AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(五)之 AFURLSessionManager
本篇是AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读的第五篇了。
AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(一)之 AFNetworkReachabilityManager
AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(二)之 AFSecurityPolicy
AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(三)之 AFURLRequestSerialization
AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(四)之 AFURLResponseSerialization
这次主要介绍AFURLSessionManager这个类了。下一篇会介绍 AFHTTPSessionManager 。它是AFURLSessionManager的一个子类。
其实,AFURLSessionManager 创建并管理着NSURLSession这个对象。而NSURLSession又基于NSURLSessionConfiguration。
AFURLSessionManager实现了四个协议:
1.NSURLSessionDelegate
URLSession:didBecomeInvalidWithError:
URLSession:didReceiveChallenge:completionHandler:
URLSessionDidFinishEventsForBackgroundURLSession:
2. NSURLSessionTaskDelegate
URLSession:willPerformHTTPRedirection:newRequest:completionHandler:
URLSession:task:didReceiveChallenge:completionHandler:
URLSession:task:didSendBodyData:totalBytesSent:totalBytesExpectedToSend:
URLSession:task:needNewBodyStream:
URLSession:task:didCompleteWithError:
3. NSURLSessionDataDelegate
URLSession:dataTask:didReceiveResponse:completionHandler:
URLSession:dataTask:didBecomeDownloadTask:
URLSession:dataTask:didReceiveData:
URLSession:dataTask:willCacheResponse:completionHandler:
4. NSURLSessionDownloadDelegate
URLSession:downloadTask:didFinishDownloadingToURL:
URLSession:downloadTask:didWriteData:totalBytesWritten:totalBytesWritten:totalBytesExpectedToWrite:
URLSession:downloadTask:didResumeAtOffset:expectedTotalBytes:
上边的这些协议方法在实现部分都会介绍到,如果自己写的子类中重写了这些代理方法,一定要调用[super xxx]。这篇也会很长,本来打算差分成两个篇幅的,先因为方法大都比较荣日理解,最终决定还是放在一篇中比较好理解。
我们对AFURLSessionManager的头文件做一个介绍:
1. @property (readonly, nonatomic, strong) NSURLSession *session;
关于NSURLSession的介绍,可以参考官方的文档 ,文档中提出,相对于NSURLConnection ,NSURLSession强大的功能是支持后台上传和下载。不过值得注意的是,这个对象与它的delegate之间的是一个强引用关系,因此在释放NSURLSession时,要做好处理。
在网上看到了这篇文章, 使用NSURLSession,可以说大体的讲了NSURLSession的用法,不过我更喜欢开头的那首诗。
有的程序员老了,还没听过NSURLSession
有的程序员还嫩,没用过NSURLConnection
有的程序员很单纯,他只知道AFN.
2.@property (readonly, nonatomic, strong) NSOperationQueue *operationQueue;
为NSURLSession 绑定一个队列。并且设置这个队列的最大并发数maxConcurrentOperationCount为1.
3.@property (nonatomic, strong) id <AFURLResponseSerialization> responseSerializer;
这是序列化响应数据的对象,默认的模式是AFJSONResponseSerializer,而且不能为空。
4.@property (nonatomic, strong) AFSecurityPolicy *securityPolicy;
安全策略,默认是defaultPolicy。
5.@property (readwrite, nonatomic, strong) AFNetworkReachabilityManager *reachabilityManager;
网络监控管理者。
跟获取会话任务相关的属性:
6.@property (readonly, nonatomic, strong) NSArray <NSURLSessionTask *> *tasks;
当前被管理的包括data upload download 的任务的集合
7.@property (readonly, nonatomic, strong) NSArray <NSURLSessionDataTask *> *dataTasks;
当前 data 的任务集合
8.@property (readonly, nonatomic, strong) NSArray <NSURLSessionUploadTask *> *uploadTasks;
当前 upload 的任务集合
9.@property (readonly, nonatomic, strong) NSArray <NSURLSessionDownloadTask *> *downloadTasks;
当前 download 的任务集合。
回调的队列
10.@property (nonatomic, strong, nullable) dispatch_queue_t completionQueue;
请求成功后,回调block会在这个队列中调用,如果为空,就在主队列。
11.@property (nonatomic, strong, nullable) dispatch_group_t completionGroup;
请求成功后,回调block会在这个组中调用,如果为空,就使用一个私有的。
修复后台操作的bug
12.@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL attemptsToRecreateUploadTasksForBackgroundSessions;
这个属性用来解决在后台创建上传任务返回nil的bug,默认为NO,如果设为YES,在后台创建上传任务失败会,会尝试重新创建该任务。
初始化相关
13.- (instancetype)initWithSessionConfiguration:(nullable NSURLSessionConfiguration *)configuration NS_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER;
这个方法是指定的初始化方法。那么什么叫指定的呢?
NS_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER
这个宏告诉开发者,如果写一个集成A类的子类B,那么就要调用父类A的制定的初始化方法。举个例子:
@interface MyClass : NSObject
@property(copy, nonatomic) NSString *name;
-(instancetype)initWithName:(NSString *)name NS_DESIGNATED_INITIALIZER;
-(instancetype)init;
@end
如果我集成了MyClass而没有时间initWithName: 方法,就会收到一个警告信息。点击这里查看详细信息
14.- (void)invalidateSessionCancelingTasks:(BOOL)cancelPendingTasks;
根据是否取消未完成的任务来是session失效。
NSURLSession有两个方法:
- -(void)finishTasksAndInvalidate; 标示待完成所有的任务后失效
- -(void)invalidateAndCancel; 标示 立即失效,未完成的任务也将结束
NSURLSessionDataTask
15.- (NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTaskWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id _Nullable responseObject, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler;
16.- (NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTaskWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
uploadProgress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *uploadProgress))uploadProgressBlock
downloadProgress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *downloadProgress))downloadProgressBlock
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id _Nullable responseObject, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler;
上边的这两个方法是和DataTask 相关的方法。
NSURLSessionUploadTask
17.- (NSURLSessionUploadTask *)uploadTaskWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
fromFile:(NSURL *)fileURL
progress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *uploadProgress))uploadProgressBlock
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id _Nullable responseObject, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler;
18.- (NSURLSessionUploadTask *)uploadTaskWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
fromData:(nullable NSData *)bodyData
progress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *uploadProgress))uploadProgressBlock
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id _Nullable responseObject, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler;
19.- (NSURLSessionUploadTask *)uploadTaskWithStreamedRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
progress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *uploadProgress))uploadProgressBlock
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id _Nullable responseObject, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler;
上边的这三个方法是和UploadTask 相关的方法。分别对应fileURL/data/request 这三种不同的数据源。
NSURLSessionDownloadTask
20.- (NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTaskWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
progress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *downloadProgress))downloadProgressBlock
destination:(nullable NSURL * (^)(NSURL *targetPath, NSURLResponse *response))destination
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, NSURL * _Nullable filePath, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler;
21.- (NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTaskWithResumeData:(NSData *)resumeData
progress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *downloadProgress))downloadProgressBlock
destination:(nullable NSURL * (^)(NSURL *targetPath, NSURLResponse *response))destination
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, NSURL * _Nullable filePath, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler;
上边的这两个方法是和DownloadTask 相关的方法。
头文件中剩余的方法就是跟最开始给出的代理有关了,让我们能够通过Block来处理那些代理的事件。在这就不做介绍了。
在这里再罗列出使用这个类中用到的通知:
- AFNetworkingTaskDidResumeNotification
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteNotification
- AFNetworkingTaskDidSuspendNotification
- AFURLSessionDidInvalidateNotification
- AFURLSessionDownloadTaskDidFailToMoveFileNotification
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteResponseDataKey
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteSerializedResponseKey
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteResponseSerializerKey
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteAssetPathKey
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteErrorKey
** 通过Block和通知,我们就有能力接收到跟网络请求先关的事件和数据。也就是我们可以使用这些来处理我们的业务逻辑。**
我们现在来看.m文件的内容
#ifndef NSFoundationVersionNumber_iOS_8_0
#define NSFoundationVersionNumber_With_Fixed_5871104061079552_bug 1140.11
#else
#define NSFoundationVersionNumber_With_Fixed_5871104061079552_bug NSFoundationVersionNumber_iOS_8_0
#endif
上边的这个宏的目的是通过NSFoundation的版本来判断当前ios版本,关键是这个宏的调试目标是IOS,来看看系统是怎么定义的:
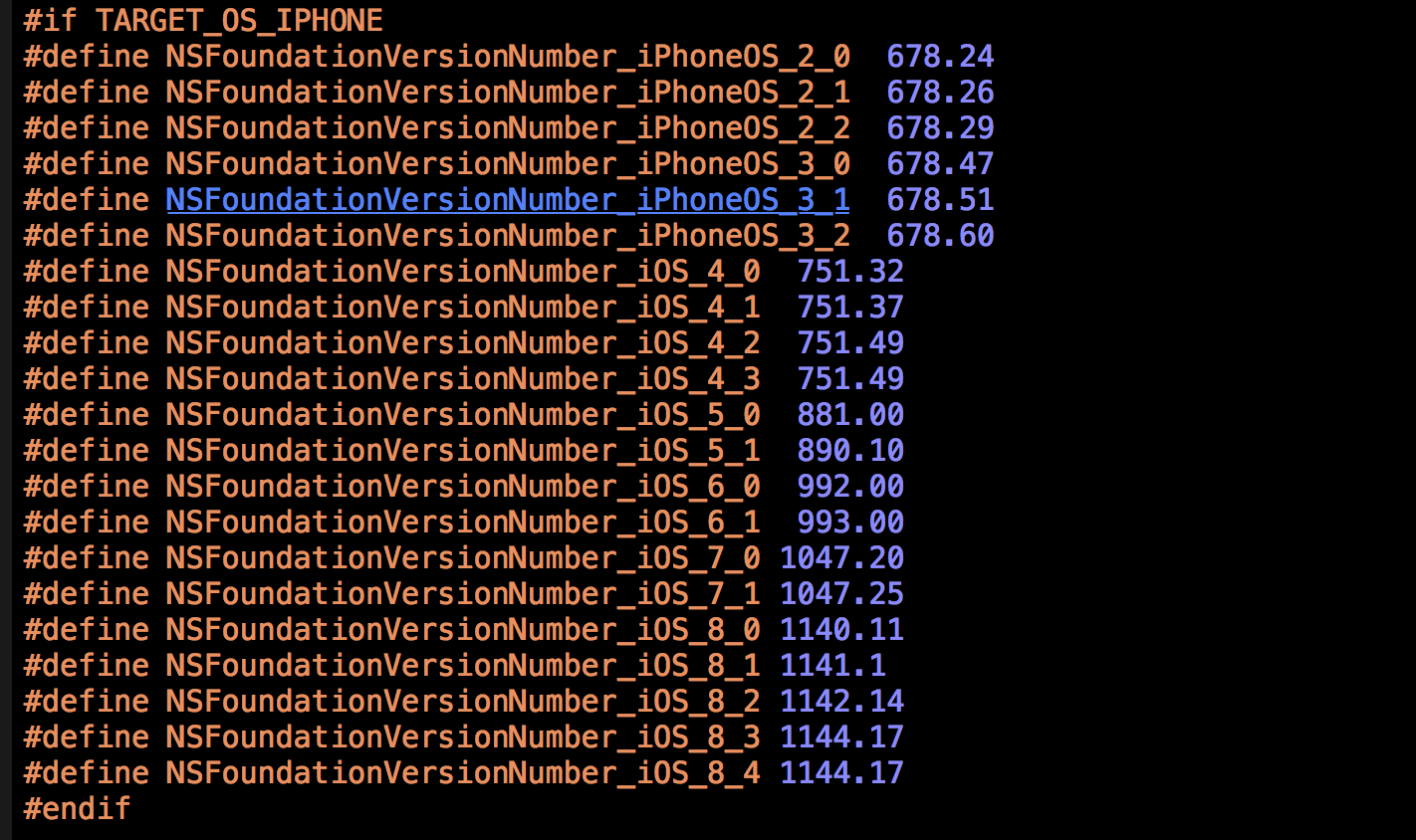
那么我们就能够联想到,目前我们能够判断系统版本号的方法有几种呢?最少三种:
- [UIDevice currentDevice].systemVersion
- 通过比较Foundation框架的版本号,iOS系统升级的同时Foundation框架的版本也会提高
- 通过在某系版本中新出现的方法来判断,UIAlertController 这个类是iOS8之后才出现的 NS_CLASS_AVAILABLE_IOS(8_0),如果当前系统版本没有这个类NSClassFromString(@"UIAlertController" == (null),从而判断当前版本是否大于等于iOS8
static dispatch_queue_t url_session_manager_creation_queue() {
static dispatch_queue_t af_url_session_manager_creation_queue;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
af_url_session_manager_creation_queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.alamofire.networking.session.manager.creation", DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL);
});
return af_url_session_manager_creation_queue;
}
AFNetworking中所有的和创建任务相关的事件都放到了一个单例的队列中,我们平时可能会使用这些方法,但还是可能会忽略一些内容,dispatch_queue_create()这个是队列的方法,第一个参数是队列的identifier,第二个参数则表示这个队列是串行队列还是并行队列。
如果第二个参数为DISPATCH_QUEUE_SERIAL或NULL 则表示队列为串行队列。如果为DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT则表示是并行队列。
关于队列的小的知识点,参考了这篇文章:Objective C 高级进阶— GCD队列浅析(一).
static void url_session_manager_create_task_safely(dispatch_block_t block) {
if (NSFoundationVersionNumber < NSFoundationVersionNumber_With_Fixed_5871104061079552_bug) {
// Fix of bug
// Open Radar:http://openradar.appspot.com/radar?id=5871104061079552 (status: Fixed in iOS8)
// Issue about:https://github.com/AFNetworking/AFNetworking/issues/2093
dispatch_sync(url_session_manager_creation_queue(), block);
} else {
block();
}
}
再看这个方法,看名字能够知道这应该是一个安全创建人物的方法,那么我们会很疑惑,为什么创建人物要是安全的呢?难道我们按照顺序创建人物,根据各自的Block回调处理事件会有问题?? 是的,按照https://github.com/AFNetworking/AFNetworking/issues/2093这个的描述:

加入我们创建了一个人物task1 对应completionHandler1,然后又创建了task2 对应的completionHandler2,这时候在task2数据还没有返回的前提下,task1的数据返回了,就会调用completionHandler2,就是这样的一个bug,造成任务的创建是不安全的,不过这个问题已经在ios8后修复了。
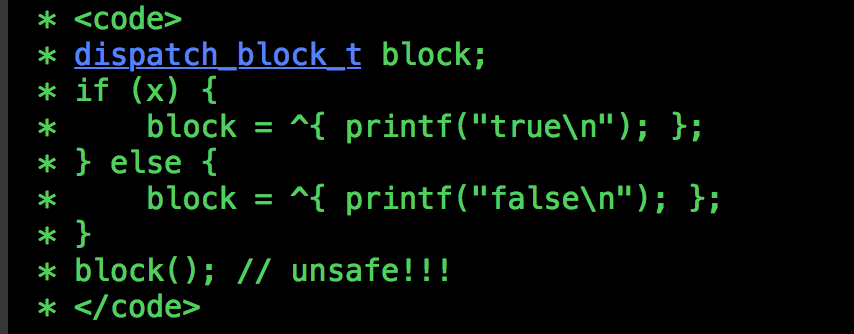
这个方法还有一个小知识点:dispatch_block_t ,点击去可以看到:
typedef void (^dispatch_block_t)(void);
关于这个Block我们应该注意几点:
- 非ARC情况下,Block被allocated或者copied到堆后,一定要记得释放它,通过[release]或者Block_release()
- 声明Block时,它是被分配到栈上的,要使用他,需要copy到堆才安全,因为栈内存是系统管理的,随时可能被释放。
static dispatch_queue_t url_session_manager_processing_queue() {
static dispatch_queue_t af_url_session_manager_processing_queue;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
af_url_session_manager_processing_queue = dispatch_queue_create("com.alamofire.networking.session.manager.processing", DISPATCH_QUEUE_CONCURRENT);
});
return af_url_session_manager_processing_queue;
}
这个方法是创建一个队列用来管理数据的处理。和上边的创建的方法对比,这个方法创建的队列是一个并行的队列,这就加快了数据的处理速度。
static dispatch_group_t url_session_manager_completion_group() {
static dispatch_group_t af_url_session_manager_completion_group;
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
af_url_session_manager_completion_group = dispatch_group_create();
});
return af_url_session_manager_completion_group;
}
typedef NSInputStream * (^AFURLSessionTaskNeedNewBodyStreamBlock)(NSURLSession *session, NSURLSessionTask *task);
大概讲一下这个的使用方法,其实这行代码的目的就是给一个Block定义一个名称,在AFNEtworking中后边的代码,在使用这个Block的时候,就这么使用
@property (readwrite, nonatomic, copy) AFURLSessionTaskNeedNewBodyStreamBlock taskNeedNewBodyStream;
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate
这个代理对象的目的是:
- 处理上传或下载的进度
- 处理获取完数据后的行为
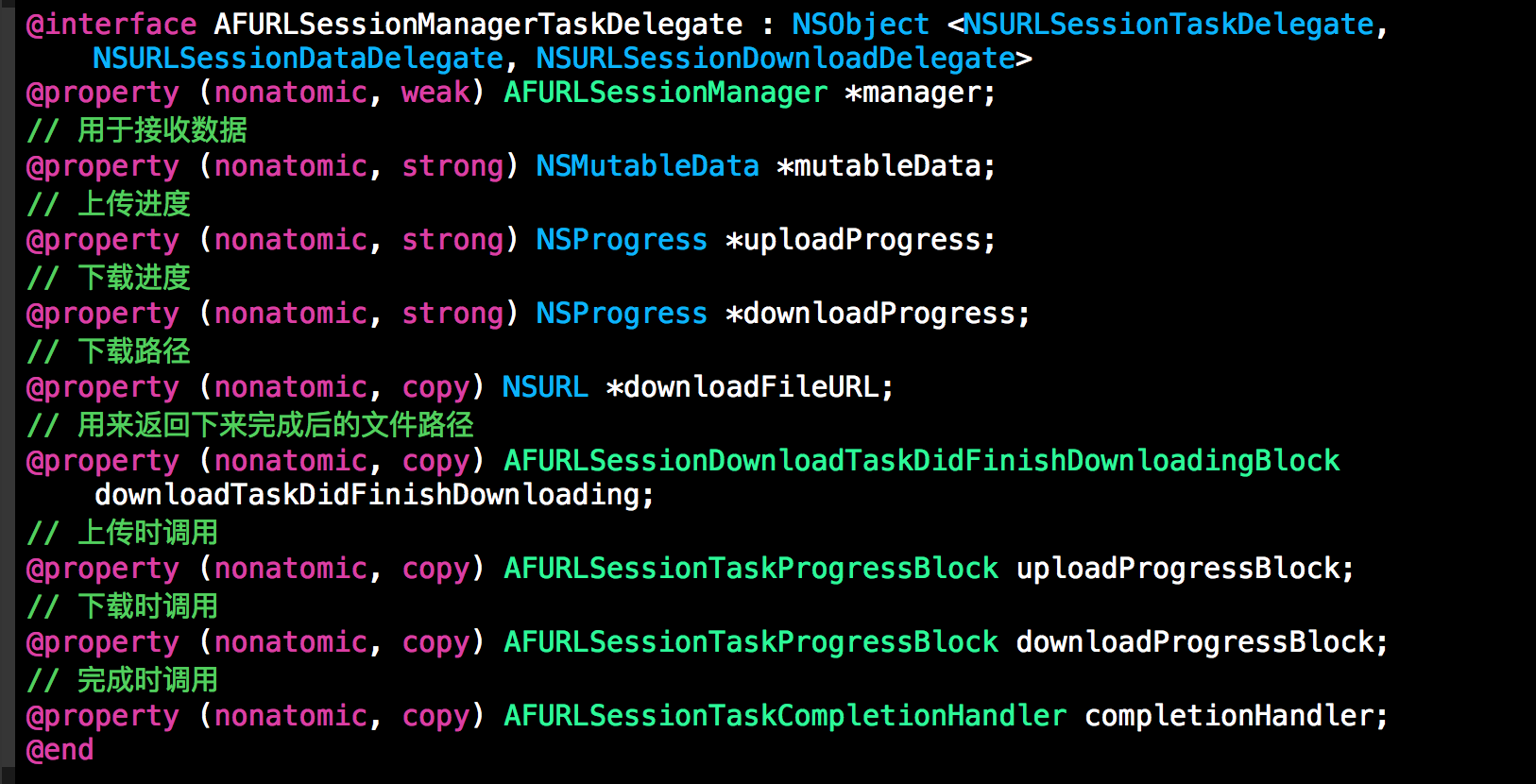
看这些属性,我们需要了解的是NSProgress这个类,这个类是apple为了管理进度在ios7新增的类。我们在ios开发中,但凡使用到跟进度相关的功能时,应尽量考虑始终它。它内部是使用kvo机制监听进度的。
- (instancetype)init {
self = [super init];
if (!self) {
return nil;
}
self.mutableData = [NSMutableData data];
self.uploadProgress = [[NSProgress alloc] initWithParent:nil userInfo:nil];
self.uploadProgress.totalUnitCount = NSURLSessionTransferSizeUnknown;
self.downloadProgress = [[NSProgress alloc] initWithParent:nil userInfo:nil];
self.downloadProgress.totalUnitCount = NSURLSessionTransferSizeUnknown;
return self;
}
来看看如何把task和进度绑定在一起
- (void)setupProgressForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
__weak __typeof__(task) weakTask = task;
// 设置进度的总单元数
self.uploadProgress.totalUnitCount = task.countOfBytesExpectedToSend;
self.downloadProgress.totalUnitCount = task.countOfBytesExpectedToReceive;
// 设置上传为可取消的
[self.uploadProgress setCancellable:YES];
[self.uploadProgress setCancellationHandler:^{
__typeof__(weakTask) strongTask = weakTask;
[strongTask cancel];
}];
// 设置上传为可暂停的
[self.uploadProgress setPausable:YES];
[self.uploadProgress setPausingHandler:^{
__typeof__(weakTask) strongTask = weakTask;
[strongTask suspend];
}];
// 设置重新开始
if ([self.uploadProgress respondsToSelector:@selector(setResumingHandler:)]) {
[self.uploadProgress setResumingHandler:^{
__typeof__(weakTask) strongTask = weakTask;
[strongTask resume];
}];
}
[self.downloadProgress setCancellable:YES];
[self.downloadProgress setCancellationHandler:^{
__typeof__(weakTask) strongTask = weakTask;
[strongTask cancel];
}];
[self.downloadProgress setPausable:YES];
[self.downloadProgress setPausingHandler:^{
__typeof__(weakTask) strongTask = weakTask;
[strongTask suspend];
}];
if ([self.downloadProgress respondsToSelector:@selector(setResumingHandler:)]) {
[self.downloadProgress setResumingHandler:^{
__typeof__(weakTask) strongTask = weakTask;
[strongTask resume];
}];
}
[task addObserver:self
forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesReceived))
options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew
context:NULL];
[task addObserver:self
forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesExpectedToReceive))
options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew
context:NULL];
[task addObserver:self
forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesSent))
options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew
context:NULL];
[task addObserver:self
forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesExpectedToSend))
options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew
context:NULL];
[self.downloadProgress addObserver:self
forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(fractionCompleted))
options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew
context:NULL];
[self.uploadProgress addObserver:self
forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(fractionCompleted))
options:NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew
context:NULL];
}
这个方法很长,但是也很简单,通过task.countOfBytesExpectedToSend能够获取到发送数据的总大小,通过task.countOfBytesExpectedToReceive能够获取到下载数据的总大小。
NSProgress 通过监听fractionCompleted这个属性来获取进度。
注意:在写监听方法的时候,这个options使用了NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew,代表什么意思呢?
点击去后看到是一个NSKeyValueObservingOptions的枚举:
- NSKeyValueObservingOptionNew 把更改之前的值提供给处理方法
- NSKeyValueObservingOptionOld 把更改之后的值提供给处理方法
- NSKeyValueObservingOptionInitial 把初始化的值提供给处理方法,一旦注册,立马就会调用一次。通常它会带有新值,而不会带有旧值
- NSKeyValueObservingOptionPrior 分2次调用。在值改变之前和值改变之后
--
// 取消监听
- (void)cleanUpProgressForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
[task removeObserver:self forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesReceived))];
[task removeObserver:self forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesExpectedToReceive))];
[task removeObserver:self forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesSent))];
[task removeObserver:self forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesExpectedToSend))];
[self.downloadProgress removeObserver:self forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(fractionCompleted))];
[self.uploadProgress removeObserver:self forKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(fractionCompleted))];
}
--
- (void)observeValueForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath ofObject:(id)object change:(NSDictionary<NSString *,id> *)change context:(void *)context {
if ([object isKindOfClass:[NSURLSessionTask class]] || [object isKindOfClass:[NSURLSessionDownloadTask class]]) {
if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesReceived))]) {
self.downloadProgress.completedUnitCount = [change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey] longLongValue];
} else if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesExpectedToReceive))]) {
self.downloadProgress.totalUnitCount = [change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey] longLongValue];
} else if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesSent))]) {
self.uploadProgress.completedUnitCount = [change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey] longLongValue];
} else if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(countOfBytesExpectedToSend))]) {
self.uploadProgress.totalUnitCount = [change[NSKeyValueChangeNewKey] longLongValue];
}
}
else if ([object isEqual:self.downloadProgress]) {
if (self.downloadProgressBlock) {
self.downloadProgressBlock(object);
}
}
else if ([object isEqual:self.uploadProgress]) {
if (self.uploadProgressBlock) {
self.uploadProgressBlock(object);
}
}
}
在这里要说一下关于task四个代理的调用问题。
task一共有4个delegate,只要设置了一个,就代表四个全部设置,有时候一些delegate不会被触发的原因在于这四种delegate是针对不同的URLSession类型和URLSessionTask类型来进行响应的,也就是说不同的类型只会触发这些delegate中的一部分,而不是触发所有的delegate。
举例说明如下
触发NSURLSessionDataDelegate
//使用函数dataTask来接收数据 -(void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask didReceiveData:(NSData *)data //则NSURLSession部分的代码如下 NSURLSessionConfiguration* ephConfiguration=[NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
NSURLSession* session=[NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:ephConfiguration delegate:self delegateQueue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]];
NSURL* url=[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.example.com/external_links/01.png"];
NSURLSessionDataTask* dataTask=[session dataTaskWithURL:url];
[dataTask resume];
触发NSURLSessionDownloadDelegate
//使用函数downloadTask来接受数据 -(void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session downloadTask:(NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTask didFinishDownloadingToURL:(NSURL *)location
//则NSURLSession部分的代码如下 NSURLSessionConfiguration* ephConfiguration=[NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
NSURLSession* session=[NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:ephConfiguration delegate:self delegateQueue:[NSOperationQueue mainQueue]];
NSURL* url=[NSURL URLWithString:@"http://www.example.com/external_links/01.png"];
NSURLSessionDownloadTask* dataTask=[session downloadTaskWithURL:url];
[dataTask resume];
这两段代码的主要区别在于NSURLSessionTask的类型的不同,造成了不同的Delegate被触发.
#pragma mark - NSURLSessionDataTaskDelegate
- (void)URLSession:(__unused NSURLSession *)session
dataTask:(__unused NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask
didReceiveData:(NSData *)data
{
[self.mutableData appendData:data];
}
--
#pragma mark - NSURLSessionTaskDelegate
- (void)URLSession:(__unused NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
didCompleteWithError:(NSError *)error
{
#pragma clang diagnostic push
#pragma clang diagnostic ignored "-Wgnu"
__strong AFURLSessionManager *manager = self.manager;
__block id responseObject = nil;
// 使用字典来存放请求的结果
__block NSMutableDictionary *userInfo = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
userInfo[AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteResponseSerializerKey] = manager.responseSerializer;
//Performance Improvement from #2672
NSData *data = nil;
if (self.mutableData) {
data = [self.mutableData copy];
//We no longer need the reference, so nil it out to gain back some memory.
self.mutableData = nil;
}
//判断是否有downloadFileURL
if (self.downloadFileURL) {
userInfo[AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteAssetPathKey] = self.downloadFileURL;
} else if (data) {
userInfo[AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteResponseDataKey] = data;
}
if (error) {
userInfo[AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteErrorKey] = error;
dispatch_group_async(manager.completionGroup ?: url_session_manager_completion_group(), manager.completionQueue ?: dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
if (self.completionHandler) {
self.completionHandler(task.response, responseObject, error);
}
// 发送通知
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteNotification object:task userInfo:userInfo];
});
});
} else {
dispatch_async(url_session_manager_processing_queue(), ^{
NSError *serializationError = nil;
// 解析数据
responseObject = [manager.responseSerializer responseObjectForResponse:task.response data:data error:&serializationError];
if (self.downloadFileURL) {
responseObject = self.downloadFileURL;
}
if (responseObject) {
userInfo[AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteSerializedResponseKey] = responseObject;
}
if (serializationError) {
userInfo[AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteErrorKey] = serializationError;
}
dispatch_group_async(manager.completionGroup ?: url_session_manager_completion_group(), manager.completionQueue ?: dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
if (self.completionHandler) {
self.completionHandler(task.response, responseObject, serializationError);
}
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteNotification object:task userInfo:userInfo];
});
});
});
}
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
}
这个方法是获取数据完成了方法。最终通过self.completionHandler和** [[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteNotification object:task userInfo:userInfo];**这两个手段来传递数据和事件。
我们主要看看这个通知的userinfo会有那些信息:
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteResponseSerializerKey -> manager.responseSerializer
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteAssetPathKey -> self.downloadFileURL
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteResponseDataKey -> data
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteErrorKey -> error
- AFNetworkingTaskDidCompleteSerializedResponseKey -> responseObject
--
#pragma mark - NSURLSessionDownloadTaskDelegate
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
downloadTask:(NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTask
didFinishDownloadingToURL:(NSURL *)location
{
NSError *fileManagerError = nil;
self.downloadFileURL = nil;
if (self.downloadTaskDidFinishDownloading) {
self.downloadFileURL = self.downloadTaskDidFinishDownloading(session, downloadTask, location);
if (self.downloadFileURL) {
[[NSFileManager defaultManager] moveItemAtURL:location toURL:self.downloadFileURL error:&fileManagerError];
if (fileManagerError) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFURLSessionDownloadTaskDidFailToMoveFileNotification object:downloadTask userInfo:fileManagerError.userInfo];
}
}
}
}
这个方法在下载完成后会调用。之前有一个使用场景,就是视频边下载边播放。要求在视频在下载完之前拿到正在下载的数据。ASI有一个属性能够拿到fileURL,AFNetworking却没有这个属性,现在看来,通过设置
- (void)setDownloadTaskDidWriteDataBlock:(nullable void (^)(NSURLSession *session, NSURLSessionDownloadTask *downloadTask, int64_t bytesWritten, int64_t totalBytesWritten, int64_t totalBytesExpectedToWrite))block;
可以把数据写到一个我们定义的临时的地方
_AFURLSessionTaskSwizzling
当时看这个私有类的时候一直想不通为什么要弄一个这样的类呢?首先看了AFNetworking给出的解释https://github.com/AFNetworking/AFNetworking/pull/2702 大概说了当初这个私有类的由来,ios7和ios8 task的父类并不一样,关键是resume and suspend这两个方法的调用。
因此,AFNetworking 利用Runtime交换了resume and suspend的方法实现。在替换的方法中发送了状态的通知。这个通知被使用在UIActivityIndicatorView+AFNetworking这个UIActivityIndicatorView的分类中。
方法的核心部分作用是层级遍历父类,替换resume and suspend的实现方法。同时也解决了锁死这个bug。
还有值得说的是 + (void)load这个方法,这个方法会在app启动时加载所有类的时候调用,且只会调用一次,所以这就有了使用场景了,当想使用运行时做一些事情的时候,就能够用上这个方法了。
举几个使用这个方法的例子:
下边就看看代码部分:
// 根据两个方法名称交换两个方法,内部实现是先根据函数名获取到对应方法实现
// 再调用method_exchangeImplementations交换两个方法
static inline void af_swizzleSelector(Class theClass, SEL originalSelector, SEL swizzledSelector) {
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(theClass, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(theClass, swizzledSelector);
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
// 给theClass添加名为selector,对应实现为method的方法
static inline BOOL af_addMethod(Class theClass, SEL selector, Method method) {
// 内部实现使用的是class_addMethod方法,注意method_getTypeEncoding是为了获得该方法的参数和返回类型
return class_addMethod(theClass, selector, method_getImplementation(method), method_getTypeEncoding(method));
}
--
+ (void)swizzleResumeAndSuspendMethodForClass:(Class)theClass {
// 因为af_resume和af_suspend都是类的实例方法,所以使用class_getInstanceMethod获取这两个方法
Method afResumeMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(af_resume));
Method afSuspendMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, @selector(af_suspend));
// 给theClass添加一个名为af_resume的方法,使用@selector(af_resume)获取方法名,使用afResumeMethod作为方法实现
if (af_addMethod(theClass, @selector(af_resume), afResumeMethod)) {
// 交换resume和af_resume的方法实现
af_swizzleSelector(theClass, @selector(resume), @selector(af_resume));
}
// 同上
if (af_addMethod(theClass, @selector(af_suspend), afSuspendMethod)) {
af_swizzleSelector(theClass, @selector(suspend), @selector(af_suspend));
}
}
--
- (NSURLSessionTaskState)state {
NSAssert(NO, @"State method should never be called in the actual dummy class");
// 初始状态是NSURLSessionTaskStateCanceling;
return NSURLSessionTaskStateCanceling;
}
- (void)af_resume {
NSAssert([self respondsToSelector:@selector(state)], @"Does not respond to state");
NSURLSessionTaskState state = [self state];
[self af_resume]; // 因为经过method swizzling后,此处的af_resume其实就是之前的resume,所以此处调用af_resume就是调用系统的resume。但是在程序中我们还是得使用resume,因为其实际调用的是af_resume
// 如果之前是其他状态,就变回resume状态,此处会通知调用taskDidResume
if (state != NSURLSessionTaskStateRunning) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFNSURLSessionTaskDidResumeNotification object:self];
}
}
// 同上
- (void)af_suspend {
NSAssert([self respondsToSelector:@selector(state)], @"Does not respond to state");
NSURLSessionTaskState state = [self state];
[self af_suspend];
if (state != NSURLSessionTaskStateSuspended) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFNSURLSessionTaskDidSuspendNotification object:self];
}
}
--
+ (void)load {
/**
WARNING: 高能预警
https://github.com/AFNetworking/AFNetworking/pull/2702
*/
// 担心以后iOS中不存在NSURLSessionTask
if (NSClassFromString(@"NSURLSessionTask")) {
/**
iOS 7和iOS 8在NSURLSessionTask实现上有些许不同,这使得下面的代码实现略显trick
关于这个问题,大家做了很多Unit Test,足以证明这个方法是可行的
目前我们所知的:
- NSURLSessionTasks是一组class的统称,如果你仅仅使用提供的API来获取NSURLSessionTask的class,并不一定返回的是你想要的那个(获取NSURLSessionTask的class目的是为了获取其resume方法)
- 简单地使用[NSURLSessionTask class]并不起作用。你需要新建一个NSURLSession,并根据创建的session再构建出一个NSURLSessionTask对象才行。
- iOS 7上,localDataTask(下面代码构造出的NSURLSessionDataTask类型的变量,为了获取对应Class)的类型是 __NSCFLocalDataTask,__NSCFLocalDataTask继承自__NSCFLocalSessionTask,__NSCFLocalSessionTask继承自__NSCFURLSessionTask。
- iOS 8上,localDataTask的类型为__NSCFLocalDataTask,__NSCFLocalDataTask继承自__NSCFLocalSessionTask,__NSCFLocalSessionTask继承自NSURLSessionTask
- iOS 7上,__NSCFLocalSessionTask和__NSCFURLSessionTask是仅有的两个实现了resume和suspend方法的类,另外__NSCFLocalSessionTask中的resume和suspend并没有调用其父类(即__NSCFURLSessionTask)方法,这也意味着两个类的方法都需要进行method swizzling。
- iOS 8上,NSURLSessionTask是唯一实现了resume和suspend方法的类。这也意味着其是唯一需要进行method swizzling的类
- 因为NSURLSessionTask并不是在每个iOS版本中都存在,所以把这些放在此处(即load函数中),比如给一个dummy class添加swizzled方法都会变得很方便,管理起来也方便。
一些假设前提:
- 目前iOS中resume和suspend的方法实现中并没有调用对应的父类方法。如果日后iOS改变了这种做法,我们还需要重新处理
- 没有哪个后台task会重写resume和suspend函数
*/
// 1) 首先构建一个NSURLSession对象session,再通过session构建出一个_NSCFLocalDataTask变量
NSURLSessionConfiguration *configuration = [NSURLSessionConfiguration ephemeralSessionConfiguration];
NSURLSession * session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:configuration];
#pragma GCC diagnostic push
#pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wnonnull"
NSURLSessionDataTask *localDataTask = [session dataTaskWithURL:nil];
#pragma clang diagnostic pop
// 2) 获取到af_resume实现的指针
IMP originalAFResumeIMP = method_getImplementation(class_getInstanceMethod([self class], @selector(af_resume)));
Class currentClass = [localDataTask class];
// 3) 检查当前class是否实现了resume。如果实现了,继续第4步。
while (class_getInstanceMethod(currentClass, @selector(resume))) {
// 4) 获取到当前class的父类(superClass)
Class superClass = [currentClass superclass];
// 5) 获取到当前class对于resume实现的指针
IMP classResumeIMP = method_getImplementation(class_getInstanceMethod(currentClass, @selector(resume)));
// 6) 获取到父类对于resume实现的指针
IMP superclassResumeIMP = method_getImplementation(class_getInstanceMethod(superClass, @selector(resume)));
// 7) 如果当前class对于resume的实现和父类不一样(类似iOS7上的情况),并且当前class的resume实现和af_resume不一样,才进行method swizzling。
if (classResumeIMP != superclassResumeIMP &&
originalAFResumeIMP != classResumeIMP) {
[self swizzleResumeAndSuspendMethodForClass:currentClass];
}
// 8) 设置当前操作的class为其父类class,重复步骤3~8
currentClass = [currentClass superclass];
}
[localDataTask cancel];
[session finishTasksAndInvalidate];
}
}
AFURLSessionManager
这个类的属性我们就不解释了,代码也不贴上来了。我们来看看初始化方法中都设置了那些默认的值:
- (instancetype)init {
return [self initWithSessionConfiguration:nil];
}
- (instancetype)initWithSessionConfiguration:(NSURLSessionConfiguration *)configuration {
self = [super init];
if (!self) {
return nil;
}
if (!configuration) {
configuration = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
}
self.sessionConfiguration = configuration;
self.operationQueue = [[NSOperationQueue alloc] init];
self.operationQueue.maxConcurrentOperationCount = 1;
self.session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:self.sessionConfiguration delegate:self delegateQueue:self.operationQueue];
self.responseSerializer = [AFJSONResponseSerializer serializer];
self.securityPolicy = [AFSecurityPolicy defaultPolicy];
#if !TARGET_OS_WATCH
self.reachabilityManager = [AFNetworkReachabilityManager sharedManager];
#endif
self.mutableTaskDelegatesKeyedByTaskIdentifier = [[NSMutableDictionary alloc] init];
self.lock = [[NSLock alloc] init];
self.lock.name = AFURLSessionManagerLockName;
[self.session getTasksWithCompletionHandler:^(NSArray *dataTasks, NSArray *uploadTasks, NSArray *downloadTasks) {
for (NSURLSessionDataTask *task in dataTasks) {
[self addDelegateForDataTask:task uploadProgress:nil downloadProgress:nil completionHandler:nil];
}
for (NSURLSessionUploadTask *uploadTask in uploadTasks) {
[self addDelegateForUploadTask:uploadTask progress:nil completionHandler:nil];
}
for (NSURLSessionDownloadTask *downloadTask in downloadTasks) {
[self addDelegateForDownloadTask:downloadTask progress:nil destination:nil completionHandler:nil];
}
}];
return self;
}
- (void)dealloc {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:self];
}
可以看出默认创建一个NSOperationQueue且并发数为一个,默认的responseSerializer响应序列化为Json,默认的securityPolicy为defaultPolicy,同时添加reachabilityManager网络监控对象。
- (NSString *)taskDescriptionForSessionTasks {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%p", self];
}
这个方法返回一个本类的地址,目的是通过这个字符串来判断请求是不是来源于AFNetworking。AFNetworking 在为每个task添加Delegate的时候,都会给task的taskDescription赋值为self.taskDescriptionForSessionTasks。在后边的- (NSArray *)tasksForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath方法中会使用到这个字符串。
- (void)taskDidResume:(NSNotification *)notification {
NSURLSessionTask *task = notification.object;
if ([task respondsToSelector:@selector(taskDescription)]) {
if ([task.taskDescription isEqualToString:self.taskDescriptionForSessionTasks]) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFNetworkingTaskDidResumeNotification object:task];
});
}
}
}
- (void)taskDidSuspend:(NSNotification *)notification {
NSURLSessionTask *task = notification.object;
if ([task respondsToSelector:@selector(taskDescription)]) {
if ([task.taskDescription isEqualToString:self.taskDescriptionForSessionTasks]) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFNetworkingTaskDidSuspendNotification object:task];
});
}
}
}
这两个是通知方法,来源于下边的两个通知的监听事件:
- (void)addNotificationObserverForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(taskDidResume:) name:AFNSURLSessionTaskDidResumeNotification object:task];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] addObserver:self selector:@selector(taskDidSuspend:) name:AFNSURLSessionTaskDidSuspendNotification object:task];
}
- (void)removeNotificationObserverForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:self name:AFNSURLSessionTaskDidSuspendNotification object:task];
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] removeObserver:self name:AFNSURLSessionTaskDidResumeNotification object:task];
}
还记得上边提到的_AFURLSessionTaskSwizzling这个私有类吗?它交换了resume and suspend这两个方法,在方法中发了下边两个通知:
- AFNSURLSessionTaskDidResumeNotification
- AFNSURLSessionTaskDidSuspendNotification
接下来就是一个很巧妙的转化过程了,按理说我们只需要接受并处理上边的两个通知不就可以了吗? 但真实情况却不是这样的,并不是所有人使用网络请求都是用AFNetworking,所以使用if ([task.taskDescription isEqualToString:self.taskDescriptionForSessionTasks])来做判断,这个task是否来自AFNetworking。
转化后我们就是用下边的通知,同时也是对外暴露出来的通知:
- AFNetworkingTaskDidResumeNotification
- AFNetworkingTaskDidSuspendNotification
- (AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *)delegateForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
NSParameterAssert(task);
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *delegate = nil;
[self.lock lock];
delegate = self.mutableTaskDelegatesKeyedByTaskIdentifier[@(task.taskIdentifier)];
[self.lock unlock];
return delegate;
}
- (void)setDelegate:(AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *)delegate
forTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
{
NSParameterAssert(task);
NSParameterAssert(delegate);
[self.lock lock];
self.mutableTaskDelegatesKeyedByTaskIdentifier[@(task.taskIdentifier)] = delegate;
[delegate setupProgressForTask:task];
[self addNotificationObserverForTask:task];
[self.lock unlock];
}
这两个方法是把AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate和task建立联系。值得注意的是:
- self.mutableTaskDelegatesKeyedByTaskIdentifier 这个字典以task.taskIdentifier为key,delegate为value。同事在读取和设置的时候采用加锁来保证安全。
- 在给task添加delegate的时候除了给self.mutableTaskDelegatesKeyedByTaskIdentifier赋值外,还需要设置delegate的ProgressForTask,且添加task的通知。
--
- (void)addDelegateForDataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask
uploadProgress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *uploadProgress)) uploadProgressBlock
downloadProgress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *downloadProgress)) downloadProgressBlock
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id responseObject, NSError *error))completionHandler
{
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *delegate = [[AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate alloc] init];
delegate.manager = self;
delegate.completionHandler = completionHandler;
dataTask.taskDescription = self.taskDescriptionForSessionTasks;
[self setDelegate:delegate forTask:dataTask];
delegate.uploadProgressBlock = uploadProgressBlock;
delegate.downloadProgressBlock = downloadProgressBlock;
}
给datatask添加delegate,AFNetworking中的每一个task肯定都有一个delegate。根据这个方法,我们可以看出给task添加代理的步骤为:
- 新建AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate

- 设置delegate
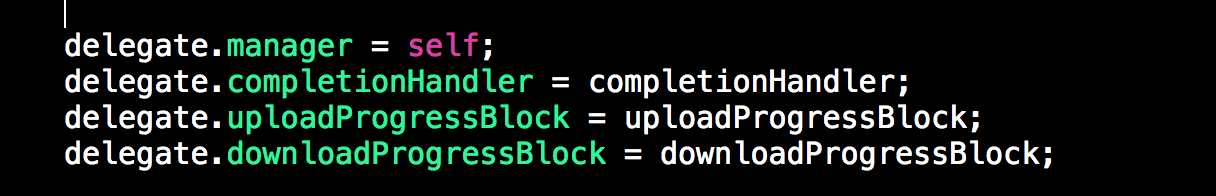
- 设置taskDescription

- 把
taskdelegateAFURLSessionManager建立联系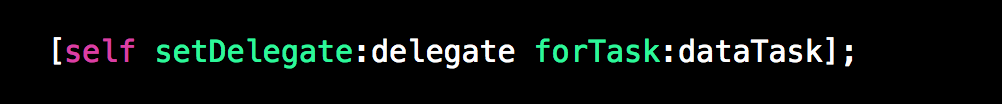
--
- (void)removeDelegateForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
NSParameterAssert(task);
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *delegate = [self delegateForTask:task];
[self.lock lock];
[delegate cleanUpProgressForTask:task];
[self removeNotificationObserverForTask:task];
[self.mutableTaskDelegatesKeyedByTaskIdentifier removeObjectForKey:@(task.taskIdentifier)];
[self.lock unlock];
}
- (NSArray *)tasksForKeyPath:(NSString *)keyPath {
__block NSArray *tasks = nil;
dispatch_semaphore_t semaphore = dispatch_semaphore_create(0);
[self.session getTasksWithCompletionHandler:^(NSArray *dataTasks, NSArray *uploadTasks, NSArray *downloadTasks) {
if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(dataTasks))]) {
tasks = dataTasks;
} else if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(uploadTasks))]) {
tasks = uploadTasks;
} else if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(downloadTasks))]) {
tasks = downloadTasks;
} else if ([keyPath isEqualToString:NSStringFromSelector(@selector(tasks))]) {
tasks = [@[dataTasks, uploadTasks, downloadTasks] valueForKeyPath:@"@unionOfArrays.self"];
}
dispatch_semaphore_signal(semaphore);
}];
dispatch_semaphore_wait(semaphore, DISPATCH_TIME_FOREVER);
return tasks;
}
getTasksWithCompletionHandler 这个方法是异步方法,上边的方法中我们需要等待这个异步方法有结果后才能进行后边的代码。 我们就可以使用dispatch_semaphore_t 这个信号来实现异步等待。
具体过程如下:
- 新建一个信号

- 在异步方法中发送信号,也就说一旦我们得到了异步的结果,我们就发一个信号

- 等待信号,只有接收到指定的信号代码才会往下走

这个信号的使用场景有很多,可以当安全锁来使用,也可以像上边一样异步等待。 假如我们有这样一个场景:我们有3个或者多个异步的网络请求,必须等待所有的请求回来后,在使用这些请求的结果来做一些事情。那么该怎么办呢? 解决方案就是:使用dispatch_group_t 和 dispatch_semaphore_t来实现。 在这里代码就不贴出来了,有兴趣的朋友而已自己google或者留言。
tasks = [@[dataTasks, uploadTasks, downloadTasks] valueForKeyPath:@"@unionOfArrays.self"];
这么使用之前确实不太知道,如果是我,可能就直接赋值给数组了。那么@unionOfArrays.self又是什么意思呢?
- @distinctUnionOfObjects 清楚重复值
- unionOfObjects 保留重复值
--
- (NSArray *)tasks {
return [self tasksForKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(_cmd)];
}
- (NSArray *)dataTasks {
return [self tasksForKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(_cmd)];
}
- (NSArray *)uploadTasks {
return [self tasksForKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(_cmd)];
}
- (NSArray *)downloadTasks {
return [self tasksForKeyPath:NSStringFromSelector(_cmd)];
}
在oc中,当方法被编译器转换成objc_msgSend函数后,除了方法必须的参数,objc_msgSend还会接收两个特殊的参数:receiver 与 selector。
objc_msgSend(receiver, selector, arg1, arg2, ...)
receiver 表示当前方法调用的类实例对象。
selector则表示当前方法所对应的selector。
这两个参数是编译器自动填充的,我们在调用方法时,不必在源代码中显示传入,因此可以被看做是“隐式参数”。
如果想要在source code中获取这两个参数,则可以用self(当前类实例对象)和_cmd(当前调用方法的selector)来表示。
- (void)viewDidLoad
{
[super viewDidLoad];
NSLog(@"Current method: %@ %@",[self class],NSStringFromSelector(_cmd));
}
输出结果为:
TestingProject[570:11303] Current method: FirstViewController viewDidLoad
- (NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTaskWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
uploadProgress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *uploadProgress)) uploadProgressBlock
downloadProgress:(nullable void (^)(NSProgress *downloadProgress)) downloadProgressBlock
completionHandler:(nullable void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id _Nullable responseObject, NSError * _Nullable error))completionHandler {
__block NSURLSessionDataTask *dataTask = nil;
url_session_manager_create_task_safely(^{
dataTask = [self.session dataTaskWithRequest:request];
});
[self addDelegateForDataTask:dataTask uploadProgress:uploadProgressBlock downloadProgress:downloadProgressBlock completionHandler:completionHandler];
return dataTask;
}
这里大概说下几种比较典型的创建task的方法,其他的方法就不做介绍了,原理大体相同。分为下边两个步骤:
- 创建task
- 给task添加Delegate
--
- (NSURLSessionUploadTask *)uploadTaskWithRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
fromFile:(NSURL *)fileURL
progress:(void (^)(NSProgress *uploadProgress)) uploadProgressBlock
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLResponse *response, id responseObject, NSError *error))completionHandler
{
__block NSURLSessionUploadTask *uploadTask = nil;
url_session_manager_create_task_safely(^{
uploadTask = [self.session uploadTaskWithRequest:request fromFile:fileURL];
});
// 当uploadtTask创建失败,且允许自动创建,会尝试创建uploadtTask
if (!uploadTask && self.attemptsToRecreateUploadTasksForBackgroundSessions && self.session.configuration.identifier) {
for (NSUInteger attempts = 0; !uploadTask && attempts < AFMaximumNumberOfAttemptsToRecreateBackgroundSessionUploadTask; attempts++) {
uploadTask = [self.session uploadTaskWithRequest:request fromFile:fileURL];
}
}
[self addDelegateForUploadTask:uploadTask progress:uploadProgressBlock completionHandler:completionHandler];
return uploadTask;
}
--
- (NSProgress *)uploadProgressForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
return [[self delegateForTask:task] uploadProgress];
}
- (NSProgress *)downloadProgressForTask:(NSURLSessionTask *)task {
return [[self delegateForTask:task] downloadProgress];
}
- (NSString *)description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<%@: %p, session: %@, operationQueue: %@>", NSStringFromClass([self class]), self, self.session, self.operationQueue];
}
假如我们自己写了一个工具类,我们最好重写description方法。
- (BOOL)respondsToSelector:(SEL)selector {
if (selector == @selector(URLSession:task:willPerformHTTPRedirection:newRequest:completionHandler:)) {
return self.taskWillPerformHTTPRedirection != nil;
} else if (selector == @selector(URLSession:dataTask:didReceiveResponse:completionHandler:)) {
return self.dataTaskDidReceiveResponse != nil;
} else if (selector == @selector(URLSession:dataTask:willCacheResponse:completionHandler:)) {
return self.dataTaskWillCacheResponse != nil;
} else if (selector == @selector(URLSessionDidFinishEventsForBackgroundURLSession:)) {
return self.didFinishEventsForBackgroundURLSession != nil;
}
return [[self class] instancesRespondToSelector:selector];
}
我们也可以使用respondsToSelector这个方法来拦截事件,把系统的事件和自定义的事件进行绑定。
NSURLSessionDelegate
// 这个方法是session收到的最后一条信息,
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
didBecomeInvalidWithError:(NSError *)error
{
// 调用block
if (self.sessionDidBecomeInvalid) {
self.sessionDidBecomeInvalid(session, error);
}
// 发送通知
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFURLSessionDidInvalidateNotification object:session];
}
--
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
didReceiveChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition, NSURLCredential *credential))completionHandler
{
// 创建默认的处理方式,PerformDefaultHandling方式将忽略credential这个参数
NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
__block NSURLCredential *credential = nil;
// 调动自身的处理方法,也就是说我们通过sessionDidReceiveAuthenticationChallenge这个block接收session,challenge 参数,返回一个NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition结果,这个业务使我们自己在这个block中完成。
if (self.sessionDidReceiveAuthenticationChallenge) {
disposition = self.sessionDidReceiveAuthenticationChallenge(session, challenge, &credential);
}
// 如果没有实现自定义的验证过程
else {
// 判断challenge的authenticationMethod
if ([challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust]) {
// 使用安全策略来验证
if ([self.securityPolicy evaluateServerTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust forDomain:challenge.protectionSpace.host]) {
// 如果验证通过,根据serverTrust创建依据
credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust];
if (credential) { // 有的话就返回UseCredential
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential;
} else {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
}
} else { // 验证没通过,返回CancelAuthenticationChallenge
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeCancelAuthenticationChallenge;
}
} else {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
}
}
if (completionHandler) {
completionHandler(disposition, credential);
}
}
着重对这个方法介绍下。
这个代理方法会在下边两种情况下被调用:
- 当远程服务器要求客户端提供证书或者Windows NT LAN Manager (NTLM)验证
- 当session初次和服务器通过SSL或TSL建立连接,客户端需要验证服务端证书链
如果没有实现这个方法,session就会调用delegate的URLSession:task:didReceiveChallenge:completionHandler: 方法。
如果challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod 在下边4个中时,才会调用
- NSURLAuthenticationMethodNTLM
- NSURLAuthenticationMethodNegotiate 是否使用 Kerberos or NTLM 验证
- NSURLAuthenticationMethodClientCertificate
- NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust
否则调用
URLSession:task:didReceiveChallenge:completionHandler:方法。
NSURLSessionTaskDelegate
// 请求改变的时候调用
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
willPerformHTTPRedirection:(NSHTTPURLResponse *)response
newRequest:(NSURLRequest *)request
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLRequest *))completionHandler
{
NSURLRequest *redirectRequest = request;
if (self.taskWillPerformHTTPRedirection) {
redirectRequest = self.taskWillPerformHTTPRedirection(session, task, response, request);
}
if (completionHandler) {
completionHandler(redirectRequest);
}
}
// 使用方法同 URLSession: didReceiveChallenge: completionHandler: 差不多
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
didReceiveChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition, NSURLCredential *credential))completionHandler
{
NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
__block NSURLCredential *credential = nil;
if (self.taskDidReceiveAuthenticationChallenge) {
disposition = self.taskDidReceiveAuthenticationChallenge(session, task, challenge, &credential);
} else {
if ([challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust]) {
if ([self.securityPolicy evaluateServerTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust forDomain:challenge.protectionSpace.host]) {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential;
credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust];
} else {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengeCancelAuthenticationChallenge;
}
} else {
disposition = NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling;
}
}
if (completionHandler) {
completionHandler(disposition, credential);
}
}
// 请求需要一个全新的,未打开的数据时调用。特别是请求一个body失败时,可以通过这个方法给一个新的body
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
needNewBodyStream:(void (^)(NSInputStream *bodyStream))completionHandler
{
NSInputStream *inputStream = nil;
if (self.taskNeedNewBodyStream) {
inputStream = self.taskNeedNewBodyStream(session, task);
} else if (task.originalRequest.HTTPBodyStream && [task.originalRequest.HTTPBodyStream conformsToProtocol:@protocol(NSCopying)]) {
inputStream = [task.originalRequest.HTTPBodyStream copy];
}
if (completionHandler) {
completionHandler(inputStream);
}
}
// 上传数据时候调用
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
didSendBodyData:(int64_t)bytesSent
totalBytesSent:(int64_t)totalBytesSent
totalBytesExpectedToSend:(int64_t)totalBytesExpectedToSend
{
int64_t totalUnitCount = totalBytesExpectedToSend;
if(totalUnitCount == NSURLSessionTransferSizeUnknown) {
NSString *contentLength = [task.originalRequest valueForHTTPHeaderField:@"Content-Length"];
if(contentLength) {
totalUnitCount = (int64_t) [contentLength longLongValue];
}
}
if (self.taskDidSendBodyData) {
self.taskDidSendBodyData(session, task, bytesSent, totalBytesSent, totalUnitCount);
}
}
// 完成时调用
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
didCompleteWithError:(NSError *)error
{
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *delegate = [self delegateForTask:task];
// delegate may be nil when completing a task in the background
if (delegate) {
[delegate URLSession:session task:task didCompleteWithError:error];
[self removeDelegateForTask:task];
}
if (self.taskDidComplete) {
self.taskDidComplete(session, task, error);
}
}
NSURLSessionDataDelegate
// 收到响应时调用
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask
didReceiveResponse:(NSURLResponse *)response
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionResponseDisposition disposition))completionHandler
{
NSURLSessionResponseDisposition disposition = NSURLSessionResponseAllow;
if (self.dataTaskDidReceiveResponse) {
disposition = self.dataTaskDidReceiveResponse(session, dataTask, response);
}
if (completionHandler) {
completionHandler(disposition);
}
}
// 当NSURLSessionDataTask变为NSURLSessionDownloadTask调用,之后NSURLSessionDataTask将不再接受消息
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask
didBecomeDownloadTask:(NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTask
{
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *delegate = [self delegateForTask:dataTask];
if (delegate) {
[self removeDelegateForTask:dataTask];
// 重新设置代理
[self setDelegate:delegate forTask:downloadTask];
}
if (self.dataTaskDidBecomeDownloadTask) {
self.dataTaskDidBecomeDownloadTask(session, dataTask, downloadTask);
}
}
// 接受数据过程中,调用,只限于NSURLSessionDataTask
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask
didReceiveData:(NSData *)data
{
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *delegate = [self delegateForTask:dataTask];
[delegate URLSession:session dataTask:dataTask didReceiveData:data];
if (self.dataTaskDidReceiveData) {
self.dataTaskDidReceiveData(session, dataTask, data);
}
}
// 即将缓存响应时调用
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
dataTask:(NSURLSessionDataTask *)dataTask
willCacheResponse:(NSCachedURLResponse *)proposedResponse
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSCachedURLResponse *cachedResponse))completionHandler
{
NSCachedURLResponse *cachedResponse = proposedResponse;
if (self.dataTaskWillCacheResponse) {
cachedResponse = self.dataTaskWillCacheResponse(session, dataTask, proposedResponse);
}
if (completionHandler) {
completionHandler(cachedResponse);
}
}
// 后台任务完成成后
- (void)URLSessionDidFinishEventsForBackgroundURLSession:(NSURLSession *)session {
if (self.didFinishEventsForBackgroundURLSession) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
self.didFinishEventsForBackgroundURLSession(session);
});
}
}
NSURLSessionDownloadDelegate
// 下载完成后调用
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
downloadTask:(NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTask
didFinishDownloadingToURL:(NSURL *)location
{
AFURLSessionManagerTaskDelegate *delegate = [self delegateForTask:downloadTask];
if (self.downloadTaskDidFinishDownloading) {
NSURL *fileURL = self.downloadTaskDidFinishDownloading(session, downloadTask, location);
if (fileURL) {
delegate.downloadFileURL = fileURL;
NSError *error = nil;
[[NSFileManager defaultManager] moveItemAtURL:location toURL:fileURL error:&error];
if (error) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:AFURLSessionDownloadTaskDidFailToMoveFileNotification object:downloadTask userInfo:error.userInfo];
}
return;
}
}
if (delegate) {
[delegate URLSession:session downloadTask:downloadTask didFinishDownloadingToURL:location];
}
}
// 下载中调用
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
downloadTask:(NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTask
didWriteData:(int64_t)bytesWritten
totalBytesWritten:(int64_t)totalBytesWritten
totalBytesExpectedToWrite:(int64_t)totalBytesExpectedToWrite
{
if (self.downloadTaskDidWriteData) {
self.downloadTaskDidWriteData(session, downloadTask, bytesWritten, totalBytesWritten, totalBytesExpectedToWrite);
}
}
// 回复下载时调用,使用fileOffset实现
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
downloadTask:(NSURLSessionDownloadTask *)downloadTask
didResumeAtOffset:(int64_t)fileOffset
expectedTotalBytes:(int64_t)expectedTotalBytes
{
if (self.downloadTaskDidResume) {
self.downloadTaskDidResume(session, downloadTask, fileOffset, expectedTotalBytes);
}
}
** 好了,这篇文章就到此为之了,到目前位置,AFNetworking已经解读了5篇了,所有的核心类也解释完毕,下一篇文章会是AFHTTPSessionManager这个类了 。我们最终的目标是写一个通用的包含大部分功能的网络框架,这个需要在解读完剩余的类之后再实现。我会演示一个从无到有的网络框架的产生过程。**
AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(五)之 AFURLSessionManager的更多相关文章
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(十一)之 UIButton/UIProgressView/UIWebView + AFNetworking
AFNetworking的源码解读马上就结束了,这一篇应该算是倒数第二篇,下一篇会是对AFNetworking中的技术点进行总结. 前言 上一篇我们总结了 UIActivityIndicatorVie ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(十)之 UIActivityIndicatorView/UIRefreshControl/UIImageView + AFNetworking
我们应该看到过很多类似这样的例子:某个控件拥有加载网络图片的能力.但这究竟是怎么做到的呢?看完这篇文章就明白了. 前言 这篇我们会介绍 AFNetworking 中的3个UIKit中的分类.UIAct ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(九)之 AFNetworkActivityIndicatorManager
让我们的APP像艺术品一样优雅,开发工程师更像是一名匠人,不仅需要精湛的技艺,而且要有一颗匠心. 前言 AFNetworkActivityIndicatorManager 是对状态栏中网络激活那个小控 ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(八)之 AFImageDownloader
AFImageDownloader 这个类对写DownloadManager有很大的借鉴意义.在平时的开发中,当我们使用UIImageView加载一个网络上的图片时,其原理就是把图片下载下来,然后再赋 ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(七)之 AFAutoPurgingImageCache
这篇我们就要介绍AFAutoPurgingImageCache这个类了.这个类给了我们临时管理图片内存的能力. 前言 假如说我们要写一个通用的网络框架,除了必备的请求数据的方法外,必须提供一个下载器来 ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(六)之 AFHTTPSessionManager
AFHTTPSessionManager相对来说比较好理解,代码也比较短.但却是我们平时可能使用最多的类. AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(一)之 AFNetworkReachabilit ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读 总结(干货)(下)
承接上一篇AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读 总结(干货)(上) 21.网络服务类型NSURLRequestNetworkServiceType 示例代码: typedef NS_ENUM(N ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(三)之 AFURLRequestSerialization
这篇就讲到了跟请求相关的类了 关于AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读 的文章篇幅都会很长,因为不仅仅要把代码进行详细的的解释,还会大概讲解和代码相关的知识点. 上半篇: URI编码的知识 关于 ...
- AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(四)之 AFURLResponseSerialization
本篇是AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读的第四篇了. AFNetworking 3.0 源码解读(一)之 AFNetworkReachabilityManager AFNetworking 3 ...
随机推荐
- 学习AOP之深入一点Spring Aop
上一篇<学习AOP之认识一下SpringAOP>中大体的了解了代理.动态代理及SpringAop的知识.因为写的篇幅长了点所以还是再写一篇吧.接下来开始深入一点Spring aop的一些实 ...
- SQLServer地址搜索性能优化例子
这是一个很久以前的例子,现在在整理资料时无意发现,就拿出来再改写分享. 1.需求 1.1 基本需求: 根据输入的地址关键字,搜索出完整的地址路径,耗时要控制在几十毫秒内. 1.2 数据库地址表结构和数 ...
- Android注解使用之注解编译android-apt如何切换到annotationProcessor
前言: 自从EventBus 3.x发布之后其通过注解预编译的方式解决了之前通过反射机制所引起的性能效率问题,其中注解预编译所采用的的就是android-apt的方式,不过最近Apt工具的作者宣布了不 ...
- nodejs利用http模块实现银行卡所属银行查询和骚扰电话验证
http模块内部封装了http服务器和客户端,因此Node.js不需要借助Apache.IIS.Nginx.Tomcat等传统HTTP服务器,就可以构建http服务器,亦可以用来做一些爬虫.下面简单介 ...
- 利用Node.js的Net模块实现一个命令行多人聊天室
1.net模块基本API 要使用Node.js的net模块实现一个命令行聊天室,就必须先了解NET模块的API使用.NET模块API分为两大类:Server和Socket类.工厂方法. Server类 ...
- [WARNING] Using platform encoding (GBK actually) to copy filtered resources, i.e. build is platform
eclipse maven clean install 报错 1. 修改properties-->resource-->utf-8仍然报错 2.修改项目pom.xml文件,增加: < ...
- 在开启DRS的集群中修复VMware虚拟主机启动问题
通过iSCSI方式连接到ESXi主机上的外挂存储意外失联了一段时间,导致部分虚拟主机在集群中呈现出孤立的状态,单独登陆到每台ESXi上可以看到这些虚拟主机都变成了unknow状态.因为有过上一次(VM ...
- Android—Volley:接收服务端发送的json数据乱码问题解决
new JsonObjectRequest中重写方法parseNetworkResponse,内容如下: /** * 重写此方法不会导致乱码 */ @Override protected Respon ...
- JAVA的内存模型(变量的同步)
一个线程中变量的修改可能不会立即对其他线程可见,事实上也许永远不可见. 在代码一中,如果一个线程调用了MyClass.loop(),将来的某个时间点,另一个线程调用了MyClass.setValue( ...
- CentOS 6.3下 安装 Mono 3.2 和Jexus 5.4
最新更新参看: Centos 7.0 安装Mono 3.4 和 Jexus 5.6 2012年初写过一篇<32和64位的CentOS 6.0下 安装 Mono 2.10.8 和Jexus 5.0 ...
