matplotlib 高阶之Transformations Tutorial
之前在legend的使用中,便已经提及了transforms,用来转换参考系,一般情况下,我们不会用到这个,但是还是了解一下比较好
| 坐标 | 转换对象 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| "data" | ax.transData | 数据的坐标系统,通过xlim, ylim来控制 |
| "axes" | ax.transAxes | Axes的坐标系统,(0, 0)代表左下角,(1, 1)代表右上角 |
| "figure" | fig.transFigure | Figure的坐标系统,(0, 0)代表左下角,(1, 1)代表右上角 |
| "figure-inches" | fig.dpi_scale_trans | 以inches来表示的Figure坐标系统,(0, 0)左下角,而(width, height)表示右上角 |
| "display" | None or IdentityTransform() | 显示窗口的像素坐标系统,(0, 0)表示窗口的左下角,而(width, height)表示窗口的右上角 |
| "xaxis", "yaxis" | ax.get_xaxis_transform(), ax.get_yaxis_transform() | 混合坐标系; 在另一个轴和轴坐标之一上使用数据坐标。没看懂 |
Data coordinates
最为常见的便是通过set_xlim, 和set_ylim来控制数据坐标
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.005)
y = np.exp(-x/2.) * np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
plt.show()
你可以通过ax.transData来将你的数据坐标,转换成再显示窗口上的像素坐标,单个坐标,或者传入序列都是被允许的
type(ax.transData)
matplotlib.transforms.CompositeGenericTransform
ax.transData.transform((5, 0)) #数据坐标(5, 0) 转换为显示窗口的像素坐标(221.4, 144.72) 这个玩意儿不一定的
array([221.4 , 144.72])
ax.transData.transform(((5, 0), (2, 3)))
array([[221.4 , 144.72],
[120.96, 470.88]])
你也可以通过使用inverted()来反转,获得数据坐标
inv = ax.transData.inverted()
type(inv)
matplotlib.transforms.CompositeGenericTransform
inv.transform((221.4, 144.72))
array([5., 0.])
下面是一个比较完整的例子
x = np.arange(0, 10, 0.005)
y = np.exp(-x/2.) * np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlim(0, 10)
ax.set_ylim(-1, 1)
xdata, ydata = 5, 0
xdisplay, ydisplay = ax.transData.transform_point((xdata, ydata))
bbox = dict(boxstyle="round", fc="0.8")
arrowprops = dict(
arrowstyle="->",
connectionstyle="angle,angleA=0,angleB=90,rad=10")
offset = 72
ax.annotate('data = (%.1f, %.1f)' % (xdata, ydata),
(xdata, ydata), xytext=(-2*offset, offset), textcoords='offset points',
bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
disp = ax.annotate('display = (%.1f, %.1f)' % (xdisplay, ydisplay),
(xdisplay, ydisplay), xytext=(0.5*offset, -offset), #xytext 好像是text离前面点的距离
xycoords='figure pixels', #这个属性来变换坐标系
textcoords='offset points',
bbox=bbox, arrowprops=arrowprops)
plt.show()
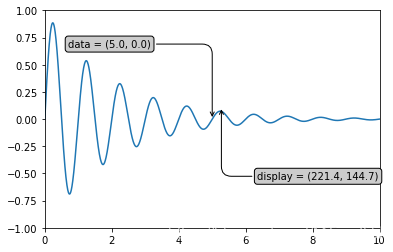
很显然的一点是,当我们改变xlim, ylim的时候,同样的数据点转换成显示窗口后发生变化
ax.transData.transform((5, 0))
array([221.4 , 144.72])
ax.set_ylim(-1, 2)
(-1, 2)
ax.transData.transform((5, 0))
array([221.4 , 108.48])
ax.set_xlim(10, 20)
(10, 20)
ax.transData.transform((5, 0))
array([-113.4 , 108.48])
Axes coordinates
除了数据坐标系,Axes坐标系是第二常用的,就像在上表中提到的(0, 0)表示左下角,而(1, 1)表示右上角,(0.5, 0.5)则表示中心。我们也可以过分一点,使用(-0.1, 1.1)会显示在axes的外围左上角部分。
fig = plt.figure()
for i, label in enumerate(('A', 'B', 'C', 'D')):
ax = fig.add_subplot(2, 2, i+1)
ax.text(0.05, 0.95, label, transform=ax.transAxes,
fontsize=16, fontweight='bold', va='top')
plt.show()
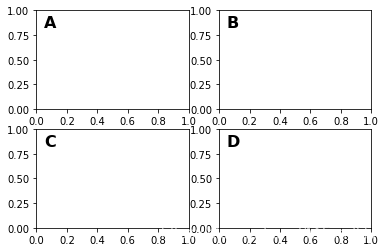
从上面的例子中我们可以看到,想在多个axes中相同的位置放置相似的东西,用ax.transAxes时非常方便的
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x, y = 10*np.random.rand(2, 1000)
ax.plot(x, y, 'go', alpha=0.2) # plot some data in data coordinates
circ = mpatches.Circle((0.5, 0.5), 0.25, transform=ax.transAxes,
facecolor='blue', alpha=0.75)
ax.add_patch(circ)
plt.show()
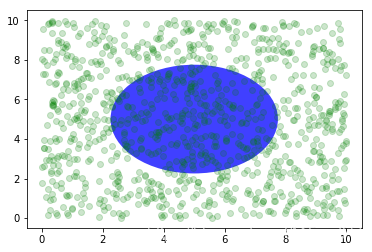
可以看到,上面的椭圆与数据坐标无关,始终放置在中间
Blended transformations 混合坐标系统
import matplotlib.transforms as transforms
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.random.randn(1000)
ax.hist(x, 30)
ax.set_title(r'$\sigma=1 \/ \dots \/ \sigma=2$', fontsize=16)
# the x coords of this transformation are data, and the
# y coord are axes
trans = transforms.blended_transform_factory(
ax.transData, ax.transAxes)
# highlight the 1..2 stddev region with a span.
# We want x to be in data coordinates and y to
# span from 0..1 in axes coords
rect = mpatches.Rectangle((1, 0), width=1, height=1,
transform=trans, color='yellow',
alpha=0.5)
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
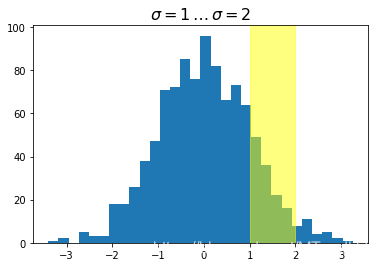
注意到,上面我们使用了混合坐标系统,x轴方向是数据坐标系,而y轴方向是axes的坐标系统,我们做一个反转试试
import matplotlib.transforms as transforms
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
x = np.random.randn(1000)
ax.hist(x, 30)
ax.set_title(r'$\sigma=1 \/ \dots \/ \sigma=2$', fontsize=16)
# the x coords of this transformation are data, and the
# y coord are axes
trans = transforms.blended_transform_factory(
ax.transAxes, ax.transData) #调了一下
# highlight the 1..2 stddev region with a span.
# We want x to be in data coordinates and y to
# span from 0..1 in axes coords
rect = mpatches.Rectangle((0.5, 0), width=0.5, height=50, #注意这里的区别
transform=trans, color='yellow',
alpha=0.5)
ax.add_patch(rect)
plt.show()
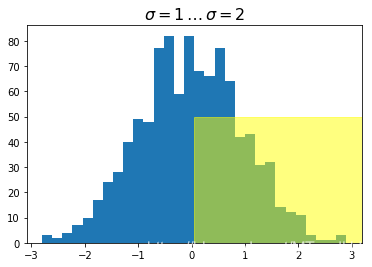
plotting in physical units
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 4))
x, y = 10*np.random.rand(2, 1000)
ax.plot(x, y*10., 'go', alpha=0.2) # plot some data in data coordinates
# add a circle in fixed-units
circ = mpatches.Circle((2.5, 2), 1.0, transform=fig.dpi_scale_trans,
facecolor='blue', alpha=0.75)
ax.add_patch(circ)
plt.show()
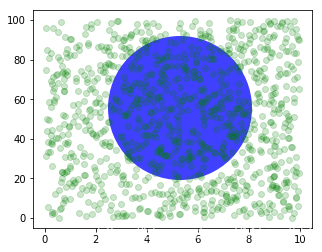
上面的圆使用了transform=fig.dpi_scale_trans坐标系统,其圆心为(2.5, 2),半径为1,显然这些都是以figsize为基准的,所以,这个圆会在图片中心,如果我们变换figsize,图片的位置(显示位置)会发生变化
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 2))
x, y = 10*np.random.rand(2, 1000)
ax.plot(x, y*10., 'go', alpha=0.2) # plot some data in data coordinates
# add a circle in fixed-units
circ = mpatches.Circle((2.5, 2), 1.0, transform=fig.dpi_scale_trans,
facecolor='blue', alpha=0.75)
ax.add_patch(circ)
plt.show()
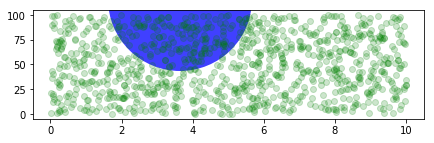
再来看一个有趣的例子,虽然我不知道改如何解释
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
xdata, ydata = (0.2, 0.7), (0.5, 0.5)
ax.plot(xdata, ydata, "o")
ax.set_xlim((0, 1))
trans = (fig.dpi_scale_trans +
transforms.ScaledTranslation(xdata[0], ydata[0], ax.transData))
# plot an ellipse around the point that is 150 x 130 points in diameter...
circle = mpatches.Ellipse((0, 0), 150/72, 130/72, angle=40,
fill=None, transform=trans)
ax.add_patch(circle)
plt.show()
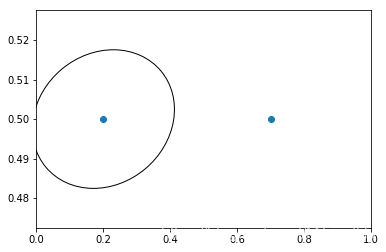
注意上面trans后面有个+号,这个表示,显示用dpi_scale_trans,即在图片(0, 0)也就是左下角位置画一个大小合适的椭圆,然后将这个椭圆移动到(x[data][0], y[data][0])位置处,感觉实现是椭圆上点每个都加上(xdata[0], ydata[0])
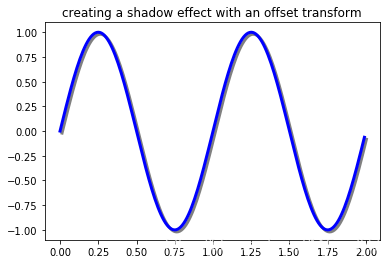
使用offset transforms 创建阴影效果
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# make a simple sine wave
x = np.arange(0., 2., 0.01)
y = np.sin(2*np.pi*x)
line, = ax.plot(x, y, lw=3, color='blue')
# shift the object over 2 points, and down 2 points
dx, dy = 2/72., -2/72.
offset = transforms.ScaledTranslation(dx, dy, fig.dpi_scale_trans)
shadow_transform = ax.transData + offset
# now plot the same data with our offset transform;
# use the zorder to make sure we are below the line
ax.plot(x, y, lw=3, color='gray',
transform=shadow_transform,
zorder=0.5*line.get_zorder())
ax.set_title('creating a shadow effect with an offset transform')
plt.show()
函数链接
matplotlib 高阶之Transformations Tutorial的更多相关文章
- matplotlib 高阶之path tutorial
目录 Bezier example 用path来画柱状图 随便玩玩 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.path import Path i ...
- matplotlib 高阶之patheffect (阴影,强调)
目录 添加阴影 使Artist变得突出 更多效果 我们可以通过path来修饰Artist, 通过set_path_effects import matplotlib.pyplot as plt imp ...
- c#语言-高阶函数
介绍 如果说函数是程序中的基本模块,代码段,那高阶函数就是函数的高阶(级)版本,其基本定义如下: 函数自身接受一个或多个函数作为输入. 函数自身能输出一个函数,即函数生产函数. 满足其中一个条件就可以 ...
- swift 的高阶函数的使用代码
//: Playground - noun: a place where people can play import UIKit var str = "Hello, playground& ...
- JavaScript高阶函数
所谓高阶函数(higher-order function) 就是操作函数的函数,它接收一个或多个函数作为参数,并返回一个新函数. 下面的例子接收两个函数f()和g(),并返回一个新的函数用以计算f(g ...
- 分享录制的正则表达式入门、高阶以及使用 .NET 实现网络爬虫视频教程
我发布的「正则表达式入门以及高阶教程」,欢迎学习. 课程简介 正则表达式是软件开发必须掌握的一门语言,掌握后才能很好地理解到它的威力: 课程采用概念和实验操作 4/6 分隔,帮助大家理解概念后再使用大 ...
- python--函数式编程 (高阶函数(map , reduce ,filter,sorted),匿名函数(lambda))
1.1函数式编程 面向过程编程:我们通过把大段代码拆成函数,通过一层一层的函数,可以把复杂的任务分解成简单的任务,这种一步一步的分解可以称之为面向过程的程序设计.函数就是面向过程的程序设计的基本单元. ...
- python学习道路(day4note)(函数,形参实参位置参数匿名参数,匿名函数,高阶函数,镶嵌函数)
1.函数 2种编程方法 关键词面向对象:华山派 --->> 类----->class面向过程:少林派 -->> 过程--->def 函数式编程:逍遥派 --> ...
- Scala的函数,高阶函数,隐式转换
1.介绍 2.函数值复制给变量 3.案例 在前面的博客中,可以看到这个案例,关于函数的讲解的位置,缺省. 4.简单的匿名函数 5.将函数做为参数传递给另一个函数 6.函数作为输出值 7.类型推断 8. ...
随机推荐
- 学习java 7.11
学习内容: 泛型定义格式:<类型> 优点:把运行时期的问题提前到编译期间:避免了强制类型转换 泛型方法:public class Fanxing { public <T> ...
- 零基础学习java------30---------wordCount案例(涉及到第三种多线程callable)
知识补充:多线程的第三种方式 来源:http://www.threadworld.cn/archives/39.html 创建线程的两种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnabl ...
- 【STM32】WS2812介绍、使用SPI+DMA发送数据
这篇要使用到SPI+DMA,需要了解的话,可以参考我另两篇博客 时钟:https://www.cnblogs.com/PureHeart/p/11330967.html SPI+DMA通信:https ...
- Camera、音频录制与Vitamio框架
一.Camera 1.概述 Android框架包含了各种相机哥相机功能的支持,是你可以在应用中捕获图像和视频. 在应用能使用设备上的相机之前,先想一想将来会如何使用此硬件: (1)Camera 应该 ...
- static JAVA
static 关键字:使用static修饰的变量是类变量,属于该类本身,没有使用static修饰符的成员变量是实例变量,属于该类的实例.由于同一个JVM内只对应一个Class对象,因此同一个JVM内的 ...
- 【Spring Framework】Spring入门教程(五)AOP思想和动态代理
本文主要讲解内容如下: Spring的核心之一 - AOP思想 (1) 代理模式- 动态代理 ① JDK的动态代理 (Java官方) ② CGLIB 第三方代理 AOP概述 什么是AOP(面向切面编程 ...
- 一、手把手教你docker搭建fastDFS文件上传下载服务器
在搭建fastDFS文件上传下载服务器之前,你需要准备的有一个可连接的linux服务器,并且该linux服务器上已经安装了docker,若还有没安装docker的,先百度自行安装docker. 1.执 ...
- maven项目install时忽略执行test
1.在项目所在文件夹根目录使用maven命令打包时: <!-- 不执行单元测试,也不编译测试类 --> mvn install -Dmaven.test.skip=true 或 <! ...
- Mockito 入门详解
一个测试方法主要包括三部分: setup 执行操作 验证结果 public class CalculatorTest { Calculator mCalculator; @Before // setu ...
- 【C/C++】输入:连续输入,以逗号隔开
连续输入,以空格或者以逗号隔开,换行符结束 [范例]输入 23 12 34 56 33或者 23,12,34,56,33 则 vector<int> data; int tmp; whil ...
