HyperLedger Fabric 1.4 单机单节点部署(10.2)
网易云课堂视频在线教学,地址:https://study.163.com/course/introduction/1209401942.htm
单机单节点指在一台电脑上部署一个排序(Orderer)服务、一个组织(Org1),一个节点(Peer,属于Org1),然后运行官方案例中的example02智能合约例子,实现转财交易和查询功能。
单机单节点部署结构图如下:
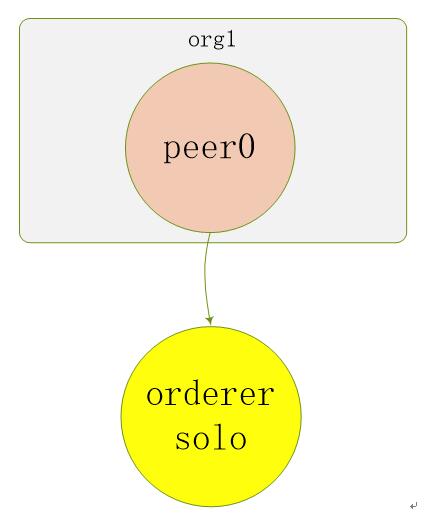
图:单机单节点部署结构图
单机单节点部署步骤如下:
1. 创建singlepeer目录
# cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric
# mkdir singlepeer
# cd singlepeer
2. 获取生成工具
把下载的hyperledger-fabric-linux-amd64-1.2.0.tar.gz二进制文件包解压,把其中的bin目录拷贝到singlepeer目录下。
# chmod -R ./bin
3. 准备生成证书和区块配置文件
配置crypto-config.yaml和configtx.yaml文件,拷贝到singlepeer目录下。
- crypto-config.yaml:
# Copyright IBM Corp. All Rights Reserved.
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# # ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "OrdererOrgs" - Definition of organizations managing orderer nodes
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
OrdererOrgs:
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Orderer
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Name: Orderer
Domain: example.com
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Specs" - See PeerOrgs below for complete description
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Specs:
- Hostname: orderer
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "PeerOrgs" - Definition of organizations managing peer nodes
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
PeerOrgs:
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Org1
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Name: Org1
Domain: org1.example.com
EnableNodeOUs: true
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Specs"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Uncomment this section to enable the explicit definition of hosts in your
# configuration. Most users will want to use Template, below
#
# Specs is an array of Spec entries. Each Spec entry consists of two fields:
# - Hostname: (Required) The desired hostname, sans the domain.
# - CommonName: (Optional) Specifies the template or explicit override for
# the CN. By default, this is the template:
#
# "{{.Hostname}}.{{.Domain}}"
#
# which obtains its values from the Spec.Hostname and
# Org.Domain, respectively.
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Specs:
# - Hostname: foo # implicitly "foo.org1.example.com"
# CommonName: foo27.org5.example.com # overrides Hostname-based FQDN set above
# - Hostname: bar
# - Hostname: baz
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Template"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Allows for the definition of or more hosts that are created sequentially
# from a template. By default, this looks like "peer%d" from to Count-.
# You may override the number of nodes (Count), the starting index (Start)
# or the template used to construct the name (Hostname).
#
# Note: Template and Specs are not mutually exclusive. You may define both
# sections and the aggregate nodes will be created for you. Take care with
# name collisions
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Template:
Count:
# Start:
# Hostname: {{.Prefix}}{{.Index}} # default
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# "Users"
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Count: The number of user accounts _in addition_ to Admin
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Users:
Count:
- configtx.yaml:
# Copyright IBM Corp. All Rights Reserved.
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: Apache-2.0
# ---
################################################################################
#
# Section: Organizations
#
# - This section defines the different organizational identities which will
# be referenced later in the configuration.
#
################################################################################
Organizations: # SampleOrg defines an MSP using the sampleconfig. It should never be used
# in production but may be used as a template for other definitions
- &OrdererOrg
# DefaultOrg defines the organization which is used in the sampleconfig
# of the fabric.git development environment
Name: OrdererOrg # ID to load the MSP definition as
ID: OrdererMSP # MSPDir is the filesystem path which contains the MSP configuration
MSPDir: crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/msp # Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For organization policies, their canonical path is usually
# /Channel/<Application|Orderer>/<OrgName>/<PolicyName>
Policies:
Readers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('OrdererMSP.member')"
Writers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('OrdererMSP.member')"
Admins:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('OrdererMSP.admin')" - &Org1
# DefaultOrg defines the organization which is used in the sampleconfig
# of the fabric.git development environment
Name: Org1MSP # ID to load the MSP definition as
ID: Org1MSP MSPDir: crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/msp # Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For organization policies, their canonical path is usually
# /Channel/<Application|Orderer>/<OrgName>/<PolicyName>
Policies:
Readers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org1MSP.admin', 'Org1MSP.peer', 'Org1MSP.client')"
Writers:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org1MSP.admin', 'Org1MSP.client')"
Admins:
Type: Signature
Rule: "OR('Org1MSP.admin')" AnchorPeers:
# AnchorPeers defines the location of peers which can be used
# for cross org gossip communication. Note, this value is only
# encoded in the genesis block in the Application section context
- Host: peer0.org1.example.com
Port: ################################################################################
#
# SECTION: Capabilities
#
# - This section defines the capabilities of fabric network. This is a new
# concept as of v1.1.0 and should not be utilized in mixed networks with
# v1..x peers and orderers. Capabilities define features which must be
# present in a fabric binary for that binary to safely participate in the
# fabric network. For instance, if a new MSP type is added, newer binaries
# might recognize and validate the signatures from this type, while older
# binaries without this support would be unable to validate those
# transactions. This could lead to different versions of the fabric binaries
# having different world states. Instead, defining a capability for a channel
# informs those binaries without this capability that they must cease
# processing transactions until they have been upgraded. For v1..x if any
# capabilities are defined (including a map with all capabilities turned off)
# then the v1..x peer will deliberately crash.
#
################################################################################
Capabilities:
# Channel capabilities apply to both the orderers and the peers and must be
# supported by both. Set the value of the capability to true to require it.
Global: &ChannelCapabilities
# V1. for Global is a catchall flag for behavior which has been
# determined to be desired for all orderers and peers running v1..x,
# but the modification of which would cause incompatibilities. Users
# should leave this flag set to true.
V1_1: true # Orderer capabilities apply only to the orderers, and may be safely
# manipulated without concern for upgrading peers. Set the value of the
# capability to true to require it.
Orderer: &OrdererCapabilities
# V1. for Order is a catchall flag for behavior which has been
# determined to be desired for all orderers running v1..x, but the
# modification of which would cause incompatibilities. Users should
# leave this flag set to true.
V1_1: true # Application capabilities apply only to the peer network, and may be safely
# manipulated without concern for upgrading orderers. Set the value of the
# capability to true to require it.
Application: &ApplicationCapabilities
# V1. for Application is a catchall flag for behavior which has been
# determined to be desired for all peers running v1..x, but the
# modification of which would cause incompatibilities. Users should
# leave this flag set to true.
V1_2: true ################################################################################
#
# SECTION: Application
#
# - This section defines the values to encode into a config transaction or
# genesis block for application related parameters
#
################################################################################
Application: &ApplicationDefaults # Organizations is the list of orgs which are defined as participants on
# the application side of the network
Organizations: # Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For Application policies, their canonical path is
# /Channel/Application/<PolicyName>
Policies:
Readers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Readers"
Writers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers"
Admins:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Admins" # Capabilities describes the application level capabilities, see the
# dedicated Capabilities section elsewhere in this file for a full
# description
Capabilities:
<<: *ApplicationCapabilities ################################################################################
#
# SECTION: Orderer
#
# - This section defines the values to encode into a config transaction or
# genesis block for orderer related parameters
#
################################################################################
Orderer: &OrdererDefaults # Orderer Type: The orderer implementation to start
# Available types are "solo" and "kafka"
OrdererType: solo Addresses:
- orderer.example.com: # Batch Timeout: The amount of time to wait before creating a batch
BatchTimeout: 2s # Batch Size: Controls the number of messages batched into a block
BatchSize: # Max Message Count: The maximum number of messages to permit in a batch
MaxMessageCount: # Absolute Max Bytes: The absolute maximum number of bytes allowed for
# the serialized messages in a batch.
AbsoluteMaxBytes: MB # Preferred Max Bytes: The preferred maximum number of bytes allowed for
# the serialized messages in a batch. A message larger than the preferred
# max bytes will result in a batch larger than preferred max bytes.
PreferredMaxBytes: KB Kafka:
# Brokers: A list of Kafka brokers to which the orderer connects. Edit
# this list to identify the brokers of the ordering service.
# NOTE: Use IP:port notation.
Brokers:
- 127.0.0.1: # Organizations is the list of orgs which are defined as participants on
# the orderer side of the network
Organizations: # Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For Orderer policies, their canonical path is
# /Channel/Orderer/<PolicyName>
Policies:
Readers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Readers"
Writers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers"
Admins:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Admins"
# BlockValidation specifies what signatures must be included in the block
# from the orderer for the peer to validate it.
BlockValidation:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers" # Capabilities describes the orderer level capabilities, see the
# dedicated Capabilities section elsewhere in this file for a full
# description
Capabilities:
<<: *OrdererCapabilities ################################################################################
#
# CHANNEL
#
# This section defines the values to encode into a config transaction or
# genesis block for channel related parameters.
#
################################################################################
Channel: &ChannelDefaults
# Policies defines the set of policies at this level of the config tree
# For Channel policies, their canonical path is
# /Channel/<PolicyName>
Policies:
# Who may invoke the 'Deliver' API
Readers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Readers"
# Who may invoke the 'Broadcast' API
Writers:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "ANY Writers"
# By default, who may modify elements at this config level
Admins:
Type: ImplicitMeta
Rule: "MAJORITY Admins" # Capabilities describes the channel level capabilities, see the
# dedicated Capabilities section elsewhere in this file for a full
# description
Capabilities:
<<: *ChannelCapabilities ################################################################################
#
# Profile
#
# - Different configuration profiles may be encoded here to be specified
# as parameters to the configtxgen tool
#
################################################################################
Profiles: OneOrgsOrdererGenesis:
<<: *ChannelDefaults
Orderer:
<<: *OrdererDefaults
Organizations:
- *OrdererOrg
Consortiums:
SampleConsortium:
Organizations:
- *Org1
OneOrgsChannel:
Consortium: SampleConsortium
Application:
<<: *ApplicationDefaults
Organizations:
- *Org1
4. 生成公私钥和证书
# ./bin/cryptogen generate --config=./crypto-config.yaml
5. 生成创世区块
# mkdir channel-artifacts
# ./bin/configtxgen -profile OneOrgsOrdererGenesis -outputBlock ./channel-artifacts/genesis.block
6. 生成通道配置区块
# ./bin/configtxgen -profile OneOrgsChannel -outputCreateChannelTx ./channel-artifacts/mychannel.tx -channelID mychannel
7. 准备docker配置文件
配置docker-compose-cli.yaml文件,拷贝到singlepeer目录下。
docker-compose-cli.yaml:
version: '' services:
orderer.example.com:
container_name: orderer.example.com
image: hyperledger/fabric-orderer
environment:
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOGLEVEL=debug
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0
- ORDERER_GENERAL_GENESISMETHOD=file
- ORDERER_GENERAL_GENESISFILE=/var/hyperledger/orderer/orderer.genesis.block
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOCALMSPID=OrdererMSP
- ORDERER_GENERAL_LOCALMSPDIR=/var/hyperledger/orderer/msp
# enabled TLS
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_ENABLED=false
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_PRIVATEKEY=/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/server.key
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_CERTIFICATE=/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/server.crt
- ORDERER_GENERAL_TLS_ROOTCAS=[/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls/ca.crt]
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric
command: orderer
volumes:
- ./channel-artifacts/genesis.block:/var/hyperledger/orderer/orderer.genesis.block
- ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/msp:/var/hyperledger/orderer/msp
- ./crypto-config/ordererOrganizations/example.com/orderers/orderer.example.com/tls/:/var/hyperledger/orderer/tls
ports:
- : peer0.org1.example.com:
container_name: peer0.org1.example.com
image: hyperledger/fabric-peer
environment:
- CORE_PEER_ID=peer0.org1.example.com
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:
- CORE_PEER_CHAINCODEADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:
- CORE_PEER_CHAINCODELISTENADDRESS=0.0.0.0:
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_EXTERNALENDPOINT=peer0.org1.example.com:
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP - CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
# the following setting starts chaincode containers on the same
# bridge network as the peers
# https://docs.docker.com/compose/networking/
- CORE_VM_DOCKER_HOSTCONFIG_NETWORKMODE=singlepeer_default
#- CORE_LOGGING_LEVEL=ERROR
- CORE_LOGGING_LEVEL=DEBUG
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ENABLED=false
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_USELEADERELECTION=true
- CORE_PEER_GOSSIP_ORGLEADER=false
- CORE_PEER_PROFILE_ENABLED=true
- CORE_PEER_TLS_CERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/server.crt
- CORE_PEER_TLS_KEY_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/server.key
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls/ca.crt
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/msp:/etc/hyperledger/fabric/msp
- ./crypto-config/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls:/etc/hyperledger/fabric/tls
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer
command: peer node start
ports:
- :
- :
- : cli:
container_name: cli
image: hyperledger/fabric-tools
tty: true
environment:
- GOPATH=/opt/gopath
- CORE_VM_ENDPOINT=unix:///host/var/run/docker.sock
- CORE_LOGGING_LEVEL=DEBUG
- CORE_PEER_ID=cli
- CORE_PEER_ADDRESS=peer0.org1.example.com:
- CORE_PEER_LOCALMSPID=Org1MSP
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ENABLED=false
- CORE_PEER_TLS_CERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/server.crt
- CORE_PEER_TLS_KEY_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/server.key
- CORE_PEER_TLS_ROOTCERT_FILE=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/peers/peer0.org1.example.com/tls/ca.crt
- CORE_PEER_MSPCONFIGPATH=/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/peerOrganizations/org1.example.com/users/Admin@org1.example.com/msp
working_dir: /opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer
volumes:
- /var/run/:/host/var/run/
- ./chaincode/go/:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/singlepeer/chaincode/go
- ./crypto-config:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/crypto/
- ./channel-artifacts:/opt/gopath/src/github.com/hyperledger/fabric/peer/channel-artifacts
depends_on:
- orderer.example.com
- peer0.org1.example.com
8. 准备部署智能合约
拷贝examples/chaincode/go/example02目录下的文件到singlepeer/chaincode/go/example02目录下。
9. 启动Fabric网络
1) 启动orderer和peer
# docker-compose -f docker-compose-cli.yaml up -d
2) 启动cli容器
# docker exec -it cli bash
3) 创建Channel
# peer channel create -o orderer.example.com: -c mychannel -f ./channel-artifacts/mychannel.tx
4) Peer加入Channel
# peer channel join -b mychannel.block
10. 安装与运行智能合约
1) 安装智能合约
# peer chaincode install -n mycc -p github.com/hyperledger/fabric/singlepeer/chaincode/go/example02/cmd/ -v 1.0
2) 实例化智能合约
区块初始化数据为a为100,b为200。
# peer chaincode instantiate -o orderer.example.com: -C mychannel -n mycc -v 1.0 -c '{"Args":["init","a","100","b","200"]}' -P "AND ('Org1MSP.peer')"
3) Peer上查询a,显示100
# peer chaincode query -C mychannel -n mycc -c '{"Args":["query","a"]}'
查询a成功结果如下图所示:
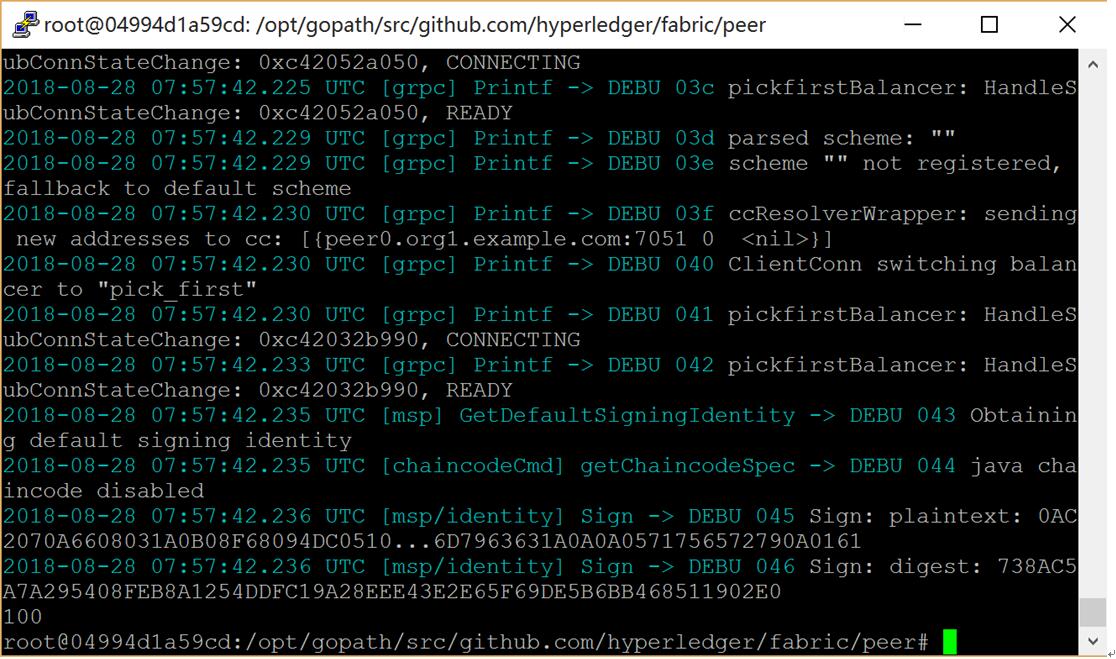
图:查询a成功结果
4) Peer上进行a向b转10交易
# peer chaincode invoke -C mychannel -n mycc -c '{"Args":["invoke","a","b","10"]}'
交易成功结果如下图所示:
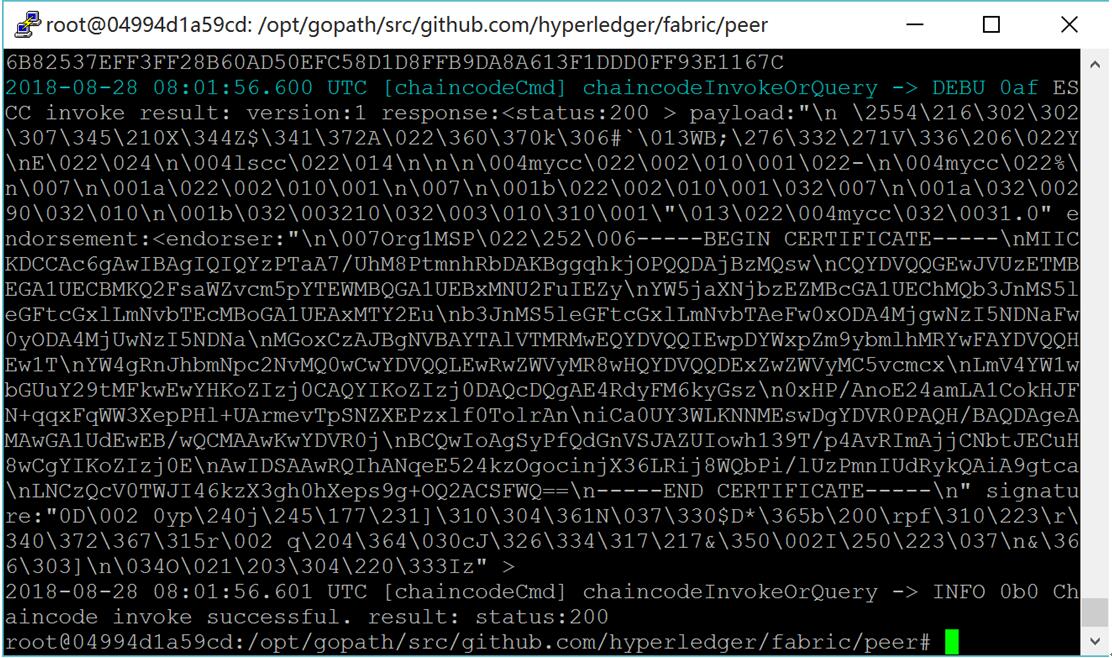
图:交易成功结果
5) Peer上查询a,显示210
# peer chaincode query -C mychannel -n mycc -c '{"Args":["query","b"]}'
查询b成功结果如下图所示:
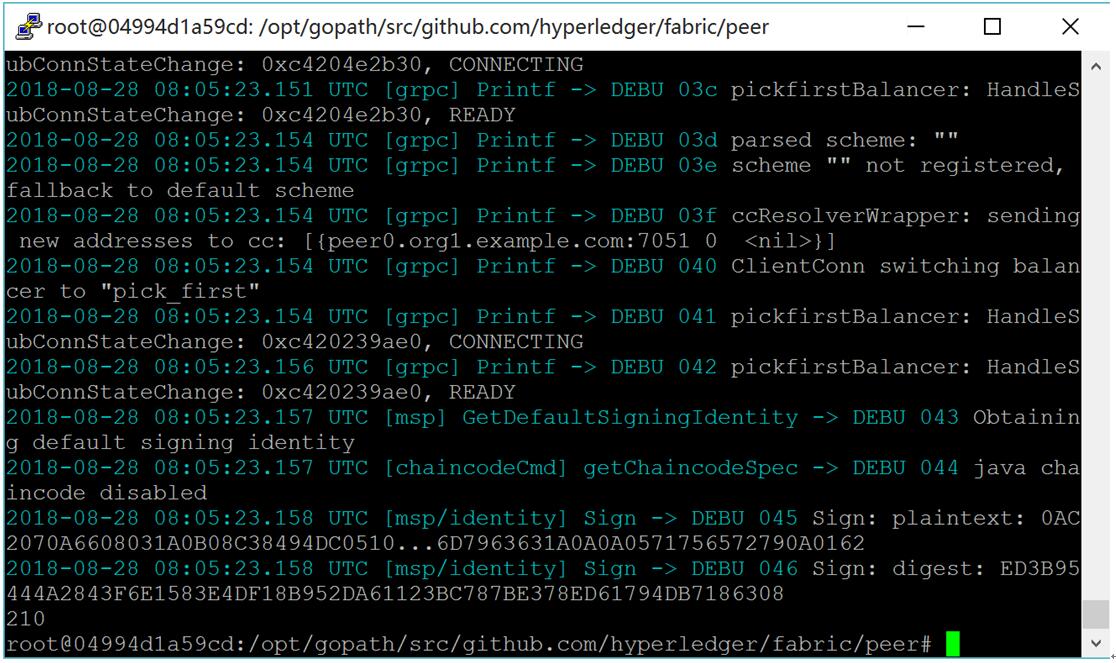
图:查询b成功结果
HyperLedger Fabric 1.4 单机单节点部署(10.2)的更多相关文章
- HyperLedger Fabric 1.1 手动部署单机单节点
手动部署单机单节点 之前发布过官方的e2e部署方案,由于环境或是访问权限等各种问题,还是有相当一部分码友无法成功跑起来,故此,本章将来一次纯手动操作的集群部署. 主要需要的步骤如下: 1:环境整理 2 ...
- Hyperledger fabric 1.3版本的安装部署(原创多机多Orderer部署
首先,我们在安装前,要考虑一个问题 Hyperledger Fabric,通过指定的节点进行背书授权,才能完成交易的存储 延伸开来,就是为了实现容错.高并发.易扩展,需要zookeeper来选择排序引 ...
- Ubuntu下用devstack单节点部署Openstack
一.实验环境 本实验是在Vmware Workstation下创建的单台Ubuntu服务器版系统中,利用devstack部署的Openstack Pike版. 宿主机:win10 1803 8G内存 ...
- .netcore consul实现服务注册与发现-单节点部署
原文:.netcore consul实现服务注册与发现-单节点部署 一.Consul的基础介绍 Consul是HashiCorp公司推出的开源工具,用于实现分布式系统的服务发现与配置.与其他分 ...
- Kubernetes 二进制部署(一)单节点部署(Master 与 Node 同一机器)
0. 前言 最近受“新冠肺炎”疫情影响,在家等着,入职暂时延后,在家里办公和学习 尝试通过源码编译二进制的方式在单一节点(Master 与 Node 部署在同一个机器上)上部署一个 k8s 环境,整理 ...
- HyperLedger Fabric 1.4 kafka生产环境部署(11.1)
11.1 Kafka模式简介 上一章介绍的Solo模式只存在一个排序(orderer)服务,是一种中心化结构,一旦排序(orderer)服务出现了问题,整个区块链网络将会崩溃,为了能在正式 ...
- 恒天云单节点部署指南--OpenStack H版本虚拟机单节点部署解决方案
本帖是openstack单节点在虚拟机上部署的实践.想要玩玩和学习openstack的小伙伴都看过来,尤其是那些部署openstack失败的小伙伴.本帖可以让你先领略一下openstack的魅力.本I ...
- Presto0.157版本单节点部署教程
因为Presto版本的更新速度较快,所以最好按照对应版本的教程进行部署,博主之前看错了版本号,拿0.100版本的教程来部署0.157版本,结果导致部署失败. 官网:https://prestodb.i ...
- Hyperledger Fabric (1.0)环境部署 chaincode【转】
三.测试Fabric 其实我们在前面运行./network_setup.sh up的时候系统已经运行了一个Example02的ChainCode测试,部署上去的ChainCodeName是mycc,所 ...
随机推荐
- 《React 与 Redux 开发实例精解》出版了!
<React 与 Redux 开发实例精解>出版了! <React 与 Redux 开发实例精解>出版了! 关于 React 与 Redux React 与 Redux, 一个 ...
- c++内存区域结构及堆栈的一些知识
一.c++在内存区域的分配图 可以看出,对于Linux系统下的,存储空间的分配有着较为层次清晰的分层.单片机大概也遵循这个分区架构. 二进制代码以及常量(CONST修饰)以及全局变量在最底层,存储空间 ...
- Java导出Highcharts需要的3个外部jar包
xerces batik fop 这三个JAR包. 绝对可用.自本用过. 如果两个项目在同一个TOMCAT下并且同时用到xerces.jar,需要前这个外放在TOMCAT下的lib目录下.其他的容器中 ...
- phoneGap的Android下编写phonegap 发送短信插件
一.前端代码的编写 <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> < ...
- CALayer & bitmap Content
Working with High-Resolution Images Layers do not have any inherent knowledge of the resolution of t ...
- BZOJ2820:YY的GCD(莫比乌斯反演)
Description 神犇YY虐完数论后给傻×kAc出了一题给定N, M,求1<=x<=N, 1<=y<=M且gcd(x, y)为质数的(x, y)有多少对kAc这种 傻×必 ...
- luogu P2617 Dynamic Rankings(分块,n <= 1e4)
嘟嘟嘟 带修改区间第k大. 然而某谷把数据扩大到了1e5,所以用分块现在只能得50分. 分块怎么做呢?很暴力的. 基本思想还是块内有序,块外暴力统计. 对于修改,直接重排修改的数所在块,时间复杂度O( ...
- 禁止查看网页源代码和F12
function disableInfo() { document.onkeydown = function() { var e = window.event || arguments[0]; //屏 ...
- ASP.NET CORE 边学边记之 SwaggerUI简单配置
前言 当使用 ASP.NET CORE 开发WebApi程序时候,一般使用SwaggerUI生成接口文档.本文记录最简单的一个配置.(生成的文档无注释) 操作 首先安装Nuget包. 然后在Start ...
- CopyOnWriteArrayList介绍
CopyOnWrite容器即写时复制的容器.通俗的理解是当我们往一个容器添加元素的时候,不直接往当前容器添加,而是先将当前容器进行Copy,复制出一个新的容器,然后新的容器里添加元素,添加完元素之后, ...
