bootrom/spl/uboot/linux逐级加载是如何实现的?
关键词:bootrom、spl、uboot、linux、mksheader、sb_header、mkimage、image_header_t等等。
首先看一个典型的bootrom->spl->uboot->linux流程log,主要分为4个部分,中间有3个衔接点。
# Hello DeepEye
-- Boot from SD card --
sdio initialize done.
sd card read done.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------->bootrom-spl分割线,以上是bootrom输出内容,从存储介质中读取spl到片内RAM中,并判断magic number。
U-Boot SPL 2016.07--g6c3df97-dirty (Aug - ::)
Boot reason: >(Normal).
ddr4 4GB init...
...
Welcome to SPL!Load U-Boot from SD ...
---------------------------------------------------------------------------->spl-uboot分割线,以上是spl运行阶段,主要进行pll、时钟、串口等初始化;最主要的是初始化了DDR以及从存储介质中将uboot加载到DDR中。
U-Boot 2016.07 (Jul - :: +)DeepEye1000 DRAM: 3.9 GiB
MMC: deepeye_sdhci: , deepeye_sdhci:
Using default environment
...
## Booting kernel from Legacy Image at ...
Image Name: Linux-4.9.
Image Type: Sandbox Linux Kernel Image (gzip compressed)
Data Size: Bytes = 4.7 MiB
Load Address:
Entry Point:
Verifying Checksum ... OK
Uncompressing Kernel Image ... OK
dtb_load_addr: 0x8F000000 Starting kernel ...
---------------------------------------------------------------------------->uboot-linux分割线,uboot相较于spl功能更加丰富。提供了丰富的命令,可以操作文件系统、脚本、加载不同操作系统等等。
[ 0.000000] Linux version 4.9. (al@al-B250-HD3) (gcc version 6.3. (C-SKY Tools V3.8.10-kstq-nd-r2 Glibc-2.9
[ 0.000000] C-SKY: https://github.com/c-sky/csky-linux
[ 0.000000] Phys. mem: 4032MB
...
[ 4.382887] Freeing unused kernel memory: 276k freed
[ 4.387879] This architecture does not have kernel memory protection.
[ 4.702756] EXT4-fs (mmcblk1p2): re-mounted. Opts: nodelalloc,data=journal
Starting mdev...
Starting network: OK
...
----------------------------------------------------------------------------->linux包括kernel和rootfs,内核中初始化了外设、操作系统组件、挂载了文件系统,并调用init初始化用户空间环境。
下面主要分析不同阶段之间如何衔接。
1. 各阶段主要作用
bootrom是固化在芯片内部的一块rom,初始化各种接口,并从中读取内容加载到片内SRAM中。因为存储设备接口相对简单,大部分不需要适配即可存取。但是DDR等需要修改代码进行适配。
所以就需要spl,spl被加载到片内SRAM中,片内SRAM不需要初始化即可运行,但是容量有限。spl运行起来后进行必要的初始化后,初始化DDR,并将uboot从存储设备中读到DDR中。
uboot运行在DDR中,则不受空间大小限制,可以进行复杂的操作。支持包括不同文件系统、脚本执行、多种操作系统加载等等操作。其中主要的工作是从存储设备中读取kernel,解析后跳转到kernel执行。
linux这里包括kernel和rootfs两部分,kernel进行系统组件初始化、设备初始化,在一切准备就绪后,调用第一个用户空间程序init进行用户空间初始化。
2. bootrom加载spl分析
bootrom从不同存储介质中读取spl,这些存储介质可能是SD、eMMC或者USB接口、串口等等。
从读取内容中解析spl的sb_header,验证magic_num、确定spl大小、加载到load_addr、进行crc校验结果crc16对比。最后跳转到entry_point进行spl运行。
下面了解一下sb_header结构体?以及sb_header是如何生成的?最后bootrom中是通过如何处理sb_header加载spl的?
2.1 sb_header数据结构
sb_header是bootrom和spl协调一致的数据结构,spl在头部包含此部分数据,bootrom在运行的时候解析它。
#define MAGIC_NUM 0x44454550
typedef struct second_boot_header{
unsigned int magic_num;----------------------------两者约定的魔数0x44454550。
unsigned int data_size;----------------------------去掉头部的spl大小。
unsigned int load_addr;----------------------------从头部开始的地址。
unsigned int entry_point;--------------------------去掉头部开始的地址。
unsigned int crc16;--------------------------------不包括sb_header的crc校验结果。
}sb_header;
2.2 从u-boot-spl->u-boot-spl.bin->u-boot-spl-bh.bin流程
生成u-boot-spl以及u-boot-spl.map文件:
cmd_spl/u-boot-spl := (cd spl && csky-abiv2-linux-ld.bfd -EL -T u-boot-spl.lds --gc-sections -Bstatic --gc-sections -Ttext 0xfc000000 arch/csky/cpu/ck807_810/start.o --start-group arch/csky/cpu/built-in.o arch/csky/cpu/ck807_810/built-in.o arch/csky/lib/built-in.o board/csky/deepeye1000/built-in.o board/csky/common/built-in.o common/spl/built-in.o common/init/built-in.o common/built-in.o cmd/built-in.o drivers/built-in.o dts/built-in.o fs/built-in.o lib/built-in.o --end-group -L /home/al/csky_toolchain/gcc_v3.8.10-kstq-nd-r2/opt/ext-toolchain/bin/../lib/gcc/csky-linux-gnuabiv2/6.3./hard-fp -lgcc -Map u-boot-spl.map -o u-boot-spl)
其中-T u-boot-spl.lds表示从u-boot-spl.lds中读取链接脚本;-Ttext 0xfc000000表示从.text段起始地址为0xfc000000,并且start.o是spl的起始;--start-group和--end-group表示一个group的起始和结束标志,中间是group的内容;-Map u-boot-spl.map表示输出map文件到u-boot-spl.map;-o u-boot-spl表示输出可执行文件到u-boot-spl。
通过u-boot-spl生成u-boot-spl-nodtb.bin文件:
cmd_spl/u-boot-spl-nodtb.bin := csky-abiv2-linux-objcopy -j .text -j .rodata -j .data -j .u_boot_list -j .dtb.init.rodata -O binary spl/u-boot-spl spl/u-boot-spl-nodtb.bin
-j表示将要copy的section名称,-O表示输出文件格式,这个命令将u-boot-spl中特定section以binary格式输出到u-boot-spl-nodtb.bin中。
u-boot-spl.bin和u-boot-spl.nodtb.bin是同样文件:
cmd_spl/u-boot-spl.bin := cp spl/u-boot-spl-nodtb.bin spl/u-boot-spl.bin
从u-boot-spl.bin到u-boot-spl-bh.bin主要是mksheader给u-boot-spl.bin加了个sb_header头。
spl/u-boot-spl.bin: spl/u-boot-spl
@:
tools/mksheader 0xfc000000 0xfc000180 spl/u-boot-spl.bin spl/u-boot-spl-bh.bin
chmod +x spl/u-boot-spl-bh.bin
2.2.1 mksheader给spl加sb_header头
给spl加sb_header头这个工作是由mksheader来做的,决定了load_addr和entry_point,然后根据结果填充了data_size和crc16。
mksheader读取u-boot-spl.bin文件,加上sb_header头之后,生成新的u-boot-spl-bh.bin文件。下面简单看看mksheader这个工具是如何给spl添加sb_header头。
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
unsigned short crc_data;
FILE *file_in = NULL;
FILE *file_out = NULL;
int len;
unsigned char *file_buff = NULL;
sb_header header_data;
unsigned int entry_point;
unsigned int load_addr; if (argc < ) {
printf("Please input like this: %s load_addr entry_addr file_input file_output\n", argv[]);
exit();
}
load_addr = strtoul(argv[], , );
entry_point = strtoul(argv[], , );-------------------分别指定load_addr和entry_point。 len = get_file_size(argv[]);---------------------------获取输入文件的大小,指为data_size。
file_buff = malloc(len);
if (!file_buff) {
perror("open file failed:\n");
exit();
} file_in = fopen(argv[], "rb+");
if(!file_in) {
perror("open file_in failed:\n");
exit();
} file_out = fopen(argv[], "wb+");
if(!file_out) {
perror("open file_out failed:\n");
exit();
} if (fread(file_buff, , len, file_in) != ) {-----------将u-boot-spl.bin文件读到file_buff中。
;
// perror("read input file failed.\n");
// exit(1);
} crc_data = check_sum(file_buff, len);-------------------对u-boot-spl.bin文件进行crc校验,结果写到crc16中。
// printf("crc_data=0x%x, len=0x%x load_addr=0x%x entry_point=0x%x\n",
// crc_data, len, load_addr ,entry_point); header_data.magic_num = 0x44454550;---------------------写入magic_num。
header_data.data_size = len;
header_data.entry_point = entry_point;
header_data.load_addr = load_addr;
header_data.crc16 = crc_data; fwrite(&header_data, , sizeof(header_data), file_out);
fwrite(file_buff, , len, file_out);--------------------分别将sb_header和u-boot-spl.bin写入到u-boot-spl-bh.bin中。 fclose(file_in);
fclose(file_out);
return ;
}
下面通过BeyondCompare对比u-boot-spl.bin和u-boot-spl-bh.bin的差异:
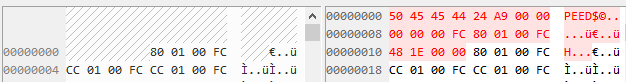
两者相差只有u-boot-spl-bh.bin多了20字节的头,分别是magic_num(0x44454550)、data_size(0x0000a924)、load_addr(0xfc000000)、entry_point(0xfc000180)、crc16(0x00001e48)。
2.3 bootrom解析sb_header头
下面以sd为例介绍bootrom是如何通过解析sb_header来加载spl的。
int sd_card_boot(void)
{
int i;
sb_header header;
u8* p_header = &header;
u32 buffer_addr = ,block_cnt=,col=;
u16 crc16 = ;
LOAD_ENTRY enter_jump_func; char buffer_r[MMC_MAX_BLOCK_LEN];
memset(buffer_r,0x00,MMC_MAX_BLOCK_LEN);-------------------------------------分配一个block大小buffer_r,即512字节。 if (mmc_bread(&sd_card_mmc,SD_CARD_BOOT_ADDR, , (u32)buffer_r) != )---------在SD的第66个sector,即33KB处读取一个block。
{
debug("mmc_bread failed.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;
}
memcpy(p_header,buffer_r,sizeof(header));-------------------------------------取buffer_r的sb_header大小内容到p_header中。
sdio_debug("magic=0x%x size=0x%x load_addr=0x%x entry_addr=0x%x crc16=0x%x \n",\
header.magic_num,header.data_size,header.load_addr,header.entry_point,header.crc16); if(header.magic_num != MAGIC_NUM)----------------------------------------------检查magic_num是否正确。
{
debug("magic_num error.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;//boot failed
}
//get data len, may be need check len (max) error return -1
if(header.data_size > SPL_MAX_LEN)
{
debug("data_size error.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;//boot failed
}
//check load address
if(header.load_addr < SRAM_START_ADDRESS)
{
debug("load_addr error.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;//boot failed
}
if((header.load_addr+header.data_size)>SPL_MAX_ADDRESS)
{
debug("the data is out of bounds.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;//boot failed
} buffer_addr = header.load_addr;--------------------------------------------将整个u-boot-spl.bin加载到的地址。
block_cnt = (header.data_size+sizeof(header)) / sd_card_mmc.read_bl_len;---需要读取总block数目。
col = (header.data_size+sizeof(header))%sd_card_mmc.read_bl_len; for(i=;i<block_cnt;i++)
{
if (mmc_bread(&sd_card_mmc,SD_CARD_BOOT_ADDR+i, , (u32)buffer_addr) != )
{
debug("mmc_bread failed.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;
}
if(i == )
{
memcpy((void*)buffer_addr,(void*)(buffer_r+sizeof(header)),(sd_card_mmc.read_bl_len-sizeof(header)));---这里注意在加载的时候已经将sb_header内容剔除,所以SRAM中load_addr地址不包含sb_header。
buffer_addr += (sd_card_mmc.read_bl_len-sizeof(header));
}
else
{
buffer_addr += sd_card_mmc.read_bl_len;
}
}
if(col)
{
if (mmc_bread(&sd_card_mmc,SD_CARD_BOOT_ADDR+block_cnt, , (u32)buffer_r) != )
{
debug("mmc_bread failed.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;
}
memcpy((void*)buffer_addr,(void*)buffer_r,col); }
info_debug("sd card read done.\n"); crc16 = check_sum((u8*)header.load_addr, header.data_size);
if(crc16 != (u16)header.crc16)----------------------------------------------进行crc校验并比较,校验的内容是u-boot-spl.bin而不是u-boot-spl-bh.bin。
{
debug("checksum error.\n");
return -BOOT_FAILED;//boot failed
} enter_jump_func = (LOAD_ENTRY)header.entry_point;---------------------------spl的执行地址。
enter_jump_func();----------------------------------------------------------将控制权交给spl。
return ;
}
bootrom中首先读取spl的sb_header,进行magic_num检查,以及一些地址范围检查;然后根据load_addr和data_size将u-boot-spl.bin加载到SRAM中;在对u-boot-spl.bin进行crc校验后,跳转到entry_point进行执行。
遗留问题:为什么entry_point和load_addr相差0x00000180。
经查跟start.S汇编中的_start入口函数的偏移有关,在_start()之前有0x180字节的异常handler。
这是跟平台相关的,比如很多平台load_addr和entry_point就是相等的。
3. spl加载uboot分析
3.1 重要数据结构
struct spl_image_info是spl加载uboot.bin所需要的信息,其全局变量为spl_image。
struct spl_image_info {
const char *name;
u8 os;------------------表示类型,为uboot。
u32 load_addr;----------uboot.bin加载到DDR中的地址。
u32 entry_point;--------从spl跳转到uboot的入口地址。
u32 size;---------------uboot大小。
u32 flags;
};
3.2 mkimage给uboot加image_header_t头
mkimage给u-boot.bin加image_header_t后变成u-boot.img。
MKIMAGEFLAGS_u-boot.img = -A $(ARCH) -T firmware -C none -O u-boot \
-a $(CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE) -e $(CONFIG_SYS_UBOOT_START) \
-n "U-Boot $(UBOOTRELEASE) for $(BOARD) board" quiet_cmd_mkimage = MKIMAGE $@
cmd_mkimage = $(objtree)/tools/mkimage $(MKIMAGEFLAGS_$(@F)) -d $< $@ \
$(if $(KBUILD_VERBOSE:=), >/dev/null)
uboot的编译从u-boot->u-boot-nodtb.bin->u-boot.bin->u-boot.img,经历的过程如下:
-Ttext 0x17a00000表示.text段其实地址为0x17a00000;-o u-boot表示可执行输出文件为u-boot;-T u-boot.lds表示从u-boot.lds中读取链接脚本;程序从start.o中起始;map文件输出到u-boot.map中。
cmd_u-boot := csky-abiv2-linux-ld.bfd -EL --gc-sections -Bstatic -Ttext 0x17a00000 -o u-boot -T u-boot.lds arch/csky/cpu/ck807_810/start.o --start-group arch/csky/cpu/built-in.o arch/csky/cpu/ck807_810/built-in.o arch/csky/lib/built-in.o board/csky/common/built-in.o board/csky/deepeye1000/built-in.o cmd/built-in.o common/built-in.o disk/built-in.o drivers/built-in.o drivers/dma/built-in.o drivers/gpio/built-in.o drivers/i2c/built-in.o drivers/mmc/built-in.o drivers/mtd/built-in.o drivers/mtd/onenand/built-in.o drivers/mtd/spi/built-in.o drivers/net/built-in.o drivers/net/phy/built-in.o drivers/pci/built-in.o drivers/power/built-in.o drivers/power/battery/built-in.o drivers/power/fuel_gauge/built-in.o drivers/power/mfd/built-in.o drivers/power/pmic/built-in.o drivers/power/regulator/built-in.o drivers/serial/built-in.o drivers/spi/built-in.o drivers/usb/common/built-in.o drivers/usb/dwc3/built-in.o drivers/usb/emul/built-in.o drivers/usb/eth/built-in.o drivers/usb/gadget/built-in.o drivers/usb/gadget/udc/built-in.o drivers/usb/host/built-in.o drivers/usb/musb-new/built-in.o drivers/usb/musb/built-in.o drivers/usb/phy/built-in.o drivers/usb/ulpi/built-in.o fs/built-in.o lib/built-in.o net/built-in.o test/built-in.o test/dm/built-in.o --end-group -L /home/al/csky_toolchain/gcc_v3.8.10-kstq-nd-r2/opt/ext-toolchain/bin/../lib/gcc/csky-linux-gnuabiv2/6.3./hard-fp -lgcc -Map u-boot.map
然后将u-boot中特殊section以binary格式拷贝到u-boot-nodtb.bin中:
cmd_u-boot-nodtb.bin := csky-abiv2-linux-objcopy --gap-fill=0xff -j .text -j .rodata -j .data -j .u_boot_list -j .dtb.init.rodata -O binary u-boot u-boot-nodtb.bin
u-boot.bin和u-boot-nodtb.bin是一样的:
cmd_u-boot.bin := cp u-boot-nodtb.bin u-boot.bin
u-boot.img是在u-boot.bin中加了
cmd_u-boot.img := ./tools/mkimage -A csky -T firmware -C none -O u-boot -a 0x17a00000 -e 0x17a00180 -n "U-Boot 2016.07-00058-g6c3df97-dirty for deepeye1000 board" -d u-boot.bin u-boot.img >/dev/null
u-boot.img相较于u-boot.bin多了个image_header/image_header_t,共64字节大小。
ih_magic(0x27051956)、ih_hcrc(0x40700f2b)、ih_time(0x5da3e81e)、ih_size(0x00028510,即去掉header之后的data大小)、ih_load(0x0a000000,uboot加载地址)、id_ep(0x0a000180,uboot入口执行地址)、ih_dcrc(0x6f71d5c9)、ih_os(0x11,IH_OS_U_BOOT)、ih_arch(0x13,IH_ARCH_SANDBOX)、ih_type(0x05,IH_TYPE_FIRMWARE)、ih_comp(0x00,IH_COMP_NONE),后面的就是ih_name字符串。
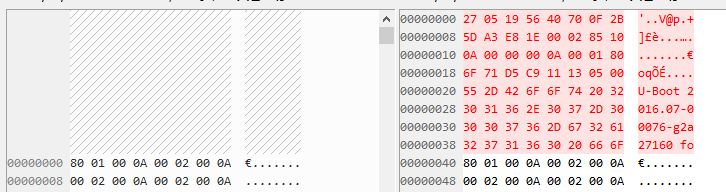
3.3 加载uboot流程
boot_init_r()中根据启动模式的不同,从存储介质指定地址中读取内容。然后从中解析image_header_t,如果不存在则通过uboot指定。但最终都是赋给spl_image。
void board_init_r(gd_t *dummy1, ulong dummy2)
{
u8 boot_mode; printf("Welcome to SPL!\n");
...
boot_mode = get_bootmode() & 0x07;
debug("%s:%d, boot mode %d\n", __FUNCTION__, __LINE__, boot_mode);
switch(boot_mode) {
...
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_SD_SUPPORT
case BOOT_TYPE_SDCARD:
printf("Load U-Boot from SD ...\n");
spl_mmc_load_image(BOOT_DEVICE_MMC2);----------------从sd中读取uboot,并解析头到spl_iamge中,将uboot加载到DDR中。
break;
#endif
...
default:
printf("Invalid boot mode 0x%x ...\n", boot_mode);
while ();
} switch (spl_image.os) {
case IH_OS_U_BOOT:
debug("Jumping to U-Boot\n");
break;
default:
debug("Unsupported OS image.. Jumping nevertheless..\n");
}
...
debug("loaded - jumping to U-Boot...");
jump_to_image_no_args(&spl_image);----------------------从spl_image.entry_point指定的地址开始执行uboot,这个程序没有返回值。 while ();
} int spl_mmc_load_image(u32 boot_device)
{
struct mmc *mmc = NULL;
u32 boot_mode;
int err = ;
__maybe_unused int part; err = spl_mmc_find_device(&mmc, boot_device);
if (err)
return err; err = mmc_init(mmc);
...
boot_mode = spl_boot_mode(boot_device);
err = -EINVAL;
switch (boot_mode) {
...
case MMCSD_MODE_RAW:
debug("spl: mmc boot mode: raw\n");
...
#if defined(CONFIG_SYS_MMCSD_RAW_MODE_U_BOOT_SECTOR)
err =mmc_load_image_raw_sector(mmc,
CONFIG_SYS_MMCSD_RAW_MODE_U_BOOT_SECTOR);--------------CONFIG_SYS_MMCSD_RAW_MODE_U_BOOT_SECTOR是uboot在sd中的起始sector。
if (!err)
return err;
#endif
...
}
return err;
} static int mmc_load_image_raw_sector(struct mmc *mmc, unsigned long sector)
{
unsigned long count;
struct image_header *header;
int ret = ; header = (struct image_header *)(CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE -
sizeof(struct image_header));---------------------CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE是uboot.bin加载到DDR中的地址,所以header即uboot.bin往前移struct image_header一段地址。 /* read image header to find the image size & load address */
count = blk_dread(mmc_get_blk_desc(mmc), sector, , header);-------将uboot.bin第一个sector写入到header地址。
debug("hdr read sector %lx, count=%lu\n", sector, count);
...
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_SPL_LOAD_FIT) &&...
} else {
ret =mmc_load_legacy(mmc, sector, header);
} end:
if (ret) {
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_LIBCOMMON_SUPPORT
puts("mmc_load_image_raw_sector: mmc block read error\n");
#endif
return -;
} return ;
} DECLARE_GLOBAL_DATA_PTR; static int mmc_load_legacy(struct mmc *mmc, ulong sector,
struct image_header *header)
{
u32 image_size_sectors;
unsigned long count;
int ret; ret =spl_parse_image_header(header);-----------------解析header数据到spl_image中。
if (ret)
return ret; /* convert size to sectors - round up */
image_size_sectors = (spl_image.size + mmc->read_bl_len - ) /
mmc->read_bl_len;------------------------将需要读取的uboot大小转换成sector数目。 /* Read the header too to avoid extra memcpy */
count = blk_dread(mmc_get_blk_desc(mmc), sector, image_size_sectors,
(void *)(ulong)spl_image.load_addr);--------读取指定数目secotor到spl_image.load_addr中。
debug("read %x sectors to %x\n", image_size_sectors,
spl_image.load_addr);
if (count != image_size_sectors)
return -EIO; return ;
} int spl_parse_image_header(const struct image_header *header)
{
u32 header_size = sizeof(struct image_header); if (image_get_magic(header) == IH_MAGIC) {-----------------定义struct image_header的情况,从header中获取信息填充spl_header。
...
} else {
#ifdef CONFIG_SPL_PANIC_ON_RAW_IMAGE
...
#else
/* Signature not found - assume u-boot.bin */
debug("mkimage signature not found - ih_magic = %x\n",
header->ih_magic);
spl_set_header_raw_uboot();---------------------------没有通过mkimage生成uboot.bin文件情况,spl_image内容不从struct image_header中获取。
#endif
}
return ;
} void spl_set_header_raw_uboot(void)
{
spl_image.size = CONFIG_SYS_MONITOR_LEN;-----------------表示uboot最大地址。
spl_image.entry_point = CONFIG_SYS_UBOOT_START;----------uboot在DDR中起始运行地址。
spl_image.load_addr = CONFIG_SYS_TEXT_BASE;--------------uboot在DDR中加载开始地址。
spl_image.os = IH_OS_U_BOOT;-----------------------------表示下一阶段文件类型是uboot。
spl_image.name = "U-Boot";
}
__weak void __noreturn jump_to_image_no_args(struct spl_image_info *spl_image)
{
typedef void __noreturn (*image_entry_noargs_t)(void);
image_entry_noargs_t image_entry =
(image_entry_noargs_t)(unsigned long)spl_image->entry_point;---跳转到entry_point地址开始执行uboot。
debug("image entry point: 0x%X\n", spl_image->entry_point);
image_entry();
}
同样遗留问题:为什么entry_point相对load_addr往后偏移0x00000180。
跟spl同样原因,因为异常处理函数地址占用了0x180字节。所以_start()函数从0x180开始。
4. uboot加载linux分析
首先分析几个重要数据结构image_header_t、bootm_headers_t,然后分析mkimage是如何给zImage加image_header_t后变成uImage的,最后是uboot命令bootm是如何解析image_header_t并加载linux的。
4.1 重要数据结构
image_header_t是legacy镜像文件的头,bootm_headers_t是bootm命令所使用的参数,这些参数主要从image_header_t中获取。
image_header_t是静态的,bootm_headers_t是动态的,还包括其他一些执行bootm执行时所需要的参数。
struct lmb是linux内存范围以及reserved区域。
typedef struct bootm_headers {
/*
* Legacy os image header, if it is a multi component image
* then boot_get_ramdisk() and get_fdt() will attempt to get
* data from second and third component accordingly.
*/
image_header_t *legacy_hdr_os; /* image header pointer */-------原始的image_header_t数据。
image_header_t legacy_hdr_os_copy; /* header copy */----------------拷贝后的image_header_t,后续修改使用。
ulong legacy_hdr_valid;--------------------------------------------对image_header_t的检验是否通过,1表示通过。
...
#ifndef USE_HOSTCC
image_info_t os; /* os image info */
ulong ep; /* entry point of OS */-----------------------------------------镜像执行的入口点。
ulong rd_start, rd_end;/* ramdisk start/end */
char *ft_addr; /* flat dev tree address */
ulong ft_len; /* length of flat device tree */
ulong initrd_start;
ulong initrd_end;
ulong cmdline_start;
ulong cmdline_end;
bd_t *kbd;
#endif
int verify; /* getenv("verify")[0] != 'n' */----------------1表示需要对data进行crc校验。
#define BOOTM_STATE_START (0x00000001)
#define BOOTM_STATE_FINDOS (0x00000002)
#define BOOTM_STATE_FINDOTHER (0x00000004)
#define BOOTM_STATE_LOADOS (0x00000008)
#define BOOTM_STATE_RAMDISK (0x00000010)
#define BOOTM_STATE_FDT (0x00000020)
#define BOOTM_STATE_OS_CMDLINE (0x00000040)
#define BOOTM_STATE_OS_BD_T (0x00000080)
#define BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP (0x00000100)
#define BOOTM_STATE_OS_FAKE_GO (0x00000200) /* 'Almost' run the OS */
#define BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO (0x00000400)
int state;
#ifdef CONFIG_LMB
struct lmb lmb; /* for memory mgmt */
#endif
} bootm_headers_t;
typedef struct image_info {
ulong start, end; /* start/end of blob */----------------------------------------整个镜像包括image_header_t和image data的起始地址。
ulong image_start, image_len; /* start of image within blob, len of image */-----对应image减去image_header_t大小的地址,image_len对应ih_size。
ulong load; /* load addr for the image */----------------------------------------对应ih_load。
uint8_t comp, type, os; /* compression, type of image, os type */----------------对应ih_comp、ih_type、ih_os。
uint8_t arch; /* CPU architecture */---------------------------------------------对应ih_arch。
} image_info_t;
typedef struct image_header {
__be32 ih_magic; /* Image Header Magic Number */---------识别镜像的magic numver:#define IH_MAGIC 0x27051956。
__be32 ih_hcrc; /* Image Header CRC Checksum */----------指的是image_header_t这部分的crc校验值,在比较之前首先将ih_crc清空,然后对image_header_t的crc校验结果和ih_hcrc进行比较。
__be32 ih_time; /* Image Creation Timestamp */-----------镜像创建时间。
__be32 ih_size; /* Image Data Size */----------------除去image_header_t后的image大小。
__be32 ih_load; /* Data Load Address */---------镜像被加载到的地址。
__be32 ih_ep; /* Entry Point Address */----------linux从此处开始执行。
__be32 ih_dcrc; /* Image Data CRC Checksum */------------镜像除去image_header_t部分的crc校验值。
uint8_t ih_os; /* Operating System */------------镜像的OS类型,比如IH_OS_LINUX、IH_OS_LINUX等等。
uint8_t ih_arch; /* CPU architecture */--------------CPU架构类型,比如IH_ARCH_ARM、IH_ARCH_SANDBOX等等。
uint8_t ih_type; /* Image Type */----------------镜像类型,比如IH_TYPE_KERNEL、IH_TYPE_RAMDISK等等。
uint8_t ih_comp; /* Compression Type */--------------镜像压缩类型。
uint8_t ih_name[IH_NMLEN]; /* Image Name */----------镜像名称。
} image_header_t;
struct lmb_property {
phys_addr_t base;
phys_size_t size;
};
struct lmb_region {
unsigned long cnt;
phys_size_t size;
struct lmb_property region[MAX_LMB_REGIONS+];
};
struct lmb {
struct lmb_region memory;
struct lmb_region reserved;
};
4.2 uImage头生成image_header_t流程
内核从vmlinux到生成uImage,经历过Image和zImage。
从vmlinux->Image->zImage->uImage,需要经历如下基本编译命令。
cmd_arch/csky/boot/Image := csky-abiv2-linux-objcopy -O binary vmlinux arch/csky/boot/Image
cmd_arch/csky/boot/zImage := (cat arch/csky/boot/Image | gzip -n -f - > arch/csky/boot/zImage) || (rm -f arch/csky/boot/zImage ; false)
cmd_arch/csky/boot/uImage := /bin/bash ./scripts/mkuboot.sh -A sandbox -O linux -C gzip -T kernel -a -e -n 'Linux-4.9.56' -d arch/csky/boot/zImage arch/csky/boot/uImage
从vmlinux到Image,objcopy仅拷贝vmlinux的binary部分到Image;从Image到zImage,使用gzip进行压缩;从zImage到uImage,经过mkuboot.sh调用mkimage命令添加image_header_t头。
所以后面对uImage的处理是一个反向的过程:需要解析头,然后进行gunzip处理,才会得到和Image同样内容。
mkimage添加image_header_t的过程参考mkimage.c和default_image.c(apt-get source u-boot-tools获取相关源码)。
static void image_set_header(void *ptr, struct stat *sbuf, int ifd,
struct image_tool_params *params)
{
uint32_t checksum;
char *source_date_epoch;
time_t time; image_header_t * hdr = (image_header_t *)ptr; checksum = crc32(,
(const unsigned char *)(ptr +
sizeof(image_header_t)),
sbuf->st_size - sizeof(image_header_t)); source_date_epoch = getenv("SOURCE_DATE_EPOCH");
if (source_date_epoch != NULL) {
time = (time_t) strtol(source_date_epoch, NULL, ); if (gmtime(&time) == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s: SOURCE_DATE_EPOCH is not valid\n",
__func__);
time = ;
}
} else {
time = sbuf->st_mtime;
} /* Build new header */
image_set_magic(hdr, IH_MAGIC);
image_set_time(hdr, time);
image_set_size(hdr, sbuf->st_size - sizeof(image_header_t));
image_set_load(hdr, params->addr);
image_set_ep(hdr, params->ep);
image_set_dcrc(hdr, checksum);
image_set_os(hdr, params->os);
image_set_arch(hdr, params->arch);
image_set_type(hdr, params->type);
image_set_comp(hdr, params->comp); image_set_name(hdr, params->imagename); checksum = crc32(, (const unsigned char *)hdr,
sizeof(image_header_t)); image_set_hcrc(hdr, checksum);
}
4.3 bootm命令解析
do_bootm()是bootm命令的函数,调用do_bootm_states()进行不同states的顺序执行。bootm_start()进行lmb准备工作;boot_find_os()检查镜像的头,并填充到bootm_headers_t中;bootm_load_os()将镜像解压到指定地址;bootm_os_get_boot_func()根据os类型,选择合适的boot_fn;之后使用boot_fn进行各种架构相关的加载工作。
int do_bootm(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char * const argv[])
{
...
/* determine if we have a sub command */
argc--; argv++;
if (argc > ) {
char *endp; simple_strtoul(argv[], &endp, ); if ((*endp != ) && (*endp != ':') && (*endp != '#'))
return do_bootm_subcommand(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv);
} return do_bootm_states(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv, BOOTM_STATE_START |
BOOTM_STATE_FINDOS | BOOTM_STATE_FINDOTHER |
BOOTM_STATE_LOADOS |
BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP | BOOTM_STATE_OS_FAKE_GO |
BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO, &images, );
} int do_bootm_states(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc, char * const argv[],
int states, bootm_headers_t *images, int boot_progress)
{
boot_os_fn *boot_fn;
ulong iflag = ;
int ret = , need_boot_fn; images->state |= states; if (states & BOOTM_STATE_START)
ret =bootm_start(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv); if (!ret && (states & BOOTM_STATE_FINDOS))
ret =bootm_find_os(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv); if (!ret && (states & BOOTM_STATE_FINDOTHER)) {
ret = bootm_find_other(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv);
argc = ; /* consume the args */
} /* Load the OS */
if (!ret && (states & BOOTM_STATE_LOADOS)) {
ulong load_end; iflag = bootm_disable_interrupts();
ret = bootm_load_os(images, &load_end, );
if (ret == )
lmb_reserve(&images->lmb, images->os.load,
(load_end - images->os.load));
else if (ret && ret != BOOTM_ERR_OVERLAP)
goto err;
else if (ret == BOOTM_ERR_OVERLAP)
ret = ;
#if defined(CONFIG_SILENT_CONSOLE) && !defined(CONFIG_SILENT_U_BOOT_ONLY)
if (images->os.os == IH_OS_LINUX)
fixup_silent_linux();
#endif
}
...
boot_fn = bootm_os_get_boot_func(images->os.os);----------------------------------根据os类型找到对应的boot_fn,对于linux即是do_bootm_linux()。
need_boot_fn = states & (BOOTM_STATE_OS_CMDLINE |
BOOTM_STATE_OS_BD_T | BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP |
BOOTM_STATE_OS_FAKE_GO | BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO);
...
/* Call various other states that are not generally used */
if (!ret && (states & BOOTM_STATE_OS_CMDLINE))------------------------------------调用boot_fn()执行不同state的功能。
ret = boot_fn(BOOTM_STATE_OS_CMDLINE, argc, argv, images);
if (!ret && (states & BOOTM_STATE_OS_BD_T))
ret = boot_fn(BOOTM_STATE_OS_BD_T, argc, argv, images);
if (!ret && (states & BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP))
ret = boot_fn(BOOTM_STATE_OS_PREP, argc, argv, images);
...
if (!ret && (states & BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO))
ret = boot_selected_os(argc, argv, BOOTM_STATE_OS_GO,
images, boot_fn);-----------------------------------------------------最后一步,切换到linux。
...
return ret;
}
bootm_start()主要更新struct lmb相关的内存数据以及reserved区域。
static int bootm_start(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc,
char * const argv[])
{
memset((void *)&images, , sizeof(images));
images.verify = getenv_yesno("verify");-----------------------------是否需要verify进行checksum。 boot_start_lmb(&images);--------------------------------------------填充images->lmb,包括总内存memory和预留内存reserved。 bootstage_mark_name(BOOTSTAGE_ID_BOOTM_START, "bootm_start");
images.state = BOOTM_STATE_START; return ;
} static void boot_start_lmb(bootm_headers_t *images)
{
ulong mem_start;
phys_size_t mem_size; lmb_init(&images->lmb); mem_start = getenv_bootm_low();
mem_size = getenv_bootm_size();-------------------------------------分别从环境变量中获取bootm_low和bootm_size两个变量。 lmb_add(&images->lmb, (phys_addr_t)mem_start, mem_size);------------增加mem region区域到数据结构中。 arch_lmb_reserve(&images->lmb);
board_lmb_reserve(&images->lmb);
}
image_get_kernel()对image文件进行验证,并输出相关信息。
Image Name: Linux-4.9.
Image Type: Sandbox Linux Kernel Image (gzip compressed)
Data Size: Bytes = 4.7 MiB
Load Address:
Entry Point:
Verifying Checksum ... OK
Uncompressing Kernel Image ... OK
bootm_find_os()主要对image_header_t进行检查,并进行镜像data的校验,填充bootm命令运行所需要的数据结构bootm_headers_t。
static int bootm_find_os(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc,
char * const argv[])
{
const void *os_hdr;
bool ep_found = false;
int ret; /* get kernel image header, start address and length */
os_hdr =boot_get_kernel(cmdtp, flag, argc, argv,
&images, &images.os.image_start, &images.os.image_len);-----返回值指向image_header_t,同时获取了镜像数据开始和大小。
...
/* get image parameters */
switch (genimg_get_format(os_hdr)) {--------------------------------os_hdr是镜像header开始,分别判断不同格式的magic number,比如image_header_t、fdt_header、andr_img_hdr。
#if defined(CONFIG_IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY)
case IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY:
images.os.type = image_get_type(os_hdr);------------------------这些数据参照bootm_headers_t和image_header_t两个数据结构。
images.os.comp = image_get_comp(os_hdr);
images.os.os = image_get_os(os_hdr); images.os.end = image_get_image_end(os_hdr);
images.os.load = image_get_load(os_hdr);
images.os.arch = image_get_arch(os_hdr);
break;
#endif
...
}
...
if (images.os.type == IH_TYPE_KERNEL_NOLOAD) {
images.os.load = images.os.image_start;
images.ep += images.os.load;
} images.os.start = map_to_sysmem(os_hdr); return ;
} static const void *boot_get_kernel(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc,
char * const argv[], bootm_headers_t *images,
ulong *os_data, ulong *os_len)
{
#if defined(CONFIG_IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY)
image_header_t *hdr;
#endif
ulong img_addr;
const void *buf;
const char *fit_uname_config = NULL;
const char *fit_uname_kernel = NULL;
#if IMAGE_ENABLE_FIT
int os_noffset;
#endif img_addr = genimg_get_kernel_addr_fit(argc < ? NULL : argv[],
&fit_uname_config,
&fit_uname_kernel);------------------bootm的入参包括了镜像文件的加载地址。 bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_MAGIC); /* copy from dataflash if needed */
img_addr = genimg_get_image(img_addr);---------------------如果没有定义CONFIG_HAS_DATAFLASH,返回的是原地址。 /* check image type, for FIT images get FIT kernel node */
*os_data = *os_len = ;
buf = map_sysmem(img_addr, );
switch (genimg_get_format(buf)) {
#if defined(CONFIG_IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY)
case IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY:
printf("## Booting kernel from Legacy Image at %08lx ...\n",
img_addr);
hdr = image_get_kernel(img_addr, images->verify);------主要对镜像的image_header_t进行magic number、header crc、data crc检查等。
if (!hdr)
return NULL;
bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_IMAGETYPE); /* get os_data and os_len */
switch (image_get_type(hdr)) {
case IH_TYPE_KERNEL:
case IH_TYPE_KERNEL_NOLOAD:
*os_data = image_get_data(hdr);
*os_len = image_get_data_size(hdr);
break;
...
} memmove(&images->legacy_hdr_os_copy, hdr,
sizeof(image_header_t)); images->legacy_hdr_os = hdr; images->legacy_hdr_valid = ;---------------------------表明image_header_t检查通过。
bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_DECOMP_IMAGE);
break;
#endif
...
default:
printf("Wrong Image Format for %s command\n", cmdtp->name);
bootstage_error(BOOTSTAGE_ID_FIT_KERNEL_INFO);
return NULL;
} debug(" kernel data at 0x%08lx, len = 0x%08lx (%ld)\n",
*os_data, *os_len, *os_len); return buf;
} int genimg_get_format(const void *img_addr)
{
#if defined(CONFIG_IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY)
const image_header_t *hdr; hdr = (const image_header_t *)img_addr;
if (image_check_magic(hdr))
return IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY;
#endif
...
return IMAGE_FORMAT_INVALID;
} static image_header_t *image_get_kernel(ulong img_addr, int verify)
{
image_header_t *hdr = (image_header_t *)img_addr; if (!image_check_magic(hdr)) {---------------------------------检查ih_magic。
puts("Bad Magic Number\n");
bootstage_error(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_MAGIC);
return NULL;
}
bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_HEADER); if (!image_check_hcrc(hdr)) {----------------------------------检查ih_hcrc,检查之前先拷贝一个image_header_t,然后清空ih_hcrc,再进行crc校验对比。
puts("Bad Header Checksum\n");
bootstage_error(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_HEADER);
return NULL;
} bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_CHECKSUM);
image_print_contents(hdr);-------------------------------------打印镜像名称、类型、大小等等信息。 if (verify) {--------------------------------------------------进行进行data部分crc校验。
puts(" Verifying Checksum ... ");
if (!image_check_dcrc(hdr)) {
printf("Bad Data CRC\n");
bootstage_error(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_CHECKSUM);
return NULL;
}
puts("OK\n");
}
bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_ARCH); if (!image_check_target_arch(hdr)) {---------------------------ih_arch检查。
printf("Unsupported Architecture 0x%x\n", image_get_arch(hdr));
bootstage_error(BOOTSTAGE_ID_CHECK_ARCH);
return NULL;
}
return hdr;
} void image_print_contents(const void *ptr)
{
const image_header_t *hdr = (const image_header_t *)ptr;
const char __maybe_unused *p; p = IMAGE_INDENT_STRING;
printf("%sImage Name: %.*s\n", p, IH_NMLEN, image_get_name(hdr));
if (IMAGE_ENABLE_TIMESTAMP) {
printf("%sCreated: ", p);
genimg_print_time((time_t)image_get_time(hdr));
}
printf("%sImage Type: ", p);
image_print_type(hdr);
printf("%sData Size: ", p);
genimg_print_size(image_get_data_size(hdr));
printf("%sLoad Address: %08x\n", p, image_get_load(hdr));
printf("%sEntry Point: %08x\n", p, image_get_ep(hdr)); if (image_check_type(hdr, IH_TYPE_MULTI) ||
image_check_type(hdr, IH_TYPE_SCRIPT)) {
int i;
ulong data, len;
ulong count = image_multi_count(hdr); printf("%sContents:\n", p);
for (i = ; i < count; i++) {
image_multi_getimg(hdr, i, &data, &len); printf("%s Image %d: ", p, i);
genimg_print_size(len); if (image_check_type(hdr, IH_TYPE_SCRIPT) && i > ) {
printf("%s Offset = 0x%08lx\n", p, data);
}
}
}
}
bootm_find_other()尝试从boot文件中解析出ramdisk等部分。
static int bootm_find_other(cmd_tbl_t *cmdtp, int flag, int argc,
char * const argv[])
{
if (((images.os.type == IH_TYPE_KERNEL) ||
(images.os.type == IH_TYPE_KERNEL_NOLOAD) ||
(images.os.type == IH_TYPE_MULTI)) &&
(images.os.os == IH_OS_LINUX ||
images.os.os == IH_OS_VXWORKS))
returnbootm_find_images(flag, argc, argv); return ;
} int bootm_find_images(int flag, int argc, char * const argv[])
{
int ret; /* find ramdisk */
ret = boot_get_ramdisk(argc, argv, &images, IH_INITRD_ARCH,
&images.rd_start, &images.rd_end);
if (ret) {
puts("Ramdisk image is corrupt or invalid\n");
return ;
}
...
return ;
} int boot_get_ramdisk(int argc, char * const argv[], bootm_headers_t *images,
uint8_t arch, ulong *rd_start, ulong *rd_end)
{
ulong rd_addr, rd_load;
ulong rd_data, rd_len;
#if defined(CONFIG_IMAGE_FORMAT_LEGACY)
const image_header_t *rd_hdr;
#endif
void *buf;
#ifdef CONFIG_SUPPORT_RAW_INITRD
char *end;
#endif const char *select = NULL; *rd_start = ;
*rd_end = ; if (argc >= )
select = argv[]; /*
* Look for a '-' which indicates to ignore the
* ramdisk argument
*/
if (select && strcmp(select, "-") == ) {
debug("## Skipping init Ramdisk\n");
rd_len = rd_data = ;
} else if (select || genimg_has_config(images)) {
...if (!rd_data) {
debug("## No init Ramdisk\n");
} else {
*rd_start = rd_data;
*rd_end = rd_data + rd_len;
}
debug(" ramdisk start = 0x%08lx, ramdisk end = 0x%08lx\n",
*rd_start, *rd_end); return ;
}
bootm_load_os()主要是将镜像的data部分调用os.comp解压算法从images.os.image_start解压到images.os.load。
static int bootm_load_os(bootm_headers_t *images, unsigned long *load_end,
int boot_progress)
{
image_info_t os = images->os;
ulong load = os.load;
ulong blob_start = os.start;
ulong blob_end = os.end;
ulong image_start = os.image_start;
ulong image_len = os.image_len;
bool no_overlap;
void *load_buf, *image_buf;
int err; load_buf = map_sysmem(load, );------------------------------os.image_start是解压前镜像存放地址,os.load是解压后镜像存放地址。
image_buf = map_sysmem(os.image_start, image_len);-----------镜像的存放地址为0x86000000,image_header_t的大小为64字节,所以os.image_start地址为0x86000040。 err =bootm_decomp_image(os.comp, load, os.image_start, os.type,
load_buf, image_buf, image_len,
CONFIG_SYS_BOOTM_LEN, load_end);---------------image_buf是解压前数据存放处,load_buf是解压后数据存放处;load是解压数据起始地址,load_end是解压后数据末地址。
if (err) {
bootstage_error(BOOTSTAGE_ID_DECOMP_IMAGE);
return err;
}
flush_cache(load, ALIGN(*load_end - load, ARCH_DMA_MINALIGN)); debug(" kernel loaded at 0x%08lx, end = 0x%08lx\n", load, *load_end);
bootstage_mark(BOOTSTAGE_ID_KERNEL_LOADED);------------------数据已经被解压加载到指定地址,可以执行。 no_overlap = (os.comp == IH_COMP_NONE && load == image_start);
...
return ;
} int bootm_decomp_image(int comp, ulong load, ulong image_start, int type,
void *load_buf, void *image_buf, ulong image_len,
uint unc_len, ulong *load_end)
{
...
switch (comp) {
...
#ifdef CONFIG_GZIP
case IH_COMP_GZIP: {
ret = gunzip(load_buf, unc_len, image_buf, &image_len);--调用具体解压算法进行解压缩。
break;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_GZIP */...
}
...
*load_end = load + image_len; puts("OK\n"); return ;
}
bootm_os_get_boot_func()根据os的类型,执行kernel的entry point。
对于Linux来说就是do_bootm_linux,根据架构进行准备必要的准备,然后跳转到entry point,将CPU执行权交给Linux。
boot_os_fn *bootm_os_get_boot_func(int os)
{
returnboot_os[os];
} static boot_os_fn *boot_os[] = {
[IH_OS_U_BOOT] = do_bootm_standalone,
#ifdef CONFIG_BOOTM_LINUX
[IH_OS_LINUX] =do_bootm_linux,
#endif...
}; int do_bootm_linux(int flag, int argc, char * const argv[],
bootm_headers_t *images)
{
void (*theKernel)(int magic, void * params);
char *tmp;
unsigned int dtb_load_addr; theKernel = (void (*)(int, void *))images->ep;----------------images->ep是uboot跳转到linux的入口点。
printf("\nStarting kernel ... \n\n"); disable_interrupts();
flush_cache(,);
theKernel (0x20150401, (void *)dtb_load_addr);----------------跳转到linux,两个入参。
return ;
}
5. 小结
从以上分析可知,每一个阶段启动下一阶段都是通过识别头开始的。
mksheader给spl加sb_header头,bootrom进行解析;mkimage给uboot加image_header_t头,spl进行解析;mkimage给kernel加image_header_t头,uboot进行解析。
都是通过工具在程序代码之前加上一个头,然后上一级工具进行解析加载。
bootrom/spl/uboot/linux逐级加载是如何实现的?的更多相关文章
- QEMU 运行uboot,动态加载内核与文件系统
背景 上一讲我们完成了 编译 QEMU 以及简单地做了仿真.这一讲在 启动uboot 的基础上进行,以加强对于 运行地址,加载地址等理解. 有关资料: uboot 与 代码重定位 有这样的约定,ubo ...
- 驱动开发学习笔记. 0.07 Uboot链接地址 加载地址 和 链接脚本地址
驱动开发学习笔记. 0.07 Uboot链接地址 加载地址 和 链接脚本地址 最近重新看了乾龙_Heron的<ARM 上电启动及 Uboot 代码分析>(下简称<代码分析>) ...
- 【easyui】treegrid逐级加载源码
当初看这源码的目的是: 1.treegrid是怎么实现逐级加载树结构的. 解: 见demo,主要就是点击节点的时候会请求后台. 2.treegrid加载后,第二次展开节点会不会再次请求后台. 解:第二 ...
- Linux内核加载全流程
无论是Linux还是Windows,在加电后的第一步都是先运行BIOS(Basic Input/Output System)程序——不知道是不是所以的电脑系统都是如此.BIOS保存在主板上的一个non ...
- linux配置加载顺序
linux加载配置项时通过下面方式 首先 加载/etc/profile配置 然后 加载/ect/profile.d/下面的所有脚本 然后 加载当前用户 .bash_profile 然后 加载.bash ...
- Linux firmware 加载【转】
转自:http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-22028680-id-3157922.html 1.request_firmware在内核使用,需要文件系统支持,就是说,启动的时候 ...
- [ARM-Linux开发]Linux下加载.ko驱动模块的两种方法:insmod与modprobe
假设要加载的驱动程序模块名为SHT21.ko 加载驱动模块 方法一: 进入SHT21.ko驱动模块文件所在的目录,然后直接 insmod SHT21.ko 即可 方法二: 将SHT21.ko文 ...
- linux C 加载so文件 指定路径
在Linux C中动态加载.so文件用dlopen("libdemo.so", RTLD_NOW); 但是默认的so搜索目录不包括当前程序目录,所以必须复制到系统的so目录 才能运 ...
- Linux开机加载过程
2015-01-06 10:29:13 目录 1 开机加载简介 2 常规加载流程 2.1 加载BIOS 2.2 读取MBR 2.3 boot loader 2.4 加载内核 2.5 init依据i ...
随机推荐
- 让终端更好看--Ubuntu OhMyZsh配置指南
查看shell列表 cat /etc/shells 如果发现没有zsh就安装 安装zsh sudo apt install zsh 设置默认shell chsh -s $(which zsh) 重启主 ...
- 2019icpc银川站 复现赛
打了计蒜客上的银川重现赛,总体感觉难度上确实比平时区域赛要低上一些. 这里补一下F题和G题的思路和代码. upd:I题也补了,理解差不多都在注释里. F题 做法,玩一下n=10的样例就出 ...
- Prometheus学习系列(二)之Prometheus FIRST STEPS
前言 本文来自Prometheus官网手册 和 Prometheus简介 说明 Prometheus是一个监控平台,通过在监控目标上的HTTP端点来收集受监控目标的指标.本指南将向您展示如何使用Pro ...
- Penetration testing“Linux install Nessus”
Ax_Download www.tenable.com/products/nessus-home,need sent email. Bx_Install su ls dpkg -i [filename ...
- 使用vsphere client 克隆虚拟机的具体操作步骤
采用 VMWare ESXi6.0,使用ESXi经常会遇到这样的问题,需要建立多个虚拟机,都是一样的操作系统,但是如果一台台装效率太低. VMware ESXi.VMware vCenter Serv ...
- oracle 查询两个字段值相同的记录
select A.* from tb_mend_enrol A, (select A.Typeid, A.address from tb_mend_enrol A group by A.Typeid, ...
- Python3 中的Number
Python3 支持 int.float.bool.complex(复数). 在Python 3里,只有一种整数类型 int,表示为长整型,没有 python2 中的 Long. 像大多数语言一样,数 ...
- Centos8 配置静态IP
安装centos 8之后,重启启动网络时,会出现以下报错 报错信息如下: Failed to start network.service: Unit network.service not found ...
- 斐波那契数列(Java)
一.什么是斐波那契数列 斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence),又称黄金分割数列.因数学家列昂纳多·斐波那契(Leonardoda Fibonacci)以兔子繁殖为例子而引入,故又称为& ...
- 改变JAVA窗体属性的操作方法
在本篇内容里小编给大家详细分析了关于改变JAVA窗体属性的操作方法和步骤,需要的朋友们学习下. 若将JDK版本升级到最新版本,Java窗体就可以简单实现窗体的透明效果,用户可以通过拉动滑块(Slide ...
