struts2学习1
struts2使用优势
自动封装参数
参数校验
结果的处理(转发|重定向)
国际化
显示等待页面
表单的防止重复提交
struts2具有更加先进的架构以及思想
使用拦截器
struts2的历史
struts2与struts1区别就是技术上没有什么关系.
struts2的前身是webwork框架.
搭建struts2框架搭建
1.导包 在项目中找
2.书写Action类(处理请求的类) 无需继承什么类
public class Hello {
public String hello() {
System.out.println("hello");
return "success";
}
}
3.书写src/struts.xml dtd约束
<struts>
<package name="hello" namespace="/hello" extends="struts-default"> 注意:继承的 不能加上 xml 后缀
<action name="HelloAction" class="com.action.HelloAction"
method="hello">
<result name="success">/index.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
</struts>
4.将struts2核心过滤器配置到web.xml 因为struct2就是基于过滤器的
<filter>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>struts</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
struts2访问流程&struts2架构

配置详解
struts.xml配置
<package name=”hello” namespace=”/hello” extends=”struts-default”>
package:将action配置封装 就是可以在package 中配置很多action
name属性:给包起个名字,起到标识的作用,不能和其他的包名重复
namespace属性:给action的访问路径中定义一个命名空间
extends属性 继承一个包
abstract属性 包是否为抽象的 标识性属性,标识该包不能被独立运行 专门被别人继承 action元素 配置action类
name属性:决定了action访问资源名
class属性:action所在的完成类名
method属性:指定调用action中指定的方法来处理请求
result元素 结果配置
name属性:标识结果处理的名称 与action方法的返回值对应
type属性:指定调用哪一个result类来处理结果,默认使用转发
标签体:填写页面的相对路径文件
<result name=”success” type=”dispatcher”>/a.jsp</result>
引入其他struts配置
<include file=”/…/…/file.xml”></include>
struts2常量配置
struts2默认常量配置位置 struts-core/default.properties 文件
修改struts2常量配置(方式先后也是加载顺序)
方式1:src/struts.xml里面添加
<constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="UTF-8"></constant>
方式2:在src下创建struts.properties
struts.i18n.encoding=utf-8
方式3:在项目的web.xml中
<context-param>
<param-name>struts.i18n.encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</context-param>
配置文件加载顺序
default.properties struts-default.xml struts-plugin.xml struts.xml struts.properties web.xml
常量配置 struct.xml文件中配置
<constant name="struts.i18n.encoding" value="utf-8"></constant>
解决post提交中文乱码问题 <constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action"></constant>
指定访问action时的后缀名 action
<constant name=”struts.devMode” value=”true”></constant>
指定struts2是否以开发模式运行
1.热加载主配置(不需要重启即可生效)
2.提供更多错误信息输出,方便调试
动态方法调用
方式1 不利于SEO优化
配置动态方法调用是否开启常量
默认是关闭的,需要开启
<constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true"></constant>
访问 Demo!find.action
方式2 和是否开启常量无关 _ 不是必须的
使用通配符: 使用{1} 取出第一个 星号通配的内容
<action name=”Demo_*” method=”{1}”>
访问 Demo_find
struts2中的默认配置(了解)
<package name="default" namespace="/default" extends="struts-default">
<default-action-ref name=”DemoAction”></default-action-ref>
<action name="abcAction" class="com.action.Demo" method="find">
<result name="success">/Hello.jsp</result>
</action>
</package>
找不到包下的action,会使用 默认的action来处理请求
默认 method属性 execute
name属性 success
type属性 dispatcher 转发
class 属性 com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport
Action类的书写方式
方式1(理想状态 开发不常用)
不用继承任何父类 也不需要实现任何接口 似的Struts2框架的代码侵入性更低
public class DemoAction
方式2:实现Action接口
里面定义了execute方法,提供了action方法的规范
Action接口里面预值了一些字符串 可以在返回结果的时候使用
Public class DemoAction implements Action
方式3:继承一个类 ActionSupport
帮我们实现了Validateable ValidationAware TextProvider LocaleProvider等接口
如果我们需要用到这些接口的实现时,不需要自己来实现了
而且在写配置文件的时候 action里面不需要写method
结果跳转方式
转发:type="dispatcher"
重定向:type="redirect" url 会变成 /hello.jsp
<!-- 重定向 -->
<action name="Demo2Action" class="cn.itheima.a_result.Demo2Action" method="execute" >
<result name="success" type="redirect" >/hello.jsp</result>
</action>
转发到Action:type = "chain"
<!-- 转发到Action -->
<action name="Demo3Action" class="cn.itheima.a_result.Demo3Action" method="execute" >
<result name="success" type="chain">
<!-- action的名字 -->
<param name="actionName">Demo1Action</param>
<!-- action所在的命名空间 -->
<param name="namespace">/</param>
</result>
</action>
重定向到Action:
<!-- 重定向到Action -->
<action name="Demo4Action" class="cn.itheima.a_result.Demo4Action" method="execute" >
<result name="success" type="redirectAction">
<param name="actionName">Demo1Action</param>
<param name="namespace">/</param>
</result>
</action>
访问servletAPI方式

通过ActionContext下面2种都是通过这种方式得来的
public String execute() throws Exception {
//request域=> map (struts2并不推荐使用原生request域)
//不推荐
Map<String, Object> requestScope = (Map<String, Object>) ActionContext.getContext().get("request");
//推荐
ActionContext.getContext().put("name", "requestTom");
//session域 => map
Map<String, Object> sessionScope = ActionContext.getContext().getSession();
sessionScope.put("name", "sessionTom");
//application域=>map
Map<String, Object> applicationScope = ActionContext.getContext().getApplication();
applicationScope.put("name", "applicationTom");
return SUCCESS;
}
通过ServletActionContext 因为纯Java操作 不推荐使用
//并不推荐
public String execute() throws Exception {
//原生request
HttpServletRequest request = ServletActionContext.getRequest();
//原生session
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
//原生response
HttpServletResponse response = ServletActionContext.getResponse();
//原生servletContext
ServletContext servletContext = ServletActionContext.getServletContext();
return SUCCESS;
}
并不推荐使用原生的 request域
因为ActionContext 域 周期和request周期一样
通过实现接口方式 依次类推 通过拦截器实现Config...
//如何在action中获得原生ServletAPI
public class Demo7Action extends ActionSupport implements ServletRequestAware { 这个里面的方法
private HttpServletRequest request; public String execute() throws Exception {
System.out.println("原生request:"+request);
return SUCCESS;
}
@Override
public void setServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
this.request = request;
}
}
Action生命周期
1.每次请求到来时,都会创建一个新的Action实例
2.Action是线程安全的.可以使用成员变量接收参数
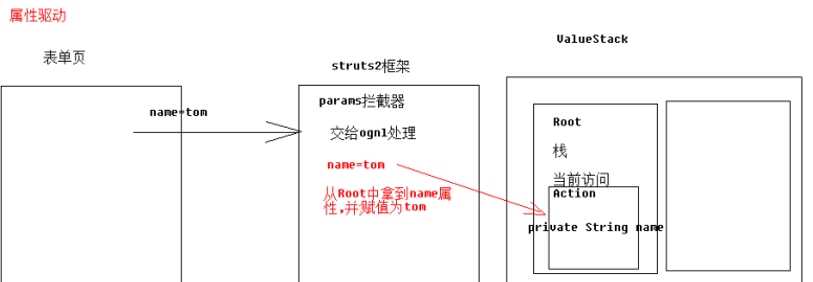
属性驱动获得参数(不常用)

//准备与参数键名称相同的属性
private String name;
//自动类型转换 只能转换8大基本数据类型以及对应包装类
private Integer age;
//支持特定类型字符串转换为Date ,例如 yyyy-MM-dd
private Date birthday;
对象驱动
<input type="text" name="u.name" /> user 是和后端的 名字相同 也可以使用get方法验证 localhost/Hello?u.name=wl & u.age=8
也是需要加上 前缀
private Users u;
public Users getU() {
return u;
}
public void setU(Users u) {
this.u = u;
}
模型驱动
<input type="text" name="name"> 不用加上 前缀
private Users u = new Users();
@Override
public Users getModel() {
return u;
}
集合类型参数封装
List http://localhost:8080/strut-first/Hello?list[0]=2&list[1]=5
<input type=”text” name=”list”/>
<input type=”text” name=”list[3]”>
private List<String> list;
Map
<input type=”text” name=”map[‘haha’]”/>
private Map<String,String> map;
注意:struts和hibernate包在合并时.javassist-3.18.1-GA.jar包是重复的,删除版本低的.
OGNL表达式
OGNL:对象视图导航语言. ${user.addr.name} 这种写法就叫对象视图导航.
OGNL不仅仅可以视图导航.支持比EL表达式更加丰富的功能.
使用OGNL准备工作
导包: struts2 的包中已经包含了.所以不需要导入额外的jar包
OGNLContext ognl上下文对象
Root:返回值任何对象 都可以作为root
Context:map 里面都是 键值对
public void fun1() throws Exception{
//准备Root
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
//准备Context
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);//将rootUser作为root部分
oc.setValues(context);将context这个Map作为Context部分
Ognl.getValue("", oc, oc.getRoot()); }
基本取值
//取出root中的属性值
public void fun2() throws Exception{
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);//取出root中user对象的name属性
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("age", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
//取出context中的属性值
public void fun3() throws Exception{
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);//取出context中键为user1对象的name属性
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user2.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#user2.age", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
//为属性赋值
public void fun4() throws Exception{
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);//将root中的user对象的name属性赋值
Ognl.getValue("name='jerry'", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("name", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.name='wl',#user1.name", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
赋值 多个赋值可以串联
调用方法
public void fun5() throws Exception{
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
//调用root中user对象的setName方法
Ognl.getValue("setName('lilei')", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#user1.setName('lucy'),#user1.getName()", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
调用静态方法
public void fun6() throws Exception{
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context);
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("@cn.itheima.a_ognl.HahaUtils@echo('hello 强勇!')", oc, oc.getRoot());
//Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@java.lang.Math@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
Double pi = (Double) Ognl.getValue("@@PI", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
创建对象(List,Map)
//ognl创建对象-list|map
public void fun7() throws Exception{
User rootUser = new User("tom",18);
Map<String,User> context = new HashMap<String,User>();
context.put("user1", new User("jack",18));
context.put("user2", new User("rose",22));
OgnlContext oc = new OgnlContext();
oc.setRoot(rootUser);
oc.setValues(context); //创建list对象
Integer size = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}[0]", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name2 = (String) Ognl.getValue("{'tom','jerry','jack','rose'}.get(1)", oc, oc.getRoot()); //创建Map对象
Integer size2 = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.size()", oc, oc.getRoot());
String name3 = (String) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}['name']", oc, oc.getRoot());
Integer age = (Integer) Ognl.getValue("#{'name':'tom','age':18}.get('age')", oc, oc.getRoot());
}
OGNL 可以赋值和取值动作一起进行
@@PI 相当于 @java.lang.Math@PI
如果添加的参数struts"看不懂".就会作为参数附加重定向的路径之后.
如果参数是动态的.可以使用${}包裹ognl表达式.动态取值
OGNL与Struts2的结合

查看值栈中两部分内容(使用DEBUG标签)在jsp页面
Root: 默认情况下,栈中放置当前访问的Action对象 Context部分就是ActionContext数据中心

struts2与ognl结合体现
参数接收


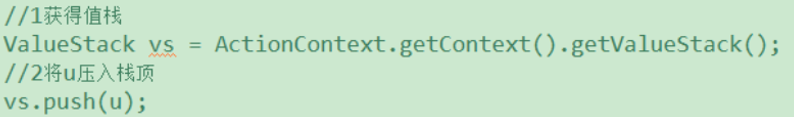
如何获得值栈对象,值栈对象与ActionContext对象是互相引用的
配置文件中使用

${ognl表达式}
扩展:request对象的getAttribute方法 wrappedRequest

查找顺序
以前的Servlet 是线程不安全的,Tomcat只会创建一个实例对象
怎么解决各个人传递的值不一致问题? 将参数放到 doGet方法里面
而Action 是线程安全的 ,所以可以直接将 参数放到成员变量中 而不用担心数据共享问题
每次请求Action时都会创建新的Action实例对象
ActionContext 所有对象都可以获取 也是一个Map
原生request/reponse/servletCContext
域对象 Map
attr 域 三个域 key相同以小的为准
默认值 这些配置都在 struct-default.xml中
include 可以引入其他 struct配置文件
开发模式
有轮训线程在轮训
消耗更多的IO
struts2学习1的更多相关文章
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记75:Struts2 学习之路-- 总结 和 目录
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- [原创]java WEB学习笔记66:Struts2 学习之路--Struts的CRUD操作( 查看 / 删除/ 添加) 使用 paramsPrepareParamsStack 重构代码 ,PrepareInterceptor拦截器,paramsPrepareParamsStack 拦截器栈
本博客的目的:①总结自己的学习过程,相当于学习笔记 ②将自己的经验分享给大家,相互学习,互相交流,不可商用 内容难免出现问题,欢迎指正,交流,探讨,可以留言,也可以通过以下方式联系. 本人互联网技术爱 ...
- Struts2学习笔记⑧
今天是Struts2学习笔记的最后一篇文章了.用什么做结尾呢,这两天其实还学了很多东西,没有记录下,今天就查漏补缺一下. 文件上传与下载.FreeMarker以及昨天没做完的例子 文件上传与下载 文件 ...
- Struts2学习笔记①
Struts2 学习笔记① 所有的程序学习都从Hello World开始,今天先跟着书做一个HW的示例. Struts2是一套MVC框架,使用起来非常方便,接触到现在觉得最麻烦的地方是配置文件.我的一 ...
- Struts2学习笔记NO.1------结合Hibernate完成查询商品类别简单案例(工具IDEA)
Struts2学习笔记一结合Hibernate完成查询商品类别简单案例(工具IDEA) 1.jar包准备 Hibernate+Struts2 jar包 struts的jar比较多,可以从Struts官 ...
- Struts2学习:interceptor(拦截器)的使用
对于需要登陆验证.权限验证等功能的网站,每一次请求,每一个action都写一段验证的代码,未免显得冗余且不易维护.struts2提供了拦截器interceptor,为这些页面提供一个切面,或者说公共组 ...
- Struts2 学习笔记(概述)
Struts2 学习笔记 2015年3月7日11:02:55 MVC思想 Strust2的MVC对应关系如下: 在MVC三个模块当中,struts2对应关系如下: Model: 负责封装应用的状态,并 ...
- Java后台处理框架之struts2学习总结
Java后台处理框架之struts2学习总结 最近我在网上了解到,在实际的开发项目中struts2的使用率在不断降低,取而代之的是springMVC.可能有很多的朋友看到这里就会说,那还不如不学str ...
- struts2学习之旅三 权限管理和导航设计
1,权限管理的db设计和dao实现,尽量简单快速有效: db的设计如下:权限按照角色来赋给用户: 权限对应每一个具体的功能,有菜单级别的,有导航级别的,还有页面级别的功能: 涉及到权限的敏感操作一般都 ...
- struts2 学习记录 过滤器 国际化
struts2接触不是一天两天了,但是一直没有用它做什么项目,但老师确一直说它有很大的学习价值,所以还是把我学习到的东西给记录一下,记录的东西没有规律,只是给自己留个备份, struts2中最关键的是 ...
随机推荐
- Airtest网易开源的一款UI自动化测试工具
Airtest网易开源的一款UI自动化测试工具 1 Airtest 简介Airtest Project是网易游戏内部工具团队开发并开源的一款UI自动化测试工具,据说曾经获得谷歌力挺. AirtestI ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security(1)——入门程序
因为项目需要,第一次接触 Spring Security,早就听闻 Spring Security 功能强大但上手困难,学习了几天出入门道,特整理这篇文章希望能让后来者少踩一点坑(本文附带实例程序,请 ...
- 全局安装npm包报错没有权限
背景:npm i npm-check -g 时报错没有权限 Error: EACCES: permission denied, access '/usr/local/lib/node_modules' ...
- CopyOnWriteArrayList 源码分析 基于jdk1.8
CopyOnWriteArrayList 源码分析: 1:成员属性: final transient ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //内部是 ...
- VS删除空白行
使用正则表达式, 搜索 (?<=\r\n)\r\n 替换空白
- freemarker模板文件的4个组成部分
FreeMarker模板文件主要由以下4个部分组成:1.文本,直接输出的部分.2.注释,即<#–…–>格式不会输出.3.插值(Interpolation):即${..}或者#{..}格式的 ...
- scala的应用--UDF:用户自定义函数
在window10下安装了hadoop,用ida创建maven项目. <properties> <spark.version>2.2.0</spark.version&g ...
- 获取豆瓣电影数据(R与API获取网页数据)
一般成熟的网站都会有反爬虫策略,例如限制访问次数,限制访问 IP,动态显示数据等.爬虫和反爬虫就是一直相爱相杀地互相钳制.如果要通过爬虫来获取某些大型网站的数据,那是一件很费时费力的活.小白总遭遇过在 ...
- Web应急:移动端劫持
PC端访问正常,移动端访问出现异常,比如插入弹窗.嵌入式广告和跳转到第三方网站,将干扰用户的正常使用,对用户体验造成极大伤害. 现象描述 部分网站用户反馈,手机打开网站就会跳转到赌博网站. 问题处理 ...
- 大数据基础总结---HDFS分布式文件系统
HDFS分布式文件系统 文件系统的基本概述 文件系统定义:文件系统是一种存储和组织计算机数据的方法,它使得对其访问和查找变得容易. 文件名:在文件系统中,文件名是用于定位存储位置. 元数据(Metad ...
