Factorization
Factorization or factoring consists of writing a number or another mathematical object as a product of several factors, usually smaller or simpler objects of the same kind. For example, 3 × 5 is a factorization of the integer 15, and (x – 2)(x + 2) is a factorization of the polynomial x^2 – 4. Matrices possess many kinds of matrix factorizations.
Although integer factorization is a sort of inverse to multiplication, it is much more difficult algorithmically, a fact which is exploited in the RSA cryptosystem to implement public-key cryptography. Pierre de Fermat was unable to discover that the 6th Fermat number 1 + 2^32 is not a prime number.
log(2)=0.3, 20位二进制约6位六进制,32位10位,64位19位, 128位38位。两个8位二进制数相乘,可写成(a*16+b)*(c*16+b)=ac*256+bc*16*ab+bb. *256放在另一个寄存器里,*16分成两截,ab和bb各最多8位。
Manipulating expressions is the basis of algebra. Factorization is one of the most important methods for expression manipulation for several reasons. If one can put an equation in a factored form E*F = 0, then the problem of solving the equation splits into two independent (and generally easier) problems E = 0 and F = 0. When an expression can be factored, the factors are often much simpler, and may thus offer some insight on the problem. But factorization is not always possible, and when it is possible, the factors are not always simpler. For example, x^10 - 1 = (x-1)*(x^9 + x^8 + ... + x + 1).
The first polynomial factorization algorithm was published by Theodor von Schubert in 1793. Leopold Kronecker rediscovered Schubert's algorithm in 1882 and extended it to multivariate polynomials and coefficients in an algebraic extension. But most of the knowledge on this topic is not older than circa 1965 and the first computer algebra systems: When the long-known finite step algorithms were first put on computers, they turned out to be highly inefficient. The fact that almost any uni- or multivariate polynomial of degree up to 100 and with coefficients of a moderate size (up to 100 bits) can be factored by modern algorithms in a few minutes of computer time indicates how successfully this problem has been attacked during the past fifteen years. (Erich Kaltofen, 1982) Nowadays, modern algorithms and computers can quickly factor univariate polynomials of degree more than 1000 having coefficients with thousands of digits. 1000位十进制数有3322个二进制位。量子计算是质变,8个4096位寄存器,baremetal能且仅能分解整数是小量变。我是外行,我不知道4096根线现实不。
Yun, David Y.Y. (1976). On square-free decomposition algorithms SYMSAC '76 Proceedings of the third ACM symposium on Symbolic and algebraic computation, pp. 26–35.
Berlekamp's algorithm is a well-known method for factoring polynomials over finite fields (also known as Galois fields). The algorithm consists mainly of matrix reduction and polynomial GCD computations. It was invented by Elwyn Berlekamp in 1967. It was the dominant algorithm for solving the problem until the Cantor–Zassenhaus algorithm of 1981. It is currently implemented in many well-known computer algebra systems.
没有一目了然的。search(github emcd123 PolynomialFactorization) 有用SageMath写的。到 cocalc 试了下:
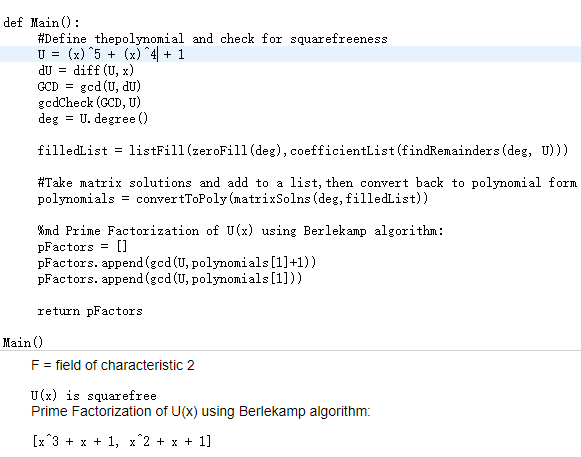
结果不对。
SageMath is a free open-source mathematics software system. It builds on top of many existing packages: NumPy, SciPy, matplotlib, Sympy, Maxima, GAP, FLINT, R and many more. Access their combined power through a common, Python-based language or directly via interfaces or wrappers. SageMath-9.3-Installer-v0.6.3.exe 820.72 MB
SymPy is a Python library for symbolic mathematics. It aims to become a full-featured computer algebra system (CAS) while keeping the code as simple as possible in order to be comprehensible and easily extensible. SymPy is written entirely in Python. It uses mpmath, which is a free Python library for real and complex floating-point arithmetic with arbitrary precision.
Combinatorics is the branch of mathematics studying the enumeration, combination, and permutation of sets of elements and the mathematical relations that characterize their properties. Mathematicians sometimes use the term "combinatorics" to refer to a larger subset of discrete mathematics that includes graph theory. search(Combinatorics fourier)
六级/考研单词: mathematics, invert, exploit, implement, prime, log, manipulate, algebra, equate, seldom, thereby, insight, compute, finite, moderate, nowadays, digit, tertiary, symposium, hardware, parcel, intelligible, arithmetic, arbitrary, graph

stackoverflow上有人说:把f(x)分解成因式就是找出f(x)=0的所有根。也许有些程序找到的不是1而是0.999999999。可x^4+1=0没有实数根啊。
Factorization的更多相关文章
- Matrix Factorization SVD 矩阵分解
Today we have learned the Matrix Factorization, and I want to record my study notes. Some kownledge ...
- Factorization Machine因子分解机
隐因子分解机Factorization Machine[http://www. w2bc. com/article/113916] https://my.oschina.net/keyven/blog ...
- 关于NMF(Non-negative Matrix Factorization )
著名的科学杂志<Nature>于1999年刊登了两位科学家D.D.Lee和H.S.Seung对数学中非负矩阵研究的突出成果.该文提出了一种新的矩阵分解思想――非负矩阵分解(Non-nega ...
- Factorization Machine
Factorization Machine Model 如果仅考虑两个样本间的交互, 则factorization machine的公式为: $\hat{y}(\mathbf{x}):=w_0 + \ ...
- 1103. Integer Factorization (30)
The K-P factorization of a positive integer N is to write N as the sum of the P-th power of K positi ...
- Factorization Machines 学习笔记(三)回归和分类
近期学习了一种叫做 Factorization Machines(简称 FM)的算法,它可对随意的实值向量进行预測.其主要长处包含: 1) 可用于高度稀疏数据场景:2) 具有线性的计算复杂度.本文 ...
- Matrix Factorization, Algorithms, Applications, and Avaliable packages
矩阵分解 来源:http://www.cvchina.info/2011/09/05/matrix-factorization-jungle/ 美帝的有心人士收集了市面上的矩阵分解的差点儿全部算法和应 ...
- Factorization Machines 学习笔记(四)学习算法
近期学习了一种叫做 Factorization Machines(简称 FM)的算法.它可对随意的实值向量进行预測.其主要长处包含: 1) 可用于高度稀疏数据场景:2) 具有线性的计算复杂度.本文 ...
- Factorization Machines 学习笔记(二)模型方程
近期学习了一种叫做 Factorization Machines(简称 FM)的算法,它可对随意的实值向量进行预測.其主要长处包含: 1) 可用于高度稀疏数据场景:2) 具有线性的计算复杂度.本文 ...
- 分解机(Factorization Machines)推荐算法原理
对于分解机(Factorization Machines,FM)推荐算法原理,本来想自己单独写一篇的.但是看到peghoty写的FM不光简单易懂,而且排版也非常好,因此转载过来,自己就不再单独写FM了 ...
随机推荐
- 并发编程从零开始(十二)-Lock与Condition
并发编程从零开始(十二)-Lock与Condition 8 Lock与Condition 8.1 互斥锁 8.1.1 锁的可重入性 "可重入锁"是指当一个线程调用 object.l ...
- 决策树 机器学习,西瓜书p80 表4.2 使用信息增益生成决策树及后剪枝
使用信息增益构造决策树,完成后剪枝 目录 使用信息增益构造决策树,完成后剪枝 1 构造决策树 1 根结点的选择 色泽 信息增益 根蒂 信息增益 敲声 信息增益 纹理 信息增益 脐部 信息增益 触感 信 ...
- Bzoj通过5题纪念
我A了五题啦!!!
- conda无法导入,pip可以导入
在conda中创建测试的虚拟环境 进入test虚拟环境,输入命令:conda install keras 输入命令python,进入python环境,输入import keras 返回错误,No mo ...
- k8s入坑之路(13)服务迁移(定时任务 微服务 传统服务)
定时任务迁移kubernetes 服务迁移步骤 1.安装好java 2.安装好maven 项目打包 mvn package 测试传参运行 java -cp cronjob-demo-1.0-SNAPS ...
- sprint boot 手动快速创建web应用(2)
1.打开Eclipse新建maven项目 2.导入maven依赖 <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId& ...
- Go语言核心36讲(Go语言进阶技术十五)--学习笔记
21 | panic函数.recover函数以及defer语句 (上) 在本篇,我要给你展示 Go 语言的另外一种错误处理方式.不过,严格来说,它处理的不是错误,而是异常,并且是一种在我们意料之外的程 ...
- 3组-Alpha冲刺-1/6
一.基本情况 队名:发际线和我作队 组长博客:链接 小组人数:10 二.冲刺概况汇报 黄新成(组长) 过去两天完成了哪些任务 文字描述 组织会议,讨论了alpha冲刺的分工,确定了收集数据的渠道,为拍 ...
- C++概述及知识点总结
经过一段时间的学习,以前从没有接触过C++这个高逼格的语言的小白,逐渐对C++有了更深的了解和认识,C++是c语言的升级版,Bjarne Stroustrup在剑桥大学计算机中心工作.他使用过Simu ...
- CF285D.D. Permutation Sum
CF285D. Permutation Sum 题目 大意 寻找a,b两个排列从0到n-1,有c[i]=(a[i]+b[i])%n+1,使得c[i]也为全排列的排列方式 思路 a中元素和b中元素的对应 ...
