曹工说Spring Boot源码(12)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:component-scan完整解析)
写在前面的话
相关背景及资源:
曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
曹工说Spring Boot源码(3)-- 手动注册Bean Definition不比游戏好玩吗,我们来试一下
曹工说Spring Boot源码(4)-- 我是怎么自定义ApplicationContext,从json文件读取bean definition的?
曹工说Spring Boot源码(5)-- 怎么从properties文件读取bean
曹工说Spring Boot源码(6)-- Spring怎么从xml文件里解析bean的
曹工说Spring Boot源码(7)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(8)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(util命名空间)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(9)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context命名空间上)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(10)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:annotation-config 解析)
曹工说Spring Boot源码(11)-- context:component-scan,你真的会用吗(这次来说说它的奇技淫巧)
工程结构图:

概要
本篇已经是spring源码第12篇,前一篇讲了context:component-scan这个元素的用法,其中涉及到了各个属性的作用。本节呢,主要就是讲解该元素的解析流程,其中就会涉及到各个属性是怎么发挥作用的。
大体流程
本来吧,这里画时序图比较好,但是uml图一直是半桶水,visio这台电脑也没装,就随便花了下流程图,将就看吧。

ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser.parse
这个就是在contextnamespacehandler里注册的,component-scan对应的beanDefinitionParser实现。
这个类呢,也是相当简洁明了,没有乱七八糟的类结构。
public class ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser {
configureScanner
类图
这个方法,最终返回了一个ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,这个类的结构如下:

父类ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider中的字段
几个接口都没实质性内容,主要是继承了一个父类,我整理了一下,父类里,大概有如下字段:
// ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider 中的fields
// 指定包下,文件很多,可能不止有class,还有xml,比如mybatis的mapper等;这里指定要获取的资源的pattern
static final String DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PATTERN = "**/*.class";
// 没啥说的,环境
private Environment environment;
// 因为用户可以自己指定resource_pattern, (不喜欢前面那个**/*.class),这个field负责来解析用户的resouce_pattern
private ResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
// 这个很重要,你给它一个class,它负责给你返回一个本class的元数据reader,通过元数据reader,你能取到class上的注解等信息
private MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory =
new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(this.resourcePatternResolver);
private String resourcePattern = DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PATTERN;
// 通过这个来划定,是不是我的小弟
private final List<TypeFilter> includeFilters = new LinkedList<TypeFilter>();
// 通过这个来划定,不是我的小弟,这个里面的都是拉黑了的
private final List<TypeFilter> excludeFilters = new LinkedList<TypeFilter>();
这里说下MetadataReaderFactory,因为吧,以后可能会频繁出现。
这是个接口,在spring-core包里,信息如下:
MetadataReader 的工厂接口,调用这个接口的方法,能得到一个MetadataReader
/**
* Factory interface for {@link MetadataReader} instances.
* Allows for caching a MetadataReader per original resource.
*
*/
public interface MetadataReaderFactory {
/**
* 根据一个类名,获取MetadataReader;这个reader,可以帮你获取class的class/注解等信息
*
* Obtain a MetadataReader for the given class name.
* @param className the class name (to be resolved to a ".class" file)
* @return a holder for the ClassReader instance (never {@code null})
* @throws IOException in case of I/O failure
*/
MetadataReader getMetadataReader(String className) throws IOException;
/**
* Obtain a MetadataReader for the given resource.
* @param resource the resource (pointing to a ".class" file)
* @return a holder for the ClassReader instance (never {@code null})
* @throws IOException in case of I/O failure
*/
MetadataReader getMetadataReader(Resource resource) throws IOException;
}
MetadataReader这个接口,也是以后的重点,这里概览一下:
/**
* 通过asm,获取类的元数据,包括注解数据
* Simple facade for accessing class metadata,
* as read by an ASM {@link org.springframework.asm.ClassReader}.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 2.5
*/
public interface MetadataReader {
/**
* Return the resource reference for the class file.
*/
Resource getResource();
/**
* 获取Class的相关信息
* Read basic class metadata for the underlying class.
*/
ClassMetadata getClassMetadata();
/**
* 这个就叼了,获取Class上的注解信息
* Read full annotation metadata for the underlying class,
* including metadata for annotated methods.
*/
AnnotationMetadata getAnnotationMetadata();
}
有人可能觉得没啥用,通过java反射也能获取;但这里的和java反射的方式不冲突,这个是通过asm框架来获取,效率会更高(效率比反射低的话,spring团队为啥不用反射呢,对吧?)
回到前面的metadataReader的factory接口,其实现类就两个,我们这次分析的源码,用了CachingMetadataReaderFactory:
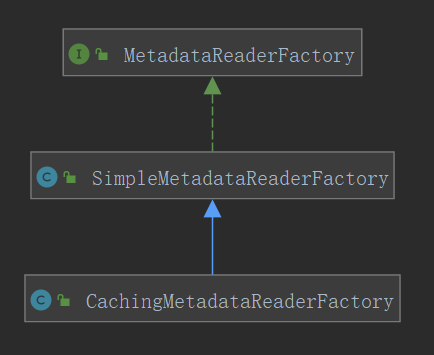
子类ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner中的字段
// beanDefinition注册中心,拿到beanDefinition后就往这里面放
private final BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
// 默认的beanDefinition配置,和xml里<beans>元素里的属性是对应的
private BeanDefinitionDefaults beanDefinitionDefaults = new BeanDefinitionDefaults();
// 自动注入时,候选bean需要满足的pattern
private String[] autowireCandidatePatterns;
// beanName 生成器
private BeanNameGenerator beanNameGenerator = new AnnotationBeanNameGenerator();
// 不是很了解,skip
private ScopeMetadataResolver scopeMetadataResolver = new AnnotationScopeMetadataResolver();
// 要不要激活 context:annotation-config元素的作用;具体可看本博文往前的两篇
private boolean includeAnnotationConfig = true;
其实,把前面父类,和现在这个子类的字段,合起来看,也就那么回事吧,主要是些配置数据,把xml里用户的配置给存起来了。
具体配置过程解析
org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser#configureScanner
protected ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner configureScanner(ParserContext parserContext, Element element) {
XmlReaderContext readerContext = parserContext.getReaderContext();
// 是否使用默认的filter,默认filter,只解析component等官方注解
boolean useDefaultFilters = true;
if (element.hasAttribute(USE_DEFAULT_FILTERS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
useDefaultFilters = Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute(USE_DEFAULT_FILTERS_ATTRIBUTE));
}
// 创建scanner
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = createScanner(readerContext, useDefaultFilters);
// 设置默认的东西
scanner.setResourceLoader(readerContext.getResourceLoader());
scanner.setEnvironment(parserContext.getDelegate().getEnvironment());
// 设置默认的东西,包括了beanDefinition的默认属性,这个是可以从外边传进来的
scanner.setBeanDefinitionDefaults(parserContext.getDelegate().getBeanDefinitionDefaults());
//这个也是外边来的,xml里没这个属性
scanner.setAutowireCandidatePatterns(parserContext.getDelegate().getAutowireCandidatePatterns());
if (element.hasAttribute(RESOURCE_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE)) {
// 这个是从xml元素来的
scanner.setResourcePattern(element.getAttribute(RESOURCE_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE));
}
try {
// 这个也是xml属性来的
parseBeanNameGenerator(element, scanner);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
readerContext.error(ex.getMessage(), readerContext.extractSource(element), ex.getCause());
}
try {
// 这个也是xml属性来的
parseScope(element, scanner);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
readerContext.error(ex.getMessage(), readerContext.extractSource(element), ex.getCause());
}
// 这个也是xml属性来的,主要是解析include/exclude filter
parseTypeFilters(element, scanner, readerContext, parserContext);
return scanner;
}
其中,有两个点值得细说:
默认的filter
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = createScanner(readerContext, useDefaultFilters); 一路简单跳转后,进入到: public ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider(boolean useDefaultFilters, Environment environment) {
if (useDefaultFilters) {
// 注册默认的filter
registerDefaultFilters();
}
this.environment = environment;
} // 注册3个注解类型的fitler,分别对应了Component/javax.annotation.ManagedBean/javax.inject.Named 这几个注解
protected void registerDefaultFilters() {
/**
* 默认扫描Component注解
*/
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class));
ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader();
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) cl.loadClass("javax.annotation.ManagedBean")), false));
}
try {
this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(
((Class<? extends Annotation>) cl.loadClass("javax.inject.Named")), false));
}
}
解析自定义的filter
protected void parseTypeFilters(
Element element, ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner, XmlReaderContext readerContext, ParserContext parserContext) { // Parse exclude and include filter elements.
ClassLoader classLoader = scanner.getResourceLoader().getClassLoader();
// 因为include-filter和exclude-filter是以子元素方式配置的,不是属性来配置的;所以获取子节点并便利
NodeList nodeList = element.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nodeList.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nodeList.item(i);
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(node);
// 如果是include类型...
if (INCLUDE_FILTER_ELEMENT.equals(localName)) {
// 创建typefilter
TypeFilter typeFilter = createTypeFilter((Element) node, classLoader);
scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
else if (EXCLUDE_FILTER_ELEMENT.equals(localName)) {
TypeFilter typeFilter = createTypeFilter((Element) node, classLoader);
scanner.addExcludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
}
}
}
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected TypeFilter createTypeFilter(Element element, ClassLoader classLoader) {
String filterType = element.getAttribute(FILTER_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
String expression = element.getAttribute(FILTER_EXPRESSION_ATTRIBUTE);
// filter 一共5种类型,所以下面在各种if判断
if ("annotation".equals(filterType)) {
return new AnnotationTypeFilter((Class<Annotation>) classLoader.loadClass(expression));
}
else if ("assignable".equals(filterType)) {
return new AssignableTypeFilter(classLoader.loadClass(expression));
}
else if ("aspectj".equals(filterType)) {
return new AspectJTypeFilter(expression, classLoader);
}
else if ("regex".equals(filterType)) {
return new RegexPatternTypeFilter(Pattern.compile(expression));
}
else if ("custom".equals(filterType)) {
Class filterClass = classLoader.loadClass(expression);
if (!TypeFilter.class.isAssignableFrom(filterClass)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Class is not assignable to [" + TypeFilter.class.getName() + "]: " + expression);
}
return (TypeFilter) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(filterClass);
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported filter type: " + filterType);
} }
表格总结一下,就是:
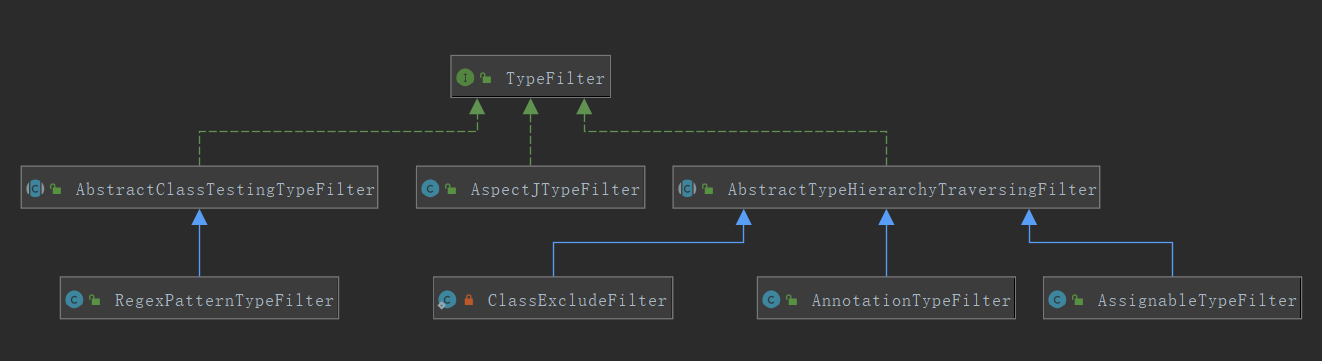
filter-type 对应类型的class 说明 我的理解 annotation AnnotationTypeFilter "annotation" indicates an annotation to be present at the type level in target components; 匹配指定类型的注解 assignable AssignableTypeFilter "assignable" indicates a class (or interface) that the target components are assignable to (extend/implement); 判断一个class是不是这里指定的类型或其子类 aspectj AspectJTypeFilter "aspectj" indicates an AspectJ type expression to be matched by the target components; 需要满足aspectj表达式,类似于指定切点那种 regex RegexPatternTypeFilter "regex" indicates a regex expression to be matched by the target components' class names; 需要满足正则表达式 custom 由xml元素里指定类型 "custom" indicates a custom implementation of the org.springframework.core.type.TypeFilter interface. 自定义实现TypeFilter接口 这里的typefilter接口,接口如下,主要就是,传给你一个class的元数据,你判断是否留下,留下就返回true:
public interface TypeFilter { /**
* Determine whether this filter matches for the class described by
* the given metadata.
* @param metadataReader the metadata reader for the target class
* @param metadataReaderFactory a factory for obtaining metadata readers
* for other classes (such as superclasses and interfaces)
* @return whether this filter matches
* @throws IOException in case of I/O failure when reading metadata
*/
boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory)
throws IOException; }
有如下实现(图小,可单独tab查看):
doScan-具体扫描beanDefinition执行者
如果大家有点忘了,可以回到最前面看下之前的图,这是主线的最后一个环节。
我们直接上code:
protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified");
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
/**
* 1:基于前面的include/exclude filter等,筛选出满足条件的beanDefinition集合
* 但这时候的beanDefinition还不是完整的,还有些属性没设置
*/
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) {
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate);
candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry);
// 一些处理,根据autowireCandidatePatterns field,判断当前bean是否够格,作为自动注入的候选者
if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName);
}
// 调用setPrimary/setLazyInit/setDependsOn/setTole来设置beanDefiniiton属性
if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate);
}
// 这里,注册到beanDefinitionRegistry
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder);
// 注册到beanDefinitionRegistry
registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry);
}
}
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
大体流程,就这样结束了。
里面有意思的细节,主要是,查找指定包下,满足条件的beanDefiniiton这块。
/**
* Scan the class path for candidate components.
* @param basePackage the package to check for annotated classes
* @return a corresponding Set of autodetected bean definitions
*/
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinition>();
try {
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + "/" + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
}
注意哈,这里获取的beanDefinition的类型是什么?
是ScannedGenericBeanDefinition。
学了这么多讲,是时候回头看看曾经走过的路了:

根据include/exclude filter来判断的过程也很有意思:
/**
* Determine whether the given class does not match any exclude filter
* and does match at least one include filter.
* @param metadataReader the ASM ClassReader for the class
* @return whether the class qualifies as a candidate component
*/
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException {
for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
return false;
}
}
for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) {
if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
AnnotationMetadata metadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
if (!metadata.isAnnotated(Profile.class.getName())) {
return true;
}
AnnotationAttributes profile = MetadataUtils.attributesFor(metadata, Profile.class);
return this.environment.acceptsProfiles(profile.getStringArray("value"));
}
}
return false;
}
总结
component-scan的探索之旅就这么结束了。欢迎大家留言,觉得有帮助的话,请关注我,后续会输出更多内容。
曹工说Spring Boot源码(12)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context:component-scan完整解析)的更多相关文章
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,咱们对着接口,逐个方法讲解
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 工程代码地址 思维导图地址 工程结构图: 正 ...
- Spring mybatis源码篇章-Mybatis的XML文件加载
通过阅读源码对实现机制进行了解有利于陶冶情操,承接前文Spring mybatis源码篇章-Mybatis主文件加载 前话 前文主要讲解了Mybatis的主文件加载方式,本文则分析不使用主文件加载方式 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码系列开讲了(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享
写在前面的话&&About me 网上写spring的文章多如牛毛,为什么还要写呢,因为,很简单,那是人家写的:网上都鼓励你不要造轮子,为什么你还要造呢,因为,那不是你造的. 我不是要 ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(9)-- Spring解析xml文件,到底从中得到了什么(context命名空间上)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(13)-- AspectJ的运行时织入(Load-Time-Weaving),基本内容是讲清楚了(附源码)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(14)-- AspectJ的Load-Time-Weaving的两种实现方式细细讲解,以及怎么和Spring Instrumentation集成
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(15)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(context:load-time-weaver 完整解析)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(16)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(aop:config完整解析【上】)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
- 曹工说Spring Boot源码(17)-- Spring从xml文件里到底得到了什么(aop:config完整解析【中】)
写在前面的话 相关背景及资源: 曹工说Spring Boot源码(1)-- Bean Definition到底是什么,附spring思维导图分享 曹工说Spring Boot源码(2)-- Bean ...
随机推荐
- 21个项目玩转深度学习:基于TensorFlow的实践详解02—CIFAR10图像识别
cifar10数据集 CIFAR-10 是由 Hinton 的学生 Alex Krizhevsky 和 Ilya Sutskever 整理的一个用于识别普适物体的小型数据集.一共包含 10 个类别的 ...
- springboot配置大全
此配置大全是在官方开发者文档中看到的,地址:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.6.RELEASE/reference/html/common-ap ...
- eclipse中maven报错--Dmaven.multiModuleProjectDirectory system propery is not set. Check $M2_HOME environment variable and mvn script match.
-Dmaven.multiModuleProjectDirectory system propery is not set. Check $M2_HOME environment variable a ...
- H3C 链路聚合分类
- apache WEB服务器安装(包括虚拟主机)
一.apache下载编译安装 yum install apr apr-devel apr-util apr-util-devel gcc-c++ wget tar -y cd /usr/src wge ...
- lambda应用
def test(a, b, func): result = func(a, b) print(result) test(10, 15, lambda x, y: x + y) #coding=utf ...
- c++ 知道旋转前后矩阵向量值 求旋转矩阵c++/c#代码 知道两个向量求他们的旋转矩阵
原文作者:aircraft 原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/DOMLX/p/12115244.html 知道旋转前后矩阵向量值 如何去求旋转矩阵R 的c++/c#代码??? ...
- 本地安装配置Gradle及IDEA使用本地Gradle
一.下载Gradle 下载地址:http://services.gradle.org/distributions/ 下载版本的bin.zip 二.配置环境变量 三.验证 在cmd模式下查看 ...
- jquery中动态添加的标签绑定的click事件失效的解决办法
把.click()换成.live('click',function(){})(如果你的jquery的版本是1.10之前) 把.click()换成.on('click',function(){})(jq ...
- ELK学习实验011:Logstash工作原理
Logstash事件处理管道包括三个阶段:输入→过滤器→输出.输入会生成事件,过滤器会对其进行修改,输出会将它们发送到其他地方.输入和输出支持编解码器,使您可以在数据进入或退出管道时对其进行编码或解码 ...
