STL标准库-算法-常用算法
技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性
介绍11种STL标准库的算法,从这11种算法中总结一下算法的基本使用
1.accumulate() 累加
2.for_each() for一段区间 做你指定的行为
3.replace(), replace_if(), replace_copy() 替换函数
4.count(), count_if() 计数
5.find() 查找
6.sort() 排序
7.binary_search()查看元素是否在指定区间
下面的仿函数都没有继承自 binary_function<T,T,bool>, unary_function<T,bool>,但是在实际操作中,声明仿函数一定要继承自binary_function<T,T,bool>,unary_function<T,bool>
下一节内容会介绍为什么要继承自这两个类
一 accumulate(),累加,将指定区域内的value累加起来
源码及参数介绍
//默认累加算法,将传进的__first(begin()迭代器)位置,至__last(end()迭代器),与init求和
template<typename _InputIterator, typename _Tp>
inline _Tp
accumulate(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last, _Tp __init)
{
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_InputIteratorConcept<_InputIterator>)
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last); for (; __first != __last; ++__first)
__init = __init + *__first;
return __init;
} //自定义accumulate 按照指定的要求做”累加”操作
template<typename _InputIterator, typename _Tp, typename _BinaryOperation>
inline _Tp
accumulate(_InputIterator __first, _InputIterator __last, _Tp __init,
_BinaryOperation __binary_op)
{
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_InputIteratorConcept<_InputIterator>)
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last); for (; __first != __last; ++__first)
__init = __binary_op(__init, *__first);
return __init;
}
基本使用
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; namespace wzj000 {
int myfunc(int x, int y) {return x+*y;} struct myclass{
int operator()(int x, int y){return x+*y;}
}; void test_accumulate()
{
int init = ;
int num[] {, , }; cout<<"default accumulate: " << accumulate(num, num+, init)<< endl; //100 + 10 + 20 + 30 默认累加 cout << "using minus: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, minus<int>())<< endl; //100 - 10 - 20 - 30 将累加改为递减 cout << "using custom function: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myfunc)<< endl; // 100 + 2*10 + 2*20 + 2*30 自定义"累加"规则 func cout << "suing custom object: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myclass())<< endl; // 100 + 3*10 + 3*20 + 3*30自定义"累加"规则 仿函数
}
}
测试结果

二 for_each() for一段区间 做你指定的行为
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class Function>
Function for_each(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Function f)
{//参数1 起始点 参数2 终点, 参数3 想要执行的操作
for( ; first != last; ++first)
{
f(*first);
}
return f;
}
基本使用
namespace wzj001 {
void myfunc(int i)
{
cout << " - " << i;
}
struct myclass{
void operator()(int i)
{
cout << " ^ " << i;
}
};
void test_for_each()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myfunc);
cout << endl;
}
void test_for_each_classFunc()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << endl;
}
}
测试结果

三 replace() 替换函数
replace_if()
replace_copy()
源码及参数介绍
template <class ForwardIterator, class T>
void replace(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T & old_value, const T& new_value)
{//范围内所有等于old_value者都一new_value取代
for( ; first != last; ++first)
{
if(*first == old_value)
*first = new_value;
}
} template <class Inputerator, class Inputerator, class T>
void replace_if(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, Predicate pred, const T& new_value)
{//范围内所有满足pred()为true之元素都以new_value取代
for( ; first != last; ++first)
{
if(pred(*first))
*first = new_value;
}
} template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class T>
Outputerator replace_copy(ForwardIterator first, ForwardIterator last, Outputerator result, const T & old_value, const T& new_value)
{//范围内所有等于old_value者都以new_value放置新区域
//不符合者原值放入新区域
for( ; first != last; ++first, ++result)
{
*result = *first == old_value ? new_value : *first;
}
}
基本使用
namespace wzj002 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ? true : false;
}
};
void test_replace()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ,);
cout << "replace: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_replace_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass(), );
cout << "replace_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_replace_copy()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
vector<int> myNewVector;
myNewVector.resize();
replace_copy(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myNewVector.begin(), , );
cout << "replace_if_New: ";
for(auto i : myNewVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "replace_if_Old: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
测试结果

四 count() 计数
count_if()
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class T>
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
count(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& value)
{
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
for( ; first != last; ++first)
if(*first == value) //满足要求 值 == value 累计+1
++n;
return n;
} template <class Inputerator, class Outputerator, class Predicate>
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
count_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Predicate pred)
{
typename iterator_traits<Inputerator>::difference_type;
for( ; first != last; ++first)
if(pred(*first)) //满足指定要求 累计 +1
++n;
return n;
}
count()和count_if()是全局算法,适用于array,vector,list,forward_list, deque
map,set,unordered_set/map由于是关联式容器,所有有自己的count()和count_if()函数
基本使用
namespace wzj003 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
};
void test_count()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
cout << "count(): "<< count(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) <<endl;
}
void test_count_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , };
cout << "count_if(): " << count_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()) <<endl;
}
}
测试结果

五 find() 查找
find_if()
find()和find_if()是全局算法,适用于array,vector,list,forward_list, deque
map,set,unordered_set/map由于是关联式容器,所有有自己的find()和find_if()函数
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class T>
Inputerator find_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& value)
{
while(first != last && *first != value)
++first;
return first;
} template <class Inputerator, class Predicate>
Inputerator find_if(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, Predicate pred)
{
while(first != last && !pred(*first))
++first;
return first;
}
基本使用
namespace wzj004 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
};
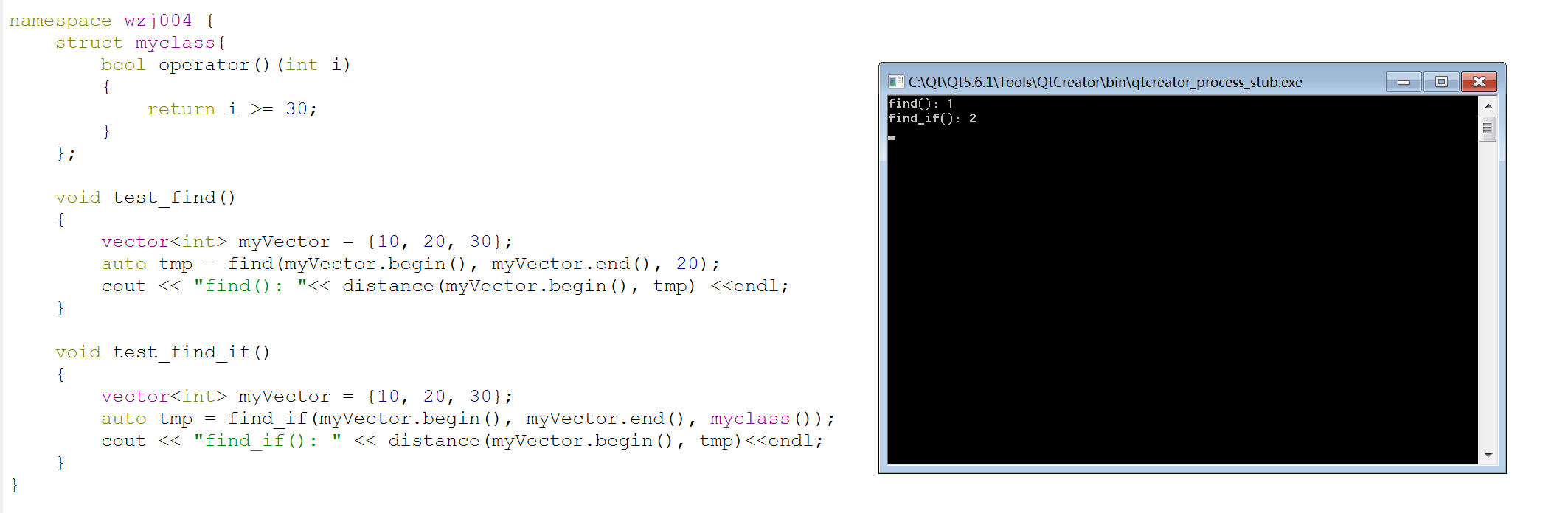
void test_find()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), );
cout << "find(): "<< distance(myVector.begin(), tmp) <<endl;
}
void test_find_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "find_if(): " << distance(myVector.begin(), tmp)<<endl;
}
}
测试结果
六 sort 排序
list和forward_list有成员sort()函数
set/map自动排序
array,vector,deque用全局sort()
namespace wzj005 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;// sort默认降序, 自定义为升序
}
};
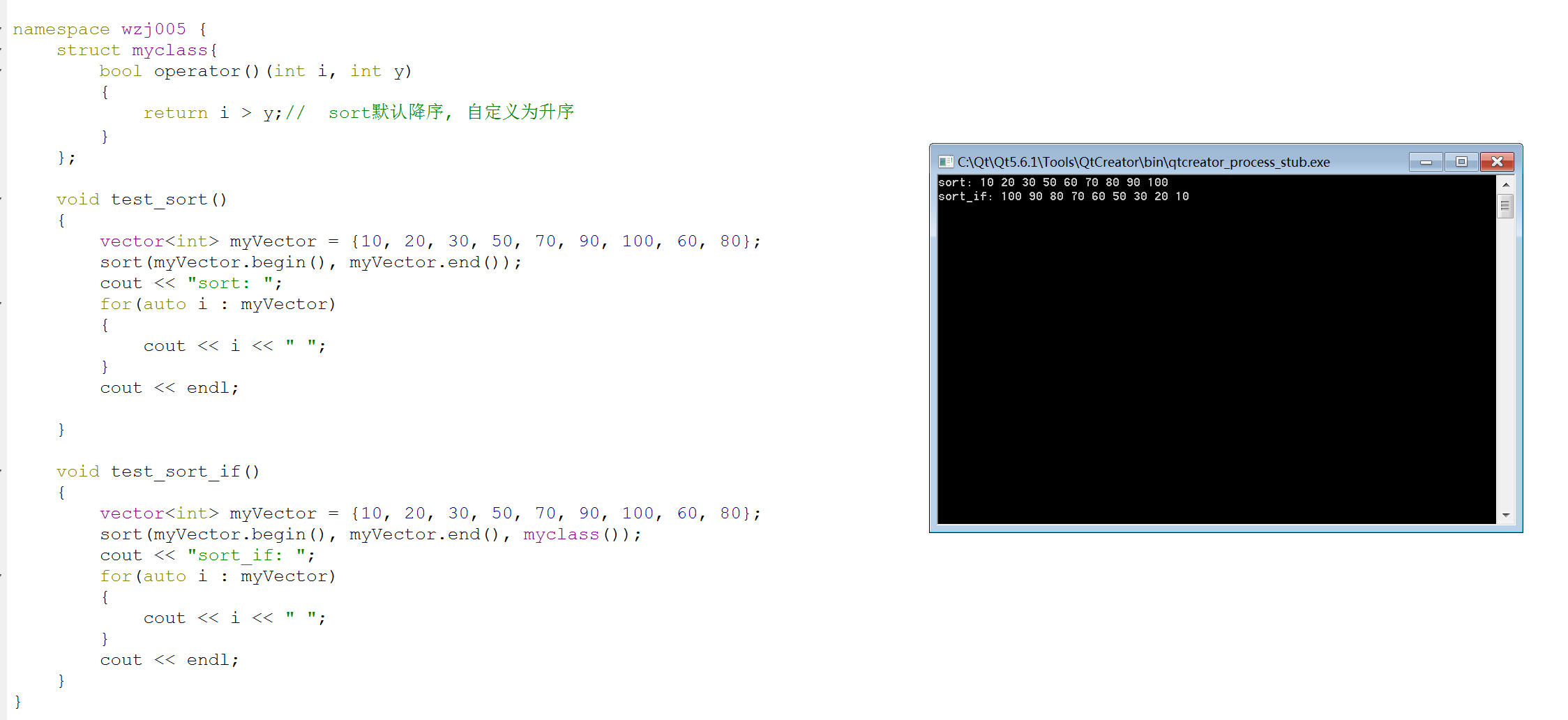
void test_sort()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end());
cout << "sort: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_sort_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "sort_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
测试结果
七 binary_search()查看元素是否在指定区间内
源码及参数介绍
template <class Inputerator, class T>
bool binary_search(Inputerator first, Inputerator last, const T& val)
{//返回元素是否在指定区间
first = std::lower_bound(first,last,val);
return (first != last && !(val < *first));
}
基本使用
namespace wzj006 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;
}
};
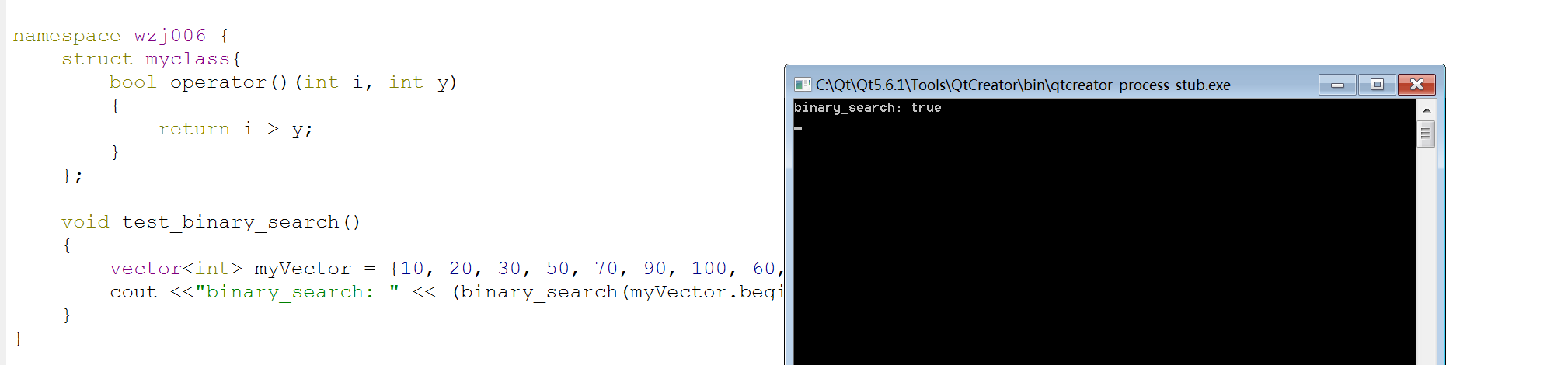
void test_binary_search()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
cout <<"binary_search: " << (binary_search(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) ? "true" : "false") << endl;
}
}
测试结果
全部测试代码
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; namespace wzj000 {
int myfunc(int x, int y) {return x+*y;} struct myclass{
int operator()(int x, int y){return x+*y;}
}; void test_accumulate()
{
int init = ;
int num[] {, , }; cout<<"default accumulate: " << accumulate(num, num+, init)<< endl; //100 + 10 + 20 + 30 默认累加 cout << "using minus: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, minus<int>())<< endl; //100 - 10 - 20 - 30 将累加改为递减 cout << "using custom function: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myfunc)<< endl; // 100 + 2*10 + 2*20 + 2*30 //自定义"累加"规则 func cout << "suing custom object: " << accumulate(num, num+, init, myclass())<< endl; // 100 + 3*10 + 3*20 + 3*30//自定义"累加"规则 仿函数
}
} namespace wzj001 {
void myfunc(int i)
{
cout << " - " << i;
} struct myclass{
void operator()(int i)
{
cout << " ^ " << i;
}
}; void test_for_each()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myfunc);
cout << endl;
} void test_for_each_classFunc()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
for_each(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << endl;
}
} namespace wzj002 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ? true : false;
}
}; void test_replace()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ,);
cout << "replace: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} void test_replace_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
replace_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass(), );
cout << "replace_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
} void test_replace_copy()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
vector<int> myNewVector;
myNewVector.resize();
replace_copy(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myNewVector.begin(), , );
cout << "replace_if_New: ";
for(auto i : myNewVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl; cout << "replace_if_Old: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
} namespace wzj003 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
}; void test_count()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
cout << "count(): "<< count(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) <<endl;
} void test_count_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , };
cout << "count_if(): " << count_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass()) <<endl;
}
} namespace wzj004 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i)
{
return i >= ;
}
}; void test_find()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), );
cout << "find(): "<< distance(myVector.begin(), tmp) <<endl;
} void test_find_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , };
auto tmp = find_if(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "find_if(): " << distance(myVector.begin(), tmp)<<endl;
}
} namespace wzj005 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;// sort默认降序, 自定义为升序
}
}; void test_sort()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end());
cout << "sort: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl; } void test_sort_if()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
sort(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), myclass());
cout << "sort_if: ";
for(auto i : myVector)
{
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
} namespace wzj006 {
struct myclass{
bool operator()(int i, int y)
{
return i > y;
}
}; void test_binary_search()
{
vector<int> myVector = {, , , , , , , , };
cout <<"binary_search: " << (binary_search(myVector.begin(), myVector.end(), ) ? "true" : "false") << endl;
}
} int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
wzj000::test_accumulate();
wzj001::test_for_each();
wzj001::test_for_each_classFunc();
wzj002::test_replace();
wzj002::test_replace_if();
wzj002::test_replace_copy();
wzj003::test_count();
wzj003::test_count_if();
wzj004::test_find();
wzj004::test_find_if();
wzj005::test_sort();
wzj005::test_sort_if();
wzj006::test_binary_search();
return ;
}
参考侯捷<<STL源码剖析>>
STL标准库-算法-常用算法的更多相关文章
- STL标准库-容器-vector
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. 向量容器vector是一个动态数组,内存连续,它是动态分配内存,且每次扩张的原来的二倍. 他的结构如下 一 定义 vector ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(一)sort
前言: 近来在学习STL标准库,做一份笔记并整理好,方便自己梳理知识.以后查找,也方便他人学习,两全其美,快哉快哉! 这里我会以中国大学慕课上北京大学郭炜老师的<程序设计与算法(一)C语言程序设 ...
- STL标准库-容器-set与multiset
技术在于交流.沟通,转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. set与multiset关联容器 结构如下 set是一种关联容器,key即value,value即key.它是自动排序,排序特点依据key se ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(二)二分查找
二.STL中的二分查找算法 1.binary_search 2.lower_bound 3.upper_bound 记得#include<algorithm>! 前言: 在这个笔记中,我把 ...
- stl标准库 iterator_traits
为什么标准库里要有traits? 我们先回忆一下,标准库提供的算法的一些特征: 参数一般包括iterator. 要根据iterator的种类,和iterator包装的元素的类型等信息,来决定使用最优化 ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(五)set
前言: 在这个笔记中,我把大多数代码都加了注释,我的一些想法和注解用蓝色字体标记了出来,重点和需要关注的地方用红色字体标记了出来,这一篇后面主要都是我的记录了,为了防止大片蓝色字体出现,后面就不改蓝色 ...
- STL标准库-容器-deque
技术在于交流.沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性. deque双向开口可进可出的容器 我们知道连续内存的容器不能随意扩充,因为这样容易扩充别人那去 deque却可以,它创造了内存 ...
- STL标准库-容器-set与map
STL标准库-容器-set与multiset C++的set https://www.cnblogs.com/LearningTheLoad/p/7456024.html STL标准库-容器-map和 ...
- C++STL标准库学习笔记(三)multiset
C++STL标准库学习笔记(三)multiset STL中的平衡二叉树数据结构 前言: 在这个笔记中,我把大多数代码都加了注释,我的一些想法和注解用蓝色字体标记了出来,重点和需要关注的地方用红色字体标 ...
随机推荐
- 【Coursera】Security Introduction -Eighth Week(2)
Review -Terminology(术语): Confidentiallity & Integrity 泄密 & 欺骗 Confidentiallity: Prevent unau ...
- nginx 80 端口默认被占用
/etc/nginx/sites-enabled,修改该目录下的default文件, 将默认端口号80改为其他端口号, /etc/nginx/nginx.conf 文件配置里的80端口就会生效
- gcc 编译出现 internal compiler error: Killed
系统没有交换分区, 编译过程中内存耗尽, 导致了编译中断 …解决方式也很简单, 就是增加一个交换分区: 创建分区文件, 大小 2G dd if=/dev/zero of=/swapfile ...
- python filter函数
number_list = range(-, ) less_than_zero = list(filter(lambda x: x < , number_list)) print(less_th ...
- shell模拟ctrl c停止
kill命令可以带信号号码选项,也可以不带. 如果没有信号号码,kill命令就会发出终止信号(15),这个信号可以被进程捕获,使得进程在退出之前可以清理并释放资源. 也可以用kill向进程发送特定的信 ...
- windows cmd 命令和 linux 命令
windows cmd 命令和 linux 命令 常用的内部命令有md.cd.rd.dir.path.copy.type.edit.ren.del.cls.ver.date.time.prompt.常 ...
- [ios]自定义UI
参考:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7b9d64af0101edqf.html 回忆一下,这么个场景. 我们在一个界面上,要排列多个相同的元素.你马上就可以想到: 1. ...
- org.apache.ibatis.binding.BindingException: Invalid bound statement (not found): 问题解决方法
在用maven配置mybatis环境时出现此BindingExceptiony异常,发现在classes文件下没有mapper配置文件,应该是maven项目没有扫描到mapper包下的xml文件,在p ...
- 12月15日 session:Ruby on Rails Security Guide//从第3节开始没有学习//关于find_by 和where的区别用法思考。
http://guides.rubyonrails.org/security.html#user-management 2.session笔记见13日的随笔. http://www.cnblogs.c ...
- Jersey 2.x 运行项目
现在我们已经有可以可以运行的项目了,让我们队这个项目进行一些测试吧. 你需要运行下面的一些命令行: mvn clean test 这个命令将会对项目进行编译后运行单元测试. 你应该会看到和下面类似的输 ...
