shell初级-----结构化命令
if-then语句
bash shell的if语句会执行if后面的那个命令,如果该命令的退出码状态为0会执行then部分的命令,如果是其他值不会执行。
格式如下:
- if command
- then
- commands
- fi
实例:
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- if pwd
- then
- echo "ok"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- /ljy
- ok
在then部分可以使用多条命令。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- testuser=ljy
- if grep $testuser /etc/passwd
- then
- echo "ok"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- ljy:x:1000:1000::/home/ljy:/bin/bash
- ok
if-then-else
格式如下:
- if command
- then
- commands
- else
- commands
- fi
用法很简单,看一个例子就行
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- testuser=ljy
- if grep $testuser /etc/passwd
- then
- echo "$testuser exit on system!"
- else
- echo "$testuser does ont on system!"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- ljy:x:1000:1000::/home/ljy:/bin/bash
- ljy exit on system!
- #此时我定义一个不存在的变量
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- testuser=ljy1
- if grep $testuser /etc/passwd
- then
- echo "$testuser exit on system!"
- else
- echo "$testuser does ont on system!"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- ljy1 does ont on system!
嵌套if
语法很简单看一个例子:
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- testuser=zhangsan
- if grep $testuser /etc/passwd
- then
- echo "$testuser exit on system!"
- else
- echo "$testuser does ont on system!"
- if ls -d /home/$testuser
- then
- echo "but $testuser have a directory!"
- fi
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- zhangsan does ont on system!
- /home/zhangsan
- but zhangsan have a directory!
也可以用else部分的另外一种形式elif
格式如下:
- if command
- then
- commands
- elif command2
- then
- more commands
- fi
实例:
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- testuser=zhangsan
- if grep $testuser /etc/passwd
- then
- echo "$testuser exit on system!"
- elif ls -d /home/$testuser
- then
- echo "but $testuser have a directory!"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- /home/zhangsan
- but zhangsan have a directory!
test命令
如果test命令中列出的条件成立,test命令就会退出并返回特推出状态码0
test 命令可以判断3类条件:
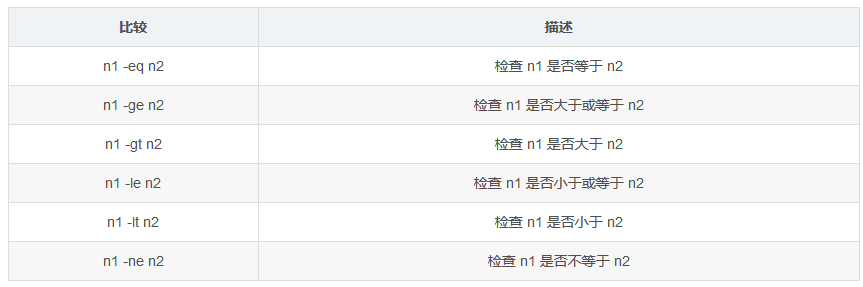
1. 数值比较
2. 字符串比较
3. 文件比较
1、数值比较
注意:test 命令中不能使用浮点数。
实例:
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- value1=10
- value2=11
- #
- if [ $value1 -gt 5 ] #左括号右侧和右括号左侧各加一个空格,否则会报错。
- then
- echo "$value1 is bigger than 5"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- 10 is bigger than 5
2、字符串比较
条件测试还允许比较字符串值

字符串比较的三大注意事项:
1. 比较的变量最好加上双引号。
2. 大于小于符号必须转义(使用\>),否则 shell 会把它们当做重定向符号而把字符串值当做文件名。
3. 大于小于顺序和 sort 命令所采用的不同。(test默认大写字母小于小写字母)
实例:
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- value1=basketball
- value2=football
- #
- if [ $value1 \> $value2 ]
- then
- echo "$value1 is greater than $value2"
- else
- echo "$value1 is less than $value2"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- basketball is less than football
-n和-z可以检查一个变量是否含有数据。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- value1=basketball
- value2=' '
- #
- if [ -n $value1 ]
- then
- echo "'$value1' is not empty"
- else
- echo "'$value1' is empty"
- fi
- #
- if [ -z $value2]
- then
- echo "'$value2' is empty"
- else
- echo "'$value2' is not empty"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- 'basketball' is not empty
- ' ' is empty
-n判断长度是否非0,-z判断长度是否为0
- 在变量可能为0的情况下,比较两个字符串是否相等可以这样:
- if [ "$test"x = "test"x ]; then
- 这里的关键有几点:
- 1 使用单个等号
- 2 注意到等号两边各有一个空格:这是unix shell的要求
- 3 注意到"$test"x最后的x,这是特意安排的,因为当$test为空的时候,上面的表达式就变成了x = testx,显然是不相等的。
- 而如果没有这个x,表达式就会报错:[: =: unary operator expected
3、文件比较
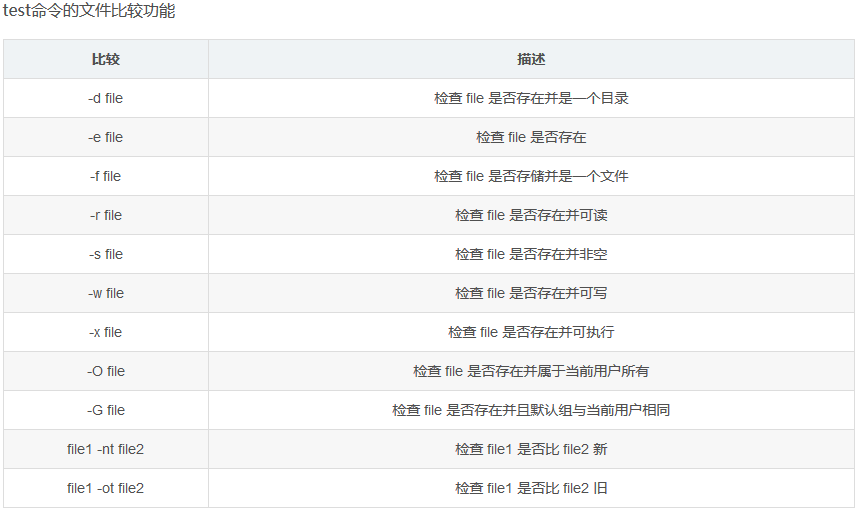
-d检测目录是否存在。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- value1=/home/ljy
- if [ -d $value1 ]
- then
- echo "$value1 is exited"
- else
- echo "$value1 is not exited"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- /home/ljy is exited
-e允许脚本代码在使用文件或者目录前先检测是否存在。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- value1='lisi'
- if [ -e /home/$value1 ]
- then
- echo "$value1 is exited"
- else
- echo "$value1 is not exited"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- lisi is exited
-f确定对象是否为文件。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- value1='zhangsan'
- if [ -e /home/$value1 ] #判断变量是否存在
- then
- echo "$value1 is exited"
- if [ -f /home/$value1 ] #判断是否为文件
- then
- echo "$value1 is a file"
- else
- echo "$value1 is a directory"
- fi
- else
- echo "$value1 is not exited"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi.sh
- zhangsan is exited
- zhangsan is a directory
-r测试文件是否可读。
- [ljy@node1 ljy]$ more ceshi2.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- pwfile=/home/lisi
- #
- if [ -r $pwfile ]
- then
- tail $pwfile
- else
- echo "this file unable to read!"
- fi
- [ljy@node1 ljy]$ sh ceshi2.sh
- this file unable to read!
-s检测文件是否为非空,尤其是在不想删除非空文件的时候。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- pwfile=/home/lisi
- #
- if [ -s $pwfile ]
- then
- echo "this file is not empty"
- else
- echo "$pwfile is empty"
- echo "Deleting empty file..."
- rm $pwfile
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh
- /home/lisi is empty
- Deleting empty file...
-w判断对文件是否可写。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- pwfile=/home/lisi
- #
- if [ -w $pwfile ]
- then
- echo "this file can be write!"
- date +%H%M >> $pwfile
- else
- echo "$pwfile can not be write"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh
- this file can be write!
-x判断文件是否有执行权限。
当然这是针对的非root用户。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- pwfile=/home/test.sh
- #
- if [ -x $pwfile ]
- then
- echo "this file can be run!"
- sh $pwfile
- else
- echo "$pwfile can not be run!"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh
- this file can be run!
复合条件测试
if-then 语句允许使用布尔逻辑来组合测试:
- 与:[ condition1 ] && [ condition2 ] 或者 [ condition1 -a condition2 ]
- 或:[ condition1 ] || [ condition2 ] 或者 [ condition1 -o condition2 ]
- 非:[ !condition ]
实例:
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- pwfile=/home/test.sh
- #
- if [ -d $pwdfile ] && [ -x $pwfile ]
- then
- echo "this file can be run!"
- sh $pwfile
- else
- echo "$pwfile can not be run!"
- fi
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh
- this file can be run!
case命令
为单个变量寻找特定的值,可以用 case 命令,而不是写那么多的 elif 语句检查。case 命令会检查单个变量列表格式的多个值:
- case variable in
- pattern1 | pattern2) commands1 ;;
- pattern3) commands2 ;;
- *) default commands ;;
- esac
case 命令会将指定的变量同不同模式进行比较。
如果变量和模式是匹配的,那么 shell 会执行为该模式指定的命令。
也可以通过竖线操作符来分割模式,在一行列出多个模式。星号会捕获所有跟所有列出的模式都不匹配的值。
- [root@node1 ljy]# more ceshi2.sh
- #!/bin/bash
- case $USER in
- root | barbara)
- echo "Welcome $USER"
- echo 'Enjoy your visit' ;;
- testing)
- echo "Special testing acount" ;;
- jessica)
- echo "Don't forget to log off" ;;
- *)
- echo "Sorry, you aren't allowed here" ;;
- esac
- [root@node1 ljy]# sh ceshi2.sh
- Welcome root
- Enjoy your visit
shell初级-----结构化命令的更多相关文章
- shell的结构化命令
shell在逻辑流程控制这里会根据设置的变量值的条件或其他命令的结果跳过一些命令或者循环执行的这些命令.这些命令通常称为结构化命令 1.if-then语句介绍 基本格式 if command then ...
- Linux&shell之结构化命令进阶
写在前面:案例.常用.归类.解释说明.(By Jim) for命令重复一系列的命令是一种常见的编程实践. #!/bin/bash # basic for command for test in A B ...
- Linux&shell之结构化命令
写在前面:案例.常用.归类.解释说明.(By Jim)使用if-then语句如果命令的退出状态是0(成功执行命令),将执行then后面的所有命令.如果命令的退出状态是0以外的其他值,那么then后面的 ...
- Shell编程—结构化命令(2)
1for命令 for命令的基本格式: for var in list do commands done 在list参数中,你需要提供迭代中要用到的一系列值. 1.1读取列表中的值 例子: $ vim ...
- Shell编程—结构化命令
1使用if-then语句 f-then语句有如下格式. if command then commands fi bash shell的if语句会运行if后面的那个命令.如果该命令的退出状态码是0(该命 ...
- linux shell脚本使用结构化命令
内容: 一.if-then命令 二.if-then-else命令 三.test命令 四.case命令 1.if-then结构化命令中最基本的类型,其格式如下: if command then comm ...
- Shell 语法之结构化命令(流程控制)
许多程序在脚本命令之间需要某种逻辑流控制,允许脚本根据变量值的条件或者其他命令的结果路过一些命令或者循环执行这些命令.这些命令通常被称为结构化命令.和其他高级程序设计语言一样,shell提供了用来控制 ...
- 《Linux命令行与shell脚本编程大全》第十二章 使用结构化命令
许多程序要就对shell脚本中的命令施加一些逻辑控制流程. 结构化命令允许你改变程序执行的顺序.不一定是依次进行的 12.1 使用if-then语句 如下格式: if command then ...
- Linux编程 23 shell编程(结构化条件判断 命令if -then , if-then ... elif-then ...else,if test)
一.概述 在上一篇里讲到了shell脚本,shell按照命令在脚本中出现的顺序依次进行处理,对于顺序操作已经足够了,但许多程序要求对shell脚本中的命令加入一些逻辑流程控制,这样的命令通常叫做 结构 ...
随机推荐
- reduce一些方法对数组进行的处理
reduce方法我之前都整理了知识点,不懂的可以看一下我之前的知识点,这次我们是整理了一些关于用reduce方法进行的一些对于数组的处理 1. reduce()求数组项之和 var arr = [3, ...
- SpringMVC @Valid,@RequestBody,@RequestParam标注参数时,进行Postman测试
@Valid(post请求) 可与@RequestBody一起使用 > (@RequestBody @Valid User user) @RequestBody(post请求) 这里的requi ...
- 织梦DEDEcms5.7解决arclist标签调用副栏目文章
使用arclist标签调用文章的时候才发现,根本无法调用相关文章. 下面给出解决办法,希望帮到需要的人. 找到/include/taglib/arclist.lib.php文件然后打开.然后在大约30 ...
- JVM常用指标查询
一.what‘s going on in Java Application 当系统卡顿,应用莫名被杀掉,我们应该怎么排查?在我已知的系统挂掉的情况,只经历过两种:1.内存申请不了(OOM):2.CPU ...
- BZOJ 3876 统一下界上下界费用流
//Mcmf LargeDumpling #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #includ ...
- win redis安装
一.下载windows版本的Redis 去官网找了很久,发现原来在官网上可以下载的windows版本的,现在官网以及没有下载地址,只能在github上下载,官网只提供linux版本的下载 官网下载地址 ...
- npm上发布vue插件
1.初始化项目 vue init webpack-simple XXXXX(此处为插件名) 使用vue创建一个简单的项目,删除src中除了main.js和app.vue外的文件,清空app.vue中无 ...
- 免费自动化测试工具Katalon Studio入门
Katalon Studio 一.简介: Katalon Studio 是一个在网页应用.移动和网页服务方面功能强大的自动化测试解决方案.基于 Selenium 和 Appium 框架,Katalon ...
- MySQL内联和外联查询
内连: 内连接是通过在查询中设置连接条件的方式,来移除查询结果集中某些数据行后的交叉连接.简单来说,就是利用条件表达式来消除交叉连接的某些数据行. 在MySQL FROM 子句中使用关键字 INNER ...
- JS 全局作用域和局部作用域
一.作用域 1.什么是作用域(Scope) 通常来说,一段程序代码中所用到的名字不总是有效和可用的,而限定这个名字的可用性的代码范围就是这个名字的作用域. JS作用域:就是代码名字(变量)作用的范围 ...
