Logistic回归的牛顿法及DFP、BFGS拟牛顿法求解
牛顿法
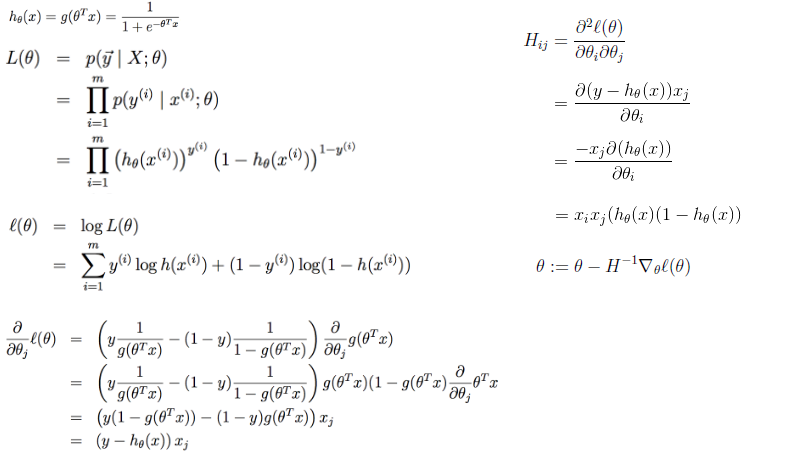
# coding:utf-8
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np def dataN(length):#生成数据
x = np.ones(shape = (length,3))
y = np.zeros(length)
for i in np.arange(0,length/100,0.02):
x[100*i][0]=1
x[100*i][1]=i
x[100*i][2]=i + 1 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2)
y[100*i]=1
x[100*i+1][0]=1
x[100*i+1][1]=i+0.01
x[100*i+1][2]=i+0.01 + np.random.uniform(0,1.2)
y[100*i+1]=0
return x,y def sigmoid(x): #simoid 函数
return 1.0/(1+np.exp(-x)) def DFP(x,y, iter):#DFP拟牛顿法
n = len(x[0])
theta=np.ones((n,1))
y=np.mat(y).T
Gk=np.eye(n,n)
grad_last = np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y)
cost=[]
for it in range(iter):
pk = -1 * Gk.dot(grad_last)
rate=alphA(x,y,theta,pk)
theta = theta + rate * pk
grad= np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y)
delta_k = rate * pk
y_k = (grad - grad_last)
Pk = delta_k.dot(delta_k.T) / (delta_k.T.dot(y_k))
Qk= Gk.dot(y_k).dot(y_k.T).dot(Gk) / (y_k.T.dot(Gk).dot(y_k)) * (-1)
Gk += Pk + Qk
grad_last = grad
cost.append(np.sum(grad_last))
return theta,cost def BFGS(x,y, iter):#BFGS拟牛顿法
n = len(x[0])
theta=np.ones((n,1))
y=np.mat(y).T
Bk=np.eye(n,n)
grad_last = np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y)
cost=[]
for it in range(iter):
pk = -1 * np.linalg.solve(Bk, grad_last)
rate=alphA(x,y,theta,pk)
theta = theta + rate * pk
grad= np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y)
delta_k = rate * pk
y_k = (grad - grad_last)
Pk = y_k.dot(y_k.T) / (y_k.T.dot(delta_k))
Qk= Bk.dot(delta_k).dot(delta_k.T).dot(Bk) / (delta_k.T.dot(Bk).dot(delta_k)) * (-1)
Bk += Pk + Qk
grad_last = grad
cost.append(np.sum(grad_last))
return theta,cost def alphA(x,y,theta,pk): #选取前20次迭代cost最小的alpha
c=float("inf")
t=theta
for k in range(1,200):
a=1.0/k**2
theta = t + a * pk
f= np.sum(np.dot(x.T,sigmoid(np.dot(x,theta))-y))
if abs(f)>c:
break
c=abs(f)
alpha=a
return alpha def newtonMethod(x,y, iter):#牛顿法
m = len(x)
n = len(x[0])
theta = np.zeros(n)
cost=[]
for it in range(iter):
gradientSum = np.zeros(n)
hessianMatSum = np.zeros(shape = (n,n))
for i in range(m):
hypothesis = sigmoid(np.dot(x[i], theta))
loss =hypothesis-y[i]
gradient = loss*x[i]
gradientSum = gradientSum+gradient
hessian=[b*x[i]*(1-hypothesis)*hypothesis for b in x[i]]
hessianMatSum = np.add(hessianMatSum,hessian)
hessianMatInv = np.mat(hessianMatSum).I
for k in range(n):
theta[k] -= np.dot(hessianMatInv[k], gradientSum)
cost.append(np.sum(gradientSum))
return theta,cost def tesT(theta, x, y):#准确率
length=len(x)
count=0
for i in xrange(length):
predict = sigmoid(x[i, :] * np.reshape(theta,(3,1)))[0] > 0.5
if predict == bool(y[i]):
count+= 1
accuracy = float(count)/length
return accuracy def showP(x,y,theta,cost,iter):#作图
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(range(iter),cost)
plt.figure(2)
color=['or','ob']
for i in xrange(length):
plt.plot(x[i, 1], x[i, 2],color[int(y[i])])
plt.plot([0,length/100],[-theta[0],-theta[0]-theta[1]*length/100]/theta[2])
plt.show()
length=200
iter=5
x,y=dataN(length) theta,cost=BFGS(x,y,iter)
print theta #[[-18.93768161][-16.52178427][ 16.95779981]]
print tesT(theta, np.mat(x), y) #0.935
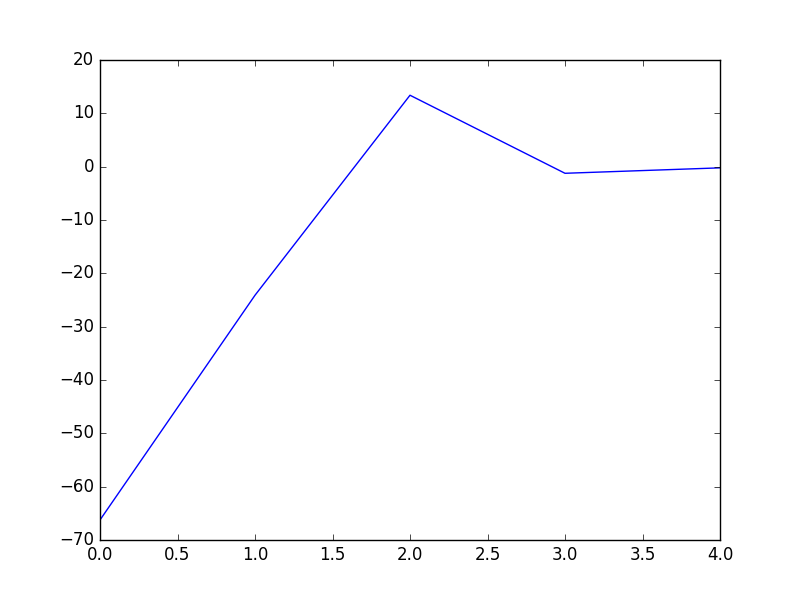
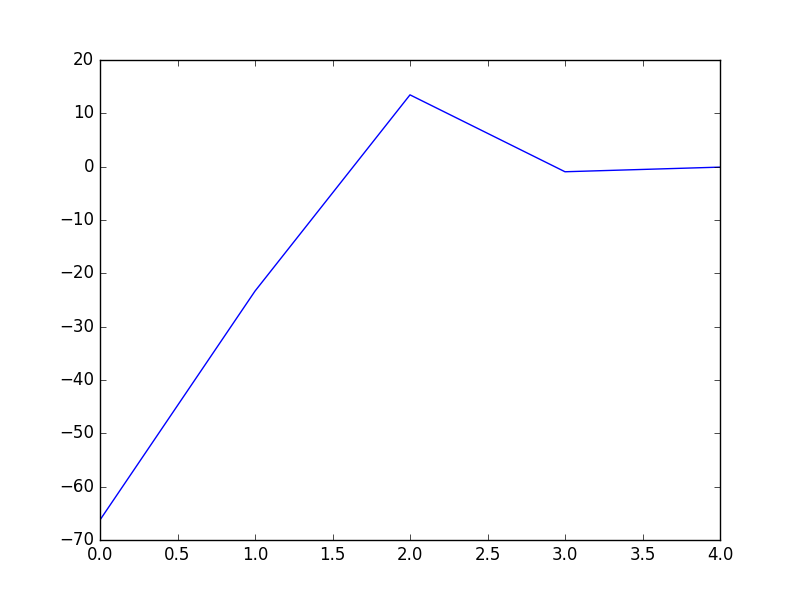
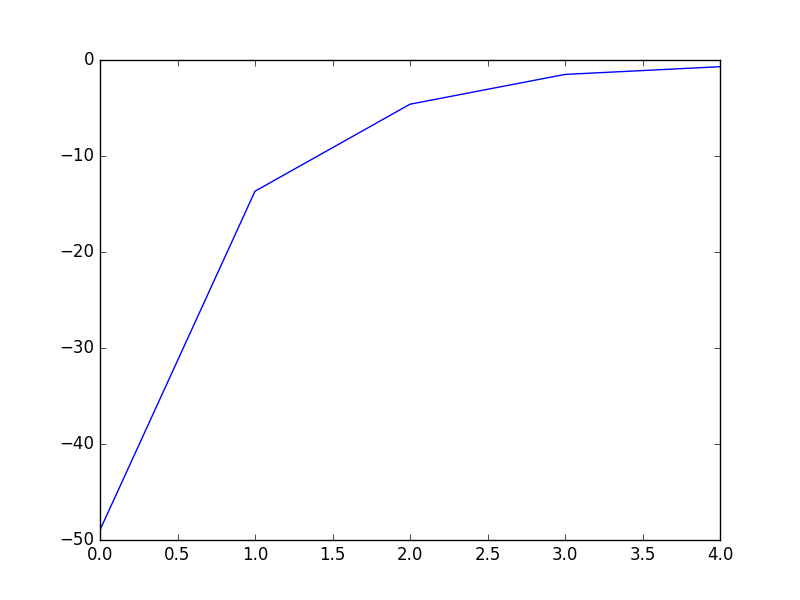
showP(x,y,theta.getA(),cost,iter) theta,cost=DFP(x,y,iter)
print theta #[[-18.51841028][-16.17880599][ 16.59649161]]
print tesT(theta, np.mat(x), y) #0.935
showP(x,y,theta.getA(),cost,iter) theta,cost=newtonMethod(x,y,iter)
print theta #[-14.49650536 -12.78692552 13.05843361]
print tesT(theta, np.mat(x), y) #0.935
showP(x,y,theta,cost,iter)

Logistic回归的牛顿法及DFP、BFGS拟牛顿法求解的更多相关文章
- 机器学习公开课笔记(3):Logistic回归
Logistic 回归 通常是二元分类器(也可以用于多元分类),例如以下的分类问题 Email: spam / not spam Tumor: Malignant / benign 假设 (Hypot ...
- 机器学习 —— 基础整理(五)线性回归;二项Logistic回归;Softmax回归及其梯度推导;广义线性模型
本文简单整理了以下内容: (一)线性回归 (二)二分类:二项Logistic回归 (三)多分类:Softmax回归 (四)广义线性模型 闲话:二项Logistic回归是我去年入门机器学习时学的第一个模 ...
- 机器学习——logistic回归,鸢尾花数据集预测,数据可视化
0.鸢尾花数据集 鸢尾花数据集作为入门经典数据集.Iris数据集是常用的分类实验数据集,由Fisher, 1936收集整理.Iris也称鸢尾花卉数据集,是一类多重变量分析的数据集.数据集包含150个数 ...
- 【机器学习速成宝典】模型篇03逻辑斯谛回归【Logistic回归】(Python版)
目录 一元线性回归.多元线性回归.Logistic回归.广义线性回归.非线性回归的关系 什么是极大似然估计 逻辑斯谛回归(Logistic回归) 多类分类Logistic回归 Python代码(skl ...
- 【导包】使用Sklearn构建Logistic回归分类器
官方英文文档地址:http://scikit-learn.org/dev/modules/generated/sklearn.linear_model.LogisticRegression.html# ...
- 对线性回归,logistic回归和一般回归的认识
原文:http://www.cnblogs.com/jerrylead/archive/2011/03/05/1971867.html#3281650 对线性回归,logistic回归和一般回归的认识 ...
- 线性回归,logistic回归和一般回归
1 摘要 本报告是在学习斯坦福大学机器学习课程前四节加上配套的讲义后的总结与认识.前四节主要讲述了回归问题,回归属于有监督学习中的一种方法.该方法的核心思想是从连续型统计数据中得到数学模型,然后将该数 ...
- 转载 Deep learning:六(regularized logistic回归练习)
前言: 在上一讲Deep learning:五(regularized线性回归练习)中已经介绍了regularization项在线性回归问题中的应用,这节主要是练习regularization项在lo ...
- 机器学习之线性回归---logistic回归---softmax回归
在本节中,我们介绍Softmax回归模型,该模型是logistic回归模型在多分类问题上的推广,在多分类问题中,类标签 可以取两个以上的值. Softmax回归模型对于诸如MNIST手写数字分类等问题 ...
随机推荐
- 等价表达式(noip2005)
3.等价表达式 [问题描述] 兵兵班的同学都喜欢数学这一科目,中秋聚会这天,数学课代表给大家出了个有关代数表达式的选择题.这个题目的题干中首先给出了一个代数表达式,然后列出了若干选项,每个选项也 ...
- JSP如何在servlet将一个数据模型对象传递给jsp页面
在servlet把对象放到request里,然后jsp里直接通过request取值如 在servlet:(简写了)public void doGet(request,response){UserInf ...
- Java custom annotations
Custom annotation definition is similar as Interface, just with @ in front. Annotation interface its ...
- 2013杭州现场赛B题-Rabbit Kingdom
杭州现场赛的题.BFS+DFS #include <iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> #define inf ...
- ++index 与 index++
摘自:C++标准程序库
- yii2.0-rules验证规则应用实例
Rules验证规则: required : 必须值验证属性||CRequiredValidator 的别名, 确保了特性不为空. [['字段名1','字段名2'],required] //字段 ...
- HDU 1074
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1074 每个任务有一个截止日期和完成时间,超过截止日期一天扣一分,问完成全部任务最少扣几分,并输出路径 最多15个 ...
- java学习第十天
第十二次课 目标 一维数组(创建访问) 一.概念与特点 1.概念 相同数据类型的有序集合[] 数组名: 容器的名字 元素: 下标变量,数组名[下标] 长度: length 下标: 位置.索引 ...
- NIO中Selector分析
NIO中,使用Selector.select()方法来侦听是否有数据可以读/写,服务端开始执行时,如果没有客户端,这里的语句将进行阻塞,等待下面三个情况出现,才会进行后续的方法之行,这里是重点 ...
- 【转】eclipse集成开发工具的插件安装
转发一:打开Eclipse下载地址(http://www.eclipse.org/downloads/),可以看到有好多版本的Eclipse可供下载,初学者往往是一头雾水,不知道下载哪一个版本. 各个 ...
