【java多线程】队列系统之LinkedBlockingDeque源码
1、简介
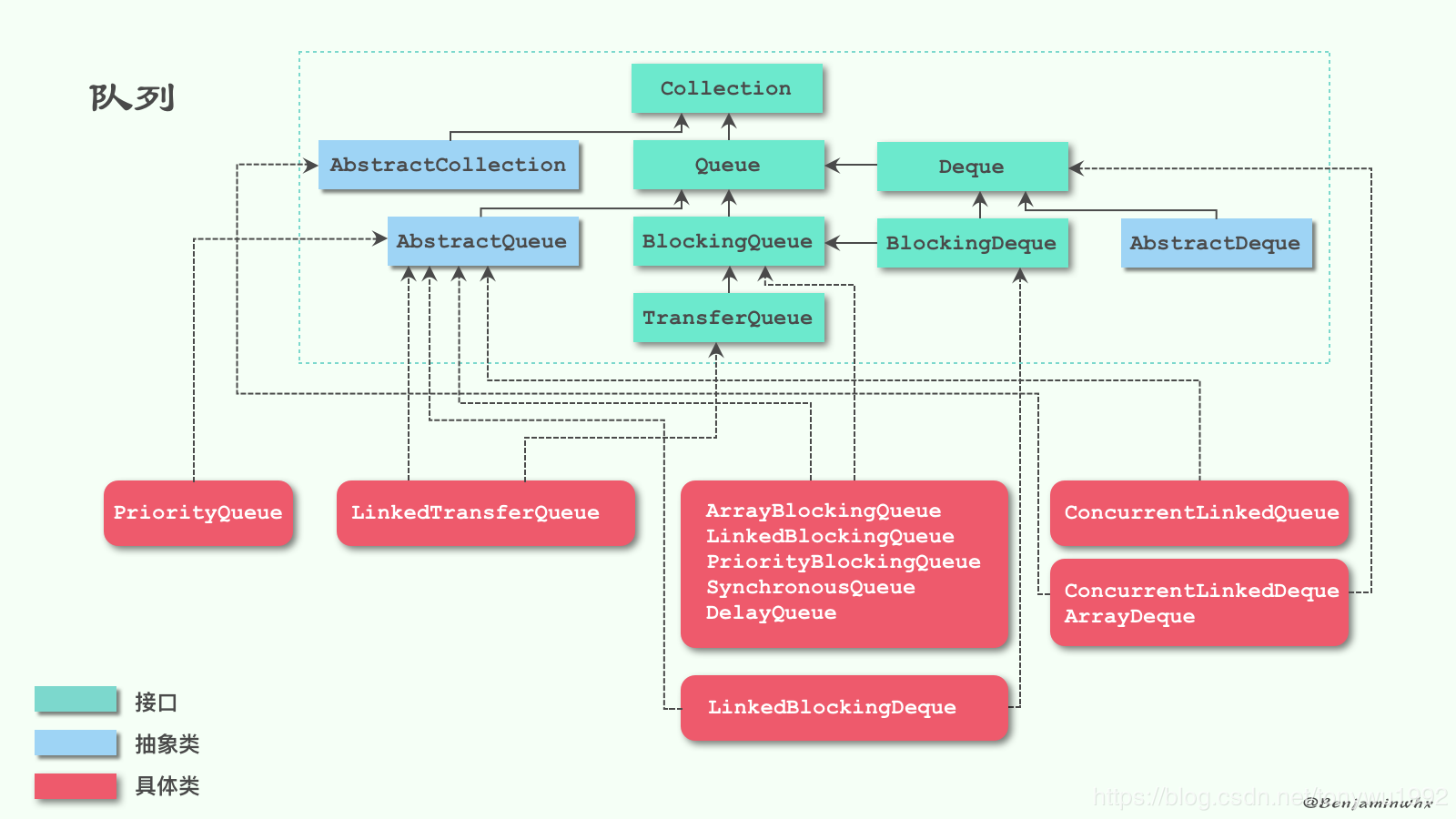
上一篇我们介绍了 LinkedBlockingDeque 的兄弟篇 LinkedBlockingQueue 。听名字也知道一个实现了 Queue 接口,一个实现了 Deque 接口,由于 Deque 接口又继承于 Queue ,所以 LinkedBlockingDeque 自然就有 LinkedBlockingQueue 的所有方法,并且还提供了双端队列的一些其他方法,不清除队列相关类的继承关系的童鞋,请移步看我之前的文章:说说队列Queue,下面的这张图就是该文章中的。
2、源码分析
2.1、属性
/**
* 节点类,维护了前一个元素和后一个元素,用来存储数据
*/
static final class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> prev;
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) {
item = x;
}
} /**
* 阻塞队列的第一个元素的节点
*/
transient Node<E> first; /**
* 阻塞队列的尾节点
*/
transient Node<E> last; /** 当前阻塞队列中的元素个数 */
private transient int count; /** 阻塞队列的大小,默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE */
private final int capacity; /** 所有访问元素时使用的锁 */
final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); /** 等待take的条件对象 */
private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition(); /** 等待put的条件对象 */
private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
由这些属性,我们可以和 LinkedBlockingQueue 进行对比。
首先是Node节点类,不同于 LinkedBlockingQueue 的单向链表,LinkedBlockingDeque 维护的是一个双向链表。
再来看count,这里是用int来进行修饰,而 LinkedBlockingQueue 确实用的AtomicInteger来修饰,这里这么做是因为 LinkedBlockingDeque 内部的每一个操作都共用一把锁,故能保证可见性。而 LinkedBlockingQueue 中维护了两把锁,在添加和移除元素的时候并不能保证双方能够看见count的修改,所以使用CAS来维护可见性。
2.2、构造函数
public LinkedBlockingDeque() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public LinkedBlockingDeque(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.capacity = capacity;
}
public LinkedBlockingDeque(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
for (E e : c) {
if (e == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!linkLast(new Node<E>(e)))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
构造函数几乎和 LinkedBlockingQueue 一样,不过少了一句 last = head = new Node<E>(null) 。因为这里不存在head节点了,而用first来代替。并且添加元素的方法也进行了重写来适应 Deque 的方法。
2.3、方法
LinkedBlockingQueue中有的方法该类中都会出现,无外乎多了队列的两端操作。这里为了方便,我会放在一起来进行说明。
2.3.1、入队方法
LinkedBlockingDeque提供了多种入队操作的实现来满足不同情况下的需求,入队操作有如下几种:
- add(E e)、addFirst(E e)、addLast(E e)
- offer(E e)、offerFirst(E e)、offerLast(E e)
- offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)、offerFirst(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)、offerLast(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
- put(E e)、putFirst(E e)、putLast(E e)
add相关的方法
public boolean add(E e) {
addLast(e);
return true;
}
public void addFirst(E e) {
if (!offerFirst(e))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
public void addLast(E e) {
if (!offerLast(e))
throw new IllegalStateException("Deque full");
}
add调用的其实是addLast方法,而addFirst和addLast都调用的offer的相关方法,这里直接看offer的方法。
offer相关的方法
public boolean offer(E e) {
return offerLast(e);
}
public boolean offerFirst(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return linkFirst(node);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean offerLast(E e) {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return linkLast(node);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
很明显,加锁以后调用linkFirst和linkLast这两个方法。
private boolean linkFirst(Node<E> node) {
if (count >= capacity)
return false;
Node<E> f = first;
node.next = f;
first = node;
// 插入第一个元素的时候才需要把last指向该元素,后面所有的操作只需要把f.prev指向node
if (last == null)
last = node;
else
f.prev = node;
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
private boolean linkLast(Node<E> node) {
if (count >= capacity)
return false;
Node<E> l = last;
node.prev = l;
last = node;
if (first == null)
first = node;
else
l.next = node;
++count;
notEmpty.signal();
return true;
}
下面给出两张图,都是队列为空的情况下,调用linkFirst和linkLast依次放入元素A和元素B的图:

offer的超时方法这里就不放出了,原理和 LinkedBlockingQueue 一样,利用了Condition的awaitNanos进行超时等待,并在外面用while循环控制等待时的中断问题。
put相关的方法
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
putLast(e);
}
public void putFirst(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 阻塞等待linkFirst成功
while (!linkFirst(node))
notFull.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void putLast(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 阻塞等待linkLast成功
while (!linkLast(node))
notFull.await();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
lock加锁后一直阻塞等待,直到元素插入到队列中。
2.3.2、出队方法
入队列的方法说完后,我们来说说出队列的方法。LinkedBlockingDeque提供了多种出队操作的实现来满足不同情况下的需求,如下:
- remove()、removeFirst()、removeLast()
- poll()、pollFirst()、pollLast()
- take()、takeFirst()、takeLast()
- poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)、pollFirst(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)、pollLast(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
remove相关的方法
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
public E removeFirst() {
E x = pollFirst();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E removeLast() {
E x = pollLast();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
remove方法调用了poll的相关方法。
poll相关的方法
public E poll() {
return pollFirst();
}
public E pollFirst() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkFirst();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E pollLast() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return unlinkLast();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
poll方法用lock加锁后分别调用了unlinkFirst和unlinkLast方法
private E unlinkFirst() {
Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
return null;
Node<E> n = f.next;
E item = f.item;
f.item = null;
f.next = f; // help GC
// first指向下一个节点
first = n;
if (n == null)
last = null;
else
n.prev = null;
--count;
notFull.signal();
return item;
}
private E unlinkLast() {
Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
return null;
Node<E> p = l.prev;
E item = l.item;
l.item = null;
l.prev = l; // help GC
// last指向下一个节点
last = p;
if (p == null)
first = null;
else
p.next = null;
--count;
notFull.signal();
return item;
}
poll的超时方法也是利用了Condition的awaitNanos来做超时等待。这里就不做过多说明了。
take相关的方法
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
return takeFirst();
}
public E takeFirst() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkFirst()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E takeLast() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
E x;
while ( (x = unlinkLast()) == null)
notEmpty.await();
return x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
还是一个套路,lock加锁,while循环重试移除,await阻塞等待。
2.3.3、获取元素方法
获取元素的方法有element和peek两种方法。
public E element() {
return getFirst();
}
public E peek() {
return peekFirst();
}
public E getFirst() {
E x = peekFirst();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E getLast() {
E x = peekLast();
if (x == null) throw new NoSuchElementException();
return x;
}
public E peekFirst() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (first == null) ? null : first.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E peekLast() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
return (last == null) ? null : last.item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
获取元素前加锁,防止并发问题导致数据不一致。利用first和last节点直接可以获得元素。
2.3.4、删除元素方法
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return removeFirstOccurrence(o);
}
public boolean removeFirstOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 从first向后开始遍历比较,找到元素后调用unlink移除
for (Node<E> p = first; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean removeLastOccurrence(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 从last向前开始遍历比较,找到元素后调用unlink移除
for (Node<E> p = last; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
void unlink(Node<E> x) {
Node<E> p = x.prev;
Node<E> n = x.next;
if (p == null) {
unlinkFirst();
} else if (n == null) {
unlinkLast();
} else {
p.next = n;
n.prev = p;
x.item = null;
// Don't mess with x's links. They may still be in use by
// an iterator.
--count;
notFull.signal();
}
}
删除元素是从头/尾向两边进行遍历比较,故时间复杂度为O(n),最后调用unlink把要移除元素的prev和next进行关联,把要移除的元素从链中脱离,等待下次GC回收。
3、总结
LinkedBlockingDeque和LinkedBlockingQueue的相同点在于:
- 基于链表
- 容量可选,不设置的话,就是Int的最大值
和LinkedBlockingQueue的不同点在于:
- 双端链表和单链表
- 不存在头节点
- 一把锁+两个条件
【java多线程】队列系统之LinkedBlockingDeque源码的更多相关文章
- Java并发包源码学习系列:阻塞队列实现之LinkedBlockingDeque源码解析
目录 LinkedBlockingDeque概述 类图结构及重要字段 linkFirst linkLast unlinkFirst unlinkLast unlink 总结 参考阅读 系列传送门: J ...
- 【java多线程】队列系统之LinkedBlockingQueue源码
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/tonywu1992/article/details/83419448 http://benjaminwhx.com/archives/ 1.简介 上 ...
- 【java多线程】队列系统之ArrayBlockingQueue源码
1.简介 ArrayBlockingQueue,顾名思义:基于数组的阻塞队列.数组是要指定长度的,所以使用ArrayBlockingQueue时必须指定长度,也就是它是一个有界队列. 它实现了Bloc ...
- lesson2:java阻塞队列的demo及源码分析
本文向大家展示了java阻塞队列的使用场景.源码分析及特定场景下的使用方式.java的阻塞队列是jdk1.5之后在并发包中提供的一组队列,主要的使用场景是在需要使用生产者消费者模式时,用户不必再通过多 ...
- Java多线程学习之线程池源码详解
0.使用线程池的必要性 在生产环境中,如果为每个任务分配一个线程,会造成许多问题: 线程生命周期的开销非常高.线程的创建和销毁都要付出代价.比如,线程的创建需要时间,延迟处理请求.如果请求的到达率非常 ...
- 【java多线程】队列系统之DelayQueue源码
一.延迟队列 延迟队列,底层依赖了优先级队列PriorityBlockingQueue 二.延迟队列案例 (1)延迟队列的任务 public class DelayTask implements De ...
- 【java多线程】队列系统之PriorityBlockingQueue源码
一.二叉堆 如题,二叉堆是一种基础数据结构 事实上支持的操作也是挺有限的(相对于其他数据结构而言),也就插入,查询,删除这一类 对了这篇文章中讲到的堆都是二叉堆,而不是斜堆,左偏树,斐波那契堆什么的 ...
- Java在线考试系统(含源码)
本文demo下载和视频教学观看地址:http://www.wisdomdd.cn/Wisdom/resource/articleDetail.htm?resourceId=1076 本实例介绍了在线考 ...
- 点菜网---Java开源生鲜电商平台-系统架构图(源码可下载)
点菜网---Java开源生鲜电商平台-系统架构图(源码可下载) 1.点菜网-生鲜电商平台的价值与定位. 生鲜电商平台是一家致力于打造全国餐饮行业智能化.便利化.平台化与透明化服务的创新型移动互联网平台 ...
随机推荐
- Learning-Python【1】:交互式环境与变量的使用
一.执行Python程序的两种方式 1. 交互式环境,打开cmd,输入python2或python3,显示提示符 “>>>”. 特点:输出代码立即执行 优点:调试程序方便 缺点:无法 ...
- Oracle三个配置文件详解
先说转自https://www.2cto.com/database/201305/211705.html ORACLE的三个配置文件介绍 在oracle安装目录$HOME/network/admin下 ...
- [python]python2与python3版本的区别
python2和python3的区别 区别: print函数 整数相除 Unicode 异常处理 xrange map函数 不支持has_key print函数: Python 2: print是语句 ...
- SpringBoot与数据访问
pom依赖: <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId> ...
- Police Stations CodeForces - 796D (bfs)
大意: 给定树, 有k个黑点, 初始满足条件:所有点到最近黑点距离不超过d, 求最多删除多少条边后, 使得原图仍满足条件. 所有黑点开始bfs, 贪心删边. #include <iostream ...
- 『TensorFlow』读书笔记_VGGNet
VGGNet网络介绍 VGG系列结构图, 『cs231n』卷积神经网络工程实践技巧_下 1,全部使用3*3的卷积核和2*2的池化核,通过不断加深网络结构来提升性能. 所有卷积层都是同样大小的filte ...
- element-ui <el-input> 注册blur事件
<template> <div class="demo"> <el-input placeholder="注册blur事件" v- ...
- String 的方法总结
1.charCodeAt方法返回一个整数,代表指定位置字符的Unicode编码. strObj.charCodeAt(index) var str = "ABC"; ...
- ELK安装使用教程
一.说明 ELK是当下流行的日志监控系统.ELK是Elasticsearch.Logstash.Kibana三个软件的统称. 在ELK日志监控系统中,Logstash负责读取和结构化各类日志+发送给E ...
- linux timing profile
double getUnixTime(void) { struct timespec tv; ) ; return (((double) tv.tv_sec) + (double) (tv.tv_ns ...
