老齐python-基础2(字符串)
1、字符串
1.1索引和切片
索引:
- >>> lang = "study python"
- >>> lang[0]
- 's'
- >>> lang[1]
- 't'
>>> "study python"[0]
's'
字符串中对应的索引:
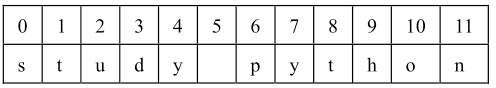
通过字符串找索引:
- >>> lang.index("p")
- 6
字符串切片:
- >>> lang = "study python"
- >>> lang[2:9]
- 'udy pyt'
- >>> lang = 'study python'
- >>> b = lang[1:] #得到从1号到末尾的字符,这时最后那个序号不用写
- >>> b
- 'tudy python'
- >>> c = lang[:] #得到所有的字符
- >>> c
- 'study python'
- >>> d = lang[:10] #得到从第一个到10号之前的字符
- >>> d
- 'study pyth'
- >>> e = lang[0:10]
- >>> e
- 'study pyth'
- >>> lang[1:11] #如果冒号后面有数字,所得到的切片不包含数字所对应的序号(前包括,后不包括)
- 'tudy pytho'
- >>> lang[1:]
- 'tudy python'
- >>> lang[1:12]
- 'tudy python'
- >>> lang[1:13]
- 'tudy python'
1.2字符串基本操作
len():求序列长度 #返回值为一个整数
+:连接2个序列
*:重复序列元素
in:判断元素是否存在于序列中
max():返回最大值
min():返回最小值
+:
- >>> str1 = 'python'
- >>> str2 = 'lisp'
- >>> str1 + str2 #字符串连接
- 'pythonlisp'
- >>> str1 + "&" + str2
- 'python&lisp'
in:
- >>> str1 = "python"
- >>> str2 = "lisp"
- >>> "p" in str1 #判断某个字符传是不是在另外一个字符串内,包含返回True 返回False
- True
- >>> "th" in str1
- True
- >>> "l" in str2
- True
- >>> "l" in str1
- False
max、min、ord、chr:
- >>> max(str1) #最值比较,按照ASCLL码
- 'y'
- >>> min(str1)
- 'h'
- >>> ord("y") #查看ASCLL码对应的顺序
- 121
- >>> ord("h")
- 104
- >>> chr(104) #通过ASCLL码顺对应顺序查找字符
- 'h'
字符串比较
- >>> 'a' > 'b'
- False
- >>> 'a' < 'b'
- True
- >>> "abc" > "aaa" #按照顺序比较字符串 1如果相等对比2,直到对比出大小
- True
- >>> "abc" < "a c"
- Fals
重复字符
- >>> a * 3
- 'hellohellohello'
- >>> print("-" * 30)
- ------------------------------
1.3字符串格式化输出
老用法不提倡:
- >>> "I like %s" % "python"
- 'I like python'
- >>> "I like %s" % "Pascal"
- 'I like Pascal'
新用法提倡:
- >>> "I like {0} and {1}".format("python","cangloshi")
- 'I like python and cangloshi'
- >>> "I like {0:10} and {1:>15}".format("python","canglaoshi")
- 'I like python and canglaoshi'
- #{0:10} 为python预留10个字符,{1:>15}右对齐预留15字符
- >>> "I like {0:^10} and {1:^15}".format("python","canglaoshi")
- 'I like python and canglaoshi '
- #居中显示
- >>> "I like {0:.2} and {1:^10.4}".format("python","canglaoshi")
- 'I like py and cang '
- #显示第一个元素的前连个字符,第二个元素占10个字符 居中显示前4个元素
- >>> "She is {0:d} years old and the breast is {1:f}cm".format(28,90.143598)
- 'She is 28 years old and the breast is 90.143598cm'
- #数字操作
- >>> "She is {0:4d} years old and the breast is {1:6.2f}cm".format(28,90.143598)
- 'She is 28 years old and the breast is 90.14cm'
- #变量1占用4字节默认右对齐,变量2占用6字节右对齐,保留小数2位
- >>> "She is {0:04d} years old and the breast is {1:06.2f}cm".format(28,90.143598)
- 'She is 0028 years old and the breast is 090.14cm'
- #位数不足用0补
- >>> "I like {lang} and {name}".format(lang="python",name='canglaoshi')
- 'I like python and canglaoshi'
- >>> data = {"name":"Canglaoshi","age":28}
- >>> "{name} is {age}".format(**data)
- 'Canglaoshi is 28'
- #字典用法
1.4常用字符串方法
- dir(str)
- #获取字符串所有方法
- help(str.isalpha)
- #多去方法帮助
1)判断是否全是字母
2)根据分隔符分割字符串
3)去掉字符串两头的空格
4)字符大小写转换
S.upper() #S中的字母转换为大写
S.lower() #S中的字母转换为小写
S.capitalize() #将首字母转换为大写
S.isupper() #判断S中的字母是否全是大写
S.islower() #判断S中的字母是否全是小写
S.istitle() #判断S是否是标题模式,即字符串中所有的单词拼写首字母为大写,且其它字母为小写
5)用join拼接字符串
6)替换字符串
te = te.replace('test','OK')
- >>> "python".isalpha() #判断是否全是字母
- True
- >>> "python2".isalpha()
- False
- >>> a = "I LOVE PYTHON" #按照空格分割,生成列表
- >>> a.split(" ")
- ['I', 'LOVE', 'PYTHON']
- >>> b = "www.itdiffer.com"
- >>> b.split(".")
- ['www', 'itdiffer', 'com']
- >>> b = " hello "
- >>> b.strip() #去掉两边的空格
- 'hello'
- >>> b #未改变字符串本身
- ' hello '
>>> b.lstrip() #去掉左边空格
'hello '
>>> b.rstrip() #去掉右边空格
' hello
- >>> a = "TAJZHANG"
- >>> a.istitle() #判断大写,返回布尔值
- False
- >>> a = "tAJZHANG"
- >>> a.istitle()
- False
- >>> a = "Taj,Zhang"
- >>> a.istitle()
- True
- >>> a = "This is a Book"
- >>> a.istitle()
- False
- >>> b = a.title()
- >>> b
- 'This Is A Book'
- >>> b.istitle()
- True
>>> a = "Tajzhang"
>>> a.isupper()
False
>>> a.upper().isupper() #全大写判断
True
>>> a.islower()
False
>>> a.lower().islower() #全小写判断
True
- >>> b = 'www.itdiffer.com'
- >>> c = b.split(".")
- >>> c
- ['www', 'itdiffer', 'com']
- >>> ".".join(c)
- 'www.itdiffer.com'
- >>> "*".join(c)
- 'www*itdiffer*com'
1.5字符编码
计算机中的编码:ASCLL、Unicode、UTF-8、gbk、gbk2312
python3中默认就是utf8不需要声明,python2中开头声明'# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-' 显示中文才不会报错
- >>> import sys
- >>> sys.getdefaultencoding() #查看目前的编码
- 'utf-8'
- >>> ord("Q") #ASCLL码互转
- 81
- >>> chr(81)
- 'Q'
pass 55页
老齐python-基础2(字符串)的更多相关文章
- Python基础数据类型-字符串(string)
Python基础数据类型-字符串(string) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 本篇博客使用的是Python3.6版本,以及以后分享的每一篇都是Python3.x版 ...
- Python基础(二) —— 字符串、列表、字典等常用操作
一.作用域 对于变量的作用域,执行声明并在内存中存在,该变量就可以在下面的代码中使用. 二.三元运算 result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2 如果条件为真:result = 值1如果条件为 ...
- python基础、字符串和if条件语句,while循环,跳出循环、结束循环
一:Python基础 1.文件后缀名: .py 2.Python2中读中文要在文件头写: -*-coding:utf8-*- 3.input用法 n为变量,代指某一变化的值 n = inpu ...
- Python基础__字符串拼接、格式化输出与复制
上一节介绍了序列的一些基本操作类型,这一节针对字符串的拼接.格式化输出以及复制的等做做详细介绍.一. 字符串的拼接 a = 'I', b = 'love', c = 'Python'. 我们的目的是: ...
- python基础类型—字符串
字符串str 用引号引起开的就是字符串(单引号,双引号,多引号) 1.字符串的索引与切片. 索引即下标,就是字符串组成的元素从第一个开始,初始索引为0以此类推. a = 'ABCDEFGHIJK' p ...
- Python基础二字符串和变量
了解一下Python中的字符串和变量,和Java,c还是有点区别的,别的不多说,上今天学习的代码 Python中没有自增自减这一项,在转义字符那一块,\n,\r\n都是表示回车,但是对于不同的操作系统 ...
- Python基础之字符串和编码
字符串和编码 字符串也是一种数据类型,但是字符串比较特殊的是还有个编码问题. 因为计算机自能处理数字,如果徐娅处理文本,就必须先把文本转换为数字才能处理,最早的计算机子设计时候采用8个比特(bit)作 ...
- Python高手之路【六】python基础之字符串格式化
Python的字符串格式化有两种方式: 百分号方式.format方式 百分号的方式相对来说比较老,而format方式则是比较先进的方式,企图替换古老的方式,目前两者并存.[PEP-3101] This ...
- Python开发【第一篇】Python基础之字符串格式化
字符串格式化 Python的字符串格式化有两种方式: 百分号方式.format方式 百分号的方式相对来说比较老,而format方式则是比较先进的方式,企图替换古老的方式,目前两者并存.[PEP-310 ...
随机推荐
- qt5.2.1在linux下去除最大化和最小化按钮
#include <QtGui/QGuiApplication> #include <QDebug> #include <QScreen> #include &qu ...
- Chunky Monkey
猴子吃香蕉可是掰成好几段来吃哦! 把一个数组arr按照指定的数组大小size分割成若干个数组块. 例如:chunk([1,2,3,4],2)=[[1,2],[3,4]]; chunk([1,2,3,4 ...
- vue 跨域
注意!只能在本地调试使用,上线后url会出错使用以下方法要先引入网络模块 先配置文件:config =>index.js以下部分改为:proxyTable: { '/apis': { // 测试 ...
- lambda表达式 <二>
概念了解: 1.什么是匿名委托(匿名方法的简单介绍.为什么要用匿名方法) 2.匿名方法的[拉姆达表达式]方法定义 3.匿名方法的调用(匿名方法的参数传递.使用过程中需要注意什么) 什么是匿名方法? 匿 ...
- 第6课:datetime模块、操作数据库、__name__、redis、mock接口
1. datetime模块 import datetime print(datetime.datetime.today()) # 当前时间 2018-01-23 17:22:35.739667 pr ...
- c# 验证码图片生成类
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Drawing; using System.Drawing.Drawing2D ...
- jQuery 滑动选项卡jQuery tabulous.js
A jQuery tabs module for todays web! 实例DEMO 运行一下 Documentation Tabulous.js can be used with any cont ...
- 通过摄像机视频设备或者流媒体服务器SDK获取到数据转换成RTMP流实现网页/手机微信播放
写这篇博客主要是为了给新入门的流媒体开发者解惑,现在看到各种开发者的需求:网页播放RTSP摄像机.微信播放RTSP摄像机.网页播放摄像机SDK输出的视频流.网页播放第三方流媒体平台输出的视频流.包括G ...
- KAFKA 0.11 RHEL6.5安装
KAFKA简介 KAFKA是一款分布式消息发布和订阅的系统. 官网:http://kafka.apache.org/ 1.下载KAFKA及JDK KAFKA下载地址: http://kafka.apa ...
- [Python] print中的左右对齐问题
一.数值类型(int.float) # %d.%f是占位符>>> a = 3.1415926>>> print("%d"%a) #%d只 ...
