ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用和方法介绍
定义
- 一个基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列。此队列按照 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序。队列的头部 是队列中时间最长的元素。队列的尾部 是队列中时间最短的元素。
新的元素插入到队列的尾部,队列获取操作从队列头部获得元素。当多个线程共享访问一个公共 collection 时,ConcurrentLinkedQueue 是一个恰当的选择。此队列不允许使用 null 元素。
offer和poll
poll()
获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
- queue.offer("哈哈哈");
- System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty());
- System.out.println("从队列中poll:" + queue.poll());
- System.out.println("pool后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty());
- }
offer是往队列添加元素,poll是从队列取出元素并且删除该元素
执行结果
- offer后,队列是否空?false
- 从队列中poll:哈哈哈
- pool后,队列是否空?true
ConcurrentLinkedQueue中的add() 和 offer() 完全一样,都是往队列尾部添加元素
还有个取元素方法peek
peek()
获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
- queue.offer("哈哈哈");
- System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty());
- System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek());
- System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek());
- System.out.println("从队列中peek:" + queue.peek());
- System.out.println("pool后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty());
- }
执行结果:
- offer后,队列是否空?false
- 从队列中peek:哈哈哈
- 从队列中peek:哈哈哈
- 从队列中peek:哈哈哈
- pool后,队列是否空?false
remove
remove(Object o)
从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)
- public static void main(String[] args) {
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
- queue.offer("哈哈哈");
- System.out.println("offer后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty());
- System.out.println("从队列中remove已存在元素 :" + queue.remove("哈哈哈"));
- System.out.println("从队列中remove不存在元素:" + queue.remove("123"));
- System.out.println("remove后,队列是否空?" + queue.isEmpty());
- }
remove一个已存在元素,会返回true,remove不存在元素,返回false
执行结果:
- offer后,队列是否空?false
- 从队列中remove已存在元素 :true
- 从队列中remove不存在元素:false
- remove后,队列是否空?true
size or isEmpty
size()
返回此队列中的元素数量
注意:
- 如果此队列包含的元素数大于 Integer.MAX_VALUE,则返回 Integer.MAX_VALUE。
- 需要小心的是,与大多数 collection 不同,此方法不是 一个固定时间操作。由于这些队列的异步特性,确定当前的元素数需要进行一次花费 O(n) 时间的遍历。
所以在需要判断队列是否为空时,尽量不要用 queue.size()>0,而是用 !queue.isEmpty()
比较size()和isEmpty() 效率的示例:
场景:10000个人去饭店吃饭,10张桌子供饭,分别比较size() 和 isEmpty() 的耗时
- public class Test01ConcurrentLinkedQueue {
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
- int peopleNum = 10000;//吃饭人数
- int tableNum = 10;//饭桌数量
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<>();
- CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(tableNum);//计数器
- //将吃饭人数放入队列(吃饭的人进行排队)
- for(int i=1;i<=peopleNum;i++){
- queue.offer("消费者_" + i);
- }
- //执行10个线程从队列取出元素(10个桌子开始供饭)
- System.out.println("-----------------------------------开饭了-----------------------------------");
- long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
- ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(tableNum);
- for(int i=0;i<tableNum;i++) {
- executorService.submit(new Dinner("00" + (i+1), queue, count));
- }
- //计数器等待,知道队列为空(所有人吃完)
- count.await();
- long time = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
- System.out.println("-----------------------------------所有人已经吃完-----------------------------------");
- System.out.println("共耗时:" + time);
- //停止线程池
- executorService.shutdown();
- }
- private static class Dinner implements Runnable{
- private String name;
- private ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue;
- private CountDownLatch count;
- public Dinner(String name, ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue, CountDownLatch count) {
- this.name = name;
- this.queue = queue;
- this.count = count;
- }
- @Override
- public void run() {
- //while (queue.size() > 0){
- while (!queue.isEmpty()){
- //从队列取出一个元素 排队的人少一个
- System.out.println("【" +queue.poll() + "】----已吃完..., 饭桌编号:" + name);
- }
- count.countDown();//计数器-1
- }
- }
- }
执行结果:
使用size耗时:757ms
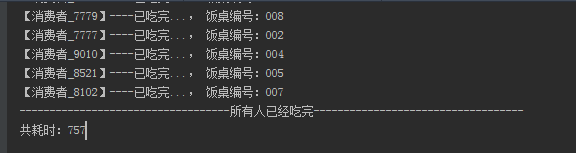
使用isEmpty耗时:210

当数据量越大,这种耗时差距越明显。所以这种判断用isEmpty 更加合理
contains
contains(Object o)
如果此队列包含指定元素,则返回 true
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue();
- queue.offer("123");
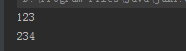
- System.out.println(queue.contains("123"));
- System.out.println(queue.contains("234"));
- }
执行结果:

toArray
toArray()
返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组
toArray(T[] a)
返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>();
- queue.offer("123");
- queue.offer("234");
- Object[] objects = queue.toArray();
- System.out.println(objects[0] + ", " + objects[1]);
- //将数据存储到指定数组
- String[] strs = new String[2];
- queue.toArray(strs);
- System.out.println(strs[0] + ", " + strs[1]);
- }
执行结果:

iterator
iterator()
返回在此队列元素上以恰当顺序进行迭代的迭代器
- public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String> queue = new ConcurrentLinkedQueue<String>();
- queue.offer("123");
- queue.offer("234");
- Iterator<String> iterator = queue.iterator();
- while (iterator.hasNext()){
- System.out.println(iterator.next());
- }
- }
ConcurrentLinkedQueue文档说明:
| 构造方法摘要 | |
|---|---|
ConcurrentLinkedQueue() 创建一个最初为空的 ConcurrentLinkedQueue。 |
|
ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) 创建一个最初包含给定 collection 元素的 ConcurrentLinkedQueue,按照此 collection 迭代器的遍历顺序来添加元素。 |
|
| 方法摘要 | ||
|---|---|---|
boolean |
add(E e) 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
|
boolean |
contains(Object o) 如果此队列包含指定元素,则返回 true。 |
|
boolean |
isEmpty() 如果此队列不包含任何元素,则返回 true。 |
|
Iterator<E> |
iterator() 返回在此队列元素上以恰当顺序进行迭代的迭代器。 |
|
boolean |
offer(E e) 将指定元素插入此队列的尾部。 |
|
E |
peek() 获取但不移除此队列的头;如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
|
E |
poll() 获取并移除此队列的头,如果此队列为空,则返回 null。 |
|
boolean |
remove(Object o) 从队列中移除指定元素的单个实例(如果存在)。 |
|
int |
size() 返回此队列中的元素数量。 |
|
Object[] |
toArray() 返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组。 |
|
|
toArray(T[] a) 返回以恰当顺序包含此队列所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的运行时类型。 |
|
ConcurrentLinkedQueue使用和方法介绍的更多相关文章
- [转载]C#读写txt文件的两种方法介绍
C#读写txt文件的两种方法介绍 by 大龙哥 1.添加命名空间 System.IO; System.Text; 2.文件的读取 (1).使用FileStream类进行文件的读取,并将它转换成char ...
- fstream的使用方法介绍
转载自: fstream的使用方法介绍 - saga's blog - C++博客 http://www.cppblog.com/saga/archive/2007/06/19/26652.html ...
- Windows下获取本机IP地址方法介绍
Windows下获取本机IP地址方法介绍 if((hostinfo = gethostbyname(name)) != NULL) { #if 1 ; printf("IP COUNT: % ...
- WebService服务调用方法介绍
1 背景概述 由于在项目中需要多次调用webservice服务,本文主要总结了一下java调用WebService常见的6种方式,即:四种框架的五种调用方法以及使用AEAI ESB进行调用的方法. 2 ...
- C#读写txt文件的两种方法介绍
C#读写txt文件的两种方法介绍 1.添加命名空间 System.IO; System.Text; 2.文件的读取 (1).使用FileStream类进行文件的读取,并将它转换成char数组,然后输出 ...
- jquery的ajax()函数传值中文乱码解决方法介绍
jquery的ajax()函数传值中文乱码解决方法介绍,需要的朋友可以参考下 代码如下: $.ajax({ dataType : ‘json', type : ‘POST', url : ‘http: ...
- UploadifyAPI-上传插件属性和方法介绍
上一篇文章简单的介绍了Uploadify上传插件的使用.但是对于常用的属性和方法并没有说明.授人以鱼不如授人以渔,我决定将常用的属性列举出来,供大伙参考参考. Uploadify属 ...
- js保留小数点后N位的方法介绍
js保留小数点后N位的方法介绍 利用toFixed函数 代码如下 复制代码 <script language="javascript"> document.write( ...
- Thinkphp里import的几个使用方法介绍
以下附上import的几个使用方法介绍 1.使用方法一 import('@.Test.Translate'); @,表示项目根文件夹.假定根文件夹是:App/ 导入类库的路径是:App/Lib/Tes ...
随机推荐
- Linux中Tomcat设置开机启动
设置方法 1.修改/etc/rc.d/rc.local,使用vi /etc/rc.d/rc.local 命令 2.在/etc/rc.d/rc.local文件最后添加下面两行脚本 export JAVA ...
- MySQL之库相关操作
一 系统数据库 information_schema: 虚拟库,不占用磁盘空间,存储的是数据库启动后的一些参数,如用户表信息.列信息.权限信息.字符信息等performance_schema: MyS ...
- python3 json模块
import json '''把python对象转化为json串(字符串), ensure_ascii处理中文乱码'''dic = {"复联4": "好看吗", ...
- L2-2 重排链表 (25 分)
给定一个单链表 L1→L2→⋯→Ln−1→Ln,请编写程序将链表重新排列为 Ln→L1→Ln−1→L2→⋯.例如:给定L为1→2→3→4→5→6,则输出 ...
- VSCode 必装的 10 个高效开发插件
本文介绍了目前前端开发最受欢迎的开发工具 VSCode 必装的 10 个开发插件,用于大大提高软件开发的效率. VSCode 的基本使用可以参考我的原创视频教程「VSCode 高效开发必装插件」. V ...
- 其它综合-有趣的linux命令行工具-lolcat
lolcat :一个在 Linux 终端中输出彩虹特效的命令行工具 何为Lolcat Lolcat 是一个针对 Linux,BSD 和 OSX 平台的工具,它类似于 cat,并为 cat 的输出添加彩 ...
- php提供的用户密码加密函数
在实际项目中,对用户的密码加密基本上采用的 md5加盐的方式, php5.5后提供了一个加密函数,不需要手动加盐,不需要去维护盐值, $str = "123456"; $pwd ...
- VMware Workstation 12 Pro安装CentOs图文教程(超级详细)
本文记录了VMware Workstation 12 Pro安装CentOs的整个过程,具体如下: VMware Workstation 12: CENTOS 6.4 : 创建虚拟机 1.首先安装好V ...
- vhdl 数组
TYPE matrix_index is array (511 downto 0) of std_logic_vector(7 downto 0);signal cnt_freq : matrix_i ...
- SPOJ-LCS Longest Common Substring 【后缀自动机】
题目分析: 用没出现过的字符搞拼接.搞出right树,找right集合的最小和最大.如果最小和最大分居两侧可以更新答案. 代码: #include<bits/stdc++.h> using ...
