Observer Pattern
Motivation
We can not talk about Object Oriented Programming without considering the state of the objects. After all object oriented programming is about objects and their interaction. The cases when certain objects need to be informed about the changes occured in other objects are frequent. To have a good design means to decouple as much as possible and to reduce the dependencies. The Observer Design Pattern can be used whenever a subject has to be observed by one or more observers.
Let's assume we have a stock system which provides data for several types of client. We want to have a client implemented as a web based application but in near future we need to add clients for mobile devices, Palm or Pocket PC, or to have a system to notify the users with sms alerts. Now it's simple to see what we need from the observer pattern: we need to separate the subject(stocks server) from it's observers(client applications) in such a way that adding new observer will be transparent for the server.
Intent
- Defines a one-to-many dependency between objects so that when one object changes state, all its dependents are notified and updated automatically.
Implementation
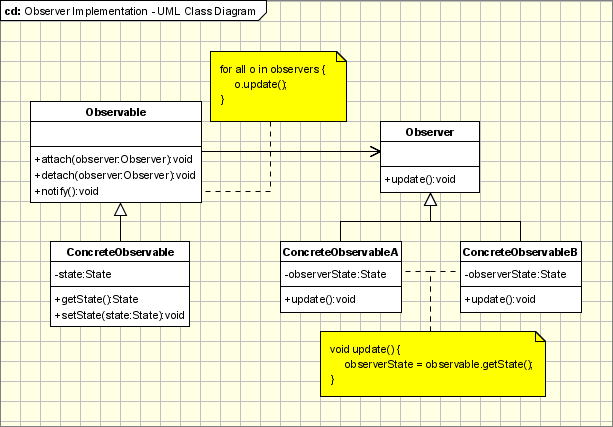
The participants classes in this pattern are:
- Observable - interface or abstract class defining the operations for attaching and de-attaching observers to the client. In the GOF book this class/interface is known as Subject.
- ConcreteObservable - concrete Observable class. It maintain the state of the object and when a change in the state occurs it notifies the attached Observers.
- Observer - interface or abstract class defining the operations to be used to notify this object.
- ConcreteObserverA, ConcreteObserver2 - concrete Observer implementations.
The flow is simple: the main framework instantiate the ConcreteObservable object. Then it instantiate and attaches the concrete observers to it using the methods defined in the Observable interface. Each time the state of the subject it's changing it notifies all the attached Observers using the methods defined in the Observer interface. When a new Observer is added to the application, all we need to do is to instantiate it in the main framework and to add attach it to the Observable object. The classes already created will remain unchanged.
Applicability & Examples
The observer pattern is used when:
- the change of a state in one object must be reflected in another object without keeping the objects tight coupled.
- the framework we are writing needs to be enhanced in future with new observers with minimal changes.
Some Classical Examples:
- Model View Controller Pattern - The observer pattern is used in the model view controller (MVC) architectural pattern. In MVC the this pattern is used to decouple the model from the view. View represents theObserver and the model is the Observable object.
- Event management - This is one of the domains where the Observer patterns is extensively used. Swing and .Net are extensively using the Observer pattern for implementing the events mechanism.
Example - News Agency
Lets' take the example of a news agency. A news agency gather news news and publish them to different subscribers. We need to create a framework for and agency to be able to inform immediately, when event occurs, its subscribers about the event. The subscribers can receive the news in different ways: Emails, SMS, ... The solution need to be extensively enough to support new types of subscribers(maybe new communication technologies will appear).
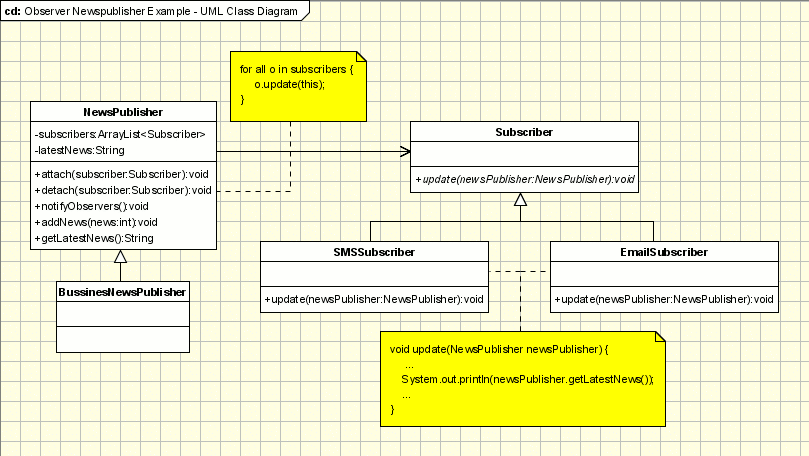
Obviously, the agency is represented by an Observable(Subject) class named NewsPublisher. This one is created as an abstract class because the agency want to create several types of Observable objects: in the beginning only for business news, but after some time sport and political new will be published. The concrete class is BusinessNewsPublisher.
The observer logic is implemented in NewsPublisher. It keeps a list of all it subscribers and it informs them about the latest news. The subscribers are represented by some observers (SMSSubscriber, EmailSubscriber). Both the observers mentioned above are inherited from the Subscriber. The subscriber is the abstract class which is known to the publisher. The publisher doesn't know about concrete observers, it knows only about their abstraction.
In the main class a publisher(Observable) is built and a few subscribers(Observers). The subscribers are subscribed to the publisher and they can be unsubscribed. In this architecture new types of subscribers can be easily added(instant messaging, ...) and new types of publishers(Weather News, Sport News, ...).
Specific Implementation Problems
Many subjects to Many observers
It's not a common situation but there are cases when a there are many observers that need to observe more than one subject. In this case the observer need to be notified not only about the change, but also which is the subject with the state changed. This can be realized very simple by adding to the subjects reference in the update notification method. The subject will pass a reference to itself(this) to the when notify the observer.
Who triggers the update?
The communication between the subject and its observers is done through the notify method declared in observer interface. But who it cat be triggered from either subject or observer object. Usually the notify method is triggered by the subject when it's state is changed. But sometimes when the updates are frequent the consecutive changes in the subject will determine many unnecessary refresh operations in the observer. In order to make this process more efficient the observer can be made responsible for starting the notify operation when it consider necessary.
Making sure Subject state is self-consistent before notification
The subject state should be consistent when the notify operation is triggered. If changes are made in the subject state after the observer is notified, it will will be refreshed with an old state. This seems hard to achieve but in practice this can be easily done when Subject subclass operations call inherited operations. In the following example, the observer is notified when the subject is in an inconsistent state:
class Observable{
|
This pitfall can be avoided using template methods in the abstract subject superclass for calling the notify operations. Then subject subclass will implement the operations(s) of the template:
class Observable{
|
The Operations defined in the subject base class which triggers notify operation should be documented.
Push and pull communication methods
There are 2 methods of passing the data from the subject to the observer when the state is being changed in the subject side:
- Push model - The subjects send detailed information about the change to the observer whether it uses it or not. Because the subject needs to send the detailed information to the observer this might be inefficient when a large amount of data needs to be sent and it is not used. Another aproach would be to send only the information required by the observer. In this case the subject should be able to distinguish between different types of observers and to know the required data of each of them, meaning that the subject layer is more coupled to observer layer.
- Pull model - The subject just notifies the observers when a change in his state appears and it's the responsibility of each observer to pull the required data from the subject. This can be inefficient because the communication is done in 2 steps and problems might appear in multithreading environments.
Specifying points of interests
The efficiency can be improved by specifying which are the events on which each observer is interested. This can be realized by adding a new class defining an aspect. When an observer is registering it will provide the aspects in which it is interested:
class Subject{
|
Encapsulating complex update semantics
When we have several subjects and observers the relations between them we'll become more complex. First of all are have a many to many relation, more difficult to manage directly. Second of all the relation between subjects and observers can contain some logic. Maybe we want to have an observer notified only when all the subjects will change their states. In this case we should introduce another object responsible (called ChangeManager) for the following actions:
- to maintain the many to many relations between the subjects and their observers.
- to encapsulate the logic of notify the observers.
- to receive the notifications from subjects and delegate them to the observers(based on the logic it encapsulate)
Basically the Change Manager is an observer because if gets notified of the changes of the subject and in the same time is an subject because it notify the observers. The ChangeManager is an implemenation of the Mediator pattern.
The Observer pattern is usually used in combination with other design patterns:
- Factory pattern - It's very likely to use the factory pattern to create the Observers so no changes will be required even in the main framework. The new observers can be added directly in the configuration files.
- Template Method - The observer pattern can be used in conjunction with the Template Method Pattern to make sure that Subject state is self-consistent before notification
- Mediator Pattern - The mediator pattern can be used when we have cases of complex cases of many subjects an many observers
Observer Pattern的更多相关文章
- Design Pattern: Observer Pattern
1. Brief 一直对Observer Pattern和Pub/Sub Pattern有所混淆,下面打算通过这两篇Blog来梳理这两种模式.若有纰漏请大家指正. 2. Use Case 首先我们来面 ...
- 深入浅出设计模式——观察者模式(Observer Pattern)
模式动机 建立一种对象与对象之间的依赖关系,一个对象发生改变时将自动通知其他对象,其他对象将相应做出反应.在此,发生改变的对象称为观察目标,而被通知的对象称为观察者,一个观察目标可以对应多个观察者,而 ...
- Learning JavaScript Design Patterns The Observer Pattern
The Observer Pattern The Observer is a design pattern where an object (known as a subject) maintains ...
- 设计模式 - 观察者模式(Observer Pattern) 详细说明
观察者模式(Observer Pattern) 详细说明 本文地址: http://blog.csdn.net/caroline_wendy/article/details/26583157 版权全部 ...
- 设计模式(二)The Observer Pattern 观察者模式
问题引入 生成一个公告板显示当时的天气状况,当天气状况发生改变的时候公告板能够实时的更新. 模式定义 定义对象之间的一对多的依赖.当一个对象改变状态时,它的全部依赖者都会自己主动收到通知并自己主动更新 ...
- [Design Pattern] Observer Pattern 简单案例
Observer Pattern,即观察者模式,当存在一对多关系,例如一个对象一有变动,就要自动通知被依赖的全部对象得场景,属于行为类的设计模式. 下面是一个观察者模式的简单案例. Observer ...
- Java设计模式模式观测(Observer Pattern)
Observer Pattern 设计模式通常用于.这是一个事件侦听器模型. 该模型有两个作用,一个是Subject, 有一个Observer.Subject 保存多个Observer参考,一旦一个特 ...
- [置顶] head first 设计模式之----Observer pattern
浅谈设计模式之----观察者模式 观察者模式也是我们日常程序编写中碰到比较多的一种设计模式.首先,所谓观察者模式定义就是指:在对象之间定义了一对多的依赖,这样一来,当一个对象的状态发生变化的 ...
- 乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 观察者模式(Observer Pattern)
原文:乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 观察者模式(Observer Pattern) [索引页][源码下载] 乐在其中设计模式(C#) - 观察者模式(Observer Pattern) 作者:weba ...
随机推荐
- 【风马一族_Android】Android 前端内容1
Android 前端内容 4.1 View 类概述 4.1.1 关于 View //类型说明 view(视图)指的是用户界面组件的基本构建基块.一个视图占据屏幕上的矩形区域,负责绘图和事件处理.视图是 ...
- corosync+pacemaker实现高可用(HA)集群
corosync+pacemaker实现高可用(HA)集群(一) 重要概念 在准备部署HA集群前,需要对其涉及的大量的概念有一个初步的了解,这样在实际部署配置时,才不至于不知所云 资源.服务与 ...
- Git错误non-fast-forward后的冲突解决(转载)
文章转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/chain2012/article/details/7476493 当要push代码到git时,出现提示: error:failed to pus ...
- Silverlight C#动态设置样式
1.从页面资源中获取样式并应用 btnTest.Style = (Style)this.Resources["BigButtonStyle"] 2.从项目中单独分开的资源字典文件( ...
- [转]WPF 依赖项属性
from:http://blog.csdn.net/datoumimi/article/details/8033682 ps:环境限制,发的东西一长就会被拦截,所以删了一部分 UI软件中经常会用到大量 ...
- poj 3237 Tree 树链剖分+线段树
Description You are given a tree with N nodes. The tree’s nodes are numbered 1 through N and its edg ...
- linux 获取cpu 个数
sysconf( )有unistd.h提供,要使用该函数需要#include<unistd.h>,其参数可以是_SC_NPROCESSORS_CONF,也可以是_SC_NPROCESSOR ...
- IE中出现 "Stack overflow at line" 错误的解决方法
在做网站时遇到一个问题,网站用的以前的程序,在没有改过什么程序的情况下,页面总是提示Stack overflow at line 0的错误,而以前的网站都正常没有出现过这种情况,在网上找了一下解决办法 ...
- vim使用手册
1. 关于Vim 1.1 Vim的几种模式 2. 启动Vim 3. 文档操作 4. 光标的移动 4.1 基本移动 4.2 翻屏 4.3 标记 5. 插入文本 5.1 基本插入 5.2 改写插入 6. ...
- git,repo学习
Repo:就是一组git命令的集合,repo init 下载一个分支. repo start 文件名 --all本地传建的另一个代码分支,用于备份作用. 比如:repo start zhao --al ...