Getting Started with ASP.NET Web API 2 (C#)
HTTP is not just for serving up web pages. It is also a powerful platform for building APIs that expose services and data. HTTP is simple, flexible, and ubiquitous. Almost any platform that you can think of has an HTTP library, so HTTP services can reach a broad range of clients, including browsers, mobile devices, and traditional desktop applications.
ASP.NET Web API is a framework for building web APIs on top of the .NET Framework. In this tutorial, you will use ASP.NET Web API to create a web API that returns a list of products.
Software versions used in the tutorial
Create a Web API Project
In this tutorial, you will use ASP.NET Web API to create a web API that returns a list of products. The front-end web page uses jQuery to display the results.
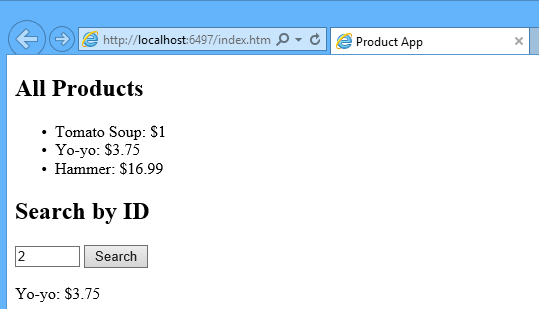
Start Visual Studio and select New Project from the Start page. Or, from the File menu, select New and then Project.
In the Templates pane, select Installed Templates and expand the Visual C# node. Under Visual C#, select Web. In the list of project templates, select ASP.NET Web Application. Name the project "ProductsApp" and click OK.
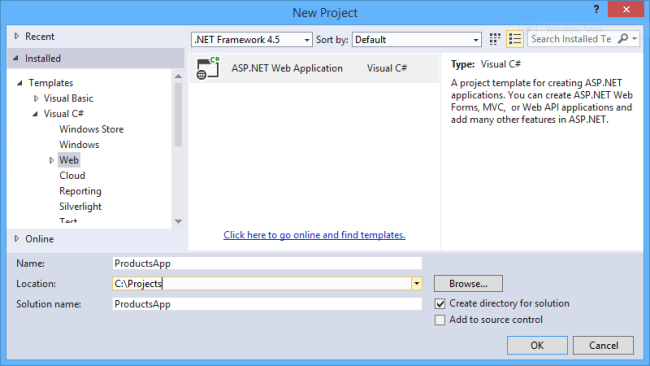
In the New ASP.NET Project dialog, select the Empty template. Under "Add folders and core references for", check Web API. Click OK.
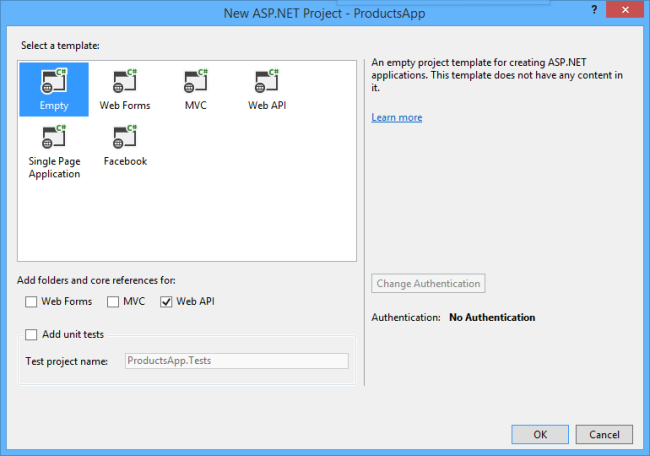
You can also create a Web API project using the "Web API" template. The Web API template uses ASP.NET MVC to provide API help pages. I'm using the Empty template for this tutorial because I want to show Web API without MVC. In general, you don't need to know ASP.NET MVC to use Web API.
Adding a Model
A model is an object that represents the data in your application. ASP.NET Web API can automatically serialize your model to JSON, XML, or some other format, and then write the serialized data into the body of the HTTP response message. As long as a client can read the serialization format, it can deserialize the object. Most clients can parse either XML or JSON. Moreover, the client can indicate which format it wants by setting the Accept header in the HTTP request message.
Let's start by creating a simple model that represents a product.
If Solution Explorer is not already visible, click the View menu and select Solution Explorer. In Solution Explorer, right-click the Models folder. From the context menu, select Add then select Class.
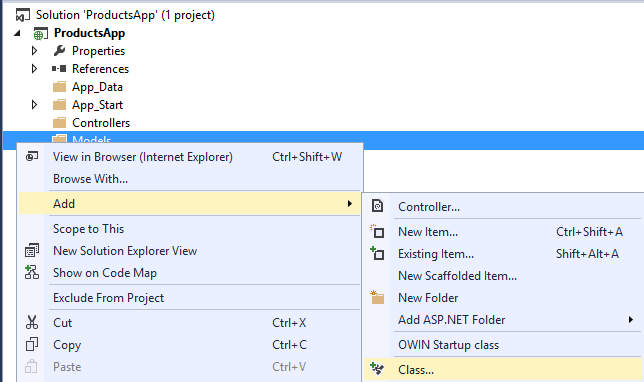
Name the class "Product". Add the following properties to the Product class.
namespace ProductsApp.Models
{
public class Product
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Category { get; set; }
public decimal Price { get; set; }
}
}
Adding a Controller
In Web API, a controller is an object that handles HTTP requests. We'll add a controller that can return either a list of products or a single product specified by ID.
Note If you have used ASP.NET MVC, you are already familiar with controllers. Web API controllers are similar to MVC controllers, but inherit the ApiController class instead of the Controller class.
In Solution Explorer, right-click the Controllers folder. Select Add and then select Controller.
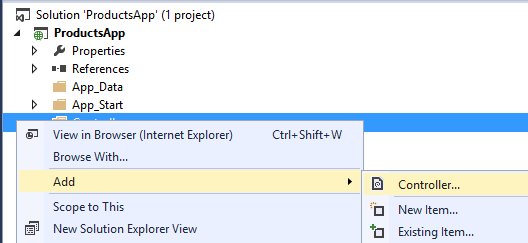
In the Add Scaffold dialog, select Web API Controller - Empty. Click Add.
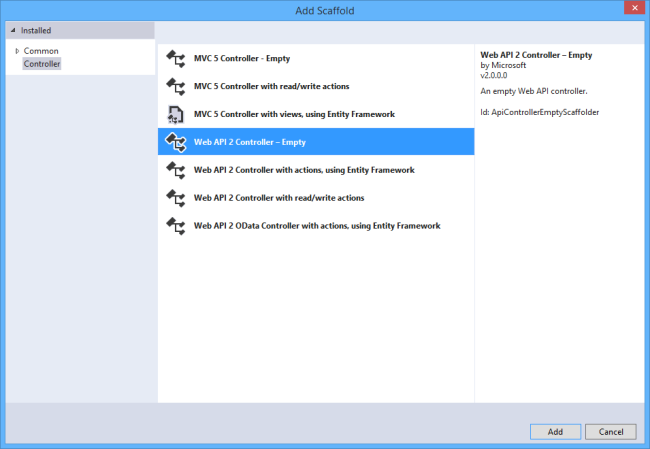
In the Add Controller dialog, name the controller "ProductsController". Click Add.
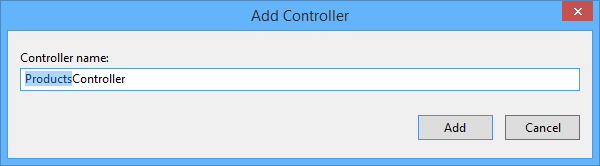
The scaffolding creates a file named ProductsController.cs in the Controllers folder.
You don't need to put your contollers into a folder named Controllers. The folder name is just a convenient way to organize your source files.
If this file is not open already, double-click the file to open it. Replace the code in this file with the following:
using ProductsApp.Models;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Net;
using System.Web.Http; namespace ProductsApp.Controllers
{
public class ProductsController : ApiController
{
Product[] products = new Product[]
{
new Product { Id = 1, Name = "Tomato Soup", Category = "Groceries", Price = 1 },
new Product { Id = 2, Name = "Yo-yo", Category = "Toys", Price = 3.75M },
new Product { Id = 3, Name = "Hammer", Category = "Hardware", Price = 16.99M }
}; public IEnumerable<Product> GetAllProducts()
{
return products;
} public IHttpActionResult GetProduct(int id)
{
var product = products.FirstOrDefault((p) => p.Id == id);
if (product == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Ok(product);
}
}
}
To keep the example simple, products are stored in a fixed array inside the controller class. Of course, in a real application, you would query a database or use some other external data source.
The controller defines two methods that return products:
- The
GetAllProductsmethod returns the entire list of products as an IEnumerable<Product> type. - The
GetProductmethod looks up a single product by its ID.
That's it! You have a working web API. Each method on the controller corresponds to one or more URIs:
| Controller Method | URI |
|---|---|
| GetAllProducts | /api/products |
| GetProduct | /api/products/id |
For the GetProduct method, the id in the URI is a placeholder. For example, to get the product with ID of 5, the URI is api/products/5.
For more information about how Web API routes HTTP requests to controller methods, see Routing in ASP.NET Web API.
Calling the Web API with Javascript and jQuery
In this section, we'll add an HTML page that uses AJAX to call the web API. We'll use jQuery to make the AJAX calls and also to update the page with the results.
In Solution Explorer, right-click the project and select Add, then select New Item.
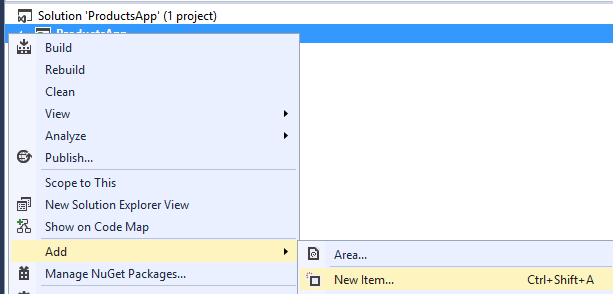
In the Add New Item dialog, select the Web node under Visual C#, and then select the HTML Page item. Name the page "index.html".
Replace everything in this file with the following:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml">
<head>
<title>Product App</title>
</head>
<body> <div>
<h2>All Products</h2>
<ul id="products" />
</div>
<div>
<h2>Search by ID</h2>
<input type="text" id="prodId" size="5" />
<input type="button" value="Search" onclick="find();" />
<p id="product" />
</div> <script src="http://ajax.aspnetcdn.com/ajax/jQuery/jquery-2.0.3.min.js"></script>
<script>
var uri = 'api/products'; $(document).ready(function () {
// Send an AJAX request
$.getJSON(uri)
.done(function (data) {
// On success, 'data' contains a list of products.
$.each(data, function (key, item) {
// Add a list item for the product.
$('<li>', { text: formatItem(item) }).appendTo($('#products'));
});
});
}); function formatItem(item) {
return item.Name + ': $' + item.Price;
} function find() {
var id = $('#prodId').val();
$.getJSON(uri + '/' + id)
.done(function (data) {
$('#product').text(formatItem(data));
})
.fail(function (jqXHR, textStatus, err) {
$('#product').text('Error: ' + err);
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
There are several ways to get jQuery. In this example, I used the Microsoft Ajax CDN. You can also download it from http://jquery.com/, and the ASP.NET "Web API" project template includes jQuery as well.
Getting a List of Products
To get a list of products, send an HTTP GET request to "/api/products".
The jQuery getJSON function sends an AJAX request. For response contains array of JSON objects. The done function specifies a callback that is called if the request succeeds. In the callback, we update the DOM with the product information.
$(document).ready(function () {
// Send an AJAX request
$.getJSON(apiUrl)
.done(function (data) {
// On success, 'data' contains a list of products.
$.each(data, function (key, item) {
// Add a list item for the product.
$('<li>', { text: formatItem(item) }).appendTo($('#products'));
});
});
});
Getting a Product By ID
To get a product by ID, send an HTTP GET request to "/api/products/id", where id is the product ID.
function find() {
var id = $('#prodId').val();
$.getJSON(apiUrl + '/' + id)
.done(function (data) {
$('#product').text(formatItem(data));
})
.fail(function (jqXHR, textStatus, err) {
$('#product').text('Error: ' + err);
});
}
We still call getJSON to send the AJAX request, but this time we put the ID in the request URI. The response from this request is a JSON representation of a single product.
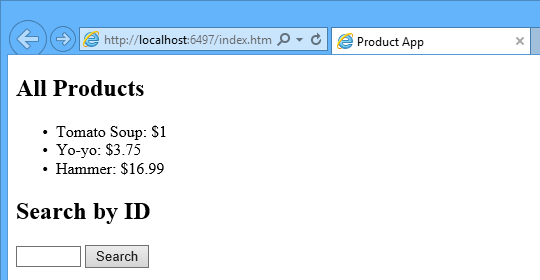
Running the Application
Press F5 to start debugging the application. The web page should look like the following:
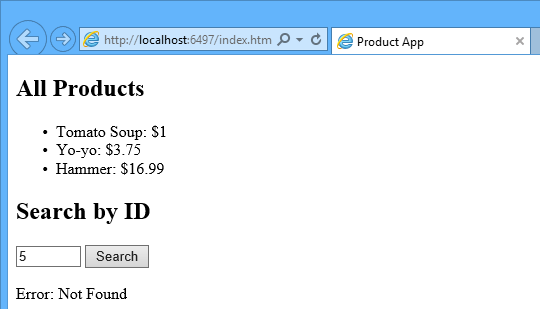
To get a product by ID, enter the ID and click Search:

If you enter an invalid ID, the server returns an HTTP error:
Using F12 to View the HTTP Request and Response
When you are working with an HTTP service, it can be very useful to see the HTTP request and request messages. You can do this by using the F12 developer tools in Internet Explorer 9. From Internet Explorer 9, press F12 to open the tools. Click the Network tab and press Start Capturing. Now go back to the web page and press F5 to reload the web page. Internet Explorer will capture the HTTP traffic between the browser and the web server. The summary view shows all the network traffic for a page:
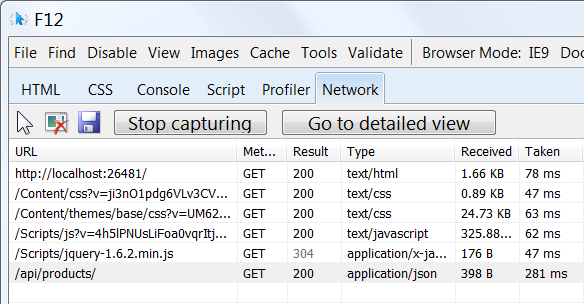
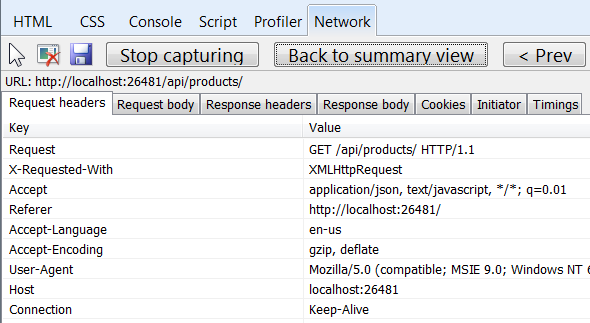
Locate the entry for the relative URI “api/products/”. Select this entry and click Go to detailed view. In the detail view, there are tabs to view the request and response headers and bodies. For example, if you click the Request headers tab, you can see that the client requested "application/json" in the Accept header.
If you click the Response body tab, you can see how the product list was serialized to JSON. Other browsers have similar functionality. Another useful tool is Fiddler, a web debugging proxy. You can use Fiddler to view your HTTP traffic, and also to compose HTTP requests, which gives you full control over the HTTP headers in the request.
See this App Running on Azure
Would you like to see the finished site running as a live web app? You can deploy a complete version of the app to your Azure account by simply clicking the following button.

You need an Azure account to deploy this solution to Azure. If you do not already have an account, you have the following options:
- Open an Azure account for free - You get credits you can use to try out paid Azure services, and even after they're used up you can keep the account and use free Azure services.
- Activate MSDN subscriber benefits - Your MSDN subscription gives you credits every month that you can use for paid Azure services.
Next Steps
- For a more complete example of an HTTP service that supports POST, PUT, and DELETE actions and writes to a database, see Using Web API 2 with Entity Framework 6.
- For more about creating fluid and responsive web applications on top of an HTTP service, see ASP.NET Single Page Application.
- For information about how to deploy a Visual Studio web project to Azure App Service, see Create an ASP.NET web app in Azure App Service.
This article was originally created on January 20, 2014
Author Information

Mike Wasson – Mike Wasson is a programmer-writer at Microsoft.
Getting Started with ASP.NET Web API 2 (C#)的更多相关文章
- 在一个空ASP.NET Web项目上创建一个ASP.NET Web API 2.0应用
由于ASP.NET Web API具有与ASP.NET MVC类似的编程方式,再加上目前市面上专门介绍ASP.NET Web API 的书籍少之又少(我们看到的相关内容往往是某本介绍ASP.NET M ...
- ASP.NET Web API Model-ActionBinding
ASP.NET Web API Model-ActionBinding 前言 前面的几个篇幅把Model部分的知识点划分成一个个的模块来讲解,而在控制器执行过程中分为好多个过程,对于控制器执行过程(一 ...
- ASP.NET Web API Model-ParameterBinding
ASP.NET Web API Model-ParameterBinding 前言 通过上个篇幅的学习了解Model绑定的基础知识,然而在ASP.NET Web API中Model绑定功能模块并不是被 ...
- ASP.NET Web API Model-ModelBinder
ASP.NET Web API Model-ModelBinder 前言 本篇中会为大家介绍在ASP.NET Web API中ModelBinder的绑定原理以及涉及到的一些对象模型,还有简单的Mod ...
- ASP.NET Web API Model-ValueProvider
ASP.NET Web API Model-ValueProvider 前言 前面一篇讲解了Model元数据,Model元数据是在Model绑定中很重要的一部分,只是Model绑定中涉及的知识点比较多 ...
- ASP.NET Web API Model-ModelMetadata
ASP.NET Web API Model-ModelMetadata 前言 前面的几个篇幅主要围绕控制器的执行过程,奈何执行过程中包含的知识点太庞大了,只能一部分一部分的去讲解,在上两篇中我们看到在 ...
- ASP.NET Web API 过滤器创建、执行过程(二)
ASP.NET Web API 过滤器创建.执行过程(二) 前言 前面一篇中讲解了过滤器执行之前的创建,通过实现IFilterProvider注册到当前的HttpConfiguration里的服务容器 ...
- ASP.NET Web API 过滤器创建、执行过程(一)
ASP.NET Web API 过滤器创建.执行过程(一) 前言 在上一篇中我们讲到控制器的执行过程系列,这个系列要搁置一段时间了,因为在控制器执行的过程中包含的信息都是要单独的用一个系列来描述的,就 ...
- ASP.NET Web API 控制器执行过程(一)
ASP.NET Web API 控制器执行过程(一) 前言 前面两篇讲解了控制器的创建过程,只是从框架源码的角度去简单的了解,在控制器创建过后所执行的过程也是尤为重要的,本篇就来简单的说明一下控制器在 ...
- ASP.NET Web API 控制器创建过程(二)
ASP.NET Web API 控制器创建过程(二) 前言 本来这篇随笔应该是在上周就该写出来发布的,由于身体跟不上节奏感冒发烧有心无力,这种天气感冒发烧生不如死,也真正的体会到了什么叫病来如山倒,病 ...
随机推荐
- [Asp.net 5] DependencyInjection项目代码分析4-微软的实现(4)
这个系列已经写了6篇,链接地址如下: [Asp.net 5] DependencyInjection项目代码分析 [Asp.net 5] DependencyInjection项目代码分析2-Auto ...
- C#进行Visio二次开发之文件导出及另存Web页面
在我前面很多关于Visio的开发过程中,介绍了各种Visio的C#开发应用场景,包括对Visio的文档.模具文档.形状.属性数据.各种事件等相关的基础处理,以及Visio本身的整体项目应用,虽然时间过 ...
- 现在就使用HTML5的十大原因
你难道还没有考虑使用HTML5? 当然我猜想你可能有自己的原因: 它现在还没有被广泛的支持,在IE中不好使,或者你就是喜欢写比较严格的XHTML代码. HTML5是Web开发世界的一次重大的改变,事实 ...
- MultiLine Text光标停留在第一行
MultiLine Text是多行文本,默认设置下,光标是停留在控件中间的,很不好看. 解决的方法是设置属性android:gravity="top",这样光标就会停留在第一行.
- 自行实现PHP代码注解特性
PHP 注解 到目前为止,PHP的反射特性中是不支持注解Annotation的,但是可以支持基本的文档注释内容的获取 ReflectionMethod::getDocComment() - 从5.1. ...
- Scalaz(21)-类型例证:Liskov and Leibniz - type evidence
Leskov,Leibniz,别扭的名字,是什么地干活?碰巧从scalaz源代码里发现了这么个东西:scalaz/BindSyntax.scala /** Wraps a value `self` a ...
- Web应用网络模型
Web应用网络模型 前言 这篇文章要介绍的是一个常见Web应用基本的过程跟网络模型,当然,对于多数的Client/Server应用也是适用的.延续这个系列文章的风格,只管通俗不管严谨. 概览 总体模型 ...
- Linux更改主机名-适用于abuntu
今天复制了个ubuntu虚拟机,于是想更改下主机名以作区别.这是搜到的比较完整的资料,适用abuntu,不过其他linux系统还有待求证. 1.查看主机名 在Ubuntu系统中,快速查看主机名有多种方 ...
- NProgress.js template
NProgress.js:加载进度条:http://ricostacruz.com/nprogress/ 基础的这几个方法 这个网站上都有 我在一个地方看到这个代码 NProgress.configu ...
- var和dynamic的区别及如何正确使用dynamic ?
C#中的很多关键词用法比较容易混淆,var和dynamic就是其中一组,他们都可以申明动态类型的变量,但是本质上他们还是有不少区别的.var 在编译阶段已经确定类型,在初始化时候,必须提供初始化的值, ...
