Python之路:Python 基础(二)
一、作用域
对于变量的作用域,执行声明并在内存中存在,该变量就可以在下面的代码中使用。
if 1==1:
name = 'lenliu'
print name
下面的结论对吗?(对)
外层变量,可以被内层变量使用
内层变量,无法被外层变量使用
二、三元运算
result = 值1 if 条件 else 值2
result = 'lenliu' if 1 == 1 else 'amy'
print result
如果条件为真:result = 值1
如果条件为假:result = 值2
三、进制
- 二进制,01
- 八进制,01234567
- 十进制,0123456789
- 十六进制,0123456789ABCDE
Python基础
对于Python,一切事物都是对象,对象基于类创建
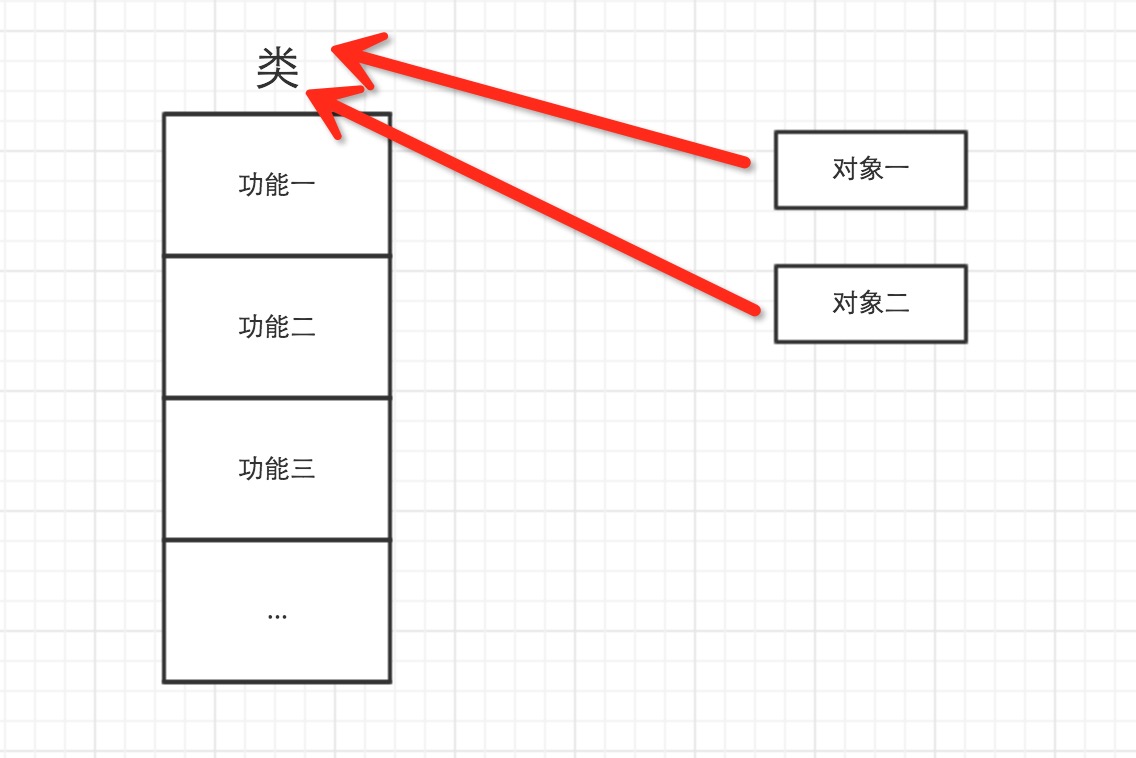
所以,以下这些值都是对象: "lenliu"、38、[ '上海', '深圳'],并且是根据不同的类生成的对象。

四、数字类型
1、整数:int()
如: 18、73、84
2、长整型:long()
可能如:2147483649、9223372036854775807
3、浮点型:float()
如:3.1415926、2.88
4、字符串:str()
如:lenliu、'amy'
五、列表:list()
如:[11,22,33]、[lenliu, 'amy']
每个元组都具备如下功能:
>>> help(list)
>>>dir(list)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__delslice__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getslice__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__setslice__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']






 删除整个列表的数据 list1.sort(reverse=False) 从小大到排序
删除整个列表的数据 list1.sort(reverse=False) 从小大到排序


六、元组:tuple (只能读取,不能被修改)
如:(11,22,33)、('wupeiqi', 'alex')
每个元组都具备如下功能:
>>>help(tuple)
>>>dir(tuple)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__getslice__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'count', 'index']



把元组拆成两部分,能后加入元素,逗号很关键 ( 删除元组 :del temp1 )

七、字典 (字典由索引key和它对应的值value组成)
如:{'name': 'wupeiqi', 'age': 18} 、{'host': '2.2.2.2', 'port': 80]}
ps:循环时,默认循环key
每个字典都具备如下功能:
>>>help(dict)
>>> dir(dict)
['__class__', '__cmp__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'clear', 'copy', 'fromkeys', 'get', 'has_key', 'items', 'iteritems', 'iterkeys', 'itervalues', 'keys', 'pop', 'popitem', 'setdefault', 'update', 'values', 'viewitems', 'viewkeys', 'viewvalues']


八、set集合
set是一个无序且不重复的元素集合
练习:寻找差异
# 数据库中原有
old_dict = {
"#1":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 },
"#2":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }
"#3":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }
} # cmdb 新汇报的数据
new_dict = {
"#1":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 800 },
"#3":{ 'hostname':c1, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }
"#4":{ 'hostname':c2, 'cpu_count': 2, 'mem_capicity': 80 }
} 需要删除、需要新建、需要更新
注意:无需考虑内部元素是否改变,只要原来存在,新汇报也存在,就是需要更新
old_set = set(old_dict.keys())
update_list = list(old_set.intersection(new_dict.keys())) new_list = []
del_list = [] for i in new_dict.keys():
if i not in update_list:
new_list.append(i) for i in old_dict.keys():
if i not in update_list:
del_list.append(i) print update_list,new_list,del_list
九、collection系列
1、计数器(counter)
Counter是对字典类型的补充,用于追踪值的出现次数。
ps:具备字典的所有功能 + 自己的功能


在上面的例子我们可以看出,Counter方法返回的是一个字典,它将字符串中出现的所有字符都进行了统计。
在这里再介绍一下update方法,这个update方法是将两次统计的结果相加,和字典的update略有不同。
2、有序字典(orderedDict )
orderdDict是对字典类型的补充,他记住了字典元素添加的顺序
3、默认字典(defaultdict)

需求:有如下值集合 [11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90...],将所有大于 66 的值保存至字典的第一个key中,将小于 66 的值保存至第二个key的值中。
即: {'k1': 大于66 , 'k2': 小于66}
# 字典解决方法
values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
my_dict = {}
for value in values:
if value>66:
if my_dict.has_key('k1'):
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k1'] = [value]
else:
if my_dict.has_key('k2'):
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'] = [value]
#默认字典解决方法
from collections import defaultdict values = [11, 22, 33,44,55,66,77,88,99,90]
my_dict = defaultdict(list)
for value in values:
if value>66:
my_dict['k1'].append(value)
else:
my_dict['k2'].append(value)
PS:defaultdict是对字典的类型的补充,他默认给字典的值设置了一个类型。
4、可命名元组(namedtuple)
根据nametuple可以创建一个包含tuple所有功能以及其他功能的类型。
import collections
Mytuple = collections.namedtuple('Mytuple',['x', 'y', 'z'])
>>> dir(Mytuple)
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__getslice__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__slots__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '_asdict', '_fields', '_make', '_replace', 'count', 'index', 'x', 'y', 'z']
5、双向队列(deque)
一个线程安全的双向队列
注:既然有双向队列,也有单项队列(先进先出 FIFO )
友情链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/4911365.html 武sir
Python之路:Python 基础(二)的更多相关文章
- 自学Python之路-Python基础+模块+面向对象+函数
自学Python之路-Python基础+模块+面向对象+函数 自学Python之路[第一回]:初识Python 1.1 自学Python1.1-简介 1.2 自学Python1.2-环境的 ...
- Python之路Python内置函数、zip()、max()、min()
Python之路Python内置函数.zip().max().min() 一.python内置函数 abs() 求绝对值 例子 print(abs(-2)) all() 把序列中每一个元素做布尔运算, ...
- Python之路Python作用域、匿名函数、函数式编程、map函数、filter函数、reduce函数
Python之路Python作用域.匿名函数.函数式编程.map函数.filter函数.reduce函数 一.作用域 return 可以返回任意值例子 def test1(): print(" ...
- Python之路Python全局变量与局部变量、函数多层嵌套、函数递归
Python之路Python全局变量与局部变量.函数多层嵌套.函数递归 一.局部变量与全局变量 1.在子程序中定义的变量称为局部变量,在程序的一开始定义的变量称为全局变量.全局变量作用域是整个程序,局 ...
- 自学Python之路-Python核心编程
自学Python之路-Python核心编程 自学Python之路[第六回]:Python模块 6.1 自学Python6.1-模块简介 6.2 自学Python6.2-类.模块.包 ...
- 自学Python之路-Python并发编程+数据库+前端
自学Python之路-Python并发编程+数据库+前端 自学Python之路[第一回]:1.11.2 1.3
- 自学Python之路-Python网络编程
自学Python之路-Python网络编程 自学Python之路[第一回]:1.11.2 1.3
- Python之路Python文件操作
Python之路Python文件操作 一.文件的操作 文件句柄 = open('文件路径+文件名', '模式') 例子 f = open("test.txt","r&qu ...
- Python之路 day1 基础1 变量 for while 用户输入
一. Python介绍 python的创始人为吉多·范罗苏姆(Guido van Rossum).1989年的圣诞节期间,吉多·范罗苏姆为了在阿姆斯特丹打发时间,决心开发一个新的脚本解释程序,作为AB ...
- python之路: 基础篇
)或>>> name = ) #按照占位符的顺序):] #下标识从0开始的 wulaoer >>> print name[:] # ...
随机推荐
- 解决:eclipse导入android时工程下没有R文件的问题,以及style.xml文件报错
解决:eclipse导入android时工程下没有R文件的问题,以及style.xml文件报错
- InnoDB引擎Myslq数据库数据恢复
首先祝愿看到这片文章的你永远不要有机会用到它... 本文指针对用InnoDB引擎的Mysql数据库的数据恢复,如果是其它引擎的Mysql或其它数据库请自行google... 如果有一天你手挫不小心删掉 ...
- 2.Freshman阶段学习内容的确定
我刷知乎.在知乎上答题的程序员,不是很牛逼就是更牛逼,说起各种系统.各种系统的各种版本.各种语言.数据库.算法.IT届的各种圣战都有板有眼.信手拈来.头头是道,不得不服.这导致了一些非常严重的问题:我 ...
- BZOJ 1189: [HNOI2007]紧急疏散evacuate( BFS + 二分答案 + 匈牙利 )
我们可以BFS出每个出口到每个人的最短距离, 然后二分答案, 假设当前答案为m, 把一个出口拆成m个表示m个时间, 点u到出口v的距离为d, 那么u->v的[d, m]所有点连边, 然后跑匈牙利 ...
- BZOJ 2662: [BeiJing wc2012]冻结(最短路)
这道题和 BZOJ 2763飞行路线 几乎一模一样..然后飞行路线我是1A,这道题WA了4次,我开始怀疑我的智商了.. ---------------------------------------- ...
- C#操作Office.word(一)
该文章主要是讲述如何使用VS2010创建word文档,因为在项目中我们可能需要点击一个按钮把数据库中的项目表单或图片显示到word文档中,因此该文章主要分析如何使用VS2010创建word文档并填写相 ...
- IE 弹出框处理经验
//各屏幕弹出窗样式 // 1366*768var style_1366x768 = "dialogWidth:950px;dialogHeight:650px;help:no;center ...
- [转]使用ping钥匙临时开启SSH:22端口,实现远程安全SSH登录管理就这么简单
原文链接:使用ping钥匙临时开启SSH:22端口,实现远程安全SSH登录管理就这么简单 这个留待后面玩一下,还是有安全隐患,非核心业务 临时用一下可以. 设置防火墙策略时,关于SSH:22访问权限, ...
- HTML5 实现图像模糊算法
做个广告,WEB/PHP/JQ/HTML5/MYSQL/QQ群6848027 项目中需要用到HTML5模糊图像,以前用GDI,GDI+中都有现成的组件来实现,HTML5中如何实现? createIma ...
- [LeetCode]题解(python):131-Palindrome Partitioning
题目来源: https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-partitioning/ 题意分析: 给定一个字符串s,将s拆成若干个子字符串,使得所有的子字符串都是回 ...


