alluxio源码解析-netty部分(2)
netty简介
netty作为alluxio中重要的通讯组件
在常见的客户端上传,下载中,都会有netty的参与
关于这个图,可以看上篇文章的介绍:
https://www.cnblogs.com/victor2302/p/10490253.html
- 解耦ufs和worker缓存的功能
- 解耦 BlockHandler和 ShortCircuitBlockHandler
- 解耦异步上传,同步上传
- 高性能传输
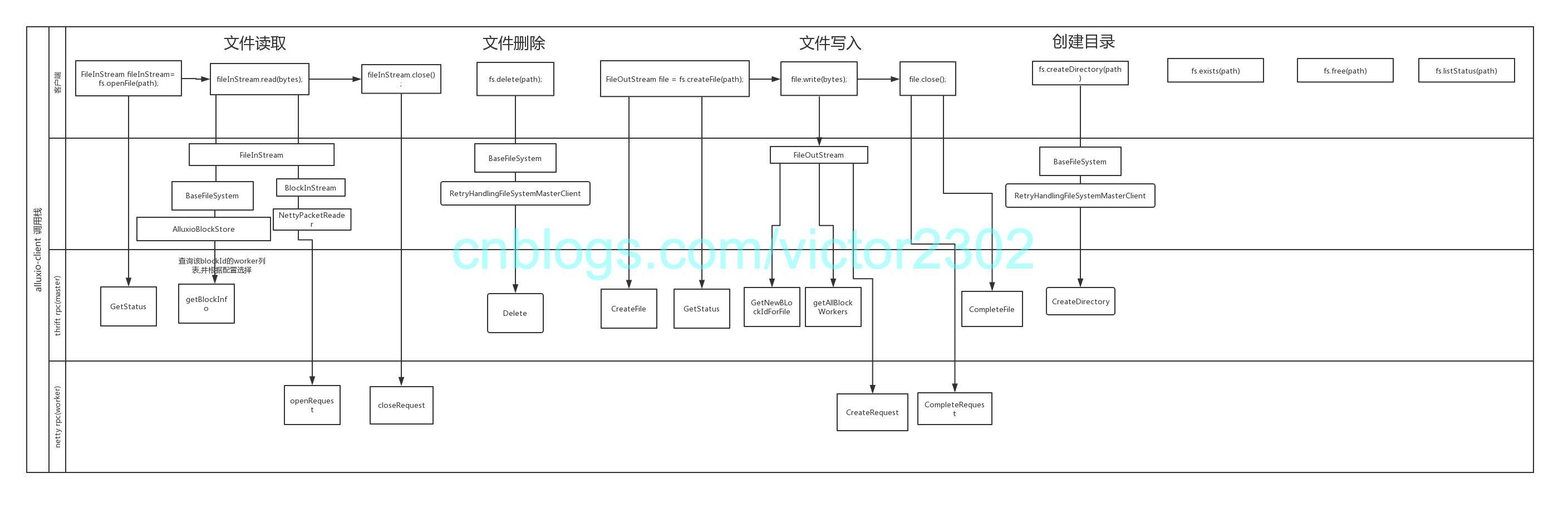
netty客户端部分:
1.固定的处理器:alluxio.network.netty.NettyClient
final Bootstrap boot = new Bootstrap(); boot.group(WORKER_GROUP)
.channel(NettyUtils.getClientChannelClass(!(address instanceof InetSocketAddress)));
boot.option(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
boot.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
boot.option(ChannelOption.ALLOCATOR, PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT);
if (NettyUtils.USER_CHANNEL_TYPE == ChannelType.EPOLL) {
boot.option(EpollChannelOption.EPOLL_MODE, EpollMode.LEVEL_TRIGGERED);
} // After 10 missed heartbeat attempts and no write activity, the server will close the channel.
final long timeoutMs = Configuration.getMs(PropertyKey.NETWORK_NETTY_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_MS);
final long heartbeatPeriodMs = Math.max(timeoutMs / 10, 1);
boot.handler(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); pipeline.addLast(RPCMessage.createFrameDecoder());
pipeline.addLast(ENCODER);
pipeline.addLast(DECODER);
pipeline.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(0, heartbeatPeriodMs, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
pipeline.addLast(new IdleWriteHandler());
}
});
2.临时的处理器:针对通用response注册回调(ShortCircuitBlockHandler 调用)
public static ProtoMessage call(final NettyRPCContext context, ProtoMessage request)
throws IOException {
Channel channel = Preconditions.checkNotNull(context.getChannel());
final Promise<ProtoMessage> promise = channel.eventLoop().newPromise();
channel.pipeline().addLast(new RPCHandler(promise));
channel.writeAndFlush(new RPCProtoMessage(request)).addListener((ChannelFuture future) -> {
if (future.cause() != null) {
future.channel().close();
promise.tryFailure(future.cause());
}
});
ProtoMessage message;
try {
message = promise.get(context.getTimeoutMs(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
CommonUtils.closeChannel(channel);
throw new IOException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
CommonUtils.closeChannel(channel);
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (channel.isOpen()) {
channel.pipeline().removeLast();
}
}
if (message.isResponse()) {
CommonUtils.unwrapResponseFrom(message.asResponse(), context.getChannel());
}
return message;
}
3.临时的处理器:针对读写操作注册回调(BlockHandler)
private NettyPacketReader(FileSystemContext context, WorkerNetAddress address,
Protocol.ReadRequest readRequest) throws IOException {
mContext = context;
mAddress = address;
mPosToRead = readRequest.getOffset();
mReadRequest = readRequest; mChannel = mContext.acquireNettyChannel(address);
mChannel.pipeline().addLast(new PacketReadHandler());
mChannel.writeAndFlush(new RPCProtoMessage(new ProtoMessage(mReadRequest)))
.addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE_ON_FAILURE);
} private NettyPacketWriter(FileSystemContext context, final WorkerNetAddress address, long id,
long length, long packetSize, Protocol.RequestType type, OutStreamOptions options,
Channel channel) {
mContext = context;
mAddress = address;
mLength = length;
Protocol.WriteRequest.Builder builder =
Protocol.WriteRequest.newBuilder().setId(id).setTier(options.getWriteTier()).setType(type);
if (type == Protocol.RequestType.UFS_FILE) {
Protocol.CreateUfsFileOptions ufsFileOptions =
Protocol.CreateUfsFileOptions.newBuilder().setUfsPath(options.getUfsPath())
.setOwner(options.getOwner()).setGroup(options.getGroup())
.setMode(options.getMode().toShort()).setMountId(options.getMountId()).build();
builder.setCreateUfsFileOptions(ufsFileOptions);
}
mPartialRequest = builder.buildPartial();
mPacketSize = packetSize;
mChannel = channel;
mChannel.pipeline().addLast(new PacketWriteResponseHandler());
}
netty服务端:
注册处理器列表:
protected void initChannel(Channel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
final long timeoutMs = Configuration.getMs(PropertyKey.NETWORK_NETTY_HEARTBEAT_TIMEOUT_MS);
// Decoders & Encoders
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", RPCMessage.createFrameDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("RPCMessageDecoder", new RPCMessageDecoder());
pipeline.addLast("RPCMessageEncoder", new RPCMessageEncoder());
// Idle Event Handlers
pipeline.addLast("idleEventHandler", new IdleStateHandler(timeoutMs, 0, 0,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
pipeline.addLast("idleReadHandler", new IdleReadHandler());
pipeline.addLast("heartbeatHandler", new HeartbeatHandler());
// Block Handlers
pipeline.addLast("blockReadHandler",
new BlockReadHandler(NettyExecutors.BLOCK_READER_EXECUTOR,
mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class), mFileTransferType));
pipeline.addLast("blockWriteHandler", new BlockWriteHandler(
NettyExecutors.BLOCK_WRITER_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class),
mWorkerProcess.getUfsManager()));
pipeline.addLast("shortCircuitBlockReadHandler",
new ShortCircuitBlockReadHandler(NettyExecutors.RPC_EXECUTOR,
mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class)));
pipeline.addLast("shortCircuitBlockWriteHandler",
new ShortCircuitBlockWriteHandler(NettyExecutors.RPC_EXECUTOR,
mWorkerProcess.getWorker(BlockWorker.class)));
pipeline.addLast("asyncCacheHandler", new AsyncCacheHandler(mRequestManager));
// UFS Handlers
pipeline.addLast("ufsFileWriteHandler", new UfsFileWriteHandler(
NettyExecutors.FILE_WRITER_EXECUTOR, mWorkerProcess.getUfsManager()));
// Unsupported Message Handler
pipeline.addLast("unsupportedMessageHandler", new UnsupportedMessageHandler());
}
写入或者读取配置
alluxio.client.file.options.CreateFileOptions是FileSystem类createFile的第二个参数,可以选定不同的写入策略
例如:
- MUST_CACHE(只写入Alluxio,必须存储在Alluxio中)
- CACHE_THROUGH(尝试缓存,同步写入到UnderFS)
- THROUGH(无缓存,同步写入到UnderFS)
- ASYNC_THROUGH(异步写入到UnderFS,实现特性)
FileOutStream createFile(AlluxioURI path, CreateFileOptions options)
throws FileAlreadyExistsException, InvalidPathException, IOException, AlluxioException;
而这种写入选项,就是通过在传递netty message时,设置不同的标识,然后在netty中分派到不同的pipeline节点,处理各自的特性的
代码实例:
是否需要写入到ufs,则在UfsFileWriteHandler的acceptMessage方法中进行判断的
alluxio.worker.netty.UfsFileWriteHandler#acceptMessage
protected boolean acceptMessage(Object object) {
if (!super.acceptMessage(object)) {
return false;
}
Protocol.WriteRequest request = ((RPCProtoMessage) object).getMessage().asWriteRequest();
return request.getType() == Protocol.RequestType.UFS_FILE;
}
alluxio源码解析-netty部分(2)的更多相关文章
- Netty 源码解析: Netty 的 ChannelPipeline
ChannelPipeline和Inbound.Outbound 我想很多读者应该或多或少都有 Netty 中 pipeline 的概念.前面我们说了,使用 Netty 的时候,我们通 ...
- alluxio源码解析-rpc调用概述-client和worker之间的block模块的通讯架构(netty版本)(3)
(1.8版本)client和worker之间的block模块的通讯架构 block作为alluxio文件读取或者存储的最小基本单位,都是通过BlockOutStream和BlockInputtream ...
- alluxio源码解析-层次化存储(4)
层次化存储-特性介绍: https://www.alluxio.org/docs/1.6/cn/Tiered-Storage-on-Alluxio.html 引入分层存储后,Alluxio管理的数据块 ...
- alluxio源码解析-rpc调用概述(1)
alluxio中几种角色以及角色之间的rpc调用: 作为分布式架构的文件缓存系统,rpc调用必不可少 client作为客户端 master提供thrift rpc的服务,管理以下信息: block信息 ...
- Netty 4源码解析:请求处理
Netty 4源码解析:请求处理 通过之前<Netty 4源码解析:服务端启动>的分析,我们知道在最前端"扛压力"的是NioEventLoop.run()方法.我们指定 ...
- Netty 4源码解析:服务端启动
Netty 4源码解析:服务端启动 1.基础知识 1.1 Netty 4示例 因为Netty 5还处于测试版,所以选择了目前比较稳定的Netty 4作为学习对象.而且5.0的变化也不像4.0这么大,好 ...
- netty服务端启动--ServerBootstrap源码解析
netty服务端启动--ServerBootstrap源码解析 前面的第一篇文章中,我以spark中的netty客户端的创建为切入点,分析了netty的客户端引导类Bootstrap的参数设置以及启动 ...
- Netty源码解析—客户端启动
Netty源码解析-客户端启动 Bootstrap示例 public final class EchoClient { static final boolean SSL = System.getPro ...
- Netty源码解析---服务端启动
Netty源码解析---服务端启动 一个简单的服务端代码: public class SimpleServer { public static void main(String[] args) { N ...
随机推荐
- vue.js 解决跨域问题
我们调试vue.js代码的时候一般都用chrome, 下载插件 进入chrome应用商店 搜索 重启chrome就可以解决跨域问题
- .Net Core 使用百度UEditor编辑器
一.准备文件 1. 下载UEditor官方版本.删除其中后端文件.保留后端文件夹中的config.json文件 2. 在NuGet管理器中搜索UEditorNetCore,拿到项目地址,下载源码 下载 ...
- Class(类)和 继承
ES6的class可以看作只是一个语法糖,它的绝大部分功能,ES5都可以做到,新的class写法只是让对象原型的写法更加清晰.更像面向对象编程的语法而已. //定义类 class Point { co ...
- python 3.7 新特性 - popitem
百度上大多文章说 popitem 随机删除字典的一个键值对 python 3.7 官方文档已经说了,popitem 删除字典最后一个添加进去的键值对
- git分支创建与切换
1. 场景描述 新版本迭代上线完成,为了保持当前版本稳定性及可回退等需求,需要切换新的分支用于下一版本的迭代开发. 2. 解决方案 2.1 切换前工作. 因发布上线当天有可能存在临时更改文件而未上传g ...
- 2017-10271weblogic漏洞exp测试及补丁测试
靶机:weblogic12.1.3.0 战斗机:kali 导弹:burpsuite 1.首先开启kali某端口监听 2.向靶机发送exp 3.查看kali监听 打码保平安~~ 4.打上补丁 5.验证补 ...
- Netty-Pipeline深度解析
首先我们知道,在NIO网络编程模型中,IO操作直接和channel相关,比如客户端的请求连接,或者向服务端发送数据, 服务端都要从客户端的channel获取这个数据 那么channelPipeline ...
- CF510C Fox And Names——拓扑排序练习
省委代码: #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cstring> #include<cmath> # ...
- UVA12657 Boxes in a Line:题解
题目链接:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/UVA12657 分析: 此题使用手写链表+模拟即可.(其实可以用list,而且更简便,但是会大大的超时) 肯定是 ...
- 个人永久性免费-Excel催化剂功能第45波-逻辑判断函数增强
自定义函数的最大的作用是可以按需定制,在Excel的原生函数不提供的场景时,传统方法需要使用大量的嵌套函数去实现,实在太累,今天Excel催化剂再次送上一波绝对十分常用的函数逻辑判断类函数给大家使用! ...
