bitmap技术解析:redis与roaringBitmap
bitmap的表象意义是,使用一个01标识位来表示是否的状态,可以达到节省空间和高效判定的效果。在我们的实际工作中,也有着许多的应用场景,相信了解bitmap定会给你带来一些额外的收获。
1. bitmap使用场景说明
比如,我想记录某用户某天是否登录过,我们有很多做法。简单的,只要用户登录,就在db中记录一条数据,要判断用户某天是否登录过,只需查询对应日期是否有记录即可。如果想统计当日登录的人数,count下记录就可以了(可能需要去重))。这样不是不可以,只是如果我们想优化下性能怎么办?这时我们就可以使用bitmap了,以日期为单位创建独立bitmap,一个用户id一个标识,要想判断用户是否登录过,直接取对应位标识即可。
再比如,我们有一批白名单用户,在白名单里则放行,否则拒绝访问。同样,我们可以用一行行的记录用db来保存处理,但这可能很占空间,或者性能不怎么样。同样,使用bitmap可以快速处理这种场景。
再比如,用于快速去重一些处理,第一次处理时,将标识位改为1,后续将进行幂等,用bitmap可以快速过滤。
2. bitmap的通俗理解
bitmap简单理解来说就是,bit的映射,将一个个的key映射到bit位上去,这样就可以快速通过key直接定位到标识上去了。另外,因都是一个个的bit,所以进行count操作很方便。对于两个bitmap的and/or位运算也是很方便和快速的。
3. redis的bitmap实现
理解了面上的bitmap的意思,要怎么做也就大概会有个思路了。
谈到redis,大家的映射问题:高性能,高并发,缓存解决方案。好像有了redis,就有了底气和别人一比高下了似的。那么,在bitmap方面,它是否也神奇之处呢?
实际上,redis的bitmap实现比较简单,和字面上的意思差不多,它是基于string实现的。
简单来说就是,string底层的存储也是二进制的,也就是说string天生就看起来和bitmap的存储类似,比如'ab'的底层存储就是\x61\x62, 拆解成二进制就是 0110 0001 0110 0010。如果我我们直接将其代表bitmap操作数,那么总共就有6个数据有值,分别是2,3,8,10,11,15位有值。这样说bitmap应该很清晰了。
接下来我们来讨论下一个空间问题。我们知道一个16位的二进制可以表示最大 65536,32位最大表示 4294967296,好像一个比较小的位就可以表示很大的数据了。但是这和我们说的bitmap还不一样,在这里,一个16位的二进制数只能表示16个bitmap值,32位数只能表示32个值。从这点来说,bitmap好像很浪费空间呢。我们知道,现在的大多数机器都是64位的。所以,如果我以这种结构存储的话,应该只能存64个标识了。
那么自然的,我们必须要使用一个合适的结构来存储这些bit,redis中使用string结构来存储bitmap,也就是说将string转换成二进制后,用其每一位来表示一个标识。这样的话,能够存放多少个标识就扩展到了string最大限制上去了。redis限制string最大是512M,也就是2^19KB=2^29B=2^32b,即最大2^32位。
redis的bitmap操作命令,简单示例如下:(咱们不是文档,如需手册,请参考官网)
setbit key offset 1|0
getbit key
bitcount key
下面,我们简单看下redis的setbit的实现源码,具体看看其处理逻辑。
// bitops.c
// 操作命令: setbit key offset 0|1
/* SETBIT key offset bitvalue */
void setbitCommand(client *c) {
robj *o;
char *err = "bit is not an integer or out of range";
uint64_t bitoffset;
ssize_t byte, bit;
int byteval, bitval;
long on;
// 解析 offset 值
if (getBitOffsetFromArgument(c,c->argv[2],&bitoffset,0,0) != C_OK)
return;
// 解析 0|1 值
if (getLongFromObjectOrReply(c,c->argv[3],&on,err) != C_OK)
return;
// 只接受0|1的输入,其他一律报错
/* Bits can only be set or cleared... */
if (on & ~1) {
addReplyError(c,err);
return;
}
// 获取key对应的string对象,方便后续操作
int dirty;
if ((o = lookupStringForBitCommand(c,bitoffset,&dirty)) == NULL) return; // 计算偏移量: 1byte=8bit, 所以真正的位所在就等于 byte大定位 + 小移位
// 从高到低计数, 即类似于 big-endian
/* Get current values */
byte = bitoffset >> 3;
byteval = ((uint8_t*)o->ptr)[byte];
bit = 7 - (bitoffset & 0x7);
bitval = byteval & (1 << bit); /* Either it is newly created, changed length, or the bit changes before and after.
* Note that the bitval here is actually a decimal number.
* So we need to use `!!` to convert it to 0 or 1 for comparison. */
if (dirty || (!!bitval != on)) {
// 先取反保留当前值, 再重新设置on 进去
/* Update byte with new bit value. */
byteval &= ~(1 << bit);
byteval |= ((on & 0x1) << bit);
((uint8_t*)o->ptr)[byte] = byteval;
// 集群扩散
signalModifiedKey(c,c->db,c->argv[1]);
notifyKeyspaceEvent(NOTIFY_STRING,"setbit",c->argv[1],c->db->id);
server.dirty++;
}
// 返回旧的值给客户端
/* Return original value. */
addReply(c, bitval ? shared.cone : shared.czero);
}
// 查找key对应的 string 对象
/* This is a helper function for commands implementations that need to write
* bits to a string object. The command creates or pad with zeroes the string
* so that the 'maxbit' bit can be addressed. The object is finally
* returned. Otherwise if the key holds a wrong type NULL is returned and
* an error is sent to the client. */
robj *lookupStringForBitCommand(client *c, uint64_t maxbit, int *dirty) {
size_t byte = maxbit >> 3;
robj *o = lookupKeyWrite(c->db,c->argv[1]);
if (checkType(c,o,OBJ_STRING)) return NULL;
if (dirty) *dirty = 0; if (o == NULL) {
o = createObject(OBJ_STRING,sdsnewlen(NULL, byte+1));
dbAdd(c->db,c->argv[1],o);
if (dirty) *dirty = 1;
} else {
o = dbUnshareStringValue(c->db,c->argv[1],o);
size_t oldlen = sdslen(o->ptr);
o->ptr = sdsgrowzero(o->ptr,byte+1);
if (dirty && oldlen != sdslen(o->ptr)) *dirty = 1;
}
return o;
}
很简单吧,不过应对一些场景还是绰绰有余了,选对场景很重要。
redis的bitmap实现简单,易于理解,但也有比较大的弊端。这种基于string的实现方式简单是简单,但存在以下几个问题:
1. 会存在较大间隙值,比如一开始就存储一个较大的偏移标识进去,比如8位的偏移,就可能让内存占用上M级别(然而你还什么都没干);
2.存储范围受限,最大只能存int型的数字偏移,如果以userid为偏移,在用户量小且以自增id生成用户id也许没问题,但其他情况就不好说了;
3.随着数据量越来越大,单次设置标识的耗时就会越来越长(大key问题),且一不小心使用get命令进行读取数据时,redis就尴尬了;
4. roaringbitmap实现
上篇讲到redis的实现,简单易懂,但是会存在一个极大空间浪费的问题,而且受限于数组大小,存储空间有限。那有没有什么办法,可以压缩存储空间?
roaringbitmap使用多级分段存储方式,避免了直接存储的问题:一是空隙值问题,二是数值限制问题。它主要通过将64位2个32位存储,将32位分2个16位存储的方式实现。其操作主要有:add/contains/getlongcadinaty... 等常规接口。
其大致存储结构图如下:
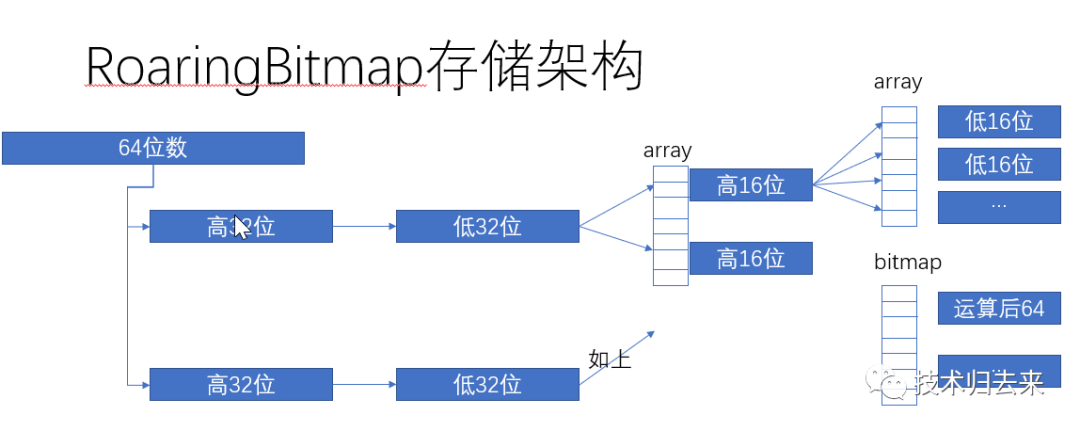
具体实现如下:
// 1. 引入依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.roaringbitmap</groupId>
<artifactId>RoaringBitmap</artifactId>
<version>0.9.28</version>
</dependency>
// 2. 建立单元测试
@Test
public void testRoaringBitmap() {
Roaring64NavigableMap bitmapObj = new Roaring64NavigableMap();
bitmapObj.add(11122233366L);
boolean exists = bitmapObj.contains(1);
long eleSize = bitmapObj.getLongCardinality();
System.out.println("exits:" + exists + ", eleSize:" + eleSize);
}
// 具体实现
// Roaring64NavigableMap
/**
* Set all the specified values to true. This can be expected to be slightly faster than calling
* "add" repeatedly. The provided integers values don't have to be in sorted order, but it may be
* preferable to sort them from a performance point of view.
*
* @param dat set values
*/
public void add(long... dat) {
for (long oneLong : dat) {
addLong(oneLong);
}
} /**
* Add the value to the container (set the value to "true"), whether it already appears or not.
*
* Java lacks native unsigned longs but the x argument is considered to be unsigned. Within
* bitmaps, numbers are ordered according to {@link Long#compareUnsigned}. We order the numbers
* like 0, 1, ..., 9223372036854775807, -9223372036854775808, -9223372036854775807,..., -1.
*
* @param x long value
*/
@Override
public void addLong(long x) {
// 高低位32位拆分 (int) (id >> 32)
int high = high(x);
int low = low(x); // Copy the reference to prevent race-condition
Map.Entry<Integer, BitmapDataProvider> local = latestAddedHigh; BitmapDataProvider bitmap;
if (local != null && local.getKey().intValue() == high) {
bitmap = local.getValue();
} else {
bitmap = highToBitmap.get(high);
if (bitmap == null) {
// 使用 RoaringBitmap 来保存低层数据, 一级存储
// 使用 treemap 保存整个结构,保证查找快速
bitmap = newRoaringBitmap();
pushBitmapForHigh(high, bitmap);
}
// 使用临时保存当前高位实例的方式,避免经常查找map带来的性能消耗
// 但实际上这要求客户端的操作是按序操作的,这样才能很好利用这个特性,如果只是随机值的话,效果就大打折扣了
latestAddedHigh = new AbstractMap.SimpleImmutableEntry<>(high, bitmap);
}
// 存储低位信息
bitmap.add(low);
// 扩容处理
invalidateAboveHigh(high);
} private void invalidateAboveHigh(int high) {
// The cardinalities after this bucket may not be valid anymore
if (compare(firstHighNotValid, high) > 0) {
// High was valid up to now
firstHighNotValid = high; int indexNotValid = binarySearch(sortedHighs, firstHighNotValid); final int indexAfterWhichToReset;
if (indexNotValid >= 0) {
indexAfterWhichToReset = indexNotValid;
} else {
// We have invalidate a high not already present: added a value for a brand new high
indexAfterWhichToReset = -indexNotValid - 1;
} // This way, sortedHighs remains sorted, without making a new/shorter array
Arrays.fill(sortedHighs, indexAfterWhichToReset, sortedHighs.length, highestHigh());
}
allValid = false;
} // 低位存储实现
// roaringbitmap
/**
* Add the value to the container (set the value to "true"), whether it already appears or not.
*
* Java lacks native unsigned integers but the x argument is considered to be unsigned.
* Within bitmaps, numbers are ordered according to {@link Integer#compareUnsigned}.
* We order the numbers like 0, 1, ..., 2147483647, -2147483648, -2147483647,..., -1.
*
* @param x integer value
*/
@Override
public void add(final int x) {
// 再分高低位存储, 即32位拆分为2个16位, (char) (x >>> 16)
final char hb = Util.highbits(x);
// 已经存储过了,则直接更新值即可
// highLowContainer = new RoaringArray();
final int i = highLowContainer.getIndex(hb);
if (i >= 0) {
// 此处查找成功,只是代表高位已经被某些值存储过了,但低位仍然在变化
highLowContainer.setContainerAtIndex(i,
highLowContainer.getContainerAtIndex(i).add(Util.lowbits(x)));
} else {
// 否则新插入一个你们数, 默认以数组形式存储, 默认初始化大小为4
final ArrayContainer newac = new ArrayContainer();
highLowContainer.insertNewKeyValueAt(-i - 1, hb, newac.add(Util.lowbits(x)));
}
} // involves a binary search
int getIndex(char x) {
// before the binary search, we optimize for frequent cases
if ((size == 0) || (keys[size - 1] == x)) {
return size - 1;
}
// 使用二分查找法查找值的存在性,实际上内部还有其他优化
// no luck we have to go through the list
return this.binarySearch(0, size, x);
}
// insert a new key, it is assumed that it does not exist
void insertNewKeyValueAt(int i, char key, Container value) {
extendArray(1);
System.arraycopy(keys, i, keys, i + 1, size - i);
keys[i] = key;
System.arraycopy(values, i, values, i + 1, size - i);
values[i] = value;
size++;
}
// RoaringArray
protected Container getContainerAtIndex(int i) {
return this.values[i];
}
// 数组的低位存储实现
// ArrayContainer
/**
* running time is in O(n) time if insert is not in order.
*/
@Override
public Container add(final char x) {
// 要插入的值大于当前容量/未大于当前容量分别处理
if (cardinality == 0 || (cardinality > 0
&& (x) > (content[cardinality - 1]))) {
// 大于 4096 后,扩展为 bitmap存储结构
if (cardinality >= DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE) {
return toBitmapContainer().add(x);
}
// 扩容,策略分多种情况处理
if (cardinality >= this.content.length) {
increaseCapacity();
}
// 直接数组存储具体值即可
// 也就是说,表面看起来这里可能会被插入重复的值,但是实际这里插入的是比最大值还大的值
// 更小的值则会先查找存在性,再进行找位插入
content[cardinality++] = x;
} else {
int loc = Util.unsignedBinarySearch(content, 0, cardinality, x);
// 小的值被插入到中间,如果找到相同的值,则本次add将被忽略
// 也就是说,这种实现的是数据的有序插入
if (loc < 0) {
// Transform the ArrayContainer to a BitmapContainer
// when cardinality = DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE
if (cardinality >= DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE) {
return toBitmapContainer().add(x);
}
if (cardinality >= this.content.length) {
increaseCapacity();
}
// insertion : shift the elements > x by one position to
// the right
// and put x in it's appropriate place
System.arraycopy(content, -loc - 1, content, -loc, cardinality + loc + 1);
content[-loc - 1] = x;
++cardinality;
}
}
return this;
}
// temporarily allow an illegally large size, as long as the operation creating
// the illegal container does not return it.
private void increaseCapacity(boolean allowIllegalSize) {
int newCapacity = (this.content.length == 0) ? DEFAULT_INIT_SIZE
: this.content.length < 64 ? this.content.length * 2
: this.content.length < 1067 ? this.content.length * 3 / 2
: this.content.length * 5 / 4;
// never allocate more than we will ever need
if (newCapacity > ArrayContainer.DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE && !allowIllegalSize) {
newCapacity = ArrayContainer.DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE;
}
// if we are within 1/16th of the max, go to max
if (newCapacity > ArrayContainer.DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE - ArrayContainer.DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE / 16
&& !allowIllegalSize) {
newCapacity = ArrayContainer.DEFAULT_MAX_SIZE;
}
this.content = Arrays.copyOf(this.content, newCapacity);
} // bitmap的低位存储实现
// BitmapContainer
// 转移老数据到bitmap的低位存储中
/**
* Copies the data in a bitmap container.
*
* @return the bitmap container
*/
@Override
public BitmapContainer toBitmapContainer() {
BitmapContainer bc = new BitmapContainer();
bc.loadData(this);
return bc;
} void loadData(final ArrayContainer arrayContainer) {
this.cardinality = arrayContainer.cardinality;
for (int k = 0; k < arrayContainer.cardinality; ++k) {
final char x = arrayContainer.content[k];
// 取整64, 这个移位是真没看懂, 反正超过31之后的
bitmap[(x) / 64] |= (1L << x);
}
} @Override
public Container add(final char i) {
final long previous = bitmap[i >>> 6];
long newval = previous | (1L << i);
bitmap[i >>> 6] = newval;
if (USE_BRANCHLESS) {
cardinality += (int)((previous ^ newval) >>> i);
} else if (previous != newval) {
++cardinality;
}
return this;
}
整体说明,当数据为空时,结构自然为空,当只有一位数据时,就非常小,当数据量越来越大,空间也跟着变大(这很正常)。只要不是超大数量级的bitmap,空间就不会很大。但如果将每个位上都存储上值,那么它占用的空间比简单的bitmap数据结构是要大些的,因为它的每个key还保存至少超过1bit的数据,甚至是原始数据,另外还有一些额外的treemap的数据结构的开销。
另外,当总体量级上千万的话,其实这种存储方案,存在大对象的问题,你可能就需要jvm参数调优来解决,或者整体换方案了。
5. 还有没有其他更好的实现?
上面两种方案,其实都不错,但好像都还有些问题存在。我们主要针对大数据量的问题,两个方案都没办法解决,那么是否就真的无解了呢?其实,办法还是有的,比如我们做一些自定义的数据分段,比如 1-100的存在bitmap1, 101-200存在bitmap2,这样就可以解决大容量的问题了。
只是这种方案需要我们小心处理自定义分段带来的技术复杂性问题,也得小心对待,尤其是重要的生产场景,必须要有大量的性能测试和准确性测试,否则挖坑给自己就不好玩了。
文章原创地址:bitmap技术解析:redis与roaringBitmap
bitmap技术解析:redis与roaringBitmap的更多相关文章
- 干货|爱奇艺CDN巡检系统技术解析
小结: 1. 中心处理系统 /1/将定制后的巡检任务拆分,通过配置与任务分发系统.CMDB*( configuration management database)将派发到边缘拨测系统/2/处理边缘拨 ...
- 互联网DSP广告系统架构及关键技术解析
互联网DSP广告系统架构及关键技术解析 宿逆 关注 1.9 2017.10.09 17:05* 字数 8206 阅读 10271评论 2喜欢 60 广告和网络游戏是互联网企业主要的盈利模式 广告是广告 ...
- Android Bitmap 全面解析(四)图片处理效果对比 ...
对比对象: UIL Volley 官方教程中的方法(此系列教程一里介绍的,ImageLoader的处理方法和官方的差不多) -------------------------------------- ...
- 36、Android Bitmap 全面解析
Android Bitmap 全面解析(一)加载大尺寸图片 http://www.eoeandroid.com/thread-331669-1-1.html Android Bitmap 全面解析(二 ...
- 学习PHP爬虫--《Webbots、Spiders和Screen Scrapers:技术解析与应用实践(原书第2版)》
<Webbots.Spiders和Screen Scrapers:技术解析与应用实践(原书第2版)> 译者序 前言 第一部分 基础概念和技术 第1章 本书主要内容3 1.1 发现互联网的真 ...
- 钟表维修管理系统技术解析(一) MVC架构搭建
钟表维修管理系统技术解析(一) MVC架构搭建 1.1新建项目 第一步:打开VS2010界面,点击左上角文件,点击新建,选择项目 1.1(图1) 第二步:点击网站Web类型,选择ASP.net MV ...
- 会员卡管理系统技术解析(十八)Timer定时监听
会员卡管理系统技术解析(十八)Timer定时监听 在web应用中,有时候客户须要一些定时程序.不须要客户自己去操作.而是由应用程序自行触发(代理)运行某些操作. 这个时候监听与定时器的配合使用就基本能 ...
- 用Netty解析Redis网络协议
用Netty解析Redis网络协议 根据Redis官方文档的介绍,学习了一下Redis网络通信协议.然后偶然在GitHub上发现了个用Netty实现的Redis服务器,很有趣,于是就动手实现了一下! ...
- Netty开发redis客户端,Netty发送redis命令,netty解析redis消息
关键字:Netty开发redis客户端,Netty发送redis命令,netty解析redis消息, netty redis ,redis RESP协议.redis客户端,netty redis协议 ...
随机推荐
- numpy---(上)
Numpy Numpy ndarray N维数组对象ndarray, 是一系列同类型数据的集合, 索引以0下标开始, 创建一个ndarray对象, 需调用array函数: numpy.array(ob ...
- ssm整合-ssmbuild
目录 项目结构 导入相关的pom依赖 Maven资源过滤设置 建立基本结构和配置框架 Mybatis层编写 Spring层 Spring整合service层 SpringMVC层 Controller ...
- k8s 初始化环境(1)
概念 k8s/kubernetes 容器化部署 解决容器编排问题,kubernetes为容器编排软件的佼佼者 kubernets为一组服务器集群 功能 自我修复 一个容器崩溃,另一个容器起来 弹性伸缩 ...
- VisualStudio安装步骤
1.下载vs2017,点击安装 2.选择asp.net选项进行安装,如果需要其他的功能,可以选上 3.更改安装路径,尽量把文件安装在c盘以外的盘上,因为c盘是系统盘,安装的东西越多电脑会越卡.注意:不 ...
- Handler异步通信系统
handler是Android给我们提供用来更新UI的一套机制,也是一套消息处理机制,我们可以发消息,也可以通过它处理消息. Handler机制主要的几个角色:Handler,Message,Loop ...
- 基于 POI 封装 ExcelUtil 精简的 Excel 导入导出
注 本文是使用 org.apache.poi 进行一次简单的封装,适用于大部分 excel 导入导出功能.过程中可能会用到反射,如若有对于性能有极致强迫症的同学,看看就好. 序 由于 poi 本身只是 ...
- Jquery_HTML-对HTML内容删除添加、操作CSS改变样式、遍历定位元素
1 <!DOCTYPE html> 2 <html lang="en"> 3 <head> 4 <meta charset="U ...
- 测试平台系列(92) 让http请求支持文件上传
大家好~我是米洛! 我正在从0到1打造一个开源的接口测试平台, 也在编写一套与之对应的教程,希望大家多多支持. 欢迎关注我的公众号米洛的测开日记,获取最新文章教程! 回顾 上一节呢,我们编写了oss的 ...
- linux创建磁盘阵例10
Linux创建RAID10 生产环境中用到的服务器一般都配备RAID阵列卡,尽管服务器的价格越来越便宜,但是我们没有必要为了做一个实验而去单独购买一台服务器,而是可以学会使用mdadm命令在Linux ...
- Flutter异步与线程详解
一:前言 - 关于多线程与异步 关于 Dart,我相信大家都知道Dart是一门单线程语言,这里说的单线程并不是说Dart没有或着不能使用多线程,而是Dart的所有API默认情况下都是单线程的.但大家也 ...
