c++中的 static 关键字
注:若没有特指是 静态成员时,默认都是普通成员;
1 类中的普通成员
类中的成员变量 和 成员函数 是分开存储的。其中,
1)每个对象都有独立的成员变量;成员变量可以存储在 栈空间、堆空间、全局数据区;
2)所有对象共享类的成员函数;成员函数 只能存储在 代码段;
2 类中的静态成员(static)
类中的静态成员
1、用 static关键字 修饰;
2、可以用 类名::成员名 访问 静态成员;
3、静态成员 属于 整个类;
4、静态成员 是所属类的成员,其它类不能访问;
5、静态成员的内存分配 是 唯一的;
1) 静态成员变量
特征:1、静态成员变量 属于 整个类所有;
2、静态成员变量的生命周期不依赖任何对象;(静态成员变量的生命周期在程序的运行期)
3、所有对象共享类的静态成员变量;
4、可以通过 类名 直接访问公有的静态成员变量;
5、可以通过 对象名 访问公有的静态成员变量;
6、静态成员变量 需要在类外单独分配空间;(类内声明、类外定义并初始化)
7、静态成员变量 在程序内部位于全局数据区,不计入类的内存计算。
原因/好处:使用静态成员变量实现多个对象之间的数据共享不会破坏隐藏的原则,保证了安全性还可以节省内存。
使用方法:
1、在类的内部,使用 static 修饰普通成员变量;
2、在类的外部(全局作用域),使用 Type ClassName::VarName = value 初始化,并申请存储空间;
注:静态成员变量不属于类的任何对象,所以并不是对象建立时被定义的,所以它不能由类的构造函数初始化,一般也不能在类内初始化;
- /*
- 静态成员变量 只能在类的内部声明,在类的外部(全局区)定义和初始化;
- */
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Test{
- public:
- int GetA() const{return a;}
- private:
- static int a; // 静态成员变量
- };
- //int Test::a;如果这样定义不赋予初值,则初值为零
- int Test::a = ;
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- Test T;
- cout << T.GetA() << endl;
- return ;
- }
静态成员变量 被类的所有对象共享,包括派生类对象;
- #include <iostream>
- using namespace std;
- class Base{
- public:
- static int a; // 静态成员变量
- };
- // int Test::a;如果这样定义不赋予初值,则初值为零
- int Base::a;
- class Derived : public Base{
- };
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- Base B;
- Derived D;
- B.a++;
- cout << B.a << endl; //
- D.a++;
- cout << D.a << endl; //
- return ;
- }
静态成员变量可以作为普通成员函数的默认形参,而普通成员变量则不可以;
- class Test{
- public:
- static int a; //静态成员变量
- int b;
- void fun_1(int i = a); //正确
- //void fun_2(int i = b); //报错
- };
静态成员变量的类型 可以是所属类的类型,而普通成员变量则不可以。普通成员变量只能声明为 所属类类型的 指针或引用;
- class Test{
- public:
- static Test a; //正确
- Test b; //报错
- Test *pTest; //正确
- Test &m_Test; //正确
- static Test *pStaticObject; //正确
- };
静态成员变量在const函数中可以修改,而普通的成员变量是万万不能修改的;
- /*
- const修饰的是当前this指针所指向的对象是const,但是静态成员变量不属于任何类的对象,它被类的所有对象修改,所以this指针不修饰静态的成员变量,所以可以更改。
- */
- class Test{
- public:
- static int a;
- int b;
- public:
- Test():b(){}
- void test() const
- {
- a++;
- //b++; // err // const指的是不能修改当前调用该函数对象的成员变量
- }
- };
- int Test::a;
2)静态成员函数
特征:1、静态成员函数 属于 整个类所有;
2、所有对象共享类的静态成员函数;
2、可以通过 类名 直接访问公有的静态成员函数;
3、可以通过 对象名 访问公有的静态成员函数;
4、静态成员函数 只能 访问静态成员,不能访问 非静态成员;
5、静态成员函数没有this指针,也就是说静态成员函数不能使用修饰符(也就是函数后面的const关键字);
原因:处理静态成员变量;
使用方法:直接用 static 修饰 普通成员函数(类内声明时),不需要 static 修饰(类外定义时);
总结: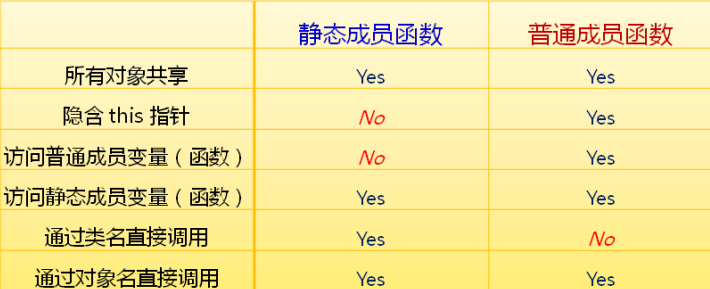
案例分析:
- /**
- * 统计某班选修课考试的平均成绩
- */
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
- class Student
- {
- private:
- string name; // 姓名
- string gender; // 性别
- float score; // 分数
- string subject; // 课程
- static float chinese_scores; // 语文分数
- static float math_scores; // 数学分数
- public:
- static int total_counts; // 总人数
- static int chinese_counts; // 语文课人数
- static int math_counts; // 数学课人数
- public:
- Student(string name, string gender, float score, string subject);
- ~Student();
- static float aveScores(string subject);
- void printStudentInfo();
- void printAveScores();
- };
- int Student::total_counts = ;
- float Student::chinese_scores = ;
- int Student::chinese_counts = ;
- float Student::math_scores = ;
- int Student::math_counts = ;
- Student::Student(string name, string gender, float score, string subject)
- {
- this->name = name;
- this->gender = gender;
- this->score = score;
- this->subject = subject;
- if(subject == "chinese" || subject == "语文")
- {
- chinese_scores += score;
- chinese_counts++;
- }
- else if(subject == "math" || subject == "数学")
- {
- math_scores += score;
- math_counts++;
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "this is no the subect:" << subject << endl;
- }
- total_counts++;
- }
- Student::~Student()
- {
- total_counts--;
- if(subject == "chinese" || subject == "语文")
- {
- chinese_counts--;
- }
- if(subject == "math" || subject == "数学")
- {
- math_counts--;
- }
- }
- float Student::aveScores(string subject)
- {
- float ave_score = ;
- if(chinese_counts > && subject == "chinese" || subject == "语文")
- {
- ave_score = (chinese_scores / chinese_counts);
- //cout << subject << "\t" << chinese_counts << "\t" << chinese_scores << endl;
- }
- else if(math_counts > && subject == "math" || subject == "数学")
- {
- ave_score = (math_scores / math_counts);
- //cout << subject << "\t" <<math_counts << "\t" << math_scores << endl;
- }
- return ave_score;
- }
- void Student::printStudentInfo()
- {
- cout << name << "\t" << gender << "\t" << score << "\t" << subject << endl;
- }
- void Student::printAveScores()
- {
- cout <<subject << " average score: " << aveScores(subject) << endl;
- }
- void function()
- {
- const int SIZE = ;
- Student stu[SIZE] =
- {
- Student("", "male", , "语文"),
- Student("", "male", , "数学"),
- Student("", "male", , "数学"),
- Student("", "male", , "语文"),
- Student("", "male", , "语文"),
- };
- for(int i = ; i < SIZE; i++)
- {
- stu[i].printStudentInfo();
- }
- stu[].printAveScores();
- stu[].printAveScores();
- cout << "语文" << " average score: " << Student::aveScores("语文") << endl;
- cout << "数学" << " average score: " << Student::aveScores("数学") << endl;
- cout << "总人数: " << Student::total_counts << endl;
- }
- int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
- {
- function();
- cout << "语文课人数: " << Student::chinese_counts << endl;
- cout << "数学课人数: " << Student::math_counts << endl;
- cout << "总人数: " << Student::total_counts << endl;
- return ;
- }
静态成员的案例1
- /**
- * 案例:有一场篮球赛,红队与蓝队各有5名队员,统计各个球队的得分情况(总分、平均分),并将获胜球队的球员信息输出
- */
- #include <iostream>
- #include <string>
- using namespace std;
- class Player
- {
- public:
- int number; // 编号
- string gender; // 性别
- int age; // 年龄
- float score; // 个人分数
- public:
- Player(int number = , int age = , float score = , string gender = "male")
- {
- this->number = number;
- this->age = age;
- this->score = score;
- this->gender = gender;
- }
- };
- class Team
- {
- private:
- string name; // 球队名称
- int sum; // 球队总分
- //static int COUNT; // 球队人数
- static const int COUNT = ; // 球队人数
- Player player[COUNT]; // 球队队员信息
- public:
- Team(string name)
- {
- this->name = name;
- for(int i = ; i < Team::COUNT; i++)
- {
- player[i] = Player( + i, + i, );
- }
- }
- string getName()
- {
- return name;
- }
- static int playersCount()
- {
- return COUNT;
- }
- int totalScore()
- {
- sum = ;
- for(int i = ; i < Team::COUNT; i++)
- {
- sum += player[i].score;
- }
- return sum;
- }
- float aveScore()
- {
- if(sum == )
- {
- totalScore();
- }
- return (sum/Team::COUNT);
- }
- bool setPlayer(int index, int num, int age, float score, bool isMale = true)
- {
- bool ret = true;
- if(Team::COUNT && index >= )
- {
- player[index].number = num;
- player[index].age = age;
- player[index].score = score;
- isMale == true ? player[index].gender = "male" : player[index].gender = "female";
- }
- else
- {
- cout << "the index of array is out of range, the max index should less than " << Team::COUNT << endl;
- ret = false;
- }
- return ret;
- }
- bool PK(Team &team)
- {
- int ret = this->sum > team.sum;
- if(ret)
- {
- cout << this->name + " 获胜" << endl;
- }
- else
- {
- cout << team.name + " 获胜" << endl;
- }
- return ret;
- }
- void print()
- {
- cout << "Team Name:" << name << endl;
- for(int i = ; i < Team::COUNT; i++)
- {
- cout << player[i].number << "\t" << player[i].gender << "\t" << player[i].age << "\t" << player[i].score << endl;
- }
- cout << name << " get total score:" << totalScore() << endl;
- cout << name << " get average score:" << aveScore() << endl;
- }
- };
- //int Team::COUNT = 5; // 初始化每支球队共有5名球员
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- Team t1("Red Team");
- t1.setPlayer(, , , );
- t1.setPlayer(, , , );
- t1.setPlayer(, , , );
- t1.setPlayer(, , , , false);
- t1.setPlayer(, , , );
- // t1.print();
- // cout << t1.getName() << " get total score:" << t1.totalScore() << endl;
- // cout << t1.getName() << " get average score:" << t1.aveScore() << endl;
- cout << endl;
- Team t2("Blue Team");
- t2.setPlayer(, , , );
- t2.setPlayer(, , , );
- t2.setPlayer(, , , );
- t2.setPlayer(, , , );
- t2.setPlayer(, , , );
- // t2.print();
- // cout << t2.getName() << " get total score:" << t2.totalScore() << endl;
- // cout << t2.getName() << " get average score:" << t2.aveScore() << endl;
- if( t1.PK(t2) )
- {
- t1.print();
- }
- else
- {
- t2.print();
- }
- return ;
- }
静态成员的案例2
c++中的 static 关键字的更多相关文章
- (转)Java中的static关键字解析
转载: http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3799052.html 一.static关键字的用途 在<Java编程思想>P86页有这样一段话: &q ...
- 关于Java中的static关键字
Java中的 static 关键字,确实是一个关键的字(key word),今天就来总结一下它的用法,说说为什么关键. Java中的 static 关键字主要是用来做内存管理的.理解了这句话才能够比较 ...
- Java中的static关键字解析
Java中的static关键字解析 static关键字是很多朋友在编写代码和阅读代码时碰到的比较难以理解的一个关键字,也是各大公司的面试官喜欢在面试时问到的知识点之一.下面就先讲述一下static关键 ...
- C++中的static关键字的总结
C++的static有两种用法:面向过程程序设计中的static和面向对象程序设计中的static.前者应用于普通变量和函数,不涉及类:后者主要说明static在类中的作用. 1.面向过程设计中的st ...
- (转)Java中的static关键字解析
转自http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3799052.html 一.static关键字的用途 在<Java编程思想>P86页有这样一段话: “sta ...
- (转)C++中的static关键字的总结
文章转自 http://www.cnblogs.com/BeyondAnyTime/archive/2012/06/08/2542315.html C++的static有两种用法:面向过程程序设计中的 ...
- Java中的static关键字解析 转载
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/dolphin0520/p/3799052.html Java中的static关键字解析 static关键字是很多朋友在编写代码和阅读代码时碰到 ...
- c++中关于static关键字的问题
C++的static关键字C++的static有两种用法:面向过程程序设计中的static和面向对象程序设计中的static.前者应用于普通变量和函数,不涉及类:后者主要说明static在类中的作用. ...
- C++中的static关键字(转)
原出处:http://blog.csdn.net/hackbuteer1/article/details/7487694 C++的static有两种用法:面向过程程序设计中的static和面向对象程序 ...
- Java中的static关键字解析(转自海子)__为什么main方法必须是static的,因为程序在执行main方法的时候没有创建任何对象,因此只有通过类名来访问。
Java中的static关键字解析 static关键字是很多朋友在编写代码和阅读代码时碰到的比较难以理解的一个关键字,也是各大公司的面试官喜欢在面试时问到的知识点之一.下面就先讲述一下static关键 ...
随机推荐
- 阿里云ECS单节点Kubernetes部署
参考资料: kubernetes官网英文版 kubernetes官网中文版 环境.工具 阿里云学生机ECS.Ubuntu.docker.kubectl1.15.4.kubelet1.15.4.kube ...
- Redis 持久化的两种方案
reids是一个key-value存储系统,为了保证效率,缓存在内存中,但是redis会周期性的把更新的数据写入磁盘或者把修改操作写入追加的记录文件,以保证数据的持久化. 所以:redis是一个支持持 ...
- 实现github的自动钩子
实现github的自动钩子 最近在学习go,也写了一些玩具放到自己的服务器中,但是感觉每次写完在本地交叉编译后上传到服务器略显麻烦,上传代码到服务器中编译也是略显麻烦,把编译文件加入到git管理中会导 ...
- 基于Netty和SpringBoot实现一个轻量级RPC框架-协议篇
基于Netty和SpringBoot实现一个轻量级RPC框架-协议篇 前提 最近对网络编程方面比较有兴趣,在微服务实践上也用到了相对主流的RPC框架如Spring Cloud Gateway底层也切换 ...
- MySQL数据库用户、角色、授权
权限包括 insert delete update select all privileges 登录MySQL > mysql -uroot -p Enter password ...
- Deferred shading rendering path翻译
Overview 概述 When using deferred shading, there is no limit on the number of lights that can affect a ...
- 加深对于 MVC、MVP、MVVM 的概念理解
目录 MVC 对 MVC 的误解及缘由 MVP MVVM MVC MVC - 维基百科,自由的百科全书 MVC 是软件工程的一种软件架构模式,它不是具体的技术,而是一种代码分层的理念,主要体现了职责分 ...
- acmPush模块示例demo
感谢论坛版主 马浩川 的分享. 模块介绍: 阿里移动推送(Alibaba Cloud Mobile Push)是基于大数据的移动智能推送服务,帮助App快速集成移动推送的功能,在实现高效.精确.实时 ...
- __call__ 方法
对象() 或 类()() 调用 __call__里面的方法 class Call: def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("Hello __c ...
- 【STACK】Several待填的坑
待学的习: https://www.cnblogs.com/xiao-ju-ruo-xjr/p/9149792.html 待写的题: loj#3184:「CEOI2018」斐波那契表示法 luoguP ...
