Android -- ViewGroup源码分析+自定义
1,我们前三篇博客了解了一下自定义View的基本方法和流程
之前,我们只是学习过自定义View,其实自定义ViewGroup和自定义View的步骤差不了多少,他们的的区别主要来自各自的作用不同,ViewGroup是容器,用来包含其他控件,而View是真正意义上看得见摸得着的,它需要将自己画出来。ViewGroup需要重写onMeasure方法测量子控件的宽高和自己的宽高,然后实现onLayout方法摆放子控件。而 View则是需要重写onMeasure根据测量模式和父控件给出的建议的宽高值计算自己的宽高,然后再父控件为其指定的区域绘制自己的图形。
但是仅仅是了解自定义view还是不够的,我们还要学习一下我们的ViewGroup,例如SlideMenu、CardLayout、 CustomLayout等。先看一下我们的官方文档来怎么描述我们的
ViewGroup是一种可以包含其他视图的特殊视图,他是各种布局和所有容器的基类,这些类也定义了ViewGroup.LayoutParams类作为类的布局参数。
所以我们现在可以自定义ViewGroup分为下面这几步:
1,继承自ViewGroup,重写构造方法
2,重写OnMeasure()方法,丈量子控件和自身宽高
3,重写OnLayout()方法,摆放子控件位置
2,实现简单的水平排列结果
先创建自定义ViewGroup,实现从左到右,排满换行的的功能
package com.qianmo.activitydetail.view; import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup; /**
* Created by wangjitao on 2017/3/23 0023.
* E-Mail:543441727@qq.com
*/ public class MyLayout extends ViewGroup {
private static String TAG = "MyLayout"; public MyLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
} public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
} public MyLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } /**
* 所有子view自己测量大小,然后根据自孩子的大小完成自己的尺寸测量
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//首先计算所有子view的宽高
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//保留测量的宽高(这里使用wrap_content和match_parent都是填充屏幕)
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec)); } /**
* 为所有的子控件摆放位置
*
* @param changed
* @param left
* @param top
* @param right
* @param bottom
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
//获取子控件数量
final int count = getChildCount();
int childMeasureWidth = 0;
int childMeasureHeight = 0; //容器已经占据的宽高度
int layoutWidth = 0;
int layoutHeight = 0; //每一行的高度是这一行中最高控件的高度
int maxChildHeight = 0; for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
//注意此处不能使用getWidth和getHeight,这两个方法必须在onLayout执行完,才能正确获取宽高
childMeasureHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
childMeasureWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); Log.i(TAG, "getWidth():" + getWidth());
Log.i(TAG, "childMeasureHeight:" + childMeasureHeight);
Log.i(TAG, "childMeasureWidth:" + childMeasureWidth);
getWidth();
if (layoutWidth < getWidth()) {
//如果一行没有排满,继续往右排列
left = layoutWidth;
right = left + childMeasureWidth;
top = layoutHeight;
bottom = top + childMeasureHeight;
} else {
//排满后就换行
layoutWidth = 0;
layoutHeight += maxChildHeight;
left = layoutWidth;
right = left + childMeasureWidth;
top = layoutHeight;
bottom = top + childMeasureHeight;
}
//宽度累加
layoutWidth += childMeasureWidth;
//记录本次最高宽度
if (childMeasureHeight > maxChildHeight) {
maxChildHeight = childMeasureHeight;
} //确定子控件的位置,四个参数分别代表上下左右的坐标值
child.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
}
}
}
布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.qianmo.activitydetail.view.MyLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:myview="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF8247"
android:padding="20dip"
android:text="按钮1"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#8B0A50"
android:padding="10dip"
android:text="按钮2222222222222"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#7CFC00"
android:padding="15dip"
android:text="按钮333333"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#1E90FF"
android:padding="10dip"
android:text="按钮4"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="10dip"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#191970"
android:padding="15dip"
android:text="按钮5"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#7A67EE"
android:padding="20dip"
android:text="按钮6"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"/> </com.qianmo.activitydetail.view.MyLayout>
看一下运行效果
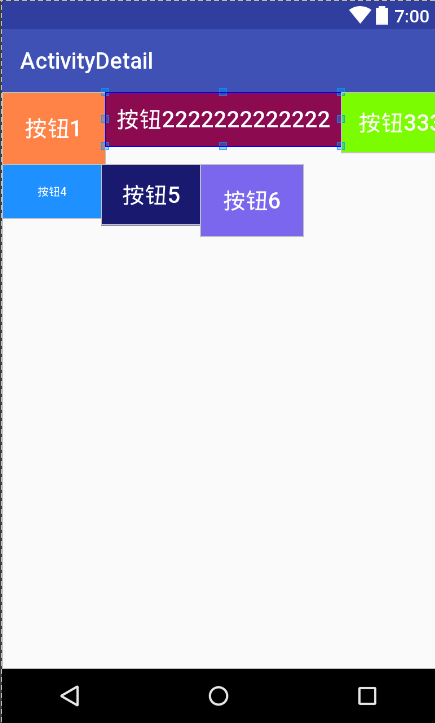
3,自定义LayoutParams,实现RelativeLayout的layout_alignLeft、layout_alignRight、layout_alignTop、layout_alignBottom功能
回想一下我们平时使用RelativeLayout的时候,在布局文件中使用android:layout_alignParentRight="true"、android:layout_centerInParent="true"等各种属性,就能控制子控件显示在父控件的上下左右、居中等效果。 在上一篇讲onMeasure的博客中,我们有了解过ViewGroup.LayoutParams类,ViewGroup中有两个内部类ViewGroup.LayoutParams和ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams,MarginLayoutParams继承自LayoutParams,这两个内部类就是ViewGroup的布局参数类,比如我们在LinearLayout等布局中使用的layout_width\layout_hight等以“layout_ ”开头的属性都是布局属性。
在View中有一个mLayoutParams的变量用来保存这个View的所有布局属性。ViewGroup.LayoutParams有两个属性layout_width和layout_height,因为所有的容器都需要设置子控件的宽高,所以这个LayoutParams是所有布局参数的基类,如果需要扩展其他属性,都应该继承自它。比如RelativeLayout中就提供了它自己的布局参数类RelativeLayout.LayoutParams,并扩展了很多布局参数。
- 大致明确布局容器的需求,初步定义布局属性
在定义属性之前要弄清楚,我们自定义的布局容器需要满足那些需求,需要哪些属性,比如,我们现在要实现像相对布局一样,为子控件设置一个位置属性layout_position=”“,来控制子控件在布局中显示的位置。暂定位置有五种:左上、左下、右上、右下、居中。有了需求,我们就在attr.xml定义自己的布局属性
<declare-styleable name="MyLayout2">
<attr name="layout_position">
<enum name="left" value="1"/>
<enum name="top" value="2"/>
<enum name="right" value="3"/>
<enum name="bottom" value="4"/>
<enum name="center" value="5"/>
</attr>
</declare-styleable>
- 继承LayoutParams,定义布局参数类
我们可以选择继承ViewGroup.LayoutParams,覆盖构造方法,然后在有AttributeSet参数的构造方法中初始化参数值,这个构造方法才是布局文件被映射为对象的时候被调用的。
package com.qianmo.activitydetail.java; import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.ViewGroup; import com.qianmo.activitydetail.R; /**
* Created by wangjitao on 2017/3/23 0023.
* E-Mail:543441727@qq.com
*/ public class MyLayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams { public static final int POSITION_LEFT = 1;
public static final int POSITION_TOP = 2;
public static final int POSITION_RIGHT = 3;
public static final int POSITION_BOTTOM = 4;
public static final int POSITION_CENTER = 5; public int position = POSITION_LEFT; public MyLayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyLayout2);
position = a.getInt(R.styleable.MyLayout2_layout_position, POSITION_LEFT);
} public MyLayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
} public MyLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
- 重写generateLayoutParams()
在ViewGroup中有下面几个关于LayoutParams的方法,generateLayoutParams (AttributeSet attrs)是在布局文件被填充为对象的时候调用的,这个方法是下面几个方法中最重要的,如果不重写它,我们布局文件中设置的布局参数都不能拿到。
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MyLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
} @Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new MyLayoutParams(p);
} @Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MyLayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
} @Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof MyLayoutParams;
}
- 在布局文件中使用布局属性
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "utf-8"?>
<com.qianmo.activitydetail.view.MyLayout2
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:myview="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#FF8247"
android:padding="20dip"
android:text="按钮1"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"
myview:layout_position="left"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#8B0A50"
android:padding="10dip"
android:text="按钮2222222222222"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="18dip"
myview:layout_position="right"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#7CFC00"
android:padding="15dip"
android:text="按钮333333"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"
myview:layout_position="bottom"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#1E90FF"
android:padding="10dip"
android:text="按钮4"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="15dip"
myview:layout_position="top"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#191970"
android:padding="15dip"
android:text="按钮5"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"
myview:layout_position="center"/>
</com.qianmo.activitydetail.view.MyLayout2>
- 在onMeasure和onLayout中使用布局参数
经过上面几步之后,我们运行程序,就能获取子控件的布局参数了,在onMeasure方法和onLayout方法中,我们按照自定义布局容器的特殊需求,对宽度和位置坐特殊处理。这里我们需要注意一下,如果布局容器被设置为包裹类容,我们只需要保证能将最大的子控件包裹住就ok,代码注释比较详细,就不多说了。
package com.qianmo.activitydetail.view; import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup; import com.qianmo.activitydetail.java.MyLayoutParams; /**
* Created by wangjitao on 2017/3/23 0023.
* E-Mail:543441727@qq.com
* 通过自定义LayoutParams设置特殊的属性
*/ public class MyLayout2 extends ViewGroup {
private static String TAG = "MyLayout"; public MyLayout2(Context context) {
this(context, null);
} public MyLayout2(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
} public MyLayout2(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); } /**
* 在ViewGroup中有下面几个关于LayoutParams的方法,generateLayoutParams (AttributeSet attrs)是在布局文件被填充为对象的时候调用的
* 如果不重写它,我么布局文件中设置的布局参数都不能拿到。
*
* @param attrs
* @return
*/ @Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MyLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
} @Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new MyLayoutParams(p);
} @Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MyLayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
} @Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof MyLayoutParams;
} /**
* 所有子view自己测量大小,然后根据自孩子的大小完成自己的尺寸测量
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取本ViewGroup上机容器为其推荐的款和高,以及计算模式
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //计算出所有子控件的宽和高
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
int chileCount = getChildCount(); //测量的父控件的宽高
int layoutHeight = 0;
int layoutWidth = 0; //进行宽度模式的判断
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
//这时不具容器的宽度模式是确定的(具体的size或者match_patent,直接使用父窗体建议的宽度)
layoutWidth = widthSize;
} else {
//如果是未指定的活wrap_content,我们一般按照包裹内容来处理,宽度就拿所有控件的宽度和为宽度
for (int i = 0; i < chileCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
//获取子控件最大宽度
layoutWidth = childWidth > layoutWidth ? childWidth : layoutWidth;
}
} //高度模式一样
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
//这时不具容器的宽度模式是确定的(具体的size或者match_patent,直接使用父窗体建议的宽度)
layoutHeight = heightSize;
} else {
//如果是未指定的活wrap_content,我们一般按照包裹内容来处理,宽度就拿所有控件的宽度和为宽度
for (int i = 0; i < chileCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
//获取子控件最大高度
layoutHeight = childHeight > layoutHeight ? childHeight : layoutHeight;
}
} //保存测量宽高数据
setMeasuredDimension(layoutWidth, layoutHeight);
} /**
* 为所有的子控件摆放位置
*
* @param changed
* @param left
* @param top
* @param right
* @param bottom
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
int chileCount = getChildCount();
MyLayoutParams params = null; for (int i = 0; i < chileCount; i++) {
childWidth = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredWidth();
childHeight = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredHeight(); params = (MyLayoutParams) getChildAt(i).getLayoutParams();
switch (params.position) {
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_LEFT:
//左上方
left = 0;
top = 0;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_TOP:
//右上方
left = getWidth() - childWidth;
top = 0;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_RIGHT:
//右下方
left = 0;
top = getHeight() - childHeight;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_BOTTOM:
left = getWidth() - childWidth;
top = getHeight() - childHeight;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_CENTER:
left = (getWidth() - childWidth) / 2;
top = (getHeight() - childHeight) / 2;
break;
default:
break;
}
// 确定子控件的位置,四个参数分别代表(左上右下)点的坐标值
getChildAt(i).layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight); }
}
}
看一下运行效果
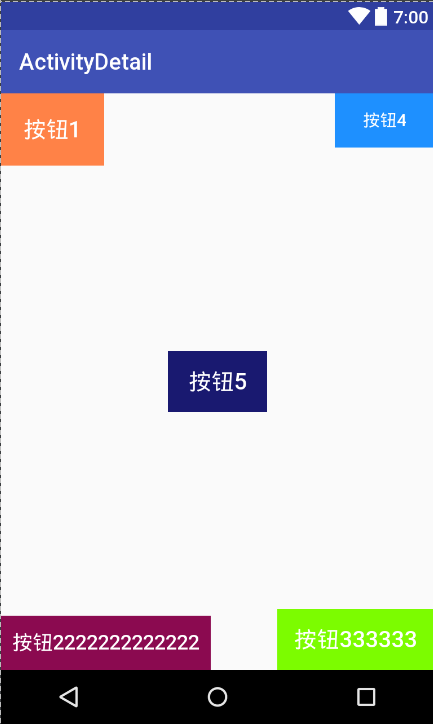
4,支持layout_margin属性
如果我们自定义的布局参数类继承自MarginLayoutParams,就自动支持了layout_margin属性了,我们需要做的就是直接在布局文件中使用layout_margin属性,然后再onMeasure和onLayout中使用margin属性值测量和摆放子控件。需要注意的是我们测量子控件的时候应该调用measureChildWithMargin()方法。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding= "utf-8"?>
<com.qianmo.activitydetail.view.MyLayout3
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:myview="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
myview:layout_position= "left"
android:layout_marginLeft = "20dip"
android:background= "#FF8247"
android:textColor= "#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"
android:padding= "20dip"
android:text="按钮1" /> <Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop = "30dip"
myview:layout_position= "top"
android:background= "#8B0A50"
android:textColor= "#ffffff"
android:textSize="18dip"
android:padding= "10dip"
android:text="按钮2222222222222" /> <Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
android:layout_marginLeft = "30dip"
android:layout_marginBottom = "10dip"
myview:layout_position= "bottom"
android:background= "#7CFC00"
android:textColor= "#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"
android:padding= "15dip"
android:text="按钮333333" /> <Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
myview:layout_position= "right"
android:layout_marginBottom = "30dip"
android:background= "#1E90FF"
android:textColor= "#ffffff"
android:textSize="15dip"
android:padding= "10dip"
android:text="按钮4" /> <Button
android:layout_width= "wrap_content"
android:layout_height= "wrap_content"
myview:layout_position= "center"
android:layout_marginBottom = "30dip"
android:layout_marginRight = "30dip"
android:background= "#191970"
android:textColor= "#ffffff"
android:textSize="20dip"
android:padding= "15dip"
android:text="按钮5" /> </com.qianmo.activitydetail.view.MyLayout3>
我们创建类继承自MarginParams类
package com.qianmo.activitydetail.java; import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.ViewGroup; import com.qianmo.activitydetail.R; /**
* Created by wangjitao on 2017/3/23 0023.
* E-Mail:543441727@qq.com
* 添加外边框参数
*/ public class MyLayoutParamsWithMargin extends ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams { public static final int POSITION_LEFT = 1;
public static final int POSITION_TOP = 2;
public static final int POSITION_RIGHT = 3;
public static final int POSITION_BOTTOM = 4;
public static final int POSITION_CENTER = 5; public int position = POSITION_LEFT; public MyLayoutParamsWithMargin(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.MyLayout2);
position = a.getInt(R.styleable.MyLayout2_layout_position, POSITION_LEFT);
} public MyLayoutParamsWithMargin(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
} public MyLayoutParamsWithMargin(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
在generateLayoutParams()方法中替换类
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MyLayoutParamsWithMargin(getContext(), attrs);
} @Override
protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return new MyLayoutParamsWithMargin(p);
} @Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new MyLayoutParamsWithMargin(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT);
} @Override
protected boolean checkLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) {
return p instanceof MyLayoutParamsWithMargin;
}
onMeasure和onLayout:
/**
* 所有子view自己测量大小,然后根据自孩子的大小完成自己的尺寸测量
*
* @param widthMeasureSpec
* @param heightMeasureSpec
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
//获取本ViewGroup上机容器为其推荐的款和高,以及计算模式
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); //计算出所有子控件的宽和高
// measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
int chileCount = getChildCount(); //测量的父控件的宽高
int layoutHeight = 0;
int layoutWidth = 0; // 计算出所有的childView的宽和高
for (int i = 0; i < chileCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
measureChildWithMargins(child, widthMeasureSpec, 0, heightMeasureSpec, 0);
}
MyLayoutParamsWithMargin params = null; //进行宽度模式的判断
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
//这时不具容器的宽度模式是确定的(具体的size或者match_patent,直接使用父窗体建议的宽度)
layoutWidth = widthSize;
} else {
//如果是未指定的活wrap_content,我们一般按照包裹内容来处理,宽度就拿所有控件的宽度和为宽度
for (int i = 0; i < chileCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
params = (MyLayoutParamsWithMargin) child.getLayoutParams();
//获取子控件最大宽度(要算上左右间距)
layoutWidth = childWidth > layoutWidth + params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin ? childWidth : layoutWidth;
}
} //高度模式一样
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
//这时不具容器的宽度模式是确定的(具体的size或者match_patent,直接使用父窗体建议的宽度)
layoutHeight = heightSize;
} else {
//如果是未指定的活wrap_content,我们一般按照包裹内容来处理,宽度就拿所有控件的宽度和为宽度
for (int i = 0; i < chileCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
params = (MyLayoutParamsWithMargin) child.getLayoutParams();
//获取子控件最大高度
layoutHeight = childHeight > layoutHeight + params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin ? childHeight : layoutHeight;
}
} //保存测量宽高数据
setMeasuredDimension(layoutWidth, layoutHeight);
} /**
* 为所有的子控件摆放位置
*
* @param changed
* @param left
* @param top
* @param right
* @param bottom
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
int childWidth = 0;
int childHeight = 0;
int chileCount = getChildCount();
MyLayoutParamsWithMargin params = null; for (int i = 0; i < chileCount; i++) {
childWidth = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredWidth();
childHeight = getChildAt(i).getMeasuredHeight(); params = (MyLayoutParamsWithMargin) getChildAt(i).getLayoutParams();
switch (params.position) {
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_LEFT:
//左上方
left = 0 + params.leftMargin;
top = 0 + params.topMargin;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_TOP:
//右上方
left = getWidth() - childWidth - params.rightMargin;
top = 0 + params.topMargin;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_RIGHT:
//左下方
left = 0 + params.leftMargin;
top = getHeight() - childHeight - params.bottomMargin;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_BOTTOM:
//右下角
left = getWidth() - childWidth - params.rightMargin;
top = getHeight() - childHeight - params.bottomMargin;
break;
case MyLayoutParams.POSITION_CENTER:
left = (getWidth() - childWidth) / 2;
top = (getHeight() - childHeight) / 2;
break;
default:
break;
}
// 确定子控件的位置,四个参数分别代表(左上右下)点的坐标值
getChildAt(i).layout(left, top, left + childWidth, top + childHeight); }
}
运行效果
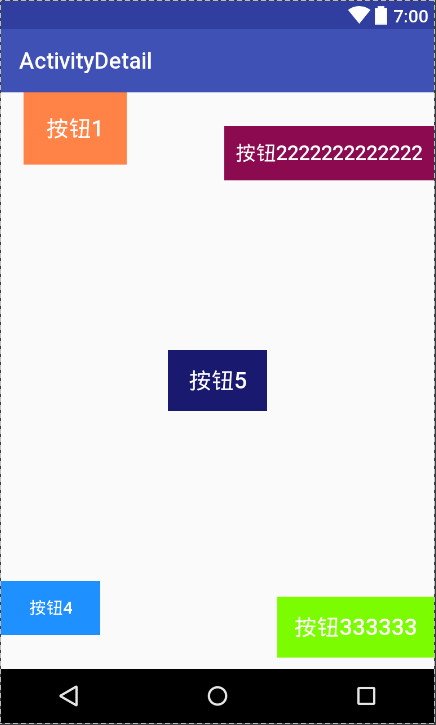
总结一下我们的学习内容
自定义ViewGroup的步骤:
①. 继承ViewGroup,覆盖构造方法
②. 重写onMeasure方法测量子控件和自身宽高
③. 实现onLayout方法摆放子控件
为布局容器自定义布局属性:
①. 大致明确布局容器的需求,初步定义布局属性
②. 继承LayoutParams,定义布局参数类
③. 重写获取布局参数的方法
④. 在布局文件中使用布局属性
⑤. 在onMeasure和onLayout中使用布局参数
Android -- ViewGroup源码分析+自定义的更多相关文章
- Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之启动运行
通过前面的两篇文章<Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之控件AndroidElement>和<Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之命令解析 ...
- Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之命令解析执行
通过上一篇文章<Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之控件AndroidElement>我们知道了Appium从pc端发送过来的命令如果是控件相关的话,最终目标控件在b ...
- Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之控件AndroidElement
通过上一篇文章<Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之简介>我们对bootstrap的定义以及其在appium和uiautomator处于一个什么样的位置有了一个初步的 ...
- Android HandlerThread 源码分析
HandlerThread 简介: 我们知道Thread线程是一次性消费品,当Thread线程执行完一个耗时的任务之后,线程就会被自动销毁了.如果此时我又有一 个耗时任务需要执行,我们不得不重新创建线 ...
- Android Choreographer 源码分析
Choreographer 的作用主要是配合 Vsync ,给上层 App 的渲染提供一个稳定的 Message 处理的时机,也就是 Vsync 到来的时候 ,系统通过对 Vsync 信号周期的调整, ...
- Android base-adapter-helper 源码分析与扩展
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/lmj623565791/article/details/44014941,本文出自:[张鸿洋的博客] 本篇博客是我加入Android 开源项 ...
- Appium Android Bootstrap源码分析之简介
在上一个系列中我们分析了UiAutomator的核心源码,对UiAutomator是怎么运行的原理有了根本的了解.今天我们会开始另外一个在安卓平台上基于UiAutomator的新起之秀--Appium ...
- SOFA 源码分析 — 自定义线程池原理
前言 在 SOFA-RPC 的官方介绍里,介绍了自定义线程池,可以为指定服务设置一个独立的业务线程池,和 SOFARPC 自身的业务线程池是隔离的.多个服务可以共用一个独立的线程池. API使用方式如 ...
- android消息处理源码分析
一.简介消息处理机制主要涉及到这几个类:1.Looper2.MessageQueue3.Message4.Handler 二.源码分析 Looper.class的关键源码: //保存Looper对象, ...
随机推荐
- RabbitMQ的Vhost,Exchange,Queue原理分析
Vhost分析 RabbitMQ的Vhost主要是用来划分不同业务模块.不同业务模块之间没有信息交互. Vhost之间相互完全隔离,不同Vhost之间无法共享Exchange和Queue.因此Vhos ...
- AIX动态增加SWAP空间
增加SWAP交换页空间 查看SWAP,使用lsps –a命令查看,默认安装SWAP是512M,例如: # lsps -a Page Space Physical V ...
- rar压缩类
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using System.Diagnostics; namespa ...
- 四、Spring Boot Web开发
四.Web开发 1.简介 使用SpringBoot: 1).创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块: 2).SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可 ...
- cd 命令
[root@localhost ~]# cd # 进入当前用户的家目录 [root@localhost ~]# cd ~ # 进入当前用户的家目录 [root@localhost ~]# cd /da ...
- Linux 磁盘空间大小统计du命令常见使用方法
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主同意不得转载. https://blog.csdn.net/hongweigg/article/details/37692057 在 Linux下,能够对某个文件 ...
- docker基本原理
写的很不错的文章,作个存档 什么是容器 容器是 种轻量级.可移植的为应用程序提供了隔离的运行空间 .每个容器内都包含一个独享的完整用户环境,并且 个容器内的环境变动不会影响其他容器的运行环境,可以使应 ...
- 显示日历的指令:cal
1.显示日历的指令:cal (1)参数: (2)实例:
- 简明 ASP.NET Core 手册2018
https://windsting.github.io/little-aspnetcore-book/book/ 中文版 https://nbarbettini.gitbooks.io/little- ...
- WINDOWS SERVER 2008 R2安装指南
说明:适用于以下几种操作系统: 1.Windows Server 2008 Standard Endition R2 2.Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Endition ...
