Java设计模式(6)——创建型模式之原型模式(Prototype)
一、概述
概念

// 引用自《Java与模式》
UML图

第二种:登记式
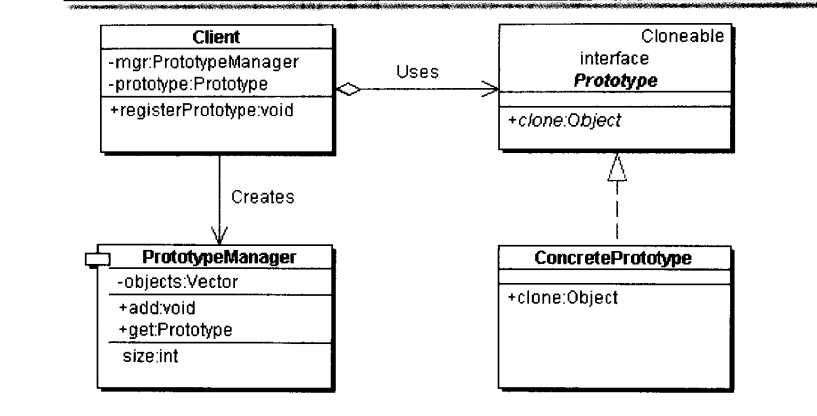
二、实践
先导知识
对象的拷贝:
直接赋值:此时只是相当于a1,a2指向同一个对象,无论哪一个操作的都是同一个对象,也就是其中一个改变对象属性时,另外一个也会收到改变
A a1 = new A();
A a2 = a1;
浅拷贝:希望直接赋值中a1,a2可以保持独立,而不是相互影响指向同一个对象,则使用浅拷贝
在介绍浅拷贝之前,先看看Object的clone干了什么事(由于是本地方法,我们看JavaDoc,IDEA中快捷键是ctrl+Q)
Creates and returns a copy of this object. The precise meaning of "copy" may depend on the class of the object. The general intent is that, for any object x, the expression:
x.clone() != x
will be true, and that the expression:
x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass()
will be true, but these are not absolute requirements. While it is typically the case that:
x.clone().equals(x)
will be true, this is not an absolute requirement.
By convention, the returned object should be obtained by calling super.clone. If a class and all of its superclasses (except Object) obey this convention, it will be the case that x.clone().getClass() == x.getClass().
By convention, the object returned by this method should be independent of this object (which is being cloned). To achieve this independence, it may be necessary to modify one or more fields of the object returned by super.clone before returning it. Typically, this means copying any mutable objects that comprise the internal "deep structure" of the object being cloned and replacing the references to these objects with references to the copies. If a class contains only primitive fields or references to immutable objects, then it is usually the case that no fields in the object returned by super.clone need to be modified.
The method clone for class Object performs a specific cloning operation. First, if the class of this object does not implement the interface Cloneable, then a CloneNotSupportedException is thrown. Note that all arrays are considered to implement the interface Cloneable and that the return type of the clone method of an array type T[] is T[] where T is any reference or primitive type. Otherwise, this method creates a new instance of the class of this object and initializes all its fields with exactly the contents of the corresponding fields of this object, as if by assignment; the contents of the fields are not themselves cloned. Thus, this method performs a "shallow copy" of this object, not a "deep copy" operation.
The class Object does not itself implement the interface Cloneable, so calling the clone method on an object whose class is Object will result in throwing an exception at run time.
百度翻译:
创建并返回此对象的副本。“复制”的确切含义可能取决于对象的类。一般的意图是,对于任何对象x,表达式:
X()!= x
将是真的,那就是表达:
X getclass() = = X getclass()()。
这是真的,但这些不是绝对要求。虽然这是典型的情况:
X(X)等于()。
这将是真实的,这不是绝对的要求。
按照惯例,返回的对象应该致电super.clone。如果一个类和它的所有父类(除对象)遵守本公约的情况下,将X()。getclass() = = X getclass()。
按照惯例,该方法返回的对象应该独立于该对象(正在克隆)。为了实现这种独立性,可能有必要修改super.clone返回对象的一个或多个字段然后返回。通常,这意味着复制任何可变对象,这些对象包含被克隆对象的内部“深层结构”,并用对副本的引用替换这些对象的引用。如果一个类只包含原始字段或对不可变对象的引用,那么它是通常的情况下,通过super.clone返回的对象中的任何字段需要修改。
类对象的方法克隆执行特定的克隆操作。首先,如果此对象的类不能实现接口Cloneable,则会抛出CloneNotSupportedException。请注意,所有的数组都被视为实现接口Cloneable,数组类型[ ]克隆方法的返回类型是[ ]其中T是任何参考或原始类型。否则,该方法将创建该对象类的一个新实例,并用该赋值对象的相应字段的所有内容初始化其字段,这些字段的内容本身并不被克隆。因此,此方法执行此对象的“浅拷贝”,而不是“深拷贝”操作。
Object类本身不实现接口Cloneable,所以调用clone方法对一个对象的类对象将导致在运行时抛出异常。
再看网友的解释:
创建一个新对象,然后将当前对象的非静态字段复制到该新对象,
如果字段是值类型的,那么对该字段执行复制;
如果该字段是引用类型的话,则复制引用但不复制引用的对象。因此,原始对象及其副本引用同一个对象。
我们直接说结论,浅拷贝中原始类型变量是值复制,引用类型变量是和直接赋值一样,将会互相影响!
例子我们参考网友的博客:http://blog.csdn.net/XIAXIA__/article/details/41652057
深拷贝:创建一个新对象,然后将当前对象的非静态字段复制到该新对象,无论该字段是值类型的还是引用类型,都乖乖的进行复制。
其实就是解决上面浅拷贝偷懒,不会进行引用类型变量赋值的问题!
例子还是上面的例子,我们需要注意的是最后一段代码的44行处的new操作(也就是原型模式需要解决的问题,原型模式不希望new)
当然,可以根据网友的评论中的使用序列化与反序列化进行深克隆,例子参见这里:http://blog.csdn.net/zhutulang/article/details/48163213
代码实践
我们把UML图中的第一种形式进行实现,这里我们把接口改为抽象类,让clone方法有个默认实现,当然,使用接口进行方法声明然后让子类来实现也是可以的。
Prototype抽象类
/**
* 原型抽象类
* 作者: Administrator
* 日期: 2017/10/27
**/
public abstract class Prototype implements Cloneable{
private String name; public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} /**
* 可以实现自己的克隆逻辑(深克隆/浅克隆)
* @return 克隆后的对象
*/
@Override
public Object clone() {
Object obj = null;
try {
obj = super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return obj;
}
}
Prototype的两个实现类:在构造方法中完成了属性的复制!
/**
* Prototype的一个子类A
* 作者: Administrator
* 日期: 2017/10/27
**/
public class PrototypeA extends Prototype{
public PrototypeA() {
setName("PrototypeA");
}
}
/**
* Prototype的一个子类B
* 作者: Administrator
* 日期: 2017/10/27
**/
public class PrototypeB extends Prototype{
public PrototypeB() {
setName("PrototypeB");
}
}
客户端使用
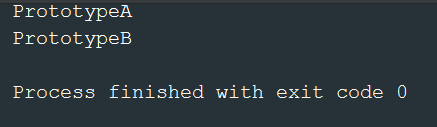
public static void main(String[] args) {
Prototype p1 = new PrototypeA("PrototypeA");
Prototype p2 = new PrototypeB("PrototypeB");
Prototype p1Clone = (Prototype) p1.clone();
Prototype p2Clone = (Prototype) p2.clone();
System.out.println(p1Clone.getName());
System.out.println(p2Clone.getName());
}
Java设计模式(6)——创建型模式之原型模式(Prototype)的更多相关文章
- Java设计模式之创建型模式
创建型模式分为五类:工厂方法模式.抽象工厂模式.单例模式.建造者模式.原型模式 一.工厂方法模式:接口-实现类.工厂类
- Java设计模式_创建型模式_单例模式
单例模式的实现: 定义一个类,在类中定义该类的静态变量,再定一个一个获取该类的静态变量的方法. UML图:
- PYTHON设计模式,创建型之工厂方法模式
我感觉和上一个差不多,可能不要动最要的地方吧... #!/usr/bin/evn python #coding:utf8 class Pizza(object): def prepare(self, ...
- PYTHON设计模式,创建型之简单工厂模式
这个系统,感觉思路清爽,,相信多练练,多思考,就会熟悉的.. http://www.jianshu.com/p/2450b785c329 #!/usr/bin/evn python #coding:u ...
- Java进阶篇设计模式之三 ----- 建造者模式和原型模式
前言 在上一篇中我们学习了工厂模式,介绍了简单工厂模式.工厂方法和抽象工厂模式.本篇则介绍设计模式中属于创建型模式的建造者模式和原型模式. 建造者模式 简介 建造者模式是属于创建型模式.建造者模式使用 ...
- Java设计模式之三 ----- 建造者模式和原型模式
前言 在上一篇中我们学习了工厂模式,介绍了简单工厂模式.工厂方法和抽象工厂模式.本篇则介绍设计模式中属于创建型模式的建造者模式和原型模式. 建造者模式 简介 建造者模式是属于创建型模式.建造者模式使用 ...
- GoF的23种设计模式之创建型模式的特点和分类
创建型模式的主要关注点是“怎样创建对象?”,它的主要特点是“将对象的创建与使用分离”.这样可以降低系统的耦合度,使用者不需要关注对象的创建细节,对象的创建由相关的工厂来完成.就像我们去商场购买商品时, ...
- Java设计模式之三建造者模式和原型模式
建造者模式 简介 建造者模式是属于创建型模式.建造者模式使用多个简单的对象一步一步构建成一个复杂的对象.这种类型的设计模式属于创建型模式,它提供了一种创建对象的最佳方式.简单的来说就是将一个复杂的东西 ...
- 建造者模式与原型模式/builder模式与prototype模式/创建型模式
建造者模式 定义 用于简化复杂对象的创建 JDK中的建造者模式 java.lang.StringBuilder中的append()方法,每次调用后返回修改后的对象本身. public StringBu ...
- 创建型模式(五) 原型模式(Prototype)
一.动机(Motivation) 在软件系统中,经常面临着"某些结构复杂的对象"的创建工作:由于需求的变化,这些对象经常面临着剧烈的变化,但是它们却拥有比较稳定一致的接口.如何应对 ...
随机推荐
- ego network的概念
转:http://greatpowerlaw.wordpress.com/2013/01/05/ego-network/ 所谓的ego network,它的节点是由唯一的一个中心节点(ego),以及这 ...
- 如何在SAP里创建configurable material物料主数据
(1) 使用tcode CT04创建characteristic: assign 所有可能的color value: (2) 使用tcode CL02创建class. 类型选择300- variant ...
- Redis 缓存穿透
Redis 缓存穿透 https://www.cnblogs.com/jiekzou/p/9212114.html 场景描述:我们在项目中使用缓存通常都是先检查缓存中是否存在,如果存在直接返回缓存内容 ...
- postgres if ,when及判断表是否存在的sql编写
判断表是否存在方法1: SELECT THEN END FROM ( select count(*) as cc from pg_class where relname = 'wo' --wo is ...
- 详解为什么32位系统只能用4G内存.
本文转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/nvd11/archive/2013/04/02/2996784.html,感谢作者的干货 既然是详解, 就从最基础的讲起了. 1. Bit( ...
- 数学归纳法·Fibonacci数列
数学归纳法 我们先来看一个例子: 我们让多诺米骨牌倒下的充要条件是: 第一块骨牌倒下: 假设当当前块骨牌倒下时,则他的后面一块也会倒下. 我们把这个例子给抽象出来就可以得到数学归纳法的证明过程: [第 ...
- window.jQuery || document.write("<script src='__PUBLIC__/assets/js/jquery.js'>"+"<"+"/script>")
今天无意中看到这样一段代码 <script type="text/javascript"> window.jQuery || document.write(" ...
- 总结PHP删除字符串最后一个字符的三种方法
一.前言 从数据库中select()读取一对多的信息时,经常需要将取出的数组用某个特定的字符分割,然后拼接成字符串. 常见的语法格式: foreach ($arr as $key => $val ...
- Fiddler学习基础(一)
Fiddler官方网站及下载地址:http://www.telerik.com/fiddler 1. Fiddler原理: 作为系统代理,所有的来自微软互联网服务(WinInet)的http请求再到达 ...
- halcon 使用elliptic_axis计算规则矩形角度
elliptic_axis算子是用于计算与Region等价椭圆的相关参数的,注意必须使用规则矩形!!!,不规则区域想其他办法比如模板匹配. elliptic_axis (Region, Ra, Rb, ...
