hdu 4366 Successor - CDQ分治 - 线段树 - 树分块
Sean owns a company and he is the BOSS.The other Staff has one Superior.every staff has a loyalty and ability.Some times Sean will fire one staff.Then one of the fired man’s Subordinates will replace him whose ability is higher than him and has the highest loyalty for company.Sean want to know who will replace the fired man.
Input
In the first line a number T indicate the number of test cases. Then for each case the first line contain 2 numbers n,m (2<=n,m<=50000),indicate the company has n person include Sean ,m is the times of Sean’s query.Staffs are numbered from 1 to n-1,Sean’s number is 0.Follow n-1 lines,the i-th(1<=i<=n-1) line contains 3 integers a,b,c(0<=a<=n-1,0<=b,c<=1000000),indicate the i-th staff’s superior Serial number,i-th staff’s loyalty and ability.Every staff ‘s Serial number is bigger than his superior,Each staff has different loyalty.then follows m lines of queries.Each line only a number indicate the Serial number of whom should be fired.
Output
For every query print a number:the Serial number of whom would replace the losing job man,If there has no one to replace him,print -1.
Sample Input
1
3 2
0 100 99
1 101 100
1
2
Sample Output
2
-1
题目大意 给定一棵树,每个点有两个权值,忠诚度和能力值,每次询问点x的子树中能力值大于它,忠诚度最高的一位的编号。
Solution 1 树分块
因为查询的时候,查询一个节点的子树实际上是等于查询一段区间内的数据,所以考虑对dfs序进行分块。
按照dfs序进行分块,块内按忠诚度进行排序,再记录后缀忠诚度最大值。
根据常用套路,每次查询,对于块两端部分,暴力for。中间每个块lower_bound upper_bound一下查询合法的一段,然后用后缀忠诚度最大值进行更新答案就好了。
(这是我比较笨的分块方法)
设块的大小为s,块的数量为c,则总时间复杂度为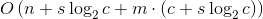
Code
/**
* hdu
* Problem#4366
* Accepted
* Time: 748ms
* Memory: 8468k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef bool boolean; typedef class Staff {
public:
int loy;
int abi;
int id; boolean operator < (Staff b) const {
if(abi != b.abi) return abi < b.abi;
return loy < b.loy;
}
}Staff; boolean operator < (const int& x, const Staff& s) {
return x < s.abi;
} const int maxcsize = ;
typedef class Chunk {
public:
int len;
Staff sta[maxcsize];
int maxv[maxcsize];
int ans[maxcsize]; void init(Staff* lis, int from, int end) {
len = end - from;
for(int i = from; i < end; i++)
sta[i - from] = lis[i];
sort(sta, sta + len);
maxv[len] = -;
ans[len] = -;
for(int i = len - ; i >= ; i--) {
if(sta[i].loy > maxv[i + ])
maxv[i] = sta[i].loy, ans[i] = sta[i].id;
else
maxv[i] = maxv[i + ], ans[i] = ans[i + ];
}
} void getAns(int limit, int& rmaxv, int& rans) {
int pos = upper_bound(sta, sta + len, limit) - sta;
if(maxv[pos] > rmaxv)
rmaxv = maxv[pos], rans = ans[pos];
}
}Chunk; int n, m;
int cs, cc;
vector<int> *g;
Staff lis[];
Staff *nlis;
Chunk chs[]; inline void init() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
g = new vector<int>[(n + )];
nlis = new Staff[(n + )];
for(int i = , x; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, &lis[i].loy, &lis[i].abi);
lis[i].id = i;
g[x].push_back(i);
}
lis[].loy = lis[].abi = ;
lis[].id = ;
cs = sqrt(n + 0.5);
} int cnt;
int visitID[], exitID[];
int visit[];
inline void dfs(int node) {
visitID[node] = ++cnt;
visit[cnt] = node;
for(int i = ; i < (signed)g[node].size(); i++)
dfs(g[node][i]);
exitID[node] = cnt;
} inline void init_chunks() {
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
nlis[i] = lis[visit[i]], nlis[i].id = i;
for(cc = ; cc * cs < n; cc++)
chs[cc + ].init(nlis, cc * cs + , min((cc + ) * cs, n) + );
} inline void solve() {
int l, r, x, maxv, ans, lim;
while(m--) {
scanf("%d", &x);
maxv = -, ans = -;
l = visitID[x], r = exitID[x], lim = lis[x].abi;
int lid = l / cs + , rid = r / cs + ;
if(lid == rid) {
for(int i = l; i <= r; i++)
if(nlis[i].abi > lim && nlis[i].loy > maxv)
maxv = nlis[i].loy, ans = i;
} else {
// if(x == 992)
// putchar('a');
for(int i = l; i <= lid * cs; i++)
if(nlis[i].abi > lim && nlis[i].loy > maxv)
maxv = nlis[i].loy, ans = i;
for(int i = (rid - ) * cs + ; i <= r; i++)
if(nlis[i].abi > lim && nlis[i].loy > maxv)
maxv = nlis[i].loy, ans = i;
for(int i = lid + ; i < rid; i++)
chs[i].getAns(lim, maxv, ans);
}
printf("%d\n", (ans == -) ? (-) : (visit[ans]));
}
} inline void clear() {
delete[] g;
delete[] nlis;
} int T;
int main() {
// freopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("a.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
init();
cnt = ;
dfs();
init_chunks();
solve();
clear();
}
// fprintf(stderr, "Time: %dms\n", clock());
return ;
}
Successor(Tree Division)
Solution 2 CDQ分治
每次查询相当于查询满足能力大于某个值,深度优先时间戳在某一段区间内的最大的忠诚度,感觉有那么一点像偏序的问题,所以上CDQ分治乱搞..
分治能力,然后对于能力大于等于mid的节点可能会对能力小于mid的节点做出贡献,所以就用一个线段树维护区间最值,对于能力值大于等于mid的节点就在线段树内将它的深度优先时间戳那一位改为它的忠诚度。对于能力值小于mid的节点x就查询[visitID[x], exitID[x]]的最值就好了。
每次询问O(1)解决。
总时间复杂度 .
.
由于自己巨懒无比,CDQ分治从来都不手写队列,直接用vector。又因为线段树和STL中的vector常数巨大无比(当然还有我的代码自带某个比较大的常数),所以直接上就TLE了。把vector全都改成手写vector才过的。
Code
/**
* hdu
* Problem#4366
* Accepted
* Time: 842ms
* Memory: 18776k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << ) - ); typedef class SegTreeNode {
public:
int val;
int maxid;
SegTreeNode *l, *r;
SegTreeNode():val(-), maxid(), l(NULL), r(NULL) { } inline void pushUp() {
if(l->val > r->val)
val = l->val, maxid = l->maxid;
else
val = r->val, maxid = r->maxid;
}
}SegTreeNode; SegTreeNode pool[];
SegTreeNode *top; inline SegTreeNode* newnode() {
top->val = -;
return top++;
} typedef class SegTree {
public:
SegTreeNode* root; SegTree():root(NULL) { }
SegTree(int n) {
build(root, , n);
} void build(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r) {
node = newnode();
if(l == r) return;
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
build(node->l, l, mid);
build(node->r, mid + , r);
} void update(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int idx, int val) {
if(l == r) {
node->val = val, node->maxid = l;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if(idx <= mid) update(node->l, l, mid, idx, val);
else update(node->r, mid + , r, idx, val);
node->pushUp();
} int query(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int& maxid) {
if(l == ql && qr == r) {
maxid = node->maxid;
return node->val;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if(qr <= mid) return query(node->l, l, mid, ql, qr, maxid);
if(ql > mid) return query(node->r, mid + , r, ql, qr, maxid);
int a, b, c;
a = query(node->l, l, mid, ql, mid, c);
b = query(node->r, mid + , r, mid + , qr, maxid);
if(a > b) maxid = c;
return max(a, b);
}
}SegTree; template<typename T>
class Vector {
protected:
int cap;
int siz;
T* l;
public:
Vector():l(NULL), cap(), siz() { } inline void push_back(T x) {
if(l == NULL) {
l = new T[];
cap = , siz = ;
}
if(siz == cap) {
l = (T*)realloc(l, sizeof(T) * cap * ); //重新申请内存,并拷贝数组
cap = cap << ;
}
l[siz++] = x;
} T& operator [] (int pos) {
return l[pos];
} inline int size() {
return siz;
} inline int capt() {
return cap;
} inline void clear() {
delete[] l;
l = NULL;
}
}; int n, m;
int valmax;
Vector<int> *g;
Vector<int> a233;
int* loys, *abis;
SegTree st; inline void init() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
top = pool;
g = new Vector<int>[(n + )];
loys = new int[(n + )];
abis = new int[(n + )];
st = SegTree(n);
loys[] = inf, abis[] = inf;
a233.clear();
for(int i = , x; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, loys + i, abis + i);
g[x].push_back(i);
a233.push_back(i);
}
} int buf[];
void discrete() {
memcpy(buf, abis, sizeof(int) * n);
sort(buf, buf + n);
valmax = unique(buf, buf + n) - buf;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++)
abis[i] = lower_bound(buf, buf + valmax, abis[i]) - buf + ;
} int cnt;
int visitID[], exitID[];
int visit[];
inline void dfs(int node) {
visitID[node] = ++cnt;
visit[cnt] = node;
for(int i = ; i < (signed)g[node].size(); i++)
dfs(g[node][i]);
exitID[node] = cnt;
} int maxvals[];
int ans[];
void CDQDividing(int l, int r, Vector<int>& q) {
if(q.size() <= ) return;
if(l == r) return; int mid = (l + r) >> , a, b; Vector<int> ql, qr;
for(int i = ; i < (signed)q.size(); i++)
if(abis[q[i]] > mid)
qr.push_back(q[i]), st.update(st.root, , n, visitID[q[i]], loys[q[i]]);
else
ql.push_back(q[i]); for(int i = ; i < (signed)ql.size(); i++) {
a = st.query(st.root, , n, visitID[ql[i]], exitID[ql[i]], b);
if(a > maxvals[ql[i]])
maxvals[ql[i]] = a, ans[ql[i]] = b;
} for(int i = ; i < (signed)qr.size(); i++)
st.update(st.root, , n, visitID[qr[i]], -); q.clear();
CDQDividing(l, mid, ql);
CDQDividing(mid + , r, qr);
} inline void solve() {
cnt = ;
dfs();
memset(maxvals, -, sizeof(int) * (n + ));
memset(ans, -, sizeof(int) * (n + ));
CDQDividing(, valmax, a233);
int x;
while(m--) {
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%d\n", (ans[x] == -) ? (-) : (visit[ans[x]]));
}
} inline void clear() {
delete[] g;
delete[] loys;
delete[] abis;
} int T;
int main() {
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
init();
discrete();
solve();
clear();
}
return ;
}
Successor(CDQ Divide and Conquer)
Sulution 3 线段树合并
对于上一种做法,为了满足子树的关系多带了个log,考虑直接dfs,每一个点先访问它的子树,再把子树信息合并起来,就可以满足子树关系了。
现在考虑如何维护子树信息。对能力值开一个值域线段树,记录当前值域内最大的忠诚度。
于是就成功把总时间复杂度优化成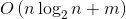 .
.
然而常数更大了,所以没有快多少。
Code
/**
* hdu
* Problem#4366
* Accepted
* Time: 436ms
* Memory: 39124k
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const signed int inf = (signed)((1u << ) - ); typedef class SegTreeNode {
public:
int val;
int maxid;
SegTreeNode *l, *r;
SegTreeNode():val(-), maxid(-), l(NULL), r(NULL) { }
SegTreeNode(SegTreeNode *p):val(-), maxid(-), l(p), r(p) { } inline void pushUp() {
if(l->val > r->val)
val = l->val, maxid = l->maxid;
else
val = r->val, maxid = r->maxid;
}
}SegTreeNode; SegTreeNode pool[];
SegTreeNode null = SegTreeNode(&null);
SegTreeNode *top; inline SegTreeNode* newnode() {
top->val = -;
top->maxid = -;
top->l = top->r = &null;
return top++;
} void merge(SegTreeNode*& a, SegTreeNode* b) {
if(b == &null) return;
if(a == &null) {
a = b;
return;
}
if(b->val > a->val)
a->val = b->val, a->maxid = b->maxid;
merge(a->l, b->l);
merge(a->r, b->r);
// a->pushUp();
} typedef class SegTree {
public:
SegTreeNode* root; SegTree():root(&null) { } void update(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int idx, int val, int id) {
if(node == &null)
node = newnode();
if(l == r) {
if(val > node->val)
node->val = val, node->maxid = id;
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if(idx <= mid) update(node->l, l, mid, idx, val, id);
else update(node->r, mid + , r, idx, val, id);
node->pushUp();
} int query(SegTreeNode*& node, int l, int r, int ql, int qr, int& maxid) {
if(l == ql && qr == r) {
maxid = node->maxid;
return node->val;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
if(qr <= mid) return query(node->l, l, mid, ql, qr, maxid);
if(ql > mid) return query(node->r, mid + , r, ql, qr, maxid);
int a, b, c;
a = query(node->l, l, mid, ql, mid, c);
b = query(node->r, mid + , r, mid + , qr, maxid);
if(a > b) maxid = c;
return max(a, b);
}
}SegTree; const int limval = ; int n, m;
int valmax;
vector<int> *g;
int* loys, *abis; inline void init() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
top = pool;
g = new vector<int>[(n + )];
loys = new int[(n + )];
abis = new int[(n + )];
loys[] = inf, abis[] = inf;
for(int i = , x; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d%d%d", &x, loys + i, abis + i);
g[x].push_back(i);
}
} int buf[];
void discrete() {
memcpy(buf, abis, sizeof(int) * n);
sort(buf, buf + n);
valmax = unique(buf, buf + n) - buf;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++)
abis[i] = lower_bound(buf, buf + valmax, abis[i]) - buf + ;
} int ans[];
int maxv[];
SegTreeNode* dfs(int node) {
SegTree st;
// if(node == 10)
// fprintf(stderr, "gg");
for(int i = ; i < (signed)g[node].size(); i++) {
SegTreeNode* buf = dfs(g[node][i]);
merge(st.root, buf);
}
if(node) {
maxv[node] = st.query(st.root, , n, abis[node] + , n, ans[node]);
st.update(st.root, , n, abis[node], loys[node], node);
} else ans[node] = -;
return st.root;
} inline void solve() {
dfs();
int x;
while(m--) {
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("%d\n", (ans[x]));
}
} inline void clear() {
delete[] g;
delete[] loys;
delete[] abis;
} int T;
int main() {
// freopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("a.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T--) {
init();
discrete();
solve();
clear();
}
return ;
}
hdu 4366 Successor - CDQ分治 - 线段树 - 树分块的更多相关文章
- HDU - 4366 Successor DFS区间+线段树
Successor:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4366 参考:https://blog.csdn.net/colin_27/article/d ...
- HDU 4366 Successor( DFS序+ 线段树 )
Successor Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)Total S ...
- hdu 5830 FFT + cdq分治
Shell Necklace Time Limit: 16000/8000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)T ...
- Successor HDU - 4366 (预处理,线段树,dfs序)
Successor HDU - 4366 Sean owns a company and he is the BOSS.The other Staff has one Superior.every s ...
- HDU 6183 Color it cdq分治 + 线段树 + 状态压缩
Color it Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 132768/132768 K (Java/Others) Pro ...
- ACdream1157 Segments(CDQ分治 + 线段树)
题目这么说的: 进行如下3种类型操作:1)D L R(1 <= L <= R <= 1000000000) 增加一条线段[L,R]2)C i (1-base) 删除第i条增加的线段, ...
- BZOJ3711 PA2014Druzyny(动态规划+cdq分治+线段树)
显然可以dp:设f[i]为前i个人最多能分多少组,则f[i]=max{f[j]}+1 (cmax<=i-j<=dmin). 容易发现d的限制是一段连续区间,二分或者随便怎么搞都行.c则有点 ...
- hdu 5126 stars cdq分治套cdq分治+树状数组
题目链接 给n个操作, 第一种是在x, y, z这个点+1. 第二种询问(x1, y1, z1). (x2, y2, z2)之间的总值. 用一次cdq分治可以将三维变两维, 两次的话就变成一维了, 然 ...
- HDU 5618 Jam's problem again (cdq分治+BIT 或 树状数组套Treap)
题意:给n个点,求每一个点的满足 x y z 都小于等于它的其他点的个数. 析:三维的,第一维直接排序就好按下标来,第二维按值来,第三维用数状数组维即可. 代码如下: cdq 分治: #pragma ...
随机推荐
- cocos2d-x JS 获取屏幕大小或中点
以一张背景图为例: var HelloWorldLayer = cc.Layer.extend({ ctor:function () { this._super(); var bg = new cc. ...
- cocos2dx JS 游戏切到后台再进入游戏的处理
由于Cocos引擎中,游戏切入后台后定时器后停掉会让某个Animation动作停止. 导致当重新进入游戏时,看到的不是你想要的画面.或者定时器倒计时的时间对不上等问题. cc.game.EVENT_H ...
- unity3d-游戏实战突出重围,第三天 绘制数字
实现效果: 准备资源 using UnityEngine; using System.Collections; public class hznum : MonoBehaviour { //存储图片资 ...
- node.js初识07
之前有说过,nodejs是 没有web容器的,阿帕奇是自带的web容器,如果希望node达到阿帕奇的效果,即http://127.0.0.1:3000/a/b/c.html 出现这样的链接访问页面,所 ...
- time_t time()
time_t atime, btime; time(&atime); btime = time(0); 两种方式效果一样.
- LeetCode111.二叉树的最小深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度. 最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量. 说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点. 示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7], ...
- Unity shader学习之标准的Unity shader
包含光照,可处理多个光源,有光照衰减和阴影的shader,代码如下: 转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/jietian331/p/7199311.html Shader & ...
- Python全栈-day5-数据类型
一.元组 1.元组基础 1)定义:不可变的‘列表’,定义方式(元素1,元素2.......) 2)用途:存多个值,但是只能读不能写 注意:元组的不可变指的是元组内元素id的不可变 t = (11,2, ...
- nw.js package一般设置
{ "name": "app name", "main": "mainpage", ...
- Mysql Federated For Windows
[1]windows环境下打开federated (1)关闭.命令:mysql> net stop mysql (2)添加federated字段.在my.ini文件中添加一个字段,注意位于[my ...
