Tree Traversals Again
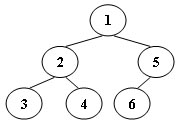
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2 lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
- Push
- Push
- Push
- Pop
- Pop
- Push
- Pop
- Pop
- Push
- Push
- Pop
- Pop
Sample Output:
可以使用堆栈以非递归方式实现顺序二进制树遍历。你的任务是给出这棵树的后序遍历序列。
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。对于每种情况,第一行包含正整数N(≤ 3 0),它是节点的总数量在树(并且因此节点编号从1到N)。然后接下来是N行,每行描述一种堆栈操作,格式为:“Push X”,其中X是被推入堆栈的节点的索引; 或“Pop”表示从堆栈中弹出一个节点。
对于每个测试用例,在一行中打印相应树的后序遍历序列。保证存在解决方案。所有数字必须用一个空格分隔,并且在行的末尾不能有额外的空格。
先给出大神的思路
对二叉树的中序遍历可以通过使用栈来避免迭代的方法,对于figure1中的6节点树而言,它的栈操作为push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop()。依据这个输入可以生成这个二叉树,要求打印出该树的后序遍历。
解法:
该题要求我们通过中序遍历的栈实现的栈操作来生成二叉树。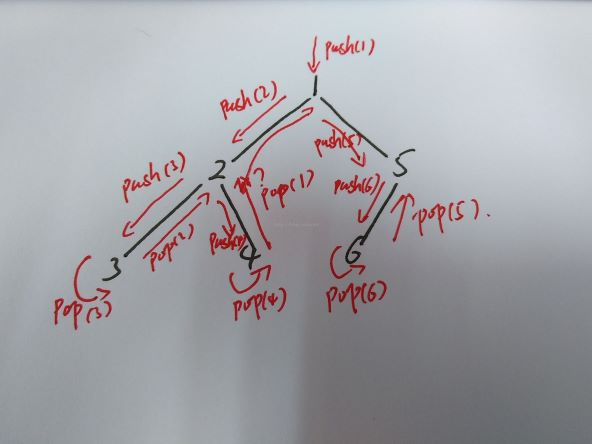
如上图,中序遍历的操作流程(其中箭头代表遍历流),我们可以看出:
1.每次push都指向一个新的节点。
2.每次pop都指向一个被抛出的节点。
3.连续的pop-pop或push-push流的方向都相同。
4.连续的push-pop指向同一个叶节点,同时执行方向转弯。(节点3)
5.连续的pop-push经过一个父节点,同时执行方向转弯。(节点2)
6.每个节点只能pop指向一次,push指向一次。(节点4到2直接跳到1)
于是我们就可以通过这些特性来构建二叉树:
1.读入第一次push构建根节点,根节点入栈。
2.读入下一个操作,有两种情况:
(1)push
说明有一个新节点出现,构建一个节点。如果上次操作为push,把该节点设为栈顶的左儿子,节点入栈。如果上次是pop,经过一个父节点,说明应该是生成了父节点的一个儿子,所以将该节点设为上次pop出来的节点的右儿子。
(2)pop
说明正在pop一个节点,不论上次操作是,该次都抛出一个节点。
这是我写的,有点菜
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stack>
- #include <string>
- #include <algorithm>
- #define MaxTree 31
- #define Null -1
- using namespace std;
- int P[MaxTree];
- int num=;
- int NUM=;
- stack<int> st;
- struct TreeNode
- {
- int date;
- int Left;
- int Right;
- }T[MaxTree];
- int BuildTree(struct TreeNode T[])
- {
- int N,m,p,i;
- string str,pre;
- int Root;
- cin>>N;
- for(i=;i<*N;i++)
- {
- cin>>str;
- if(str=="Push")
- {
- cin>>m;
- if(i==)
- {
- Root=;
- T[num].date=m;
- T[num].Left=Null;
- T[num].Right=Null;
- st.push(num);
- pre=str;
- }
- else if(pre=="Push")
- {
- T[num].Left=num+;
- num++;
- T[num].date=m;
- T[num].Left=Null;
- T[num].Right=Null;
- st.push(num);
- pre=str;
- }
- else if(pre=="Pop")
- {
- T[p].Right=num+;
- num++;
- T[num].date=m;
- T[num].Left=Null;
- T[num].Right=Null;
- st.push(num);
- pre=str;
- }
- }
- else if(str=="Pop")
- {
- p=st.top();
- st.pop();
- pre=str;
- }
- }
- if(N==)
- {
- Root=Null;
- }
- return Root;
- }
- void search(int Tree)
- {
- if(Tree==Null)
- return;
- search(T[Tree].Left);
- search(T[Tree].Right);
- P[NUM++]=T[Tree].date;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int Tree;
- Tree=BuildTree(T);
- search(Tree);
- int i;
- for(i=;i<NUM;i++)
- {
- if(i==)
- cout<<P[i];
- else
- cout<<' '<<P[i];
- }
- return ;
- }
下面是别人用动态链表实现的,值得一看
- #include <cstdio>
- #include <stack>
- using namespace std;
- int preorder[], inorder[];
- int n, preid = , inid = , cnt = ;
- int get(){
- char s[];
- scanf("%s", s);
- if (s[] == 'o') return -;
- int a;
- scanf("%d", &a);
- return a;
- }
- void build(int preb, int pree, int inb, int ine){
- if (preb > pree) return;
- int root = preorder[preb];
- int inroot = inb;
- while (inorder[inroot] != root) ++inroot;
- build(preb+, preb+inroot-inb, inb, inroot-);
- build(preb+inroot-inb+, pree, inroot+, ine);
- if (cnt++ != ) putchar(' ');
- printf("%d", root);
- }
- int main(){
- scanf("%d", &n);
- stack<int> st;
- for (int i = ; i < n*; ++i){
- int a = get();
- if (a != -){
- st.push(a);
- preorder[preid++] = a;
- }else{
- inorder[inid++] = st.top();
- st.pop();
- }
- }
- build(, n-, , n-);
- return ;
- }
- #include <string>
- #include <iostream>
- #include <stack>
- using namespace std;
- const string PUSH("Push");
- const string POP("Pop");
- typedef struct Node
- {
- int data;
- Node* left;
- Node* right;
- Node(int d):data(d), left(NULL), right(NULL){}
- }Node;
- void PostOrderTraverse(Node *root)
- {
- Node* temp = root;
- Node* pre = NULL;
- stack<Node*> S;
- int flag = ;
- while(temp || !S.empty())
- {
- if(temp)
- {
- S.push(temp);
- temp = temp->left;
- }
- else
- {
- temp = S.top();
- if(temp->right && temp->right != pre)
- temp = temp->right;
- else
- {
- if(!flag)
- {
- flag = ;
- cout<< temp->data;
- }
- else
- cout<<" "<<temp->data;
- S.pop();
- pre = temp;
- temp = NULL;
- }
- }
- }
- cout<<endl;
- }
- int main()
- {
- int n, data;
- string act;
- stack<Node*> S;
- Node* root = NULL, *pre = NULL;
- int l = , r = ;
- cin >> n;
- //First, build the tree , root of tree is *root.
- for(int i=; i <= *n; i++)
- {
- Node* temp;
- cin >> act;
- if(act == PUSH)
- {
- cin >> data;
- temp = new Node(data);
- if(i == )
- {
- root = temp;
- }
- S.push(temp);
- if(pre)
- {
- if(l == )
- pre->left = temp;
- else
- pre->right = temp;
- }
- l = ;
- pre = temp;
- }
- else if(act == POP)
- {
- pre = S.top();
- S.pop();
- l = ;
- }
- }
- PostOrderTraverse(root);
- system("pause");
- return ;
- }
Tree Traversals Again的更多相关文章
- Tree Traversals
Tree Traversals 原题链接 常见的二叉树遍历的题目,根据后序遍历和中序遍历求层次遍历. 通过后序遍历和中序遍历建立起一棵二叉树,然后层序遍历一下,主要难点在于树的建立,通过中序遍历和后序 ...
- HDU 1710 二叉树的遍历 Binary Tree Traversals
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- hdu1710(Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU1710Binary Tree Traversals
HDU1710Binary Tree Traversals 题目大意:给一个树的前序遍历和中序遍历,要求输出后序遍历. (半年前做这道题做了两天没看懂,今天学了二叉树,回来AC了^ ^) 首先介绍一下 ...
- HDU-1701 Binary Tree Traversals
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 已知先序和中序遍历,求后序遍历二叉树. 思路:先递归建树的过程,后后序遍历. Binary Tree Tr ...
- 03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25)
03-树2. Tree Traversals Again (25) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- HDU 1710-Binary Tree Traversals(二进制重建)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- PAT1086:Tree Traversals Again
1086. Tree Traversals Again (25) 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 16000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 CHEN, Yue ...
- Binary Tree Traversals(HDU1710)二叉树的简单应用
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- 【PAT】1020 Tree Traversals (25)(25 分)
1020 Tree Traversals (25)(25 分) Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive int ...
随机推荐
- ADO.Net中DataSet的应用
一.知识点描述 1.DataSet是ADO.NET的中心概念.可以把DataSet当成内存中的数据库,DataSet是不依赖于数据库的独立数据集合.也就是说,即使断开数据链路,或者关闭数据库,Data ...
- IDEA 自动生成Hibernate实体类和Mapping文件
一.新建工程Demo(如果选的时候勾选了hibernate,IDEA会自动下载Hibernate包,不需要手动导入) 二.导入相关包 Mysql && Hibernate 三.添加Hi ...
- ubuntu编译安装opencv
简易安装opencv2: conda install --channel https://conda.anaconda.org/menpo opencv 或: sudo apt-get install ...
- UITableView(自定义cell)试水心得
初次试水自定义cell的UITableView 实现目标 最终实现结果 界面复原度:98% 未能完全复刻的地方:下半部分的tableview与头部的控件间距上的误差 原因:在做table ...
- 微信小程序上传后发布或者体验版测试无数据解决办法
在做微信小程序开发的过程中,发现小程序在本地调用接口的数据都显示,但是上传之后,发现手机体验没有数据.以下为解决办法: 1.先清除缓存试试. 2.打开微信小程序工具右上角的详情——项目设置,将“不校验 ...
- Redis的使用原理
原理介绍 (1)什么是redis? Redis 是一个基于内存的高性能key-value数据库. (有空再补充,有理解错误或不足欢迎指正) (2)Reids的特点 Redis本质上是一个Key-Val ...
- hbuilder中的wap2app (将M站快速转换成App的开发框架)使用过程有关原生标题的关闭
首先,我最近在做有关将M站快速转换成App的项目,在网上看了很多,最终结合同学的推荐,我选择了hbuilder,有关于hbuilder的下载还有具体使用方法,官网都有详细的说明,我就不介绍了,我重点介 ...
- 关于修改banner信息;nginx反向代理apache应用
本周实验 1. Linux下Apache部署一个php页面,返回http数据包中查看server信息,修改Apache 配置使server banner自定义. 2. nginx设置反向代理,代理上面 ...
- LeetCode - Robot Room Cleaner
Given a robot cleaner in a room modeled as a grid. Each cell in the grid can be empty or blocked. Th ...
- Android Studio学习之 日志工具
Log.v() 低级日志 Log.d(' ',' ') debug调试信息 第一个参数tag,当前类名 第二个参数msg,打印具体内容 Log.i() info数据 Log.w() warn警 ...