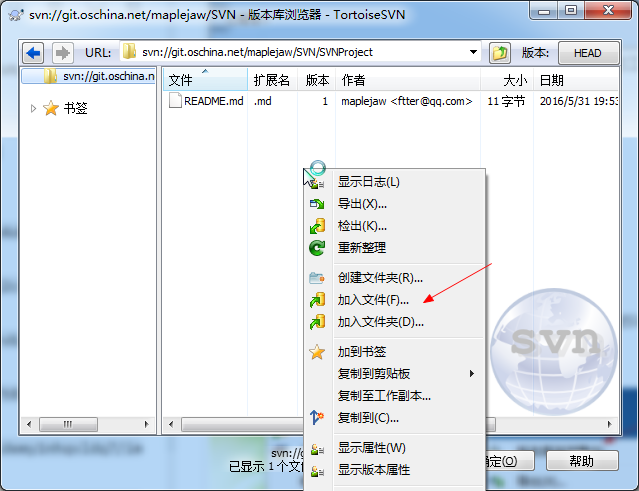
比如我现在有个项目叫SVNProject,我想把它传到SVN上

那么我只需选择加入文件夹即可。

务必要输入提交信息。这样别人才能知道你干了什么
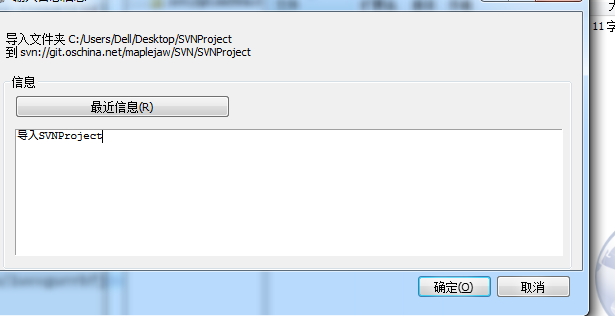
导入成功就能看到目录。

但是,不要以为导入成功就可以了。你还得重新检出,重新检出的项目才是受SVN控制的,务必记得检出

在SVNProject上右键检出到本地,然后在里面进行修改。现在就可以愉快的工作了。
检出过后的右键菜单变成了这样。
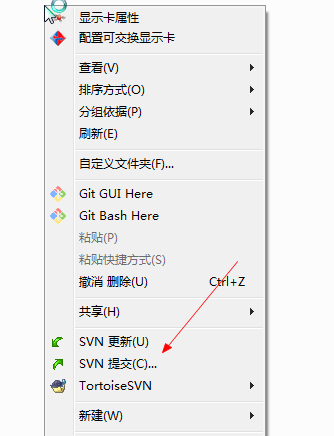
绿色表示当前文件没有被修改过(看不见颜色的重启下电脑就好了)。

假如我现在在我是新项目.txt中加了一行字,然后保存
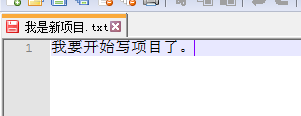
发现现在变成了红色,红色表示已修改
怎么提交修改?
在根目录下,右键选择提交。
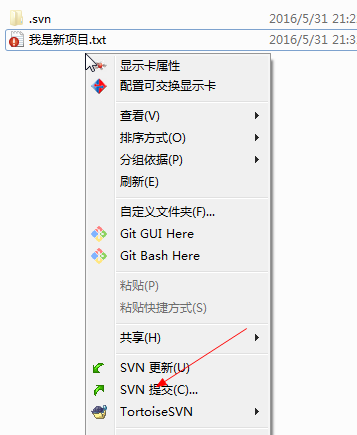
务必记得输入提交信息(虽然不输入也能提交),提交信息可以方便日后查看。

提交完毕后,可以发现又恢复到了绿色

假如现在加入了一个新文件。可以看出是蓝色的。蓝色表示不属于版本库的未知文件,未知文件是不能提交的。
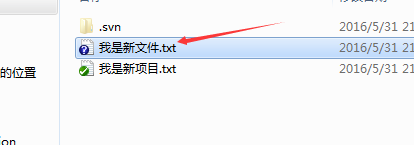
记住选择增加把它加入到版本库里面去

增加完毕后,变成了蓝色加号,表示新增加的版本库文件

接下来,只需写代码,然后提交即可。
删除文件也应该右键提交,如下。
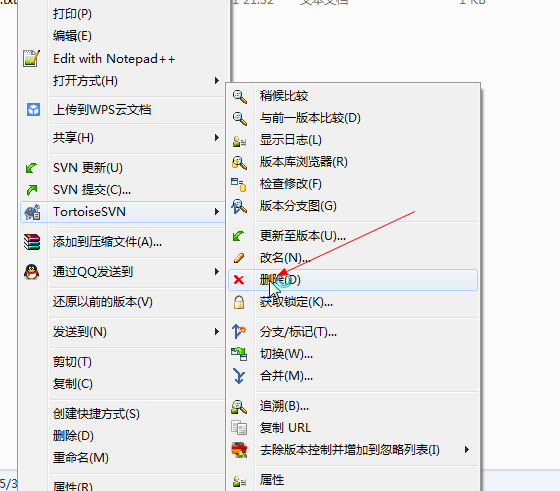
记得随时检查你的文件状态,如果没有添加到版本控制里要及时添加进去,不然你的文件提交不上去。
2.3.3 更新
假如你和B同学在协作。B同学写完代码提交到了SVN上,如果你想获取最新修改,就需要选择更新(如果服务器上已经有别人提交过的新的,你是提交不上去的,必须先更新再提交)。
怎么知道服务器有没有更新?你可以直接选择更新,有没有更新一下就知道。或者右键检查修改,然后检查版本库,就能看到服务器上改了哪些文件

右键选择HEAD和BASE比较。

左边的表示你的代码,右边的表示服务器上的代码
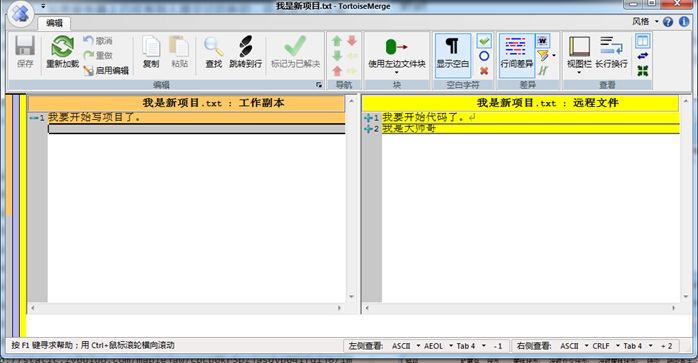
如果有修改记得及时更新到本地然后再继续工作
但是有时候更新会冲突,比如你和服务器上的改了同一个地方。
这时候你需要更新下来解决冲突。

它会提示你哪个文件冲突,你只需打开那个文件,按照需求解决冲突即可
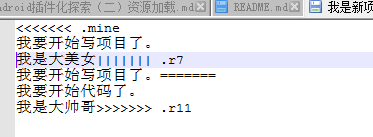
<<<<<<.mine到====表示你的代码,其他表示服务器的代码。你只需改成你想要的
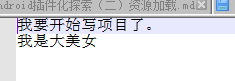
然后选择解决,告诉SVN我已经解决冲突了就行了
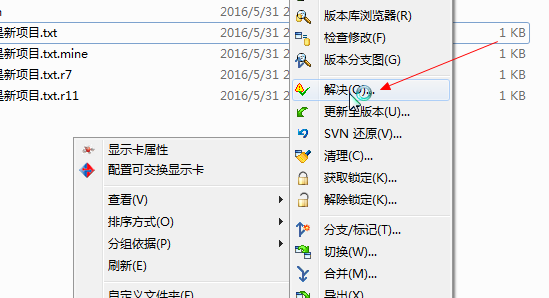
剩下的就是团队协作间的更新提交操作,这里不做赘述
2.3.4 查看日志
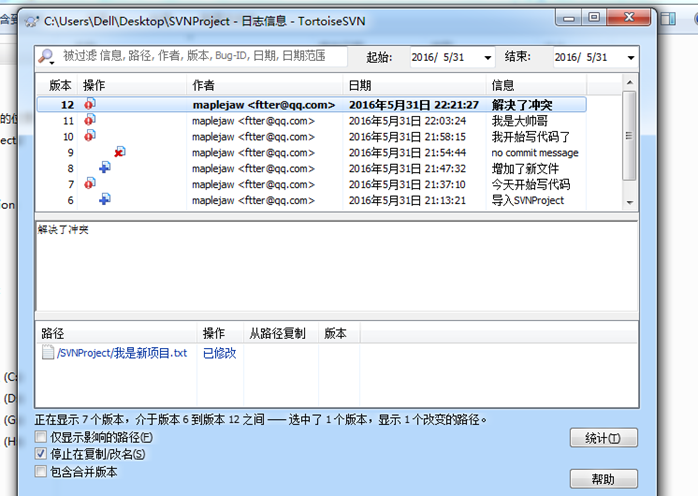
选择显示日志,可以看出团队里面的人干了什么

可以看出谁谁谁,什么时间,干了什么事。最后那一列信息是自己提交的时候写的。建议大家提交时务必要填写提交信息,这样别人一看就知道你干了什么。提交信息对于自己也是有好处的,时间长了也能看到当初做了什么。
2.3.5 版本回滚
如果你改了东西,但是还没有提交,可以使用还原功能。
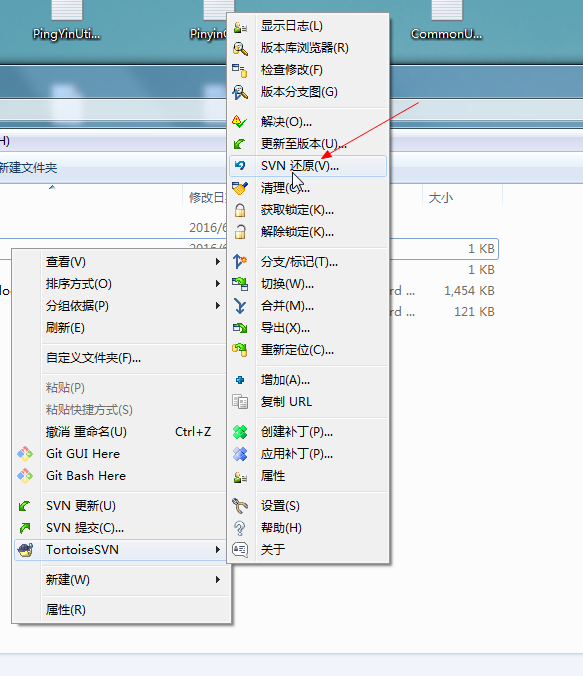
但是如果我们写错了东西并且提交了上去怎么办?通过版本回滚可以将文件恢复到
以前的版本。右键更新至版本,通过查看日志来选择版本,然后回滚即可

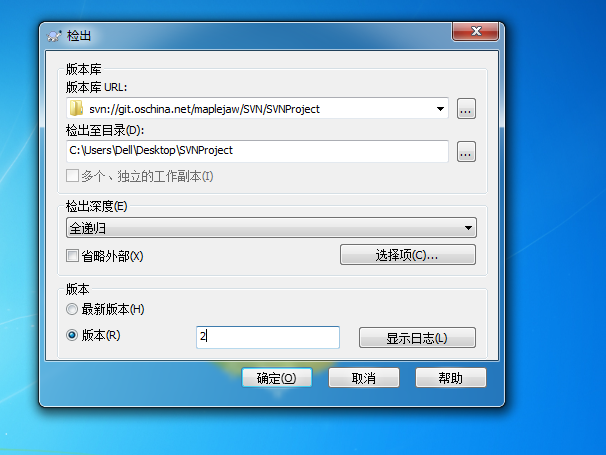
有时候我们需要查看以前版本的代码。此时我们可以新建个文件夹检出到指定版本
2.3.6 版本控制
版本控制有好几种方法,如下。
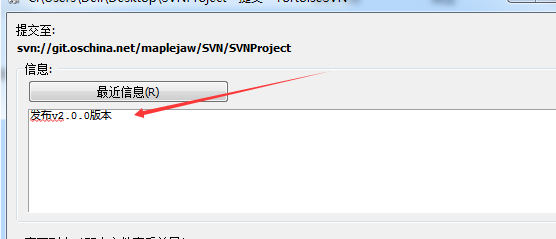
在提交发布版本时添加版本信息,这是最简单的一种方法。
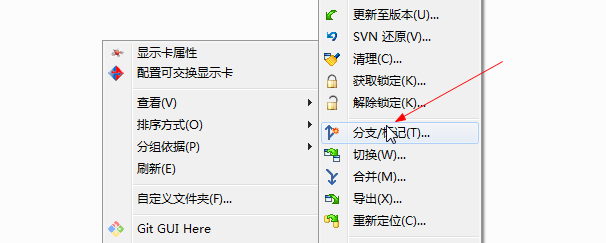
打标签
每次发布版本时应该打标签。右键选择分支/标记。在至路径以版本号打上标签即可
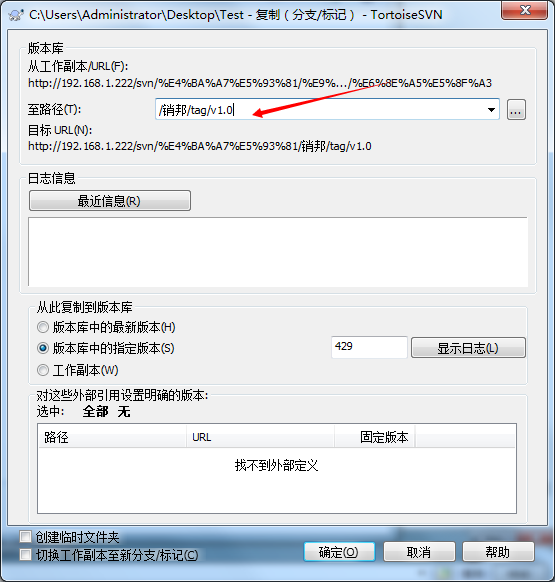
这样你就有了一个v1.0版本的标签。
以后如果你想查看某个版本的代码,只需切换过去就行
部分摘自这位大佬的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/maplejaw_/article/details/52874348
SVN搭建以及客户端使用的更多相关文章
- svn 服务器的搭建以及客户端的使用
1.svn 服务器的搭建以及客户端的使用,安装见下面的博客 https://blog.csdn.net/zh123456zh789/article/details/80921179 说明:服务器只是用 ...
- centos7搭建svn服务器及客户端设置
centos7搭建svn服务器及客户端设置 centos7貌似预装了svn服务(有待确认),因此我们直接启动该服务即可 一.svn服务端配置(服务器IP假设为192.168.100.1) 步骤1:创建 ...
- window系统下SVN服务器和客户端的搭建和使用
SVN服务器下载地址: http://subversion.apache.org/packages.html 这里我选用VisualSVN server 服务端和 TortoiseSVN客户端搭配使用 ...
- 转载-Linux下svn搭建配置流程
Linux下svn搭建配置流程 一. 源文件编译安装.源文件共两个,为: 1. 下载subversion源文件 subversion-1.6.1.tar.gz http://d136 ...
- svn搭建
原文:svn搭建 二.Subversion的安装与测试 Subversion的配置方式有很多种,同时也可以配置不同的操作系统之上,本文我讲解的是Subversion 1.5.4 for Apache2 ...
- Svn———搭建及配置
一.Svn介绍 subversion(简称svn)是近几年崛起的版本管理软件,是cvs的接班人,目前绝大多数开源软件都使用svn作为代码版本管理软件.Subversion支持linux和windows ...
- jenkins和svn搭建自动代码构建发布
jenkins安装和配置 .安装jenkins .yum install java wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/jenkins.repo https://pkg.jenkins. ...
- Docker+Jenkins+Maven+SVN搭建持续集成环境
Docker+Jenkins+Maven+SVN搭建持续集成环境 环境拓扑图(实验项目使用PHP环境) 发布流程图 环境说明 系统:Centos 7.4 x64 Docker版本:18.09.0 Ma ...
- SVN学习---使用 Visual SVN 搭建SVN服务器
1.1. 使用 Visual SVN 搭建SVN服务器 搭建纯粹SVN服务器 --- svn:// 访问资源 将SVN 和 Apache服务器整合 ,搭建web SVN服务器 ---- https: ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript(9)—— CSS定位综合练习
画布上画矩形 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UT ...
- Vuex模块:开启命名空间
模块开启命名空间后,享有独自的命名空间. { "模块1":{ state:{}, getters:{}, mutations:{}, actions:{} }, "模块2 ...
- SpringBoot + thymeleaf 实现分页
SpringBoot结合Thymeleaf实现分页,很方便. 效果如下 后台代码 项目结构 1. 数据库Config 由于hibernate自动建表字符集为latin不能插入中文,故需要在applic ...
- 创建vue 项目
sudo npm install -g @vue/cli-init vue init webpack my-project cd my-project/ npm install npm run dev
- 【机器学习】ICA 原理以及相关概率论,信息论知识简介
看完了sparse coding,开始看ICA模型,本来ng的教程上面就只有一个简短的介绍,怎奈自己有强迫症,爱钻牛角尖,于是乎就搜索了一些ICA的介绍文章(都是从百度文库中搜来的),看完之后感觉这个 ...
- Excel小技巧(随机点名)
如图,想要做一个随机点名的表格,同样可以石头剪刀布的场合,随机选人. 如何做呢? 第一步,填好想要的数据 第二步,在空的位置输入=INDIRECT("A"&RANDBETW ...
- PTA (Advanced Level)1077.Kuchiguse
The Japanese language is notorious for its sentence ending particles. Personal preference of such pa ...
- [转帖]为何 linux 要用 tar.gz,而不用 7z 或 zip?
为何 linux 要用 tar.gz,而不用 7z 或 zip? http://embeddedlinux.org.cn/emb-linux/entry-level/201908/13-8776.ht ...
- 小记--------sqoop的简单从mysql导入到hbase操作
sqoop import -D sqoop.hbase.add.row.key=true //是否将rowkey相关字段列入列族中,默认为false :该 ...
- linux常用终端命令(三)远程管理命令
三.远程管理常用命令 关机/重启 shutdown 查看或配置网卡信息 ifconfig ping 远程登录和复制文件 ssh scp 1.关机/重启 序号 命令 对应英文 作用 01 shutdow ...
