Android:Fragment
Fragment 概念
把 Activity 中的一段 UI 和逻辑封装到一个 Fragment 中,实现可拔插,减少对 Activity 代码的侵入。
Fragment 定义和管理自己的布局,具有自己的生命周期,并且可以处理自己的输入事件。Fragment 不能独立存在,而是必须由 Activity 或另一个 Fragment 托管。
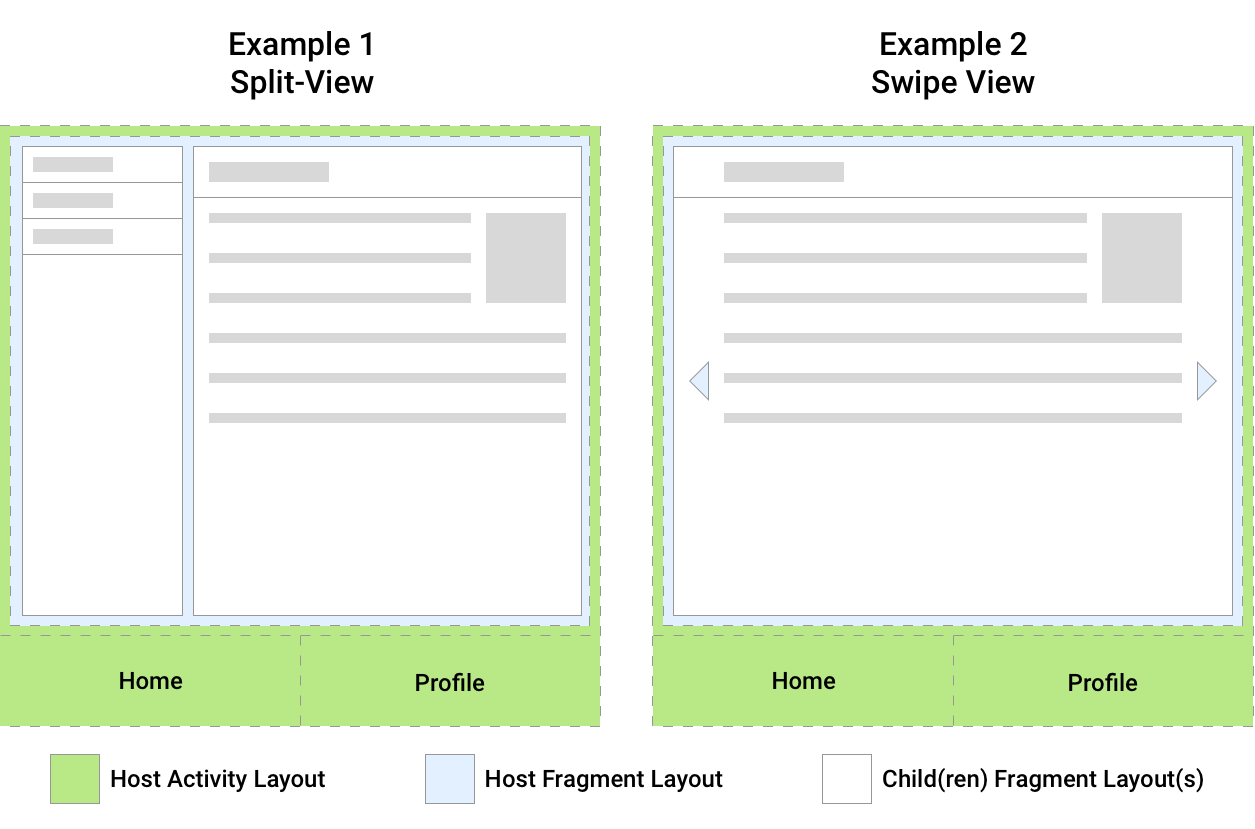
图中 Example1,一共有三个 Fragment,蓝色的 Fragment 嵌套了两个子 Fragment。Example2 是一个 swipe 视图,蓝色的 Fragment 有两个以上的 Fragment。
Fragment 应该管理它自己的界面所需的逻辑,避免让一个 Fragment 依赖于另一个 Fragment 或从一个 Fragment 操控另一个 Fragment。
- 模块:可以在同一 Activity 或多个 Activity 中使用同一 Fragment;或者把一个 Activity 划分为多个 Fragment 进行布局。
- 嵌套:Fragment 可以作为另一个 Fragment 的父级。
创建 Fragment
FragmentContainerView
创建一个 Fragment XML 视图 fragment_index.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Index Fragment"
android:textSize="30sp" />
</FrameLayout>
创建一个 Fragment 实现类,IndexFragment:
class IndexFragment : Fragment(R.layout.fragment_index) {
}
在 activity_main.xml 添加一个 FragmentContainerView:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FFC107"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/fragment_container_view"
android:name="com.example.chap04.IndexFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="531dp"
android:background="#009688"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
属性 name 添加 IndexFragment,启动 Activity 时会把 fragment_index.xml 视图插入到 FragmentContainerView 中。

通过上图得知,绿色区域是 IndexFragment,橙色区域是 Activity,我们通过 Fragment 实现了划分 Activity 布局的管理,接下来将通过 Kotlin 代码实现对 Fragment 的替换、删除、增加操作,进一步了解 Fragment。
FragmentManager
FragmentManager 可以替换、删除、增加 Fragment。在 activity_main.xml 中,删除 FragmentContainerView 的 name 属性,而是通过 FragmentManager 把 Fragment 的视图插入到 Activity 中:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#FFC107"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/fragment_container_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="531dp"
android:background="#009688"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
你需要获取 FragmentManager,并调用 beginTransaction() 得到 FragmentTransaction。调用 add() 添加 Fragment 到指定 View 中,这里是资源 ID 为 fragment_container_view 的 View(也就是 FragmentContainerView)。最后,调用 commit() 提交 FragmentTransaction。
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(R.layout.activity_main) {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
supportFragmentManager
.beginTransaction()
.setReorderingAllowed(true)
.add(R.id.fragment_container_view, IndexFragment(), null)
.commit()
}
}
当 FragmentManager 执行 FragmentTransaction 时,特别是堆栈上运行并运行动画和转换时(Fragment 切换其他 Fragment 时执行的动画效果),应该总是使用 setReorderingAllowed(true)。调用这个方法可确保如果同时执行多个 FragmentTransaction 时,任何一个 Fragment 都不会经历生命周期更改或执行其动画或转换。了解更多关于 setReorderingAllowed 的信息,请看官方文档的 Fragment Transaction。简而言之,调用这个函数可以提升性能,避免过多更改堆栈上其他 Fragment 的生命周期。
Bundle 传递数据
Fragment 可以接收从 Activity 传递过来的 Bundle 类型数据。在 add() 方法被调用时传入参数,Fragment 通过 requireArguments() 就可以获取到。
MainActivity.kt:
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(R.layout.activity_main) {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
if (savedInstanceState == null) {
val bundle = Bundle()
bundle.putInt("param", 20);
supportFragmentManager
.beginTransaction()
.setReorderingAllowed(true)
.add(R.id.fragment_container_view, IndexFragment().javaClass, bundle, null)
.commit()
}
}
}
IndexFragment.kt:
class IndexFragment : Fragment(R.layout.fragment_index) {
override fun onViewCreated(view: View, savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
val int = requireArguments().getInt("param")
Log.d("Test", int.toString())
}
}
接下来对if (savedInstanceState == null)进行一个解释。直接通过现象来观察一个问题:
1️⃣去掉这一个判断,来看看会发生什么:

我切换了黑夜/白昼模式,Logcat 中就打印了多次,说明我们的 onCreate 函数多次被调用,同时也多次重复添加 Fragment。
2️⃣加上这一个判断,再来看看会发生什么:

屏幕反转、屏幕黑夜/白昼模式切换都会触发onCreate(),而 savedInstanceState 能记录 Activity 的变化,当 Activity 初始时它才是 null。所以要加上一个判断,Activity 第一次创建时才增加 Fragment 到视图中,避免重复添加 Fragment。
实现 TabBar
前面已经简单地了解了 FragmentManager 和 FragmentTransaction。现在通过 Tabbar 案例来实现 Fragment 的切换。
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/fragment_container_view"
android:name="com.example.chap04.IndexFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/tabbar"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tabbar"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/nav_index"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="首页" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/nav_dynamic"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="动态" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/nav_person"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="我的" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(R.layout.activity_main) {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
if (savedInstanceState == null) {
findViewById<TextView>(R.id.nav_index).setOnClickListener {
supportFragmentManager
.beginTransaction()
.setReorderingAllowed(true)
.replace(R.id.fragment_container_view, IndexFragment().javaClass, null)
.commit()
}
findViewById<TextView>(R.id.nav_dynamic).setOnClickListener {
supportFragmentManager
.beginTransaction()
.setReorderingAllowed(true)
.replace(R.id.fragment_container_view, DynamicFragment().javaClass, null)
.commit()
}
findViewById<TextView>(R.id.nav_person).setOnClickListener {
supportFragmentManager
.beginTransaction()
.setReorderingAllowed(true)
.replace(R.id.fragment_container_view, PersonFragment().javaClass, null)
.commit()
}
}
}
}
实现效果

这种 TabBar 的切换方式是通过 FragmentManager 和 FragmentTransaction 替换视图中的 FragmentContainerView,还有一种是不借助这两个类实现页面切换,通过 ViewPager2 来实现页面,而且也是实现页面滑动的最简单方式。
借助 ViewPager2 实现 TabBar
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.viewpager2.widget.ViewPager2
android:id="@+id/view_pager2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/tabbar"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/tabbar"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal|center_vertical"
android:orientation="horizontal"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/nav_index"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="首页" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/nav_dynamic"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="动态" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/nav_person"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="我的" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
页面和上面的没多大区别,只是把 FragmentContainerView 替换成了 ViewPager2。
ViewPager2Adapter.kt
class ViewPage2Adapter(fragmentActivity: FragmentActivity, fragments: List<Fragment>) : FragmentStateAdapter(fragmentActivity) {
private var fragments: List<Fragment>
init {
this.fragments = fragments
}
override fun getItemCount(): Int {
return fragments.size
}
override fun createFragment(position: Int): Fragment {
return fragments[position]
}
}
MainActivity.kt
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity(R.layout.activity_main) {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
if (savedInstanceState == null) {
val pager = findViewById<ViewPager2>(R.id.view_pager2)
val navBars = listOf<TextView>(findViewById(R.id.nav_index), findViewById(R.id.nav_dynamic), findViewById(R.id.nav_person))
val fragments = listOf(IndexFragment(), DynamicFragment(), PersonFragment())
pager.adapter = ViewPage2Adapter(this, fragments)
var lastPosition = 0
pager.registerOnPageChangeCallback(object : ViewPager2.OnPageChangeCallback() {
override fun onPageSelected(currPosition: Int) {
navBars[lastPosition].setBackgroundResource(R.color.white)
navBars[currPosition].setBackgroundResource(R.color.nav_selected)
lastPosition = currPosition
}
})
navBars[0].setOnClickListener {
pager.currentItem = 0
}
navBars[1].setOnClickListener {
pager.currentItem = 1
}
navBars[2].setOnClickListener {
pager.currentItem = 2
}
}
}
}
切换 ViewPager2 的项时也需要改变底部导航栏的背景颜色,所以需要给 ViewPager2 注册一个监听器(registerOnPageChangeCallback),动态地得到 position,从而实现鼠标滑动时也改变底部导航栏对应的背景颜色。
实现效果

Gitee 仓库地址:Chap04-Fragment
Android:Fragment的更多相关文章
- Android:Fragment+ViewPager实现Tab滑动
public class FragAdapter extends FragmentPagerAdapter { private List<Fragment> fragments ; pub ...
- Android:手把手教你 实现Activity 与 Fragment 相互通信,发送字符串信息(含Demo)
前言Activity 与 Fragment 的使用在Android开发中非常多今天,我将主要讲解 Activity 与 Fragment 如何进行通信,实际上是要解决两个问题: Activity 如何 ...
- Android:理解Fragment
最近都在公司搞测试,静不下心来学android.今天就把Fragment搞懂吧. Fragment的几点要点: 1.用于大屏幕平板,容纳更多组件,可复用2.Fragment必须嵌入Activity中 ...
- android 学习随笔二十三(动画:Fragment )
Fragment * 用途:在一个Activity里切换界面,切换界面时只切换Fragment里面的内容 * 在一个Activity中切换多个界面,每个界面就是一个Fragment* Fragmnen ...
- android UI:Fragment碎片
碎片(Fragment) 嵌入与活动中的UI片段,为了合理的分配布局而存在,这是我的简单理解.多用于兼顾手机与平板的UI,也适用于灵活高级的UI制作. Demo 简单的按键切换两片不同的Demo 新建 ...
- Android用户界面开发:Fragment
Android用户界面开发:Fragment 1:注意事项 3.0以前的Android 版本要使用FragmentActivity 来装载Fragment ,使用到support v4包. 3.0 ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(四三):Fragment(8):再谈Transaction和管理器
目录(?)[-] Transaction的一些操作 再谈FragmentManager 调用其他fragment的方法 唤起activity 唤起fragment和相互通信 一些其它 Transact ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(四二):Fragment(7):切换效果
目录(?)[-] 利用setTransition 利用setCustomAnimations 通过ObjectAnimator自定义动态效果 程序代码的编写 利用fragment transactio ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(四十):Fragment(5):适应不同屏幕或排版
目录(?)[-] 设置横排和竖排的不同排版风格 改写代码 对于fragment,经常涉及不同屏幕尺寸和不同的排版风格.我们在基础小例子上做一下改动,在横排的时候,仍是现实左右两个fragment,在竖 ...
- 【转】 Pro Android学习笔记(四一):Fragment(6):数据保留
目录(?)[-] 通过fragment参数实现数据保留 对TitleFragment进行修改 对DetailActivity进行修改 通过savedInstanceState进行数据保留 保留frag ...
随机推荐
- JavaEE Day08 HTML&CSS
今日内容 HTML标签:表单标签 CSS:页面样式控制,美化页面,完成页面布局 一.表单标签 1.概述 用于采集用户输入数据的,如输入的用户名和密码,用于与服务器进行交互 使用from标签 form ...
- 【每日一题】【将cur的next尾插到pre后面,尾插k-1次】25. K 个一组翻转链表-211115&220120
给你一个链表,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回翻转后的链表. k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度. 如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序. 进阶: 你可以设 ...
- 【Java难点攻克】「NIO和内存映射性能提升系列」彻底透析NIO底层的内存映射机制原理与Direct Memory的关系
NIO与内存映射文件 Java类库中的NIO包相对于IO包来说有一个新功能就是 [内存映射文件],在业务层面的日常开发过程中并不是经常会使用,但是一旦在处理大文件时是比较理想的提高效率的手段,之前已经 ...
- JuiceFS CSI Driver 常见问题排查指南
Kubernetes 作为资源调度和应用编排的开源系统,正在成为云计算和现代 IT 基础架构的通用平台.JuiceFS CSI Driver 实现了容器编排系统的存储接口,使得用户可以在 Kubern ...
- [OpenCV实战]23 使用OpenCV获取高动态范围成像HDR
目录 1 背景 1.1 什么是高动态范围(HDR)成像? 1.2 高动态范围(HDR)成像如何工作? 2 代码 2.1 运行环境配置 2.2 读取图像和曝光时间 2.3 图像对齐 2.4 恢复相机响应 ...
- Spring Cloud Alibaba组件之Sentinel
目录 一 引入Sentinel学习 二 Sentinel入门 三 搭建Sentinel Dashboard 四 Springboot项目接入Sentinel 五 接入限流埋点 六 限流配置 七 熔断降 ...
- python之路53 ajax补充返回序列化数据,多对多创建三种方式,django内置序列化组件(drf前身),批量操作数据,自定义分页器,form组件
ajax补充说明 主要是针对回调函数args接收到的响应数据 1.后端request.is_ajax() 用于判断当前请求是否由ajax发出 2.后端返回的三板斧都会被args接收不再影响整个浏览器页 ...
- Java进阶篇——springboot2源码探究
1.@EnableAutoConfiguration 除了元注解之外,EnableAutoConfiguration包含了两大重要部分: 1)@AutoConfigurationPackage注解 该 ...
- Java基础篇——JUC初步
1.基础知识 java默认的两个线程:Main线程+GC守护线程 java并不能开启线程,需要调用底层用c语言写的本地方法 wait和sleep的区别: wait方法会释放线程锁,并且只能在同步代码块 ...
- Xversion 在 macOS12.4
很多同学发现在macOS12.4上已经不用使用cornerstone 4的svn了 针对macOS12.4,Xversion照样能使用 但是有些时候我们需要提交.a文件,Xversion中又看不到,针 ...
