Mybatis工作流程源码分析
1.简介
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生类型、接口和 Java 的 POJO(Plain Old Java Objects,普通老式 Java 对象)为数据库中的记录《摘自mybatis官网》。
mybatis在我们开发中经常使用,所以搞清楚mybatis的工作流程还是比较重要的,下面就开始我们的分析。
2.Mybatis中的核心对象
2.1mybatis使用示例
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建sqlSessionFactory对象
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml"));
//2.创建会话
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
//3.获取mapper代理对象
BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class);
//4.执行mapper接口方法
Blog blog = mapper.selectBlogById(1);
System.out.println(blog);
} finally {
session.close();
}
}
2.2核心对象
通过上面的示例可以看出mybatis里面的几个核心对象:SqlSessionFactoryBuilder、SqlSessionFactory、SqlSession和Mapper对象,
1.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder:会话工厂构建者,用来构建SqlSessionFactory,在应用中,SqlSessionFactory作为单例对象存在,所以,创建SqlSessionFactory后,SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的任务也就完成了。所以他的生命周期为方法局部。
2.SqlSessionFactory:会话工厂类,用来创建会话,有了工厂,我们就可以创建SqlSession,而创建SqlSession只需要一个工厂就足够了,所以SqlSessionFactory为单例。 我们每次访问数据库都需要创建会话,这个过程贯穿应用的整个生命周期,所以SqlSessionFactory的生命周期为应用级别。
3.SqlSession:会话,内部持有与数据库的连接(connection),线程不安全,每次使用后需要及时关闭。生命周期为一次请求或一次事务。
4.Mapper:mapper对象实际是一个代理对象,从SqlSession中获取。BlogMapper mapper = session.getMapper(BlogMapper.class); 作用是发送sql语句操作数据,生命周期为SqlSession事务方法内。
3.工作流程
3.1 创建sqlSessionFactory对象
public class SqlSessionFactoryBuilder {
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
//创建xml配置构建器
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
//解析配置文件返回configuration对象,使用configuration对象创建会话工厂
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
}
调用了XMLConfigBuilder 的parse()方法
public class XMLConfigBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
//...
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
//配置文件只能解析一次
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//解析properties标签,读取外部引入的配置文件,包括相对路径和绝对路径,
//将解析结果defaults,最后将defaults设置到XPathParser和Configuration的properties属性
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
//解析别名,解析完成后将别名与class的映射保存到Configuration的typeAliasRegistry中
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
//解析<plugins>标签,比如常用的分页插件,解析为Interceptor,设置到Configuration的
//interceptorChain(持有一个拦截器List)属性中
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
//解析<objectFactory> 和<objectWrapperFactory>标签,分别生成objectFactory和
//objectWrapperFactory,同样设置到Configuration的属性中,用来实例化对象使用。
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectionFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectionFactory"));
//
settingsElement(root.evalNode("settings"));
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
//解析 databaseIdProvider 标签,生成 DatabaseIdProvider对象,用来支持不同厂商的数据库
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
//解析类型处理器元素,用来保存JavaType和JdbcType的映射关系,设置到Configuration的typeHandlerRegistry
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
//解析<mappers>标签,只有是接口才会解析,然后判断是否已经注册,单个Mapper重复注册会抛出异常
//将解析的mapper保存到Configuration的mapperRegistry中,并解析注解信息
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
//...
}
通过parser.parse()拿到解析配置文件得到的Configuration对象,调用build()方法,创建默认的SqlSessionFactory对象并返回。
下面来看一下上面代码的运行时序图:
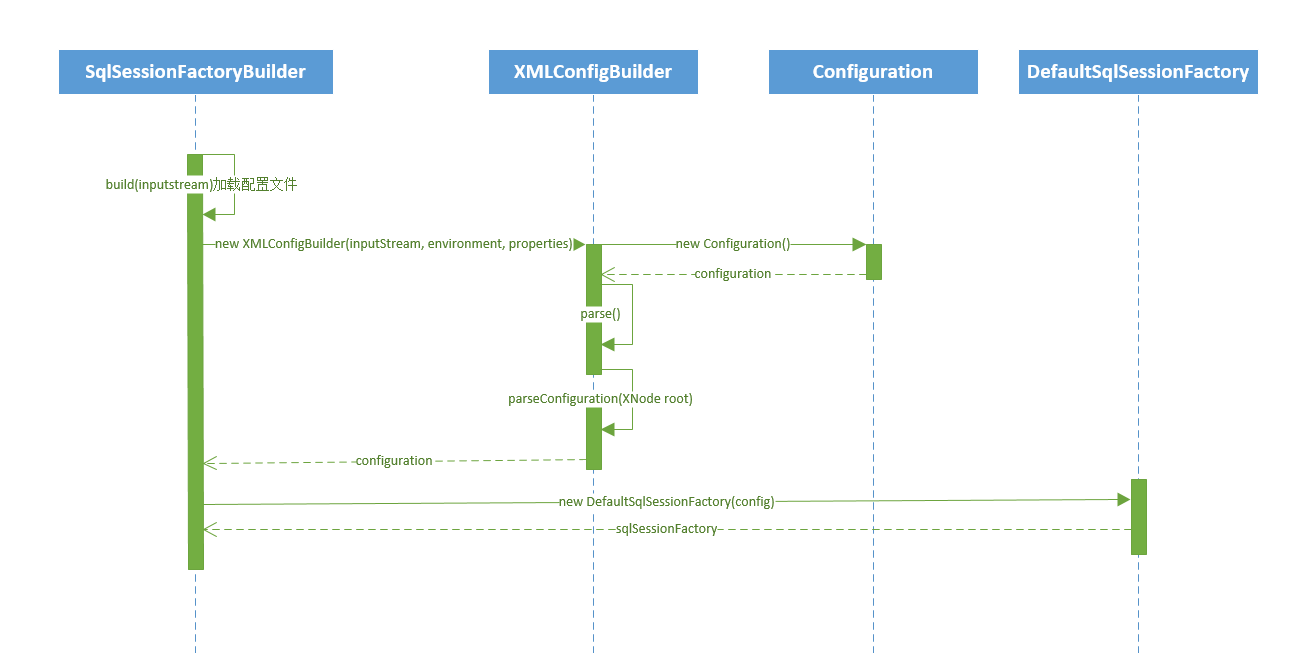
3.2 创建会话
调用DefaultSqlSessionFactory 的openSession()方法获取会话
public class DefaultSqlSessionFactory implements SqlSessionFactory {
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
}
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
//获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
//创建执行器,默认使用SimpleExecutor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
//创建会话
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
下面来看一下创建会话的运行时序图:
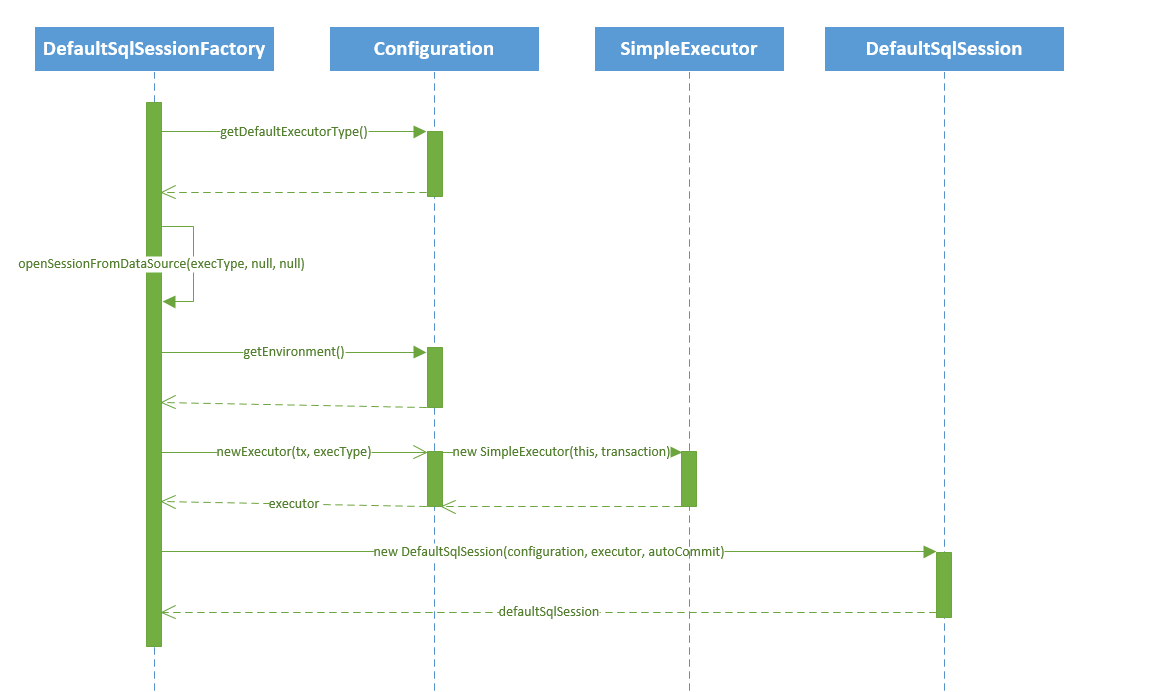
3.3获取mapper代理对象
调用session.getMapper方法获取mapper代理对象
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
//...
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.<T>getMapper(type, this);
}
//...
}
继续调用Configuration的getMapper方法
public class Configuration {
//...
//Mapper注册器,所有的mapper在解析配置文件时保存到该对象中
protected MapperRegistry mapperRegistry = new MapperRegistry(this);
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
//...
}
继续调用mapperRegistry的getMapper方法
public class MapperRegistry {
private final Configuration config;
//以接口的class为key,mapper代理工厂为value的map,MapperProxyFactory在加载配置文件扫描mapper所在包时创建,用来创建MapperProxy
private final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>>();
public MapperRegistry(Configuration config) {
this.config = config;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
//调用工厂方法创建mapper接口的代理对象
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
//...
}
调用mapper代理工厂的newInstance方法为mapper创建代理对象
public class MapperProxyFactory<T> {
//mapper接口对应class
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
//方法缓存,为了提升性能,会在MapperProxy中使用,所有mapper的所有方法都将缓存在该map中
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<Method, MapperMethod>();
public MapperProxyFactory(Class<T> mapperInterface) {
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
}
public Class<T> getMapperInterface() {
return mapperInterface;
}
public Map<Method, MapperMethod> getMethodCache() {
return methodCache;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
//创建jdk动态代理,第三个参数是mapperProxy,所以对T对象的所有的所有调用都将调用mapperProxy的invoke方法
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<T>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
}
上面使用jdk动态代理为mapper创建了代理对象,所以对mapper的所有调用将调用mapperProxy类的invoke方法,下面来看一下mapperProxy的代码
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;
private final SqlSession sqlSession;
private final Class<T> mapperInterface;
private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;
public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;
this.methodCache = methodCache;
}
//所有对mapper的调用都将调用该方法
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
//获取缓存的mapper方法,如果不存在,则创建并缓存
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
//不像常规的动态代理,并没有调用method.invoke(target, args),因为mapper只是一个接口,并没有实现类
//这里动态代理的意义在于统一处理对mapper方法的调用
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
}
到这里为什么mapper接口不需要实现类就可以操作数据库就很清楚了,对mapper接口的调用实际会调用mapperMethod.execute()方法,在mapperMethod内部调用sqlSession的增删改查方法。
下面来看一下获取mapper代理对象的运行时序图:

3.4执行mapper接口方法
上面已经说到对mapper接口的方法调用都将调用MapperProxy的invoke方法,invoke方法又会调用mapperMethod的execute()方法,下面来看一下execute()方法:
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
//方法签名
private final MethodSignature method;
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
//判断sql类型,执行相应逻辑
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) {
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
//转换参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
//方法是否RowBounds(分页)参数
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
return result;
}
public static class SqlCommand {
//mapperInterface.getName() + "." + method.getName();
private final String name;
//sql类型:UNKNOWN, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, SELECT, FLUSH;
private final SqlCommandType type;
//...
}
public static class MethodSignature{
private boolean returnsMany;
private boolean returnsMap;
private boolean returnsVoid;
private Class<?> returnType;
//方法是否有MapKey.class注解,如果有就是注解的值
private String mapKey;
//ResultHandler.class类型参数在方法参数中的索引
private Integer resultHandlerIndex;
//RowBounds.class类型参数在方法参数中的索引
private rowBoundsIndex;
//key为index,有Param注解的value为注解值,没有的也是index
private SortedMap<Integer, String> params;
//方法参数中是否有Param注解
private boolean hasNamedParameters
//...
}
}
在execute()方法内部根据sql的类型执行不同的增删改查逻辑,这里以select为例,mapper方法有多个返回值的情况调用executeForMany(sqlSession, args)方法,内部继续调用sqlSession的selectList()方法:
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//获取configuration中缓存的MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//调用执行器方法进行查询
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
拿到MappedStatement,调用执行器进行查询:
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//从数据库查询数据
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//开始执行查询
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
}
query()方法调用重载的query()方法,如果没有命中缓存,则调用queryFromDatabase()从数据库查询数据,继续调用SimpleExecutor的doQuery()方法:
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//创建statement处理器,默认PreparedStatement
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.<E>query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
stmt = handler.prepare(connection);
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}
}
创建Statement处理器:
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
//创建路由Statement处理器,根据statementType创建不同的statement处理器,委派模式的体现
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
//创建statement处理器拦截器链,这里先不深入看,默认没有使用拦截器,后面的文章单独分析
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
在创建Statement处理器时返回的是RoutingStatementHandler对象,从名字就可以看出来,他不是真正工作的StatementHandler,其路由的功能,在内部会根据StatementType创建相应的StatementHandler,对RoutingStatementHandler 的所有调用都将委派给具体的StatementHandler(delegate)去处理:
public class RoutingStatementHandler implements StatementHandler {
private final StatementHandler delegate;
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
//根据statementType创建不同的策略,委派给具体的statement处理器(策略模式与委派模式的体现)
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
//默认使用PreparedStatementHandler
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
@Override
public Statement prepare(Connection connection) throws SQLException {
return delegate.prepare(connection);
}
@Override
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
delegate.parameterize(statement);
}
@Override
public void batch(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
delegate.batch(statement);
}
@Override
public int update(Statement statement) throws SQLException {
return delegate.update(statement);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
return delegate.<E>query(statement, resultHandler);
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql() {
return delegate.getBoundSql();
}
@Override
public ParameterHandler getParameterHandler() {
return delegate.getParameterHandler();
}
}
回到doQuery()方法中,继续调用StatementHandler 的query(stmt, resultHandler)方法,query方法会调用到PreparedStatementHandler 的query()方法:
public class PreparedStatementHandler extends BaseStatementHandler {
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;
//执行PreparedStatement
ps.execute();
//结果集处理器处理结果集并返回结果
return resultSetHandler.<E> handleResultSets(ps);
}
}
在PreparedStatementHandler 的query方法中执行PreparedStatement,并将PreparedStatement传给resultSetHandler处理结果集并返回。
上面的执行过程还是比较复杂的,下面来看一下时序图:
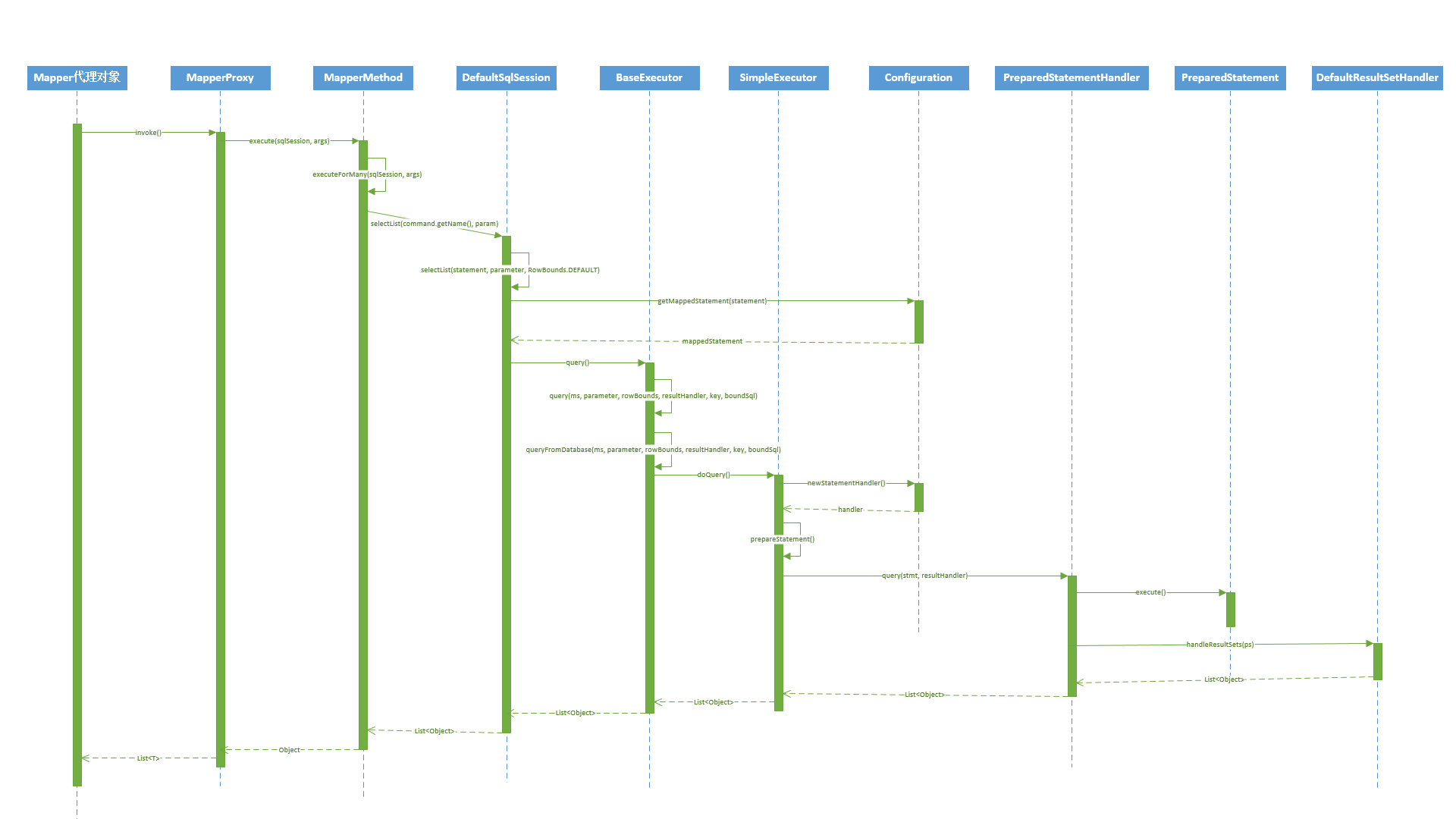
以上就是对mybatis工作流程的所有分析了。
因个人能力有限,如果有错误之处,还请指出,谢谢!
Mybatis工作流程源码分析的更多相关文章
- Mybatis执行流程源码分析
第一部分:项目结构 user_info表:只有id和username两个字段 User实体类: public class User { private String username; private ...
- 转:Spring与Mybatis整合的MapperScannerConfigurer处理过程源码分析
原文地址:Spring与Mybatis整合的MapperScannerConfigurer处理过程源码分析 前言 本文将分析mybatis与spring整合的MapperScannerConfigur ...
- springboot 事务创建流程源码分析
springboot 事务创建流程源码分析 目录 springboot 事务创建流程源码分析 1. 自动加载配置 2. InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator类 3 ...
- [Android]从Launcher开始启动App流程源码分析
以下内容为原创,欢迎转载,转载请注明 来自天天博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/tiantianbyconan/p/5017056.html 从Launcher开始启动App流程源码 ...
- [Android]Android系统启动流程源码分析
以下内容为原创,欢迎转载,转载请注明 来自天天博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/tiantianbyconan/p/5013863.html Android系统启动流程源码分析 首先 ...
- Android系统默认Home应用程序(Launcher)的启动过程源码分析
在前面一篇文章中,我们分析了Android系统在启动时安装应用程序的过程,这些应用程序安装好之后,还须要有一个Home应用程序来负责把它们在桌面上展示出来,在Android系统中,这个默认的Home应 ...
- Android Content Provider的启动过程源码分析
本文參考Android应用程序组件Content Provider的启动过程源码分析http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6963418和 ...
- Android应用程序绑定服务(bindService)的过程源码分析
Android应用程序组件Service与Activity一样,既能够在新的进程中启动,也能够在应用程序进程内部启动:前面我们已经分析了在新的进程中启动Service的过程,本文将要介绍在应用程序内部 ...
- Spring加载流程源码分析03【refresh】
前面两篇文章分析了super(this)和setConfigLocations(configLocations)的源代码,本文来分析下refresh的源码, Spring加载流程源码分析01[su ...
随机推荐
- 工厂模式(C++)
转载来源:https://www.runoob.com/design-pattern/ 工厂模式 创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式. 在工厂模式中,我们在创建对象时不会对客户端暴露创建逻辑, ...
- 学习笔记45_log4net日志
1.配置添加一个App.config *对于网站,就使用web.config ***对于App.config和web.config的配置,在表现形式上是不一致的,使用的时候应该在网上查对于的配置设置. ...
- LNMP下zabbix_server安装部署二
上一篇中搭建完成了zabbix的web端,但是虚拟机有点问题,所以转到笔记本上来写笔记本环境 server:192.168.112.9 agent:192.168.112.8 上一篇中完成了web ...
- [考试反思]1012csp-s模拟测试70:盘旋
这套题比较烂... 上来看到T2是原题,一想上一次考试遇到原题就不换,这次应该也是,于是直接开始码,码了一半然后换题了 T1打表找规律或者推式子都不难... T2水的一匹暴力剪枝即可,但是我并不知道数 ...
- DOM增删改替换
一.在创建元素的时候为什么要把创建元素到也页面写到后面? 要求:创建一个div,在div中创建10个span. var div = document.createElement("div ...
- 使用Typescript重构axios(六)——实现基础功能:获取响应数据
0. 系列文章 1.使用Typescript重构axios(一)--写在最前面 2.使用Typescript重构axios(二)--项目起手,跑通流程 3.使用Typescript重构axios(三) ...
- 「POJ 3268」Silver Cow Party
更好的阅读体验 Portal Portal1: POJ Portal2: Luogu Description One cow from each of N farms \((1 \le N \le 1 ...
- [转载]2.2 UiPath条件判断活动Flow Decision的介绍和使用
一.Flow Decision介绍 FlowDecision节点是一个条件节点,它根据指定条件是否成立来控制流程的两个分支. 当条件为True时,流程执行一个分支 当条件为False时,流程执行另外一 ...
- 初识web API接口及Restful接口规范
一.web API接口 什么是web API接口?: 明确了请求方式,提供对应后台所需参数,请求url链接可以得到后台的响应数据 url : 返回数据的url https://api.map.baid ...
- tornado的使用-上传图片
tornado的使用-上传图片
