shell脚本 3 流程控制
shell流程控制
流程控制是改变程序运行顺序的指令。linux shell有一套自己的流程控制语句,其中包括条件语句(if),循环语句(for,while),选择语句(case)。下面我将通过例子介绍下,各个语句使用方法
if语句
格式:
格式:if list; then list; [ elif list; then list; ] ... [ else list; ] fi 1.1 单分支
if 条件表达式; then
命令
fi 实例:
#!/bin/bash
N=10
if [ $N -gt 5 ]; then
echo yes
fi # bash test.sh
yes 1.2 双分支 if 条件表达式; then
命令
else
命令
fi 实例1: #!/bin/bash
N=10
if [ $N -lt 5 ]; then
echo yes
else
echo no
fi # bash test.sh
no 实例2:判断crond进程是否正在运行 -v: 表示取反
-c: 即count,取代通常的输出,显示行数 #!/bin/bash
NAME=crond
NUM=$(ps aux | grep $NAME | grep -vc grep)
if [ $NUM -eq 1 ]; then
echo "$NAME running."
else
echo "$NAME is not running!"
fi 实例3:检查主机是否在线
-c:表示发送几次包
-w:表示等待时间。当试图检测不可达主机时此选项很有用。 #!/bin/bash
if ping -c 1 192.168.1.1 &>/dev/null; then
echo "OK."
else
echo "NO!"
fi
if 语句可以直接对命令状态进行判断,就省去了获取$?这一步! 1.3 多分支 if 条件表达式; then
命令
elif 条件表达式; then
命令
else
命令
fi 当不确定条件符合哪一个时,就可以把已知条件判断写出来,做相应的处理。 实例1:
$1:表示接受用户输入参数 #!/bin/bash
N=$1
if [ $N -eq 3 ]; then
echo "eq 3"
elif [ $N -eq 5 ]; then
echo "eq 5"
elif [ $N -eq 8 ]; then
echo "eq 8"
else
echo "no"
fi 如果第一个条件符合就不再向下匹配。
shell编程之if语句实战案例
需求:
1. 完成用户输入文件或者目录的自动复制,并可以实现用户指定复制目标位置。
2. 用户体验佳。 #!/bin/bash
read -p "please enter a file you want to copy:" file
if [ -f $file -o -d $file ];then
read -p "do you want to copy the $file?(y/n)" sure
confirm=$(echo ${sure} | tr A-Z a-z)
if [ "$confirm" == "y" ];then
read -p "where do you want to copy?" dire
if [ -d $dire ];then
cp -a $file $dire
echo "the $file copied to $dire"
else
echo "the $dire is not exists"
exit 1
fi
elif [ "$confirm" == "n" ];then
echo "bye"
else
echo "pls input y or n"
fi
else
echo "the $file is not exists"
fi
练习题1:尝试写一个shell简单的计算器,实现加减乘除。
请输入一个数字: 7
请输入运算符:+
请输入第二个数字:7
7+7=14

练习题2:输入一个用户,用脚本判断判断该用户是否存在。

for语句
格式:for name [ [ in [ word ... ] ] ; ] do list ; done for 变量名 in 取值列表; do
命令
done 或者
for 变量名 in 取值列表 do 命令 done 实例1:
#!/bin/bash
for i in {1..3}; do
echo $i
done # bash test.sh
1
2
3 实例2:计算100以内偶数和
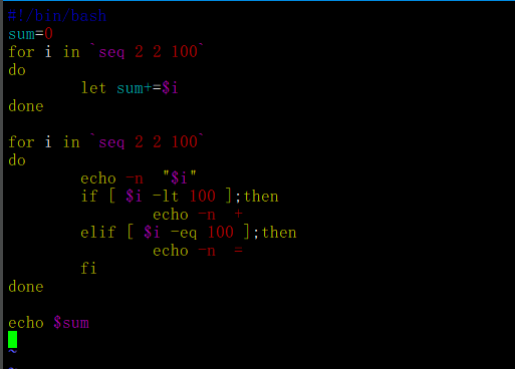
#!/bin/bash
sum=0
for i in `seq 2 2 100`
do
let sum+=$i
done
echo "$sum" shell编程之for语句实战案例 需求:
1. 批量检查当前教室主机是否在线 #!/bin/bash
. /etc/init.d/functions
ip=192.168.7.
for i in {100..150}
do
if ping -c 1 -w 1 $ip$i &>/dev/null;then
echo -n "$ip$i在线!"
success
echo ""
else
echo -n "$ip$i不在线!"
failure
echo ""
fi
done
练习题1:计算100以内的偶数和
练习题2:判断/root目录下面的文件类型

while语句 条件为真就进入死循环;条件为假就退出循环 格式:while list; do list; done
while 条件表达式; do
命令
done 实例1: #!/bin/bash
N=0
while [ $N -lt 5 ]; do
let N++
echo $N
done # bash test.sh
1
2
3
4
5 当条件表达式为 false 时,终止循环。 实例2:条件表达式为 true,将会产生死循环
#!/bin/bash
while [ 1 -eq 1 ]; do
echo "yes"
done 也可以条件表达式直接用 true: #!/bin/bash
while true; do
echo "yes"
done 死循环有什么作用那?
可以用来后台运行检测脚本,如下是是一个检测脑裂的脚本 我们只需要在命令行中输入 nohup bash naolie.sh & 即可在后台持续运行该脚本 例子1:检测脑裂 #!/bin/bash
while true
do
ip=`ip a s eth0 | awk -F " +" 'NR==4{print $3}' | awk -F "/" '{print $1}' | awk -F "." '{print $4}'`1
ping -c 3 -i 1 -W 1 10.220.5.166 &>/dev/null
if [ $? -eq 0 ] && [ $ip = 1001 ];then
echo "happed naolie"
else
echo "everything is ok"
fi
done 例子2:检测终端数量 #!/bin/bash
while true
do
num=`who | wc -l`
echo "当前打开终端数量为:$num"
sleep 5
done 要想使用 while 循环逐行读取 a.txt 文件,有三种方式: 方式 1: #!/bin/bash
cat ./a.txt | while read LINE; do
echo $LINE
done
方式2: #!/bin/bash
while read LINE; do
echo $LINE
done < ./a.txt
方式3: exec < ./a.txt # 读取文件作为标准输出
while read LINE; do
echo $LINE
done
与 while 关联的还有一个 until 语句,它与 while 不同之处在于,是当条件表达式为 false 时才循环,实际使用中比较少,这里不再讲解。 #!/bin/bash
n=0
until [ $n -eq 5 ]
do
let n++
echo "$n" done break和continue语句
break 是终止循环。
continue 是跳出当前循环。 示例 1:在死循环中,满足条件终止循环 #!/bin/bash
N=0
while true; do
let N++
if [ $N -eq 5 ]; then
break
fi
echo $N
done # bash test.sh
1
2
3
4 里面用了 if 判断,并用了 break 语句,它是跳出循环。与其关联的还有一个 continue 语句,它是跳出本次循环。 示例 2:举例子说明 continue 用法
#!/bin/bash
N=0
while [ $N -lt 5 ]; do
let N++
if [ $N -eq 3 ]; then
continue
fi
echo $N
done # bash test.sh
1
2
4 当变量 N 等于 3 时,continue 跳过了本次循环,没有执行下面的 echo。 注意:continue 与 break 语句只能循环语句中使用。 [root@ken-node1 ~]# cat test.sh
#!/bin/bash
st=0
while true
do
let st++
if [ $st -eq 5 ];then
continue
elif [ $st -eq 10 ];then
break
else
echo "$st"
fi done
[root@ken-node1 ~]# bash test.sh
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
9 case语句
case 语句一般用于选择性来执行对应部分块命令。
case 模式名 in
模式 1)
命令
;;
模式 2)
命令
;;
*)
不符合以上模式执行的命令
esac 每个模式必须以右括号结束,命令结尾以双分号结束,最后一个模式不需要添加;;。 示例1:根据位置参数匹配不同的模式
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
start)
echo "start."
;;
stop)
echo "stop."
;;
restart)
echo "restart."
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart}"
esac # bash test.sh
Usage: test.sh {start|stop|restart} # bash test.sh start
start. # bash test.sh stop
stop. # bash test.sh restart
restart. 实例2:
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
[0-9])
echo "match number."
;;
[a-z])
echo "match letter."
;;
'-h'|'--help')
echo "help"
;;
*)
echo "Input error!"
exit
esac # bash test.sh 1
match number. # bash test.sh a
match letter. # bash test.sh -h
help # bash test.sh --help
help
模式支持的正则有:*、?、[ ]、[.-.]、|。后面有章节单独讲解 Shell 正则表达式。 shell编程高级实战 实战1:写一个猜数字的小游戏
要求:
1. 猜对退出
2. 数字随机
3. 使用体验佳 #!/bin/bash
clear
num=`echo $RANDOM`
count=0
while true
do
let count++
read -p "pls enter a num you guess:" guessnum
if [ $guessnum -lt $num ]; then
echo "the num is so smaller!"
elif [ $guessnum -gt $num ];then
echo "the num is so bigger!"
elif [ $guessnum -eq $num ];then
echo "right!wonderful! "
break
else
echo "good bye"
exit
fi
done
echo -e "\033[36myou guess $count times\033[0m" #-e允许对下面列出的加反斜线转义的字符进行解释. 实战2:检测当前教室在线IP地址
要求:
1.显示美观 #!/bin/bash
. /etc/init.d/functions
ip=172.20.10.
for i in {1..255}
do
if ping -c 1 $ip$i &>/dev/null ;then
echo -n "$ip$i" #-n表示不输出行尾的换行符
success
echo ""
else
echo -n "$ip$i"
failure
echo ""
fi
done
实战3:检查软件包是否安装
要求:
1.用户输入软件名即可进行查询
#!/bin/bash
read -p "pls enter a softname:" softname
if rpm -q $softname &>/dev/null ;then
echo "the $softname is already installed"
else
echo "the $softname" is not installed
fi 实战4:打印九九乘法表
#!/bin/bash
for i in `seq 9`
do
for a in `seq 9`
do
if [ $a -le $i ];then
echo -n "$a*$i=$(($i*$a)) "
fi
done
echo ""
done 补充练习题
1.实现简单计算器(加减乘除) #!/bin/bash
read -p "请输入第一个数字:" a
read -p "请输入运算符[+-*/]:" b
read -p "请输入第二个数字:" c
if [ -n $a -a -n $b -a -n $c ];then
if [ "$b" == "+" ];then
echo "$a+$c=$(($a+$c))"
elif [ "$b" == "-" ];then
echo "$a-$c=$(($a-$c))"
elif [ "$b" == "*" ];then
echo "$a*$c=$(($a*$c))"
elif [ "$b" == "/" ];then
echo "$a/$c=$(($a/$c))"
else
echo "请输入+—*%"
fi
else
echo "请按照要求输入内容!"
fi 2. 批量创建100个以数字开头的文件,并每隔一秒钟输出到终端 #!/bin/bash
for i in {1..100}
do
touch ${i}.txt
echo "${i}.txt"
sleep 1
done 3.动态持续监测本机linux系统内存剩余量(仅显示数值),并在终端输出 #!/bin/bash
while true
do
mem=`free -h | grep "Mem" | cut -d "M" -f 4 | tr -d " "`
echo $mem
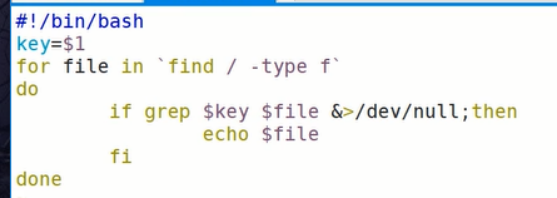
sleep 1 done nohup bash 脚本名 & # 可以将脚本挂在后台运行 4.搜索带有指定的关键词的文件,并且输出文件名
shell脚本 3 流程控制的更多相关文章
- shell脚本之流程控制
shell脚本之流程控制 shell脚本之流程控制 条件语句 条件判断 循环语句for,while,until for循环 while循环 until循环 循环控制语句continue 循环控制语 ...
- Shell脚本学习 - 流程控制和函数
继续Shell的学习.上两篇是关于基本数据类型,基本语法以及运算符相关,这一篇是流程控制相关(if, for, while) 流程控制 if else 流程控制不可为空,如果else没有语句执行,就不 ...
- Shell脚本之流程控制(if、for、while)
if 判断 if语句的三种格式: (1)if (2)if else (3)if elif else 语法格式如下: #if 语法格式 if 条件 then 命令1... 命令2... fi #if e ...
- shell脚本(10)-流程控制while
一.while循环介绍 while循环与for一样,一般不知道循环次数使用for,不知道循环的次数时推荐使用while 二.while语法 while [ condition ] #条件为真才会循环, ...
- shell脚本(11)-流程控制case
一.case介绍 生产环境下,遇到要根据不同的状况执行不同的预案的情况,首先根据可能出现的情况写出对应预案,根据出现的情况来加载不同的预案 特点:根据给予的不同的代码块 二.case语法 case 变 ...
- 【Shell 编程基础第二部分】Shell里的流程控制、Shell里的函数及脚本调试方法!
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaominghimi/article/details/7603003 本站文章均为李华明Himi原创,转载务必在明显处注明:转载自[黑米GameDev街区 ...
- Shell命令和流程控制
Shell命令和流程控制 在shell脚本中可以使用三类命令: 1)Unix 命令: 虽然在shell脚本中可以使用任意的unix命令,但是还是由一些相对更常用的命令.这些命令通常是用来进行文件和文字 ...
- Shell脚本的条件控制和循环语句
条件判断:if语句 语法格式: if [ expression ] then Statement(s) to be executed if expression is true fi 注意:expre ...
- Shell命令和流程控制[linux常用命令的使用]
在shell脚本中使用三类命令: unix命令 概念:管道.重定向.backtick 流程控制 1 unix命令 echo "some text":在屏幕上输出信息 ls:文件列表 ...
随机推荐
- 系统错误,MSVCP100D.dll找不到或丢失!
文章首发 | 公众号:lunvey 今日研究c++,找了一些示例程序,发现无法打开.弹出如下的报错提示: 作为新时代人类,遇见问题第一件事情就是问度娘.然而眼花缭乱的检索数据,大家众说纷纭,不知道如何 ...
- Python3网络爬虫-- 使用代理,轮换使用各种IP访问
# proxy_list 代理列表 run_times = 100000 for i in range(run_times): for item in proxy_list: proxies = { ...
- HashSet为什么可以有序输出?
首先HashSet是不保证有序,而不是保证无序,因为在HashSet中,元素是按照他们的hashCode值排序存储的.对于单个字符而言,这些hashCode就是ASCII码,因此,当按顺序添加自然数或 ...
- Vue框架- 指令操作
目录 一.Vue指令操作 1. 表单指令 2. 条件指令 3. 循环指令 4. 斗篷指令 5. 实例成员:delimiter分隔符(了解) 6. filter过滤器 7. computed计算属性 8 ...
- hexo 报错 use_date_for_updated is deprecated...
hexo 报错 use_date_for_updated is deprecated... WARN Deprecated config detected: "use_date_for_up ...
- 面试系列二:精选大数据面试真题JVM专项-附答案详细解析
公众号(五分钟学大数据)已推出大数据面试系列文章-五分钟小面试,此系列文章将会深入研究各大厂笔面试真题,并根据笔面试题扩展相关的知识点,助力大家都能够成功入职大厂! 大数据笔面试系列文章分为两种类型: ...
- pytorch(04)简单的线性回归
线性回归 线性回归是分析一个变量与另外一个变量之间关系的方法 因变量:y 自变量:x 关系:线性 y = wx+b 分析:求解w,b 求解步骤: 确定模型,Model:y = wx+b 选择损失函数, ...
- JPress企业站主题-zbout
JPress企业站主题-zbout 经典的黑白灰颜色搭配风格,首页配置有轮播图.案例展示.公司简介.新闻中心.联系方式以及合作伙伴模块,全站使用了响应式结构,可以自适应电脑端和手机端浏览器访问.主题整 ...
- RPC基础以及造一个RPC的轮子需要注意些什么
RPC基础以及造一个RPC的轮子需要注意些什么 前言 rpc即远程过程调用,是分布式系统常用的通信方法.远程可以是在一台机器上的不同进程或在不同一个机器上的不同进程.rpc更看重速度,像调用本地方法一 ...
- Java概述与准备
Java概述 Java语言背景介绍 Java之父:詹姆斯·高斯林(James Gosling) java语言的三个版本: JavaSE: Java 语言的(标准版),用于桌面应用的开发,是其他两个 ...
