使用OpenMP加快OpenCV图像处理性能 | speed up opencv image processing with openmp
本文首发于个人博客https://kezunlin.me/post/7a6ba82e/,欢迎阅读!
speed up opencv image processing with openmp
Series
- Part 1: compile opencv on ubuntu 16.04
- Part 2: compile opencv with CUDA support on windows 10
- Part 3: opencv mat for loop
- Part 4: speed up opencv image processing with openmp
Guide
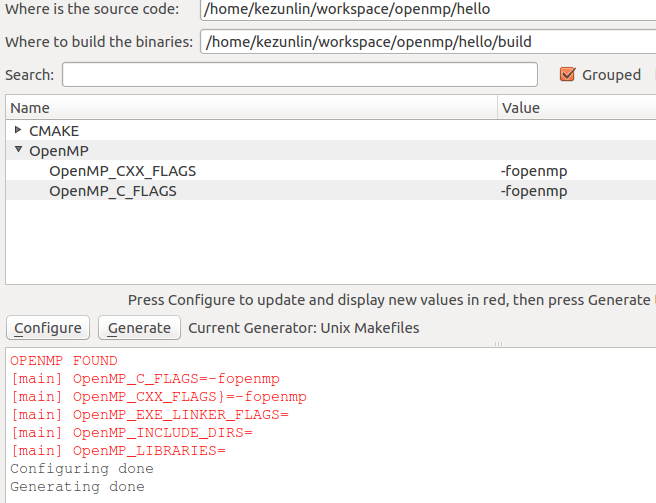
config
- linux/window: cmake with
CXX_FLAGS=-fopenmp - window VS: VS also support openmp,
C/C++| Language | /openmp
usage
#include <omp.h>
#pragma omp parallel for
for loop ...
code
#include <iostream>
#include <omp.h>
int main()
{
omp_set_num_threads(4);
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
/*
i = 0, I am Thread 0
i = 1, I am Thread 0
i = 4, I am Thread 2
i = 5, I am Thread 2
i = 6, I am Thread 3
i = 7, I am Thread 3
i = 2, I am Thread 1
i = 3, I am Thread 1
*/
CMakeLists.txt
use CXX_FLAGS=-fopenmp in CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.0)
project(hello)
find_package(OpenMP REQUIRED)
if(OPENMP_FOUND)
message("OPENMP FOUND")
message([main] " OpenMP_C_FLAGS=${OpenMP_C_FLAGS}") # -fopenmp
message([main] " OpenMP_CXX_FLAGS}=${OpenMP_CXX_FLAGS}") # -fopenmp
message([main] " OpenMP_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS=${OpenMP_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS}") # ***
# no use for xxx_INCLUDE_DIRS and xxx_libraries for OpenMP
message([main] " OpenMP_INCLUDE_DIRS=${OpenMP_INCLUDE_DIRS}") # ***
message([main] " OpenMP_LIBRARIES=${OpenMP_LIBRARIES}") # ***
set(CMAKE_C_FLAGS "${CMAKE_C_FLAGS} ${OpenMP_C_FLAGS}")
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} ${OpenMP_CXX_FLAGS}")
set(CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS "${CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS} ${OpenMP_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS}")
endif()
add_executable(hello hello.cpp)
#target_link_libraries(hello xxx)
options
or use g++ hello.cpp -fopenmp to compile
view demo
list dynamic dependencies (ldd)
ldd hello
linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007ffd71365000)
libstdc++.so.6 => /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libstdc++.so.6 (0x00007f8ea7f00000)
libgomp.so.1 => /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgomp.so.1 (0x00007f8ea7cde000)
libc.so.6 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x00007f8ea7914000)
libm.so.6 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libm.so.6 (0x00007f8ea760b000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f8ea8282000)
libgcc_s.so.1 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgcc_s.so.1 (0x00007f8ea73f5000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libdl.so.2 (0x00007f8ea71f1000)
libpthread.so.0 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libpthread.so.0 (0x00007f8ea6fd4000)
libgomp.so.1 => /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libgomp.so.1
list names (nm)
nm hello
0000000000602080 B __bss_start
0000000000602190 b completed.7594
U __cxa_atexit@@GLIBC_2.2.5
0000000000602070 D __data_start
0000000000602070 W data_start
0000000000400b00 t deregister_tm_clones
0000000000400b80 t __do_global_dtors_aux
0000000000601df8 t __do_global_dtors_aux_fini_array_entry
0000000000602078 d __dso_handle
0000000000601e08 d _DYNAMIC
0000000000602080 D _edata
0000000000602198 B _end
0000000000400d44 T _fini
0000000000400ba0 t frame_dummy
0000000000601de8 t __frame_dummy_init_array_entry
0000000000400f18 r __FRAME_END__
0000000000602000 d _GLOBAL_OFFSET_TABLE_
0000000000400c28 t _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
w __gmon_start__
0000000000400d54 r __GNU_EH_FRAME_HDR
U GOMP_parallel@@GOMP_4.0
U __gxx_personality_v0@@CXXABI_1.3
00000000004009e0 T _init
0000000000601df8 t __init_array_end
0000000000601de8 t __init_array_start
0000000000400d50 R _IO_stdin_used
w _ITM_deregisterTMCloneTable
w _ITM_registerTMCloneTable
0000000000601e00 d __JCR_END__
0000000000601e00 d __JCR_LIST__
w _Jv_RegisterClasses
0000000000400d40 T __libc_csu_fini
0000000000400cd0 T __libc_csu_init
U __libc_start_main@@GLIBC_2.2.5
0000000000400bc6 T main
0000000000400c3d t main._omp_fn.0
U omp_get_num_threads@@OMP_1.0
U omp_get_thread_num@@OMP_1.0
0000000000400b40 t register_tm_clones
0000000000400ad0 T _start
0000000000602080 d __TMC_END__
0000000000400bea t _Z41__static_initialization_and_destruction_0ii
U _ZNSolsEPFRSoS_E@@GLIBCXX_3.4
U _ZNSt8ios_base4InitC1Ev@@GLIBCXX_3.4
U _ZNSt8ios_base4InitD1Ev@@GLIBCXX_3.4
0000000000602080 B _ZSt4cout@@GLIBCXX_3.4
U _ZSt4endlIcSt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_ostreamIT_T0_ES6_@@GLIBCXX_3.4
0000000000602191 b _ZStL8__ioinit
U _ZStlsISt11char_traitsIcEERSt13basic_ostreamIcT_ES5_c@@GLIBCXX_3.4
omp_get_num_threads,omp_get_thread_num
OpenMP Introduction
OpenMP的指令格式
#pragma omp directive [clause[clause]…]
#pragma omp parallel private(i, j)
parallelis directive,privateis clause
directive
- parallel,用在一个代码段之前,表示这段代码将被多个线程并行执行
- for,用于for循环之前,将循环分配到多个线程中并行执行,必须保证每次循环之间无相关性。
- parallel for, parallel 和 for语句的结合,也是用在一个for循环之前,表示for循环的代码将被多个线程并行执行。
- sections,用在可能会被并行执行的代码段之前
- parallel sections,parallel和sections两个语句的结合
- critical,用在一段代码临界区之前
- single,用在一段只被单个线程执行的代码段之前,表示后面的代码段将被单线程执行。
- flush,
- barrier,用于并行区内代码的线程同步,所有线程执行到barrier时要停止,直到所有线程都执行到barrier时才继续往下执行。
- atomic,用于指定一块内存区域被制动更新
- master,用于指定一段代码块由主线程执行
- ordered, 用于指定并行区域的循环按顺序执行
- threadprivate, 用于指定一个变量是线程私有的。
parallel for
OpenMP 对可以多线程化的循环有如下五个要求:
- 循环的变量变量(就是i)必须是有符号整形,其他的都不行。
- 循环的比较条件必须是< <= > >=中的一种
- 循环的增量部分必须是增减一个不变的值(即每次循环是不变的)。
- 如果比较符号是< <=,那每次循环i应该增加,反之应该减小
- 循环必须是没有奇奇怪怪的东西,不能从内部循环跳到外部循环,goto和break只能在循环内部跳转,异常必须在循环内部被捕获。
如果你的循环不符合这些条件,那就只好改写了.
avoid race condition
当一个循环满足以上五个条件时,依然可能因为数据依赖而不能够合理的并行化。当两个不同的迭代之间的数据存在依赖关系时,就会发生这种情况。
// 假设数组已经初始化为1
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 2; i < 10; i++) {
factorial[i] = i * factorial[i-1];
}
ERROR.
omp_set_num_threads(4);
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
same as
omp_set_num_threads(4);
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
parallel sections
#pragma omp parallel sections # parallel
{
#pragma omp section # thread-1
{
function1();
}
#pragma omp section # thread-2
{
function2();
}
}
parallel sections里面的内容要并行执行,具体分工上,每个线程执行其中的一个section
clause
- private, 指定每个线程都有它自己的变量私有副本。
- firstprivate,指定每个线程都有它自己的变量私有副本,并且变量要被继承主线程中的初值。
- lastprivate,主要是用来指定将线程中的私有变量的值在并行处理结束后复制回主线程中的对应变量。
- reduce,用来指定一个或多个变量是私有的,并且在并行处理结束后这些变量要执行指定的运算。
- nowait,忽略指定中暗含的等待
- num_threads,指定线程的个数
- schedule,指定如何调度for循环迭代
- shared,指定一个或多个变量为多个线程间的共享变量
- ordered,用来指定for循环的执行要按顺序执行
- copyprivate,用于single指令中的指定变量为多个线程的共享变量
- copyin,用来指定一个threadprivate的变量的值要用主线程的值进行初始化。
- default,用来指定并行处理区域内的变量的使用方式,缺省是shared
private
#pragma omp parallel
{
int x; // private to each thread ? YES
}
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; ++i)
{
int x; // private to each thread ? YES
}
local variables are automatically private to each thread.
The reason for the existence of theprivateclause is so that you don't have to change your code.
see here
The only way to parallelize the following code without the private clause
int i,j;
#pragma omp parallel for private(j)
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//do something
}
}
is to change the code. For example like this:
int i;
#pragma omp parallel for
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int j; // mark j as local variable to worker thread
for(j = 0; j < n; j++) {
//do something
}
}
reduction
例如累加
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += array[i]; // sum需要私有才能实现并行化,但是又必须是公有的才能产生正确结果
}
上面的这个程序里,sum公有或者私有都不对,为了解决这个问题,OpenMP 提供了reduction语句;
int sum = 0;
#pragma omp parallel for reduction(+:sum)
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
sum += array[i];
}
内部实现中,OpenMP为每个线程提供了私有的sum变量(初始化为0),当线程退出时,OpenMP再把每个线程私有的sum加在一起得到最终结果。
num_threads
num_threads(4) same as omp_set_num_threads(4)
// `num_threads(4)` same as `omp_set_num_threads(4)`
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(4)
{
printf("Hello, I am Thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num()); // 0,1,2,3,
}
schedule
format
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(kind [, chunk size])
kind: see openmp-loop-scheduling and whats-the-difference-between-static-and-dynamic-schedule-in-openmp
static: Divide the loop into equal-sized chunks or as equal as possible in the case where the number of loop iterations is not evenly divisible by the number of threads multiplied by the chunk size.By default, chunk size is loop_count/number_of_threads.dynamic: Use the internal work queue to give a chunk-sized block of loop iterations to each thread. When a thread is finished, it retrieves the next block of loop iterations from the top of the work queue.By default, the chunk size is 1. Be careful when using this scheduling type because of the extra overhead involved.guided: special case ofdynamic. Similar to dynamic scheduling, but the chunk size starts off large and decreases to better handle load imbalance between iterations. The optional chunk parameter specifies them minimum size chunk to use.By default the chunk size is approximately loop_count/number_of_threads.auto: When schedule (auto) is specified, the decision regardingscheduling is delegated to the compiler. The programmer gives the compiler the freedom to choose any possible mapping of iterations to threads in the team.runtime: with ENVOMP_SCHEDULE, we can test 3 types scheduling:static,dynamic,guidedwithout recompile the code.
The optional parameter (chunk), when specified, must be a positive integer.
默认情况下,OpenMP认为所有的循环迭代运行的时间都是一样的,这就导致了OpenMP会把不同的迭代等分到不同的核心上,并且让他们分布的尽可能减小内存访问冲突,这样做是因为循环一般会线性地访问内存, 所以把循环按照前一半后一半的方法分配可以最大程度的减少冲突. 然而对内存访问来说这可能是最好的方法, 但是对于负载均衡可能并不是最好的方法, 而且反过来最好的负载均衡可能也会破坏内存访问. 因此必须折衷考虑.
内存访问vs负载均衡,需要折中考虑。
openmp默认使用的schedule是取决于编译器实现的。gcc默认使用schedule(dynamic,1),也就是动态调度并且块大小是1.
线程数不要大于实际核数,否则就是oversubscription
isprime可以对dynamic做一个展示。
functions
omp_get_num_procs, 返回运行本线程的多处理机的处理器个数。omp_set_num_threads, 设置并行执行代码时的线程个数omp_get_num_threads, 返回当前并行区域中的活动线程(active thread)个数,如果没有设置,默认为1。omp_get_thread_num, 返回线程号(0,1,2,...)omp_init_lock, 初始化一个简单锁omp_set_lock, 上锁操作omp_unset_lock, 解锁操作,要和omp_set_lock函数配对使用omp_destroy_lock,关闭一个锁,要和omp_init_lock函数配对使用
check cpu
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep name | cut -f2 -d: | uniq -c
8 Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7700HQ CPU @ 2.80GHz
omp_get_num_procsreturn8.
OpenMP Example
omp_get_num_threads
void test0()
{
printf("I am Thread %d, omp_get_num_threads = %d, omp_get_num_procs = %d\n",
omp_get_thread_num(),
omp_get_num_threads(),
omp_get_num_procs()
);
}
/*
I am Thread 0, omp_get_num_threads = 1, omp_get_num_procs = 8
*/
parallel
case1
void test1()
{
// `parallel`,用在一个代码段之前,表示这段代码block将被多个线程并行执行
// if not set `omp_set_num_threads`, by default use `omp_get_num_procs`, eg 8
//omp_set_num_threads(4); // 设置线程数,一般设置的线程数不超过CPU核心数
#pragma omp parallel
{
printf("Hello, I am Thread %d, omp_get_num_threads = %d, omp_get_num_procs = %d\n",
omp_get_thread_num(),
omp_get_num_threads(),
omp_get_num_procs()
);
}
}
/*
Hello, I am Thread 3, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 7, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 1, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 6, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 5, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 4, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 2, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 0, omp_get_num_threads = 8, omp_get_num_procs = 8
*/
case2
void test1_2()
{
// `parallel`,用在一个代码段之前,表示这段代码block将被多个线程并行执行
omp_set_num_threads(4); // 设置线程数,一般设置的线程数不超过CPU核心数
#pragma omp parallel
{
printf("Hello, I am Thread %d, omp_get_num_threads = %d, omp_get_num_procs = %d\n",
omp_get_thread_num(),
omp_get_num_threads(),
omp_get_num_procs()
);
//std::cout << "Hello" << ", I am Thread " << omp_get_thread_num() << std::endl; // 0,1,2,3
}
}
/*
# use `cout`
HelloHello, I am Thread Hello, I am Thread , I am Thread Hello, I am Thread 2
1
3
0
*/
/* use `printf`
Hello, I am Thread 0, omp_get_num_threads = 4, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 3, omp_get_num_threads = 4, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 1, omp_get_num_threads = 4, omp_get_num_procs = 8
Hello, I am Thread 2, omp_get_num_threads = 4, omp_get_num_procs = 8
*/
notice the difference of
std::coutandprintf
case3
void test1_3()
{
// `parallel`,用在一个代码段之前,表示这段代码block将被多个线程并行执行
omp_set_num_threads(4);
#pragma omp parallel
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
/*
i = 0, I am Thread 1
i = 1, I am Thread 1
i = 2, I am Thread 1
i = 0, I am Thread 3
i = 1, I am Thread 3
i = 2, I am Thread 3
i = 0, I am Thread 2
i = 1, I am Thread 2
i = 2, I am Thread 2
i = 0, I am Thread 0
i = 1, I am Thread 0
i = 2, I am Thread 0
*/
omp parallel/for
omp parallel + omp for
void test2()
{
// `omp parallel` + `omp for` === `omp parallel for`
// `omp for` 用在一个for循环之前,表示for循环的每一次iteration将被分配到多个线程并行执行。
// 此处8次iteration被平均分配到4个thread执行,每个thread执行2次iteration
/*
iter #thread id
0,1 0
2,3 1
4,5 2
6,7 3
*/
omp_set_num_threads(4);
#pragma omp parallel
{
#pragma omp for
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
}
/*
i = 0, I am Thread 0
i = 1, I am Thread 0
i = 2, I am Thread 1
i = 3, I am Thread 1
i = 6, I am Thread 3
i = 7, I am Thread 3
i = 4, I am Thread 2
i = 5, I am Thread 2
*/
omp parallel for
void test2_2()
{
// `parallel for`,用在一个for循环之前,表示for循环的每一次iteration将被分配到多个线程并行执行。
// 此处8次iteration被平均分配到4个thread执行,每个thread执行2次iteration
/*
iter #thread id
0,1 0
2,3 1
4,5 2
6,7 3
*/
omp_set_num_threads(4);
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
/*
i = 0, I am Thread 0
i = 1, I am Thread 0
i = 4, I am Thread 2
i = 5, I am Thread 2
i = 6, I am Thread 3
i = 7, I am Thread 3
i = 2, I am Thread 1
i = 3, I am Thread 1
*/
sqrt case
void base_sqrt()
{
boost::posix_time::ptime pt1 = boost::posix_time::microsec_clock::local_time();
float a = 0;
for (int i=0;i<1000000000;i++)
a = sqrt(i);
boost::posix_time::ptime pt2 = boost::posix_time::microsec_clock::local_time();
int64_t cost = (pt2 - pt1).total_milliseconds();
printf("Worker Thread = %d, cost = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), cost);
}
void test2_3()
{
boost::posix_time::ptime pt1 = boost::posix_time::microsec_clock::local_time();
omp_set_num_threads(8);
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i=0;i<8;i++)
base_sqrt();
boost::posix_time::ptime pt2 = boost::posix_time::microsec_clock::local_time();
int64_t cost = (pt2 - pt1).total_milliseconds();
printf("Main Thread = %d, cost = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), cost);
}
sequential
time ./demo_openmp
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1746 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1711 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1736 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1734 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1750 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1718 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1769 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1732 ms
Main Thread = 0, cost = 13899 ms
./demo_openmp 13.90s user 0.00s system 99% cpu 13.903 total
parallel
time ./demo_openmp
Worker Thread = 1, cost = 1875 ms
Worker Thread = 6, cost = 1876 ms
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1876 ms
Worker Thread = 7, cost = 1876 ms
Worker Thread = 5, cost = 1877 ms
Worker Thread = 3, cost = 1963 ms
Worker Thread = 4, cost = 2000 ms
Worker Thread = 2, cost = 2027 ms
Main Thread = 0, cost = 2031 ms
./demo_openmp 15.10s user 0.01s system 740% cpu 2.041 total
2031s + 10ms(system) = 2041ms (total)
2.041* 740% = 15.1034 s
parallel sections
void test3()
{
boost::posix_time::ptime pt1 = boost::posix_time::microsec_clock::local_time();
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// `parallel sections`里面的内容要并行执行,具体分工上,每个线程执行其中的一个`section`
#pragma omp parallel sections // parallel
{
#pragma omp section // thread-0
{
base_sqrt();
}
#pragma omp section // thread-1
{
base_sqrt();
}
#pragma omp section // thread-2
{
base_sqrt();
}
#pragma omp section // thread-3
{
base_sqrt();
}
}
boost::posix_time::ptime pt2 = boost::posix_time::microsec_clock::local_time();
int64_t cost = (pt2 - pt1).total_milliseconds();
printf("Main Thread = %d, cost = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), cost);
}
/*
time ./demo_openmp
Worker Thread = 0, cost = 1843 ms
Worker Thread = 1, cost = 1843 ms
Worker Thread = 3, cost = 1844 ms
Worker Thread = 2, cost = 1845 ms
Main Thread = 0, cost = 1845 ms
./demo_openmp 7.39s user 0.00s system 398% cpu 1.855 total
*/
private
error case
void test4_error()
{
int i,j;
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// we get error result, because `j` is shared between all worker threads.
#pragma omp parallel for
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
printf("Worker Thread = %d, j = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), j);
}
}
}
/*
Worker Thread = 3, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 7 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 0 ms
*/
error results.
fix1 by changing code
void test4_fix1()
{
int i;
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// we get error result, because `j` is shared between all worker threads.
// fix1: we have to change original code to make j as local variable
#pragma omp parallel for
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int j; // fix1: `int j`
for(j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
printf("Worker Thread = %d, j = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), j);
}
}
}
/*
Worker Thread = 0, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 7 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 7 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 7 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 7 ms
*/
fix2 by private(j)
void test4_fix2()
{
int i,j;
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// we get error result, because `j` is shared between all worker threads.
// fix1: we have to change original code to make j as local variable
// fix2: use `private(j)`, no need to change original code
#pragma omp parallel for private(j) // fix2
for(i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for(j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
printf("Worker Thread = %d, j = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), j);
}
}
}
/*
Worker Thread = 0, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 0, j = 7 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 2, j = 7 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 3 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 1, j = 7 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 3, j = 7 ms
*/
reduction
error case
void test5_error()
{
int array[8] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
int sum = 0;
omp_set_num_threads(4);
//#pragma omp parallel for reduction(+:sum)
#pragma omp parallel for // ERROR
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
sum += array[i];
printf("Worker Thread = %d, sum = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), sum);
}
printf("Main Thread = %d, sum = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), sum);
}
/*
// ERROR RESULT
Worker Thread = 0, sum = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 0, sum = 9 ms
Worker Thread = 3, sum = 8 ms
Worker Thread = 3, sum = 16 ms
Worker Thread = 1, sum = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 1, sum = 19 ms
Worker Thread = 2, sum = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 2, sum = 24 ms
Main Thread = 0, sum = 24 ms
*/
reduction(+:sum)
void test5_fix()
{
int array[8] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
int sum = 0;
/*
sum需要私有才能实现并行化,但是又必须是公有的才能产生正确结果;
sum公有或者私有都不对,为了解决这个问题,OpenMP提供了reduction语句.
内部实现中,OpenMP为每个线程提供了私有的sum变量(初始化为0),
当线程退出时,OpenMP再把每个线程私有的sum加在一起得到最终结果。
*/
omp_set_num_threads(4);
#pragma omp parallel for reduction(+:sum)
//#pragma omp parallel for // ERROR
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
sum += array[i];
printf("Worker Thread = %d, sum = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), sum);
}
printf("Main Thread = %d, sum = %d ms\n",omp_get_thread_num(), sum);
}
/*
Worker Thread = 0, sum = 0 ms
Worker Thread = 0, sum = 1 ms
Worker Thread = 1, sum = 2 ms
Worker Thread = 1, sum = 5 ms
Worker Thread = 3, sum = 6 ms
Worker Thread = 3, sum = 13 ms
Worker Thread = 2, sum = 4 ms
Worker Thread = 2, sum = 9 ms
Main Thread = 0, sum = 28 ms
*/
num_threads
void test6()
{
// `num_threads(4)` same as `omp_set_num_threads(4)`
#pragma omp parallel num_threads(4)
{
printf("Hello, I am Thread %d\n", omp_get_thread_num()); // 0,1,2,3,
}
}
/*
Hello, I am Thread 0
Hello, I am Thread 2
Hello, I am Thread 3
Hello, I am Thread 1
*/
schedule
(static,2)
void test7_1()
{
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// static, num_loop/num_threads
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(static,2)
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
/*
i = 2, I am Thread 1
i = 3, I am Thread 1
i = 6, I am Thread 3
i = 7, I am Thread 3
i = 4, I am Thread 2
i = 5, I am Thread 2
i = 0, I am Thread 0
i = 1, I am Thread 0
*/
(static,4)
void test7_2()
{
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// static, num_loop/num_threads
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(static,4)
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
/*
i = 0, I am Thread 0
i = 1, I am Thread 0
i = 2, I am Thread 0
i = 3, I am Thread 0
i = 4, I am Thread 1
i = 5, I am Thread 1
i = 6, I am Thread 1
i = 7, I am Thread 1
*/
(dynamic,1)
void test7_3()
{
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// dynamic
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(dynamic,1)
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
/*
i = 0, I am Thread 2
i = 4, I am Thread 2
i = 5, I am Thread 2
i = 6, I am Thread 2
i = 7, I am Thread 2
i = 3, I am Thread 3
i = 1, I am Thread 0
i = 2, I am Thread 1
*/
(dynamic,3)
void test7_4()
{
omp_set_num_threads(4);
// dynamic
#pragma omp parallel for schedule(dynamic,3)
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++)
{
printf("i = %d, I am Thread %d\n", i, omp_get_thread_num());
}
}
/*
i = 0, I am Thread 0
i = 1, I am Thread 0
i = 2, I am Thread 0
i = 6, I am Thread 2
i = 7, I am Thread 2
i = 3, I am Thread 1
i = 4, I am Thread 1
i = 5, I am Thread 1
*/
schedule compare
#define NUM 100000000
int isprime( int x )
{
for( int y = 2; y * y <= x; y++ )
{
if( x % y == 0 )
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
void test8()
{
int sum = 0;
#pragma omp parallel for reduction (+:sum) schedule(dynamic,1)
for( int i = 2; i <= NUM ; i++ )
{
sum += isprime(i);
}
printf( "Number of primes numbers: %d", sum );
}
no schedule
Number of primes numbers: 5761455./demo_openmp 151.64s user 0.04s system 582% cpu 26.048 total
schedule(static,1)
Number of primes numbers: 5761455./demo_openmp 111.13s user 0.00s system 399% cpu 27.799 total
schedule(dynamic,1)
Number of primes numbers: 5761455./demo_openmp 167.22s user 0.02s system 791% cpu 21.135 total
schedule(dynamic,200)
Number of primes numbers: 5761455./demo_openmp 165.96s user 0.02s system 791% cpu 20.981 total
OpenCV with OpenMP
see how-opencv-use-openmp-thread-to-get-performance
3 type OpenCV implementation
- sequential implementation: default (slowest)
- parallel implementation: OpenMP / TBB
- GPU implementation: CUDA(fastest) / OpenCL
With CMake-gui, Building
OpenCVwith theWITH_OPENMPflag means that the internal functions will useOpenMPto parallelize some of the algorithms, likecvCanny,cvSmoothandcvThreshold.
In OpenCV, an algorithm can have a
sequential (slowest) implementation; aparallel implementationusingOpenMPorTBB; and aGPU implementationusingOpenCLorCUDA(fastest). You can decide with theWITH_XXXflags which version to use.
Of course, not every algorithm can be parallelized.
Now, if you want to parallelize your methods with OpenMP, you have to implement it yourself.
concepts
avoiding extra copying
from improving-image-processing-speed
There is one important thing about increasing speed in OpenCV not related to processor nor algorithm and it is avoiding extra copying when dealing with matrices. I will give you an example taken from the documentation:
"...by constructing a header for a part of another matrix. It can be a single row, single column, several rows, several columns, rectangular region in the matrix (called a minor in algebra) or a diagonal. Such operations are also O(1), because the new header will reference the same data. You can actually modify a part of the matrix using this feature, e.g."
parallel for
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/features2d/features2d.hpp"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <omp.h>
void opencv_vector()
{
int imNum = 2;
std::vector<cv::Mat> imVec(imNum);
std::vector<std::vector<cv::KeyPoint>>keypointVec(imNum);
std::vector<cv::Mat> descriptorsVec(imNum);
cv::Ptr<cv::ORB> detector = cv::ORB::create();
cv::Ptr<DescriptorMatcher> matcher = cv::DescriptorMatcher::create("BruteForce-Hamming");
std::vector< cv::DMatch > matches;
char filename[100];
double t1 = omp_get_wtime();
//#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i=0;i<imNum;i++){
sprintf(filename,"rgb%d.jpg",i);
imVec[i] = cv::imread( filename, CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE );
detector->detect( imVec[i], keypointVec[i] );
detector->compute( imVec[i],keypointVec[i],descriptorsVec[i]);
std::cout<<"find "<<keypointVec[i].size()<<" keypoints in im"<<i<<std::endl;
}
double t2 = omp_get_wtime();
std::cout<<"time: "<<t2-t1<<std::endl;
matcher->match(descriptorsVec[0], descriptorsVec[1], matches, 2); // uchar descriptor Mat
cv::Mat img_matches;
cv::drawMatches( imVec[0], keypointVec[0], imVec[1], keypointVec[1], matches, img_matches );
cv::namedWindow("Matches",CV_WINDOW_AUTOSIZE);
cv::imshow( "Matches", img_matches );
cv::waitKey(0);
}
parallel sections
#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
{
std::cout<<"processing im0"<<std::endl;
im0 = cv::imread("rgb0.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE );
detector.detect( im0, keypoints0);
extractor.compute( im0,keypoints0,descriptors0);
std::cout<<"find "<<keypoints0.size()<<"keypoints in im0"<<std::endl;
}
#pragma omp section
{
std::cout<<"processing im1"<<std::endl;
im1 = cv::imread("rgb1.jpg", CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE );
detector.detect( im1, keypoints1);
extractor.compute( im1,keypoints1,descriptors1);
std::cout<<"find "<<keypoints1.size()<<"keypoints in im1"<<std::endl;
}
}
Reference
- openmp
- openmp + MPI
- openmp
- how-opencv-use-openmp-thread-to-get-performance
- csdn opencv with openmp for+section
- openmp functions
- improving-image-processing-speed
- openmp-are-local-variables-automatically-private
- whats-the-difference-between-static-and-dynamic-schedule-in-openmp
- dynamic openmp with isprime
History
- 20190403: created.
Copyright
- Post author: kezunlin
- Post link: https://kezunlin.me/post/7a6ba82e/
- Copyright Notice: All articles in this blog are licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 unless stating additionally.
使用OpenMP加快OpenCV图像处理性能 | speed up opencv image processing with openmp的更多相关文章
- 使用OpenCL提升OpenCV图像处理性能 | speed up opencv image processing with OpenCL
本文首发于个人博客https://kezunlin.me/post/59afd8b3/,欢迎阅读最新内容! speed up opencv image processing with OpenCL G ...
- javacpp-opencv图像处理3:使用opencv原生方法遍历摄像头设备及调用(增加实时帧率计算方法)
javaCV图像处理系列: javaCV图像处理之1:实时视频添加文字水印并截取视频图像保存成图片,实现文字水印的字体.位置.大小.粗度.翻转.平滑等操作 javaCV图像处理之2:实时视频添加图片水 ...
- OpenCV图像处理篇之边缘检测算子
OpenCV图像处理篇之边缘检测算子 转载: http://xiahouzuoxin.github.io/notes/ 3种边缘检测算子 一阶导数的梯度算子 高斯拉普拉斯算子 Canny算子 Open ...
- Python+OpenCV图像处理(一)
Python+OpenCV图像处理(一): 读取,写入和展示图片 调用摄像头拍照 调用摄像头录制视频 1. 读取.写入和展示图片 图像读入:cv2.imread() 使用函数cv2.imread() ...
- Python+OpenCV图像处理(一)——读取显示一张图片
先在此处先声明,后面学习python+opencv图像处理时均参考这位博主的博文https://blog.csdn.net/u011321546/article/category/7495016/2? ...
- 1.5快速上手OpenCV图像处理
在上一节中,已经完成了OPENCV的配置,在本节接触几个Opencv图像处理相关的程序,看看opencv用简洁的代码能够实现哪些有趣的图像效果. 1.第一个程序:图像显示 #include<op ...
- 《OpenCV图像处理编程实例》
<OpenCV图像处理编程实例>例程复现 随书代码下载:http://www.broadview.com.cn/28573 总结+遇到的issue解决: 第一章 初识OpenCV 1.VS ...
- OpenCV -Python 性能衡量和提升技术 | 十二
目标 在图像处理中,由于每秒要处理大量操作,因此必须使代码不仅提供正确的解决方案,而且还必须以最快的方式提供.因此,在本章中,你将学习 衡量代码的性能. 一些提高代码性能的技巧. 你将看到以下功能:c ...
- OpenCV图像处理学习笔记-Day1
OpenCV图像处理学习笔记-Day1 目录 OpenCV图像处理学习笔记-Day1 第1课:图像读入.显示和保存 1. 读入图像 2. 显示图像 3. 保存图像 第2课:图像处理入门基础 1. 基本 ...
随机推荐
- vue-cli3没有config文件解决方案,在根目录加上vue.config.js文件
module.exports = { /** 区分打包环境与开发环境 * process.env.NODE_ENV==='production' (打包环境) * process.env.NODE_E ...
- fenby C语言 P14
打赌 条件运算符 (表达式?值1:值2) 赌注内容 奖励 奖励 y=(x==2?100:50): x==2,那么y=100 x!=2,那么y=50 #include int main() { int ...
- ulua、tolua原理解析
在聊ulua.tolua之前,我们先来看看Unity热更新相关知识. 什么是热更新 举例来说: 游戏上线后,玩家下载第一个版本(70M左右或者更大),在运营的过程中,如果需要更换UI显示,或者修改游戏 ...
- 使用koa-mysql-session时报错
描述 在本地测试代码没问题,但是部署到服务器上时就报错. 错误 > cross-env WEBPACK_TARGET=node NODE_ENV=production node ./server ...
- Docker安装ElasticSearch 以及使用LogStash实现索引库和数据库同步
1:下载 ElasticSearch 镜像 docker pull docker.io/elasticsearch:5.6.8 2:创建 ElasticSearch 容器: 注意:5.0默认分配jvm ...
- 前端技术之:Prisma Demo服务部署过程记录
安装前提条件: 1.已经安装了docker运行环境 2.以下命令执行记录发生在MackBook环境 3.已经安装了PostgreSQL(我使用的是11版本) 4.Node开发运行环境可以正常工作 ...
- [考试反思]1005csp-s模拟测试61:休止
连续不知道多少场了,都是一场10名以内一场20以外...波动极大...还极有规律... 拿到这套题,看到T1大模拟无话可说. 然后考场上我觉得T2很简单....然后就码了两个半小时. T3数据水了暴力 ...
- [考试反思]0805NOIP模拟测试13:窒息
呼啊...苟住了.rank #3 第二次分机房的收官之战.发挥比较稳定 然而差点就不稳定了!!! 过了一遍题目,难度大约是升序,但是一道都不会做!!! 本来感觉T1是一道数学题,以为45分钟以内可以切 ...
- 网站安全配置Nginx防止网站被攻击
https://blog.csdn.net/u011078940/article/details/51426288
- CPU负载和CPU使用率
参考CSDN博客:https://blog.csdn.net/ffzhihua/article/details/87257607 一.概念(本人理解) CPU负载:平均负载(load average) ...
