PCL采样一致性算法
在计算机视觉领域广泛的使用各种不同的采样一致性参数估计算法用于排除错误的样本,样本不同对应的应用不同,例如剔除错误的配准点对,分割出处在模型上的点集,PCL中以随机采样一致性算法(RANSAC)为核心,同时实现了五种类似与随机采样一致形算法的随机参数估计算法,例如随机采样一致性算法(RANSAC)最大似然一致性算法(MLESAC),最小中值方差一致性算法(LMEDS)等,所有估计参数算法都符合一致性原则。在PCL中设计的采样一致性算法的应用主要就是对点云进行分割,根据设定的不同的几个模型,估计对应的几何参数模型的参数,在一定容许的范围内分割出在模型上的点云。
(1)RANSAC随机采样一致性算法的介绍
RANSAC是“RANdom SAmple Consensus(随机抽样一致)”的缩写。它可以从一组包含“局外点”的观测数据集中,通过迭代方式估计数学模型的参数。它是一种不确定的算法——它有一定的概率得出一个合理的结果;为了提高概率必须提高迭代次数。
数 据分两种:有效数据(inliers)和无效数据(outliers)。偏差不大的数据称为有效数据,偏差大的数据是无效数据。如果有效数据占大多数,无 效数据只是少量时,我们可以通过最小二乘法或类似的方法来确定模型的参数和误差;如果无效数据很多(比如超过了50%的数据都是无效数据),最小二乘法就 失效了,我们需要新的算法
一个简单的例子是从一组观测数据中找出合适的2维直线。假设观测数据中包含局内点和局外点,其中局内点近似的被直线所通过,而局外点远离于直线。简单的最 小二乘法不能找到适应于局内点的直线,原因是最小二乘法尽量去适应包括局外点在内的所有点。相反,RANSAC能得出一个仅仅用局内点计算出模型,并且概 率还足够高。但是,RANSAC并不能保证结果一定正确,为了保证算法有足够高的合理概率,我们必须小心的选择算法的参数。

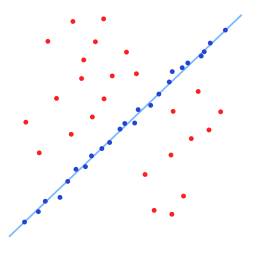
左图:包含很多局外点的数据集 右图:RANSAC找到的直线(局外点并不影响结果)
概述
RANSAC算法的输入是一组观测数据,一个可以解释或者适应于观测数据的参数化模型,一些可信的参数。
RANSAC通过反复选择数据中的一组随机子集来达成目标。被选取的子集被假设为局内点,并用下述方法进行验证:
1.有一个模型适应于假设的局内点,即所有的未知参数都能从假设的局内点计算得出。
2.用1中得到的模型去测试所有的其它数据,如果某个点适用于估计的模型,认为它也是局内点。
3.如果有足够多的点被归类为假设的局内点,那么估计的模型就足够合理。
4.然后,用所有假设的局内点去重新估计模型,因为它仅仅被初始的假设局内点估计过。
5.最后,通过估计局内点与模型的错误率来评估模型。
算法
伪码形式的算法如下所示:
输入:
data —— 一组观测数据
model —— 适应于数据的模型
n —— 适用于模型的最少数据个数
k —— 算法的迭代次数
t —— 用于决定数据是否适应于模型的阀值
d —— 判定模型是否适用于数据集的数据数目
输出:
best_model —— 跟数据最匹配的模型参数(如果没有找到好的模型,返回null)
best_consensus_set —— 估计出模型的数据点
best_error —— 跟数据相关的估计出的模型错误
iterations = 0
best_model = null
best_consensus_set = null
best_error = 无穷大
while ( iterations < k )
maybe_inliers = 从数据集中随机选择n个点
maybe_model = 适合于maybe_inliers的模型参数
consensus_set = maybe_inliers
for ( 每个数据集中不属于maybe_inliers的点 )
if ( 如果点适合于maybe_model,且错误小于t )
将点添加到consensus_set
if ( consensus_set中的元素数目大于d )
已经找到了好的模型,现在测试该模型到底有多好
better_model = 适合于consensus_set中所有点的模型参数
this_error = better_model究竟如何适合这些点的度量
if ( this_error < best_error )
我们发现了比以前好的模型,保存该模型直到更好的模型出现
best_model = better_model
best_consensus_set = consensus_set
best_error = this_error
增加迭代次数
返回 best_model, best_consensus_set, best_error
(2)最小中值法(LMedS)
LMedS的做法很简单,就是从样本中随机抽出N个样本子集,使用最大似然(通常是最小二乘)对每个子集计算模型参数和该模型的偏差,记录该模型参 数及子集中所有样本中偏差居中的那个样本的偏差(即Med偏差),最后选取N个样本子集中Med偏差最小的所对应的模型参数作为我们要估计的模型参数。
在PCL中sample_consensus模块支持的几何模型
- SACMODEL_PLANE - used to determine plane models. The four coefficients of the plane are its Hessian Normal form: [normal_x normal_y normal_z d]
- SACMODEL_LINE - used to determine line models. The six coefficients of the line are given by a point on the line and the direction of the line as: [point_on_line.x point_on_line.y point_on_line.z line_direction.x line_direction.y line_direction.z]
- SACMODEL_CIRCLE2D - used to determine 2D circles in a plane. The circle's three coefficients are given by its center and radius as: [center.x center.y radius]
- SACMODEL_CIRCLE3D - used to determine 3D circles in a plane. The circle's seven coefficients are given by its center, radius and normal as: [center.x, center.y, center.z, radius, normal.x, normal.y, normal.z]
- SACMODEL_SPHERE - used to determine sphere models. The four coefficients of the sphere are given by its 3D center and radius as: [center.x center.y center.z radius]
- SACMODEL_CYLINDER - used to determine cylinder models. The seven coefficients of the cylinder are given by a point on its axis, the axis direction, and a radius, as: [point_on_axis.x point_on_axis.y point_on_axis.z axis_direction.x axis_direction.y axis_direction.z radius]
- SACMODEL_CONE - used to determine cone models. The seven coefficients of the cone are given by a point of its apex, the axis direction and the opening angle, as: [apex.x, apex.y, apex.z, axis_direction.x, axis_direction.y, axis_direction.z, opening_angle]
- SACMODEL_TORUS - not implemented yet
- SACMODEL_PARALLEL_LINE - a model for determining a line parallel with a given axis, within a maximum specified angular deviation. The line coefficients are similar to SACMODEL_LINE.
- SACMODEL_PERPENDICULAR_PLANE - a model for determining a plane perpendicular to an user-specified axis, within a maximum specified angular deviation. The plane coefficients are similar to SACMODEL_PLANE.
- SACMODEL_PARALLEL_LINES - not implemented yet
- SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE - a model for determining plane models using an additional constraint: the surface normals at each inlier point has to be parallel to the surface normal of the output plane, within a maximum specified angular deviation. The plane coefficients are similar to SACMODEL_PLANE.
- SACMODEL_PARALLEL_PLANE - a model for determining a plane parallel to an user-specified axis, within a maximum specified angular deviation. SACMODEL_PLANE.
- SACMODEL_NORMAL_PARALLEL_PLANE defines a model for 3D plane segmentation using additional surface normal constraints. The plane must lie parallel to a user-specified axis. SACMODEL_NORMAL_PARALLEL_PLANE therefore is equivalent to SACMODEL_NORMAL_PLANE + SACMODEL_PARALLEL_PLANE. The plane coefficients are similar to SACMODEL_PLANE.
(2)PCL中Sample_consensus模块及类的介绍
PCL中Sample_consensus库实现了随机采样一致性及其泛化估计算法,例如平面,柱面,等各种常见的几何模型,用不同的估计算法和不同的几何模型自由的结合估算点云中隐含的具体几何模型的系数,实现对点云中所处的几何模型的分割,线,平面,柱面 ,和球面都可以在PCL 库中实现,平面模型经常被用到常见的室内平面的分割提取中, 比如墙,地板,桌面,其他模型常应用到根据几何结构检测识别和分割物体中,一共可以分为两类:一类是针对采样一致性及其泛化函数的实现,一类是几个不同模型的具体实现,例如:平面,直线,圆球等
pcl::SampleConsensusModel< PointT >是随机采样一致性估计算法中不同模型实现的基类,所有的采样一致性估计模型都继承与此类,定义了采样一致性模型的相关的一般接口,具体实现由子类完成,其继承关系:

类成员的介绍
Public Member Functions |
|
| SampleConsensusModel (const PointCloudConstPtr &cloud, const std::vector< int > &indices, bool random=false) | |
| SampleConsensusModel类的构造函数,cloud为输入点云对象的指针,indices为算法使用点云索引向量,如果设置random=true则用当前时间初始化随机化函数的种子否则使用12345作为种子 | |
| virtual void | getSamples (int &iterations, std::vector< int > &samples) |
| 获取一组随机采样点数据以点云中点的索引方式存储到samples,iterations为迭代次数 | |
| virtual bool | computeModelCoefficients (const std::vector< int > &samples, Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients)=0 |
| 纯虚函数检查给定的点云索引样本samples能否一个有效的模型, | |
| virtual void | optimizeModelCoefficients (const std::vector< int > &inliers, const Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients, Eigen::VectorXf &optimized_coefficients)=0 |
| 优化初始估计的模型参数,inliers设定的局内点,model_coefficients初始估计的模型的系数,optimized_coefficients优化后的模型系数 | |
| virtual void | getDistancesToModel (const Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients, std::vector< double > &distances)=0 |
| 计算点云中所有点到给定模型中model_coefficients的距离,存储到distances | |
| virtual void | selectWithinDistance (const Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients, const double threshold, std::vector< int > &inliers)=0 |
| 从点云中选择所有到给定模型model_coefficients的距离小于给定的阀值 threshold 的点为局内点,inliers存储最终输出的局内点 | |
| virtual int | countWithinDistance (const Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients, const double threshold)=0 |
| 统计点云到给定模型model_coefficients距离小于阀值的点的个数 | |
| virtual void | projectPoints (const std::vector< int > &inliers, const Eigen::VectorXf &model_coefficients, PointCloud &projected_points, bool copy_data_fields=true)=0 |
| 将局内点inliner投影到model_coefficients上创建一组新的点云projected_points, | |
| (太多了 太耽误时间了)************************** | |
(2)pcl::SampleConsensus< T > 是采样一致性算法的基类
Public Member Functions |
|
| SampleConsensus (const SampleConsensusModelPtr &model, double threshold, bool random=false) | |
| 其中model设置随机采样性算法使用的模型,threshold 阀值 | |
| void | setSampleConsensusModel (const SampleConsensusModelPtr &model) |
| Set the Sample Consensus model to use. | |
| void | setDistanceThreshold (double threshold) |
| Set the distance to model threshold. | |
| double | getDistanceThreshold () |
| Get the distance to model threshold, as set by the user. | |
| void | setMaxIterations (int max_iterations) |
| Set the maximum number of iterations. | |
| int | getMaxIterations () |
| Get the maximum number of iterations, as set by the user. | |
| void | setProbability (double probability) |
| Set the desired probability of choosing at least one sample free from outliers. | |
| double | getProbability () |
| Obtain the probability of choosing at least one sample free from outliers, as set by the user. | |
| virtual bool | computeModel (int debug_verbosity_level=0)=0 |
| Compute the actual model. | |
| virtual bool | refineModel (const double sigma=3.0, const unsigned int max_iterations=1000) |
| Refine the model found. | |
| void | getRandomSamples (const boost::shared_ptr< std::vector< int > > &indices, size_t nr_samples, std::set< int > &indices_subset) |
| Get a set of randomly selected indices. | |
| void | getModel (std::vector< int > &model) |
(3)pcl::RandomizedMEstimatorSampleConsensus< PointT > 实现了RANSAC算法,RANSAC算法适用与处理数据点中局内点比例比较大的情况,科快速的进行局外点的剔除。
class pcl::SampleConsensusModelCircle2D< PointT >实现采样一致性 计算二位平面圆周模型
class pcl::SampleConsensusModelCone< PointT, PointNT > 实现采样一致性计算的三维椎体模型
太多了
| class | pcl::LeastMedianSquares< PointT > |
| LeastMedianSquares represents an implementation of the LMedS (Least Median of Squares) algorithm. | |
| class | pcl::MaximumLikelihoodSampleConsensus< PointT > |
| MaximumLikelihoodSampleConsensus represents an implementation of the MLESAC (Maximum Likelihood Estimator SAmple Consensus) algorithm, as described in: "MLESAC: A new robust estimator with application to estimating image geometry", P.H.S. | |
| class | pcl::MEstimatorSampleConsensus< PointT > |
| MEstimatorSampleConsensus represents an implementation of the MSAC (M-estimator SAmple Consensus) algorithm, as described in: "MLESAC: A new robust estimator with application to estimating image geometry", P.H.S. | |
| class | pcl::ProgressiveSampleConsensus< PointT > |
| RandomSampleConsensus represents an implementation of the RANSAC (RAndom SAmple Consensus) algorithm, as described in: "Matching with PROSAC – Progressive Sample Consensus", Chum, O. | |
| class | pcl::RandomSampleConsensus< PointT > |
| RandomSampleConsensus represents an implementation of the RANSAC (RAndom SAmple Consensus) algorithm, as described in: "Random Sample Consensus: A Paradigm for Model Fitting with Applications to Image Analysis and Automated Cartography", Martin A. | |
| class | pcl::RandomizedMEstimatorSampleConsensus< PointT > |
| RandomizedMEstimatorSampleConsensus represents an implementation of the RMSAC (Randomized M-estimator SAmple Consensus) algorithm, which basically adds a Td,d test (see RandomizedRandomSampleConsensus) to an MSAC estimator (see MEstimatorSampleConsensus). | |
| class | pcl::RandomizedRandomSampleConsensus< PointT > |
| RandomizedRandomSampleConsensus represents an implementation of the RRANSAC (Randomized RAndom SAmple Consensus), as described in "Randomized RANSAC with Td,d test", O. | |
| class | pcl::SampleConsensusModelNormalParallelPlane< PointT, PointNT > |
| SampleConsensusModelNormalParallelPlane defines a model for 3D plane segmentation using additional surface normal constraints. | |
| class | pcl::SampleConsensusModelNormalSphere< PointT, PointNT > |
| SampleConsensusModelNormalSphere defines a model for 3D sphere segmentation using additional surface normal constraints. | |
| class | pcl::SampleConsensusModelParallelLine< PointT > |
| SampleConsensusModelParallelLine defines a model for 3D line segmentation using additional angular constraints. |
代码实例 random_sample_consensus.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/console/parse.h>
#include <pcl/filters/extract_indices.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/ransac.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/sac_model_plane.h>
#include <pcl/sample_consensus/sac_model_sphere.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp> boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer>
simpleVis (pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::ConstPtr cloud)
{
// --------------------------------------------
// -----Open 3D viewer and add point cloud-----
// --------------------------------------------
boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer (new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer ("3D Viewer"));
viewer->setBackgroundColor (, , );
viewer->addPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud, "sample cloud");
viewer->setPointCloudRenderingProperties (pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, , "sample cloud");
//viewer->addCoordinateSystem (1.0, "global");
viewer->initCameraParameters ();
return (viewer);
}
/******************************************************************************************************************
对点云进行初始化,并对其中一个点云填充点云数据作为处理前的的原始点云,其中大部分点云数据是基于设定的圆球和平面模型计算
而得到的坐标值作为局内点,有1/5的点云数据是被随机放置的组委局外点。
*****************************************************************************************************************/
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 初始化点云对象
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); //存储源点云
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr final (new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>); //存储提取的局内点 // 填充点云数据
cloud->width = ; //填充点云数目
cloud->height = ; //无序点云
cloud->is_dense = false;
cloud->points.resize (cloud->width * cloud->height);
for (size_t i = ; i < cloud->points.size (); ++i)
{
if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-s") >= || pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-sf") >= )
{
//根据命令行参数用x^2+y^2+Z^2=1设置一部分点云数据,此时点云组成1/4个球体作为内点
cloud->points[i].x = * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0);
cloud->points[i].y = * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0);
if (i % == )
cloud->points[i].z = * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); //此处对应的点为局外点
else if(i % == )
cloud->points[i].z = sqrt( - (cloud->points[i].x * cloud->points[i].x)
- (cloud->points[i].y * cloud->points[i].y));
else
cloud->points[i].z = - sqrt( - (cloud->points[i].x * cloud->points[i].x)
- (cloud->points[i].y * cloud->points[i].y));
}
else
{ //用x+y+z=1设置一部分点云数据,此时地拿云组成的菱形平面作为内点
cloud->points[i].x = * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0);
cloud->points[i].y = * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0);
if( i % == )
cloud->points[i].z = * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0); //对应的局外点
else
cloud->points[i].z = - * (cloud->points[i].x + cloud->points[i].y);
}
} std::vector<int> inliers; //存储局内点集合的点的索引的向量 //创建随机采样一致性对象
pcl::SampleConsensusModelSphere<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr
model_s(new pcl::SampleConsensusModelSphere<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud)); //针对球模型的对象
pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr
model_p (new pcl::SampleConsensusModelPlane<pcl::PointXYZ> (cloud)); //针对平面模型的对象
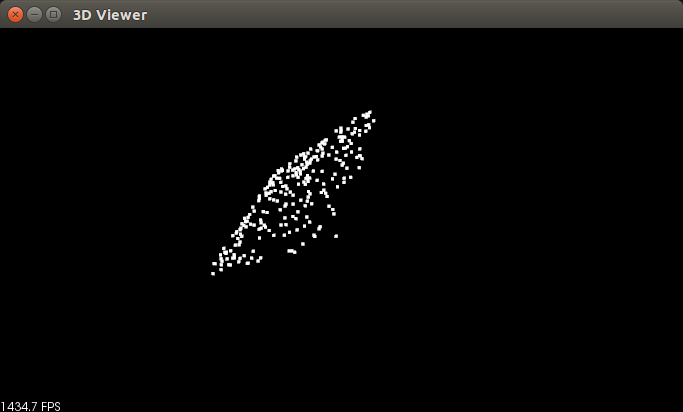
if(pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-f") >= )
{ //根据命令行参数,来随机估算对应平面模型,并存储估计的局内点
pcl::RandomSampleConsensus<pcl::PointXYZ> ransac (model_p);
ransac.setDistanceThreshold (.); //与平面距离小于0.01 的点称为局内点考虑
ransac.computeModel(); //执行随机参数估计
ransac.getInliers(inliers); //存储估计所得的局内点
}
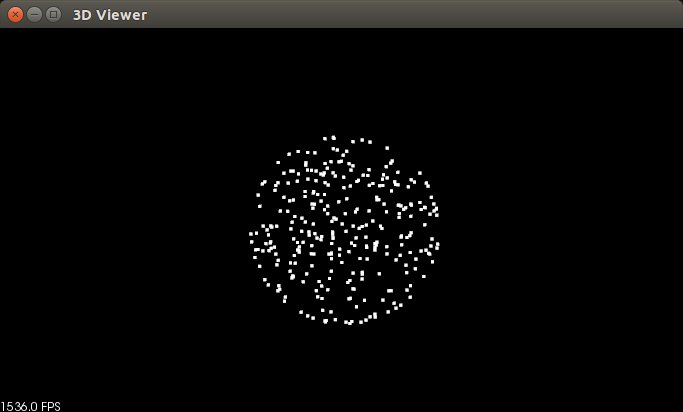
else if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-sf") >= )
{
//根据命令行参数 来随机估算对应的圆球模型,存储估计的内点
pcl::RandomSampleConsensus<pcl::PointXYZ> ransac (model_s);
ransac.setDistanceThreshold (.);
ransac.computeModel();
ransac.getInliers(inliers);
} // 复制估算模型的所有的局内点到final中
pcl::copyPointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>(*cloud, inliers, *final); // 创建可视化对象并加入原始点云或者所有的局内点 boost::shared_ptr<pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer> viewer;
if (pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-f") >= || pcl::console::find_argument (argc, argv, "-sf") >= )
viewer = simpleVis(final);
else
viewer = simpleVis(cloud);
while (!viewer->wasStopped ())
{
viewer->spinOnce ();
boost::this_thread::sleep (boost::posix_time::microseconds ());
}
return ;
}
运行结果:
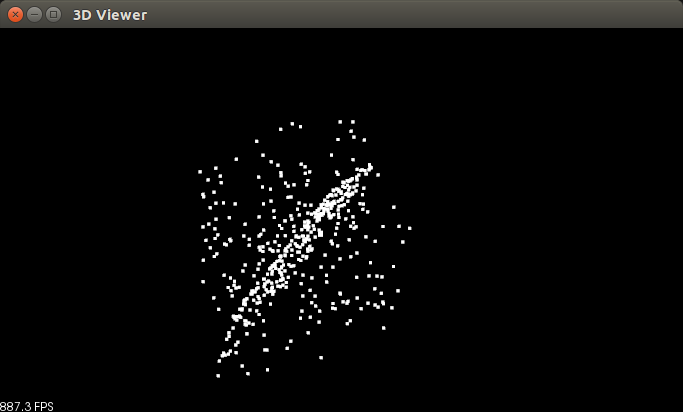
在没有任何参数的情况下,三维窗口显示创建的原始点云(含有局内点和局外点),如图所示,很明显这是一个带有噪声的菱形平面,噪声点是立方体,自己要是我们在产生点云是生成的是随机数生在(0,1)范围内。
./random_sample_consensus
./random_sample_consensus -f
./random_sample_consensus -sf
未完待续****************************************************8
PCL采样一致性算法的更多相关文章
- RANSAC - 随机采样一致性算法
RANSAC范例的正式描述如下: 首先,要给定: 1一个模型,该模型需要最少n个数据点去实例化它的自由参数: 2一组数据点P,P中包含数据点的数量#(P)大于n. 然后, 从P中随机地选择n个点(组成 ...
- 分布式一致性算法--Paxos
Paxos算法是莱斯利·兰伯特(Leslie Lamport)1990年提出的一种基于消息传递的一致性算法.Paxos算法解决的问题是一个分布式系统如何就某个值(决议)达成一致.在工程实践意义上来说, ...
- 一致性算法RAFT详解
原帖地址:http://www.solinx.co/archives/415?utm_source=tuicool&utm_medium=referral一致性算法Raft详解背景 熟悉或了解 ...
- 分布式系统一致性问题和Raft一致性算法
一致性问题 一致性算法是用来解决一致性问题的,那么什么是一致性问题呢? 在分布式系统中,一致性问题(consensus problem)是指对于一组服务器,给定一组操作,我们需要一个协议使得最后它们的 ...
- 一致性算法Paxos详解
分布式系统除了能提升整个系统的性能外还有一个重要的特性就是提高系统的可靠性,可靠性指的是当分布式系统中一台或N台机器宕掉后都不会导致系统不可用,分布式系统是state machine replicat ...
- 随机抽样一致性算法(RANSAC)示例及源代码
作者:王先荣 大约在两年前翻译了<随机抽样一致性算法RANSAC>,在文章的最后承诺写该算法的C#示例程序.可惜光阴似箭,转眼许久才写出来,实在抱歉.本文将使用随机抽样一致性算法来来检测直 ...
- [转载] 一致性问题和Raft一致性算法
原文: http://daizuozhuo.github.io/consensus-algorithm/ raft 协议确实比 paxos 协议好懂太多了. 一致性问题 一致性算法是用来解决一致性问题 ...
- 一致性算法--Raft
分布式一致性算法--Raft 前面一篇文章讲了Paxos协议,这篇文章讲它的姊妹篇Raft协议,相对于Paxos协议,Raft协议更为简单,也更容易工程实现.有关Raft协议和工程实现可以参考这个链接 ...
- 一致性算法--Paxos
分布式一致性算法--Paxos Paxos算法是莱斯利·兰伯特(Leslie Lamport)1990年提出的一种基于消息传递的一致性算法.Paxos算法解决的问题是一个分布式系统如何就某个值(决议) ...
随机推荐
- MySQL通过Explain查看select语句的执行计划结果触发写操作
[背景] 某某同学执行了一下Explain结果结果发现数据库有了一条写入操作,恭喜这位同学你的锅到货了,你签收一下: 对! 你没有听错,在一种场景下就算是Explain也会引发数据的写操作,就这是外层 ...
- 硬盘 SMART 检测参数详解[转]
一.SMART概述 硬盘的故障一般分为两种:可预测的(predictable)和不可预测的(unpredictable).后者偶而会发生,也没有办法去预防它,例如芯片突然失效,机械撞击等.但像电机轴承 ...
- 微信小程序之顶部固定和底部固定
顶部固定 <view style="position:fixed;top:0;"> ...... </view> 底部固定 <view style=& ...
- Storm工作流程
为什么storm的数据来自于消息队列? Storm的解决问题的scope主要在于流计算,说流计算之前我们先简单的说下一般数据处理系统的过程.一般数据处理简单说要有几个环节:数据采集,数据计算,结果输出 ...
- Android 启动、绘制、显示过程
Activity 启动过程: startActivity()-> Instrumentation.execStartActivity()-> Binder->ActivityMana ...
- 使用gradle多渠道打包
以友盟的多渠道打包为例,如果我们须要打包出例如以下渠道:UMENG, WANDOUJIA, YINGYONGBAO. 第一种方法.是须要创建文件的. 我们在写完我们的代码之后,在app/src以下.分 ...
- ITOO高校云平台V3.1--项目总结(二)
自身责任要明白 心态要明白 布置任务要有反馈 总结 今天下午.举办了一场ITOO高校云平台3.1总结大会,针对3.1开发的过程中统计上来的问题进行讨论. 通过讨论统计上来的问题,映射到自身,看看自己还 ...
- tmux用于恢复远程屏幕
1.我主要用tmux在远程登陆后,恢复以前会话时候用. 2.tmux创建新会话: tmux new -s 会话名 3.返回控制台: Ctrl+b d ,Ctrl+b命令是tmux前置命令,每次都要先输 ...
- 译: 2. Apache Axis2安装指南
Apache Axis2安装指南 本文档提供有关Axis2分发包,系统先决条件以及设置环境变量和工具的信息,然后提供有关安装方法的详细说明. 请将您的反馈发送至:java-dev@axis.apach ...
- 【Unity】12.1 基本概念
开发环境:Win10.Unity5.3.4.C#.VS2015 创建日期:2016-05-09 一.简介 导航网格(Navmesh)是世界坐标系中几何体的简化表示,被游戏代理用来进行全局导航.通常,代 ...
