AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
1 简介
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer简称AQS是一个抽象同步框架,可以用来实现一个依赖状态的同步器。
JDK1.5中提供的java.util.concurrent包中的大多数的同步器(Synchronizer)如Lock, Semaphore, Latch, Barrier等,这些类之间大多可以互相实现,如使用Lock实现一个Semaphore或者反过来,但是它们都是基于java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer这个类的框架实现的,理解了这个稍微复杂抽象的类再去理解其他的同步器就很轻松了。
2 原理介绍
AQS的核心是一个线程等待队列,采用的是一个先进先出FIFO队列。用来实现一个非阻塞的同步器队列有主要有两个选择Mellor-Crummey and Scott (MCS) locks和Craig, Landin, and Hagersten (CLH) locks的变种。CLH锁更适合处理取消和超时,所以AQS基于CLH进行修改作为线程等待队列。
CLH队列使用pred引用前节点形成一个队列,入队enqueue和出队dequeue操作都可以通过原子操作完成。
在 AQS 内部,通过维护一个FIFO 队列来管理多线程的排队工作。在公平竞争的情况下,无法获取同步状态的线程将会被封装成一个节点,置于队列尾部。入队的线程将会通过自旋的方式获取同步状态,若在有限次的尝试后,仍未获取成功,线程则会被阻塞住。大致示意图如下:

当头结点释放同步状态后,且后继节点对应的线程被阻塞,此时头结点线程将会去唤醒后继节点线程。后继节点线程恢复运行并获取同步状态后,会将旧的头结点从队列中移除,并将自己设为头结点。大致示意图如下:

其中每个节点包含如下状态:
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread has cancelled */
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
/** waitStatus value to indicate successor's thread needs unparking */
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
/** waitStatus value to indicate thread is waiting on condition */
static final int CONDITION = -2;
/**
* waitStatus value to indicate the next acquireShared should
* unconditionally propagate
*/
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
/**
* Status field, taking on only the values:
* SIGNAL: The successor of this node is (or will soon be)
* blocked (via park), so the current node must
* unpark its successor when it releases or
* cancels. To avoid races, acquire methods must
* first indicate they need a signal,
* then retry the atomic acquire, and then,
* on failure, block.
* CANCELLED: This node is cancelled due to timeout or interrupt.
* Nodes never leave this state. In particular,
* a thread with cancelled node never again blocks.
* CONDITION: This node is currently on a condition queue.
* It will not be used as a sync queue node
* until transferred, at which time the status
* will be set to 0. (Use of this value here has
* nothing to do with the other uses of the
* field, but simplifies mechanics.)
* PROPAGATE: A releaseShared should be propagated to other
* nodes. This is set (for head node only) in
* doReleaseShared to ensure propagation
* continues, even if other operations have
* since intervened.
* 0: None of the above
*
* The values are arranged numerically to simplify use.
* Non-negative values mean that a node doesn't need to
* signal. So, most code doesn't need to check for particular
* values, just for sign.
*
* The field is initialized to 0 for normal sync nodes, and
* CONDITION for condition nodes. It is modified using CAS
* (or when possible, unconditional volatile writes).
*/
CANCELED表示线程等待已经取消,是唯一一个大于0的状态。
SINALG表示需要唤醒next节点
CONDITION表明线程正在等待一个条件
PROPAGATE用于acquireShared中向后传播
3 acquire
/**
* Acquires in exclusive mode, ignoring interrupts. Implemented
* by invoking at least once {@link #tryAcquire},
* returning on success. Otherwise the thread is queued, possibly
* repeatedly blocking and unblocking, invoking {@link
* #tryAcquire} until success. This method can be used
* to implement method {@link Lock#lock}.
*
* @param arg the acquire argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryAcquire} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
*/
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
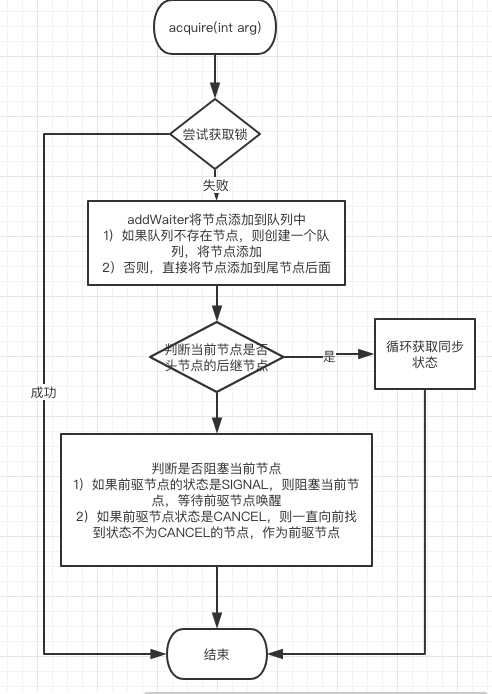
1、如果尝试获取锁成功整个获取操作就结束,否则转到2. 尝试获取锁是通过方法tryAcquire来实现的,AQS中并没有该方法的具体实现,只是简单地抛出一个不支持操作异常,在AQS简介中谈到tryAcquire有很多实现方法,这里不再细化,只需要知道如果获取锁成功该方法返回true即可;
2、如果获取锁失败,那么就创建一个代表当前线程的结点加入到等待队列的尾部,是通过addWaiter方法实现的,来看该方法的具体实现:
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
enq(node);
return node;
}
该方法创建了一个独占式结点,然后判断队列中是否有元素,如果有(pred!=null)就设置当前结点为队尾结点,即将当前节点插入到尾节点的后面,然后返回;
如果没有元素(pred==null),表示队列为空,走的是入队操作
/**
* Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above.
* @param node the node to insert
* @return node's predecessor
*/
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
enq方法采用的是变种CLH算法,先看头结点是否为空,如果为空就创建一个傀儡结点,头尾指针都指向这个傀儡结点,这一步只会在队列初始化时会执行;
如果头结点非空,就采用CAS操作将当前结点插入到头结点后面,如果在插入的时候尾结点有变化,就将尾结点向后移动直到移动到最后一个结点为止,然后再把当前结点插入到尾结点后面,尾指针指向当前结点,入队成功。
3、将新加入的结点放入队列之后,这个结点有两种状态,要么获取锁,要么就挂起,如果这个结点不是头结点的后继节点,就看看这个结点是否应该挂起,如果应该挂起,就挂起当前结点,是否应该挂起是通过shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire方法来判断的
/**
* Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in
* queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire.
*
* @param node the node
* @param arg the acquire argument
* @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting
*/
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
//判断前驱节点是否是头节点,如果是,则循环获取同步
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//如果获取同步状态失败或者前驱节点不是头节点,则判断是否将当前节点挂起
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
/**
* Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire.
* Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal
* control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev
*
* @param pred node's predecessor holding status
* @param node the node
* @return {@code true} if thread should block
*/
/**
* 该方法主要用途是,当线程在获取同步状态失败时,根据前驱节点的等待状态,决定后续的动作。比如前驱
* 节点等待状态为 SIGNAL,表明当前节点线程应该被阻塞住了。不能老是尝试,避免 CPU 忙等。
* —————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
* | 前驱节点等待状态 | 相应动作 |
* —————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
* | SIGNAL | 阻塞 |
* | CANCELLED | 向前遍历, 移除前面所有为该状态的节点 |
* | waitStatus < 0 | 将前驱节点状态设为 SIGNAL, 并再次尝试获取同步状态 |
* —————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
*/
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
//首先检查前趋结点的waitStatus位,如果为SIGNAL,表示前趋结点会通知它,那么它可以放心大胆地挂起了
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
//如果前趋结点是一个被取消的结点怎么办呢?那么就向前遍历跳过被取消的结点,直到找到一个没有被取消的结点为止,将找到的这个结点作为它的前趋结点,
//将找到的这个结点的waitStatus位设置为SIGNAL,返回false表示线程不应该被挂起,继续尝试获取锁
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
/*
* 等待状态为 0 或 PROPAGATE,设置前驱节点等待状态为 SIGNAL,
* 并再次尝试获取同步状态。
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 调用 LockSupport.park 阻塞自己
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
4 release
/**
* Releases in exclusive mode. Implemented by unblocking one or
* more threads if {@link #tryRelease} returns true.
* This method can be used to implement method {@link Lock#unlock}.
*
* @param arg the release argument. This value is conveyed to
* {@link #tryRelease} but is otherwise uninterpreted and
* can represent anything you like.
* @return the value returned from {@link #tryRelease}
*/
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
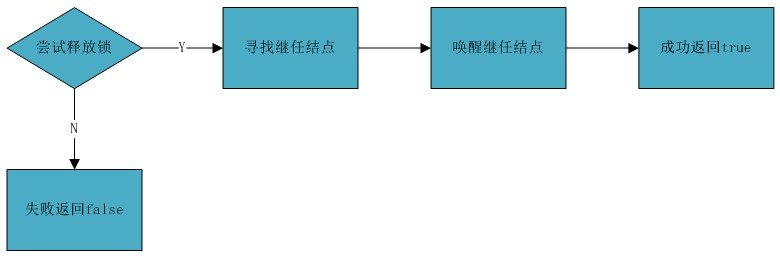
1、release过程比acquire要简单,首先调用tryRelease释放锁,如果释放失败,直接返回;
2、释放锁成功后需要唤醒继任结点,是通过方法unparkSuccessor实现的
/**
* Wakes up node's successor, if one exists.
*
* @param node the node
*/
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); /*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
1、node参数传进来的是头结点,首先检查头结点的waitStatus位,如果为负,表示头结点还需要通知后继结点,这里不需要头结点去通知后继,因此将该该标志位清0.
2、然后查看头结点的下一个结点,如果下一个结点不为空且它的waitStatus<=0,表示后继结点没有被取消,是一个可以唤醒的结点,于是唤醒后继结点返回;如果后继结点为空或者被取消了怎么办?寻找下一个可唤醒的结点,然后唤醒它返回。
这里并没有从头向尾寻找,从队列尾部开始向前查找,找到队列最前面没有被取消的节点,然后,将其唤醒。
为什么需要从队列尾部开始向前查找呢?
因为在CLH队列中的结点随时有可能被中断,被中断的结点的waitStatus设置为CANCEL,而且它会被踢出CLH队列,如何个踢出法,就是它的前趋结点的next并不会指向它,而是指向下一个非CANCEL的结点,而它自己的next指针指向它自己。一旦这种情况发生,如何从头向尾方向寻找继任结点会出现问题,因为一个CANCEL结点的next为自己,那么就找不到正确的继任接点。
有的人又会问了,CANCEL结点的next指针为什么要指向它自己,为什么不指向真正的next结点?为什么不为NULL?
第一个问题的答案是这种被CANCEL的结点最终会被GC回收,如果指向next结点,GC无法回收。
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的更多相关文章
- 多线程条件通行工具——AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
本文原创,转载请注明出处! 参考文章: <"JUC锁"03之 公平锁(一)> <"JUC锁"03之 公平锁(二)> AbstractOw ...
- Java并发基础框架AbstractQueuedSynchronizer初探(ReentrantLock的实现分析)
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer是实现Java并发类库的一个基础框架,Java中的各种锁(RenentrantLock, ReentrantReadWriteLock)以及同步工具 ...
- 【JUC】JDK1.8源码分析之AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(二)
一.前言 在锁框架中,AbstractQueuedSynchronizer抽象类可以毫不夸张的说,占据着核心地位,它提供了一个基于FIFO队列,可以用于构建锁或者其他相关同步装置的基础框架.所以很有必 ...
- 转载:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的介绍和原理分析
简介 提供了一个基于FIFO队列,可以用于构建锁或者其他相关同步装置的基础框架.该同步器(以下简称同步器)利用了一个int来表示状态,期望它能够成为实现大部分同步需求的基础.使用的方法是继承,子类通过 ...
- 并发编程 20—— AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 深入分析
Java并发编程实践 目录 并发编程 01—— ThreadLocal 并发编程 02—— ConcurrentHashMap 并发编程 03—— 阻塞队列和生产者-消费者模式 并发编程 04—— 闭 ...
- Java Concurrent之 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
ReentrantLock/CountDownLatch/Semaphore/FutureTask/ThreadPoolExecutor的源码中都会包含一个静态的内部类Sync,它继承了Abstrac ...
- 深度解析Java8 – AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的实现分析(下)
本文首发在infoQ 作者:刘锟洋 前言 经过本系列的上半部分JDK1.8 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的实现分析(上)的解读,相信很多读者已经对AbstractQueu ...
- 深度解析Java8 – AbstractQueuedSynchronizer的实现分析(上)
本文首发在infoQ :www.infoq.com/cn/articles/jdk1.8-abstractqueuedsynchronizer 前言: Java中的FutureTask作为可异步执行任 ...
- Java 线程 — AbstractQueuedSynchronizer
锁 锁就是一种状态,比如互斥锁:同一时间只能有一个线程拥有,可以使用一个整型值来标志当前的状态 0:表示没有现成占有锁 1:表示锁已经被占用 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 实现 ...
- Java并发包源码学习之AQS框架(四)AbstractQueuedSynchronizer源码分析
经过前面几篇文章的铺垫,今天我们终于要看看AQS的庐山真面目了,建议第一次看AbstractQueuedSynchronizer 类源码的朋友可以先看下我前面几篇文章: <Java并发包源码学习 ...
随机推荐
- CSS回顾(基础知识,元素,选择器,盒子,颜色)
元素分类: 1.行级元素:内联元素 inline 特征:内容决定元素所占位置,不可以通过CSS改变宽高 span strong em a del 2.块级元素:block特征:独占一行,可 ...
- 2015年6月6日,杨学明老师《IT技术人才管理角色转型与实践》专题培训在苏宁云商成功举办!
2015.6.6,在中国南京苏宁总部,研发资深顾问.资深讲师为苏宁易购IT事业部全体产品总监.研发总监进行了为期一天的<IT技术人才管理角色转型与实践>的内训服务. 杨学明老师分别从技术人 ...
- javascript:正则表达式、一个表单验证的例子
本文内容: 正则表达式 正则表达式的使用方法 正则表达式的特殊匹配字符 正则表达式修饰符 利用正则表达式进行表单验证的例子 首发日期:2018-05-13 正则表达式: 正则表达式的使用方法: 首先创 ...
- Java:字节流和字符流(输入流和输出流)
本文内容: 什么是流 字节流 字符流 首发日期:2018-07-24 什么是流 流是个抽象的概念,是对输入输出设备的抽象,输入流可以看作一个输入通道,输出流可以看作一个输出通道. 输入流是相对程序而言 ...
- Linux命令工作中常用总结
1. 搜索 在vi和vim中如果打开一个很大的文件,不容易找到对应的内容,可以使用自带的搜索关键字进行搜索定位: 在vi和vim界面中输入:"/"(反斜杠),之后会出现一个输入框让 ...
- matlab练习程序(曲面拟合)
这里用到的还是最小二乘方法,和上一次这篇文章原理差不多. 就是首先构造最小二乘函数,然后对每一个系数计算偏导,构造矩阵乘法形式,最后解方程组. 比如有一个二次曲面:z=ax^2+by^2+cxy+dx ...
- C#多线程图片爬虫
写了个简单的多线程图片爬虫,整理一下.数据已经爬下来了,图片URL需要自行拼接,首先从Lawyers表中取的RawData字段,RawData中有一个list字段是json格式的数据,需要的只是lis ...
- Linux中如何通过设备号找到设备
关于Linux中的设备文件,设备文件用来为操作系统和用户提供它们代表的设备接口.所有的Linux设备文件均位于/dev目录下,是根(/)文件系统的一个组成部分,因为这些设备文件在操作系统启动过程中必须 ...
- Win10 C盘桌面文件右上方的两个蓝色箭头解决方案
之前看网上有很多桌面蓝色箭头的解决方案,也进行了一些尝试 可是每次Win10系统更新之后蓝色箭头就会重新显示. 最终方案:将建立在桌面的C盘文件移到D盘,桌面创建对应的快捷方式. 一劳永逸,暴力破解.
- MyBatis:参数传递 [转]
一.单个参数: public List<XXBean> getXXBeanList(String xxCode); <select id="getXXXBeanList&q ...
