Kafka(四) —— KafkaProducer源码阅读
一、doSend()方法
Kafka中的每一条消息都对应一个ProducerRecord对象。
public class ProducerRecord<K, V> {
private final String topic;
private final Integer partition;
private final Headers headers;
private final K key;
private final V value;
private final Long timestamp;
}
doSend() 源码如下:
private Future<RecordMetadata> doSend(ProducerRecord<K, V> record, Callback callback) {
TopicPartition tp = null;
try {
throwIfProducerClosed();
// first make sure the metadata for the topic is available
ClusterAndWaitTime clusterAndWaitTime;
// 1、获取集群的元数据
try {
clusterAndWaitTime = waitOnMetadata(record.topic(), record.partition(), maxBlockTimeMs);
} catch (KafkaException e) {
if (metadata.isClosed())
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while send in progress", e);
throw e;
}
long remainingWaitMs = Math.max(0, maxBlockTimeMs - clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs);
Cluster cluster = clusterAndWaitTime.cluster;
//2、 Key、Value 序列化
byte[] serializedKey;
try {
serializedKey = keySerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.headers(), record.key());
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new SerializationException("Can't convert key of class " + record.key().getClass().getName() +
" to class " + producerConfig.getClass(ProducerConfig.KEY_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG).getName() +
" specified in key.serializer", cce);
}
byte[] serializedValue;
try {
serializedValue = valueSerializer.serialize(record.topic(), record.headers(), record.value());
} catch (ClassCastException cce) {
throw new SerializationException("Can't convert value of class " + record.value().getClass().getName() +
" to class " + producerConfig.getClass(ProducerConfig.VALUE_SERIALIZER_CLASS_CONFIG).getName() +
" specified in value.serializer", cce);
}
// 3、分区器
int partition = partition(record, serializedKey, serializedValue, cluster);
// 对topic和分区进行封装,封装后的结果 topic-partition ,[return topic + "-" + partition;]
tp = new TopicPartition(record.topic(), partition);
setReadOnly(record.headers());
Header[] headers = record.headers().toArray();
int serializedSize = AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic(),
compressionType, serializedKey, serializedValue, headers);
ensureValidRecordSize(serializedSize);
long timestamp = record.timestamp() == null ? time.milliseconds() : record.timestamp();
log.trace("Sending record {} with callback {} to topic {} partition {}", record, callback, record.topic(), partition);
// producer callback will make sure to call both 'callback' and interceptor callback
Callback interceptCallback = new InterceptorCallback<>(callback, this.interceptors, tp);
if (transactionManager != null && transactionManager.isTransactional())
transactionManager.maybeAddPartitionToTransaction(tp);
// 4、将数据放到accumulator中
RecordAccumulator.RecordAppendResult result = accumulator.append(tp, timestamp, serializedKey,
serializedValue, headers, interceptCallback, remainingWaitMs);
// 5、如果batch已经满了,唤醒 Sender线程发送数据
if (result.batchIsFull || result.newBatchCreated) {
log.trace("Waking up the sender since topic {} partition {} is either full or getting a new batch", record.topic(), partition);
this.sender.wakeup();
}
return result.future;
} catch (Exception e) {
// ...
}
}
获取集群元数据
doSend()中相关的源码
try {
clusterAndWaitTime = waitOnMetadata(record.topic(), record.partition(), maxBlockTimeMs);
} catch (KafkaException e) {
if (metadata.isClosed())
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while send in progress", e);
throw e;
}
long remainingWaitMs = Math.max(0, maxBlockTimeMs - clusterAndWaitTime.waitedOnMetadataMs);
Cluster cluster = clusterAndWaitTime.cluster;
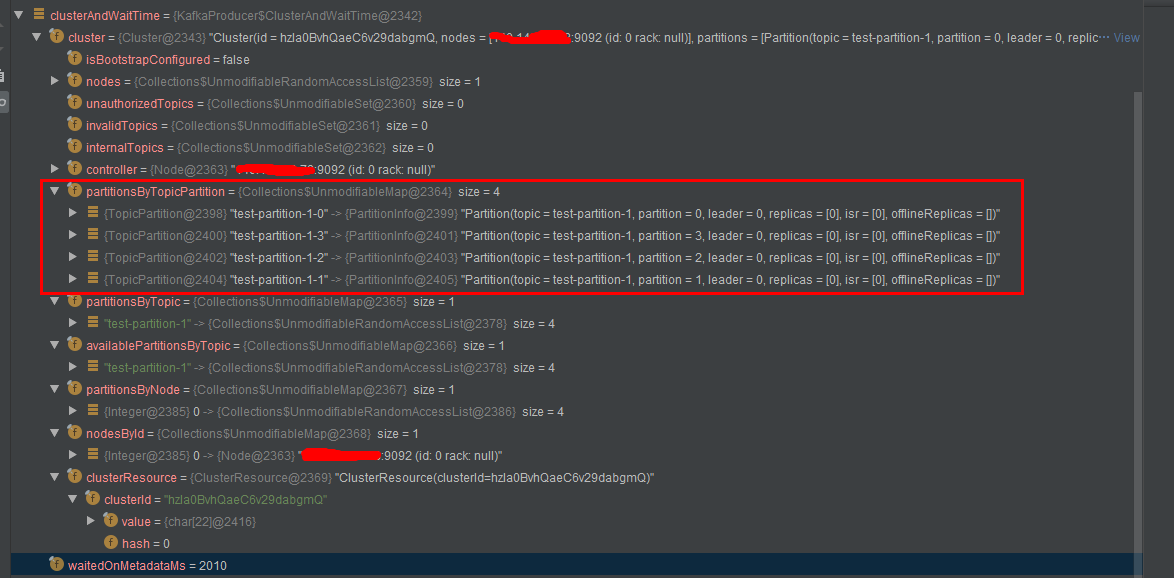
Cluster类定义
public final class Cluster {
private final boolean isBootstrapConfigured;
// broker 节点列表
private final List<Node> nodes;
private final Set<String> unauthorizedTopics;
private final Set<String> invalidTopics;
private final Set<String> internalTopics;
// controller所在节点
private final Node controller;
// 记录TopicPartition和PartitionInfo的管理
// TopicPartition中定义了partition、topic两个字段
// PartitionInfo记录详细的partition信息,定义了leader节点的位置、以Node数组的形式定义了 副本节点的位置、ISR、offline副本
private final Map<TopicPartition, PartitionInfo> partitionsByTopicPartition;
//Topic 与 分区 的映射关系
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByTopic;
private final Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> availablePartitionsByTopic;
private final Map<Integer, List<PartitionInfo>> partitionsByNode;
private final Map<Integer, Node> nodesById;
private final ClusterResource clusterResource;
}
调试获得clusterAndWaitTime对象的显示结果
二、partition()方法
当Record没有被指定分区时,会调用partiton方法,分配到分区。
传入的参数是,record的topic、k-v序列化、以及集群信息。
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes, Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
// 从集群中获取Topic对应的分区信息
List<PartitionInfo> partitions = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
int numPartitions = partitions.size();
//判断key是否为空
if (keyBytes == null) {
int nextValue = nextValue(topic);
List<PartitionInfo> availablePartitions = cluster.availablePartitionsForTopic(topic);
if (availablePartitions.size() > 0) {
int part = Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % availablePartitions.size();
return availablePartitions.get(part).partition();
} else {
// no partitions are available, give a non-available partition
return Utils.toPositive(nextValue) % numPartitions;
}
} else {
// 若key不为空,则对key进行hash,然后对分区数取余
// hash the keyBytes to choose a partition
return Utils.toPositive(Utils.murmur2(keyBytes)) % numPartitions;
}
}
三、append()方法
在调用KafkaProducer构造方法的时候,会创建Accumulator对象。
RecordAccumulator
RecordAccumulator主要用来缓存消息以便Sender线程可以批量发送数据,减少网络传输的资源消耗,以提升性能。
RecordAccumulator内部每个分区都维护一个Deque,其中ProducerBatch包含一至多个ProducerRecord。
消息写入缓存(RecordAccumulator)时,消息(ProducerRecord)会追加到双端队列(Deque)尾部,追加的过程是,找到分区对应的Deque,然后取出Deque最后一个ProducerBatch,看能否追加,若追加不了,则新建一个ProducerBatch,将消息追加到ProducerBatch中。ProducerBatch的大小,由参数batch.size来确定。
Sender读取消息时,会从双端队列头部读取消息。
RecordAccumulator类定义
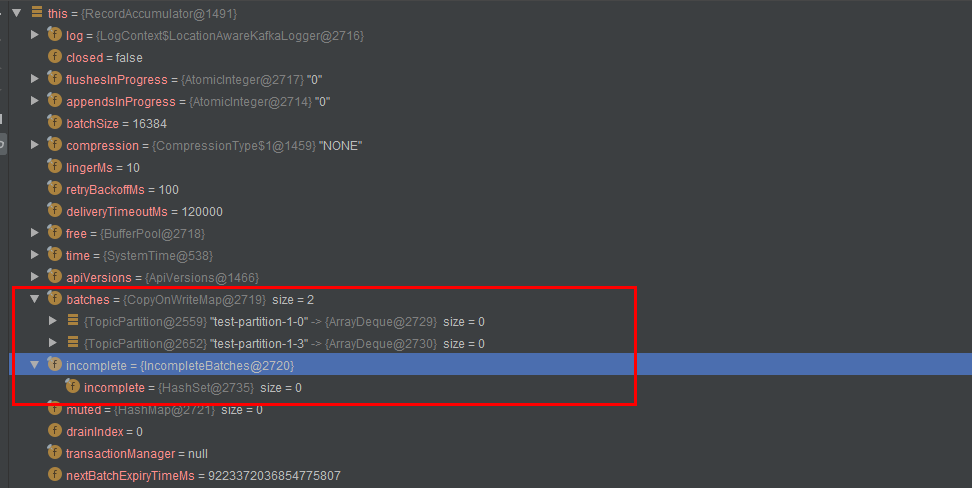
public final class RecordAccumulator {
private final Logger log;
private volatile boolean closed;
private final AtomicInteger flushesInProgress;
private final AtomicInteger appendsInProgress;
private final int batchSize;
private final CompressionType compression;
private final int lingerMs;
private final long retryBackoffMs;
private final int deliveryTimeoutMs;
private final BufferPool free;
private final Time time;
private final ApiVersions apiVersions;
// 在RecordAccumulator的构造方法中实例化 this.batches = new CopyOnWriteMap<>();
private final ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>> batches;
private final IncompleteBatches incomplete;
// The following variables are only accessed by the sender thread, so we don't need to protect them.
private final Map<TopicPartition, Long> muted;
private int drainIndex;
private final TransactionManager transactionManager;
private long nextBatchExpiryTimeMs = Long.MAX_VALUE;
}
调试结果
append()方法
public RecordAppendResult append(TopicPartition tp,
long timestamp,
byte[] key,
byte[] value,
Header[] headers,
Callback callback,
long maxTimeToBlock) throws InterruptedException {
// We keep track of the number of appending thread to make sure we do not miss batches in
// abortIncompleteBatches().
appendsInProgress.incrementAndGet();
ByteBuffer buffer = null;
if (headers == null) headers = Record.EMPTY_HEADERS;
try {
// check if we have an in-progress batch
// 从上文中我们知道batches的结构是ConcurrentMap<TopicPartition, Deque<ProducerBatch>>
// 从batches中检查是否存在这个tp,如果有则返回Deque,若没有则创建
// 这里的Deque是ArrayDeque
Deque<ProducerBatch> dq = getOrCreateDeque(tp);
synchronized (dq) {
if (closed)
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while send in progress");
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, dq);
if (appendResult != null)
return appendResult;
}
// 下面一大步是将record中的信息转成buffer对象,进而封装成ProducerBatch对象,再放到dq中。
// we don't have an in-progress record batch try to allocate a new batch
byte maxUsableMagic = apiVersions.maxUsableProduceMagic();
int size = Math.max(this.batchSize, AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(maxUsableMagic, compression, key, value, headers));
log.trace("Allocating a new {} byte message buffer for topic {} partition {}", size, tp.topic(), tp.partition());
buffer = free.allocate(size, maxTimeToBlock);
synchronized (dq) {
// Need to check if producer is closed again after grabbing the dequeue lock.
if (closed)
throw new KafkaException("Producer closed while send in progress");
RecordAppendResult appendResult = tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, dq);
if (appendResult != null) {
// Somebody else found us a batch, return the one we waited for! Hopefully this doesn't happen often...
return appendResult;
}
MemoryRecordsBuilder recordsBuilder = recordsBuilder(buffer, maxUsableMagic);
ProducerBatch batch = new ProducerBatch(tp, recordsBuilder, time.milliseconds());
FutureRecordMetadata future = Utils.notNull(batch.tryAppend(timestamp, key, value, headers, callback, time.milliseconds()));
dq.addLast(batch);
incomplete.add(batch);
// Don't deallocate this buffer in the finally block as it's being used in the record batch
buffer = null;
return new RecordAppendResult(future, dq.size() > 1 || batch.isFull(), true);
}
} finally {
if (buffer != null)
free.deallocate(buffer);
appendsInProgress.decrementAndGet();
}
}
四、BufferPool
ByteBuffer的创建和释放比较消耗资源,所以Kafka客户端使用BufferPool来实现ByteBuffer的复用。
public class BufferPool {
private final long totalMemory;
private final int poolableSize;
private final ReentrantLock lock;
private final Deque<ByteBuffer> free;
// ...
}
五、Sender
run()方法
/**
* Run a single iteration of sending
*
* @param now The current POSIX time in milliseconds
*/
void run(long now) {
// 省略前面的代码
long pollTimeout = sendProducerData(now);
client.poll(pollTimeout, now);
}
sendProducerData()方法
private long sendProducerData(long now) {
// 获取Kafka集群元数据
Cluster cluster = metadata.fetch();
// get the list of partitions with data ready to send
// 获取准备发送数据的partition列表
// ReadyCheckResult的成员变量有Set<Node> readyNodes(准备发送的节点),Set<String> unknownLeaderTopics
RecordAccumulator.ReadyCheckResult result = this.accumulator.ready(cluster, now);
// if there are any partitions whose leaders are not known yet, force metadata update
// 如果有不知道leader节点在哪的partition,强制更新元数据
// 向元数据中增加topic,并且进行更新
if (!result.unknownLeaderTopics.isEmpty()) {
// The set of topics with unknown leader contains topics with leader election pending as well as
// topics which may have expired. Add the topic again to metadata to ensure it is included
// and request metadata update, since there are messages to send to the topic.
for (String topic : result.unknownLeaderTopics)
this.metadata.add(topic);
this.metadata.requestUpdate();
}
// remove any nodes we aren't ready to send to
// 移除所有不准备发送的节点
Iterator<Node> iter = result.readyNodes.iterator();
long notReadyTimeout = Long.MAX_VALUE;
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Node node = iter.next();
if (!this.client.ready(node, now)) {
iter.remove();
notReadyTimeout = Math.min(notReadyTimeout, this.client.connectionDelay(node, now));
}
}
// create produce requests
// 创建一个produce 请求
Map<Integer, List<ProducerBatch>> batches = this.accumulator.drain(cluster, result.readyNodes,
this.maxRequestSize, now);
if (guaranteeMessageOrder) {
// Mute all the partitions drained
for (List<ProducerBatch> batchList : batches.values()) {
for (ProducerBatch batch : batchList)
this.accumulator.mutePartition(batch.topicPartition);
}
}
List<ProducerBatch> expiredBatches = this.accumulator.expiredBatches(this.requestTimeout, now);
// Reset the producer id if an expired batch has previously been sent to the broker. Also update the metrics
// for expired batches. see the documentation of @TransactionState.resetProducerId to understand why
// we need to reset the producer id here.
if (!expiredBatches.isEmpty())
log.trace("Expired {} batches in accumulator", expiredBatches.size());
for (ProducerBatch expiredBatch : expiredBatches) {
failBatch(expiredBatch, -1, NO_TIMESTAMP, expiredBatch.timeoutException(), false);
if (transactionManager != null && expiredBatch.inRetry()) {
// This ensures that no new batches are drained until the current in flight batches are fully resolved.
transactionManager.markSequenceUnresolved(expiredBatch.topicPartition);
}
}
sensors.updateProduceRequestMetrics(batches);
// If we have any nodes that are ready to send + have sendable data, poll with 0 timeout so this can immediately
// loop and try sending more data. Otherwise, the timeout is determined by nodes that have partitions with data
// that isn't yet sendable (e.g. lingering, backing off). Note that this specifically does not include nodes
// with sendable data that aren't ready to send since they would cause busy looping.
long pollTimeout = Math.min(result.nextReadyCheckDelayMs, notReadyTimeout);
if (!result.readyNodes.isEmpty()) {
log.trace("Nodes with data ready to send: {}", result.readyNodes);
// if some partitions are already ready to be sent, the select time would be 0;
// otherwise if some partition already has some data accumulated but not ready yet,
// the select time will be the time difference between now and its linger expiry time;
// otherwise the select time will be the time difference between now and the metadata expiry time;
pollTimeout = 0;
}
sendProduceRequests(batches, now);
return pollTimeout;
}
参考文档
Kafka(四) —— KafkaProducer源码阅读的更多相关文章
- 36 网络相关函数(四)——live555源码阅读(四)网络
36 网络相关函数(四)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 36 网络相关函数(四)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 简介 7)createSocket创建socket方法 8)closeSoc ...
- 【原】AFNetworking源码阅读(四)
[原]AFNetworking源码阅读(四) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 上一篇还遗留了很多问题,包括AFURLSessionManagerTaskDe ...
- 【原】SDWebImage源码阅读(四)
[原]SDWebImage源码阅读(四) 本文转载请注明出处 —— polobymulberry-博客园 1. 前言 SDWebImage中主要实现了NSURLConnectionDataDelega ...
- 40 网络相关函数(八)——live555源码阅读(四)网络
40 网络相关函数(八)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 40 网络相关函数(八)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 简介 15)writeSocket向套接口写数据 TTL的概念 函数send ...
- 39 网络相关函数(七)——live555源码阅读(四)网络
39 网络相关函数(七)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 39 网络相关函数(七)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 简介 14)readSocket从套接口读取数据 recv/recvfrom ...
- 38 网络相关函数(六)——live555源码阅读(四)网络
38 网络相关函数(六)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 38 网络相关函数(六)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 简介 12)makeSocketNonBlocking和makeSocket ...
- 37 网络相关函数(五)——live555源码阅读(四)网络
37 网络相关函数(五)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 37 网络相关函数(五)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 简介 10)MAKE_SOCKADDR_IN构建sockaddr_in结构体 ...
- 35 网络相关函数(三)——live555源码阅读(四)网络
35 网络相关函数(三)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 35 网络相关函数(三)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 简介 5)NoReuse不重用地址类 6)initializeWinsock ...
- 34 网络相关函数(二)——live555源码阅读(四)网络
34 网络相关函数(二)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 34 网络相关函数(二)——live555源码阅读(四)网络 2)socketErr 套接口错误 3)groupsockPriv函数 4) ...
随机推荐
- Bean named 'XXX' is expected to be of type [XXX] but was actually of type [com.sun.proxy.$Proxy7
AOP原理 <aop:aspectj-autoproxy />声明自动为spring容器中那些配置@aspectJ切面的bean创建代理,织入切面. <aop:aspectj-aut ...
- Vue v-bind与v-model的区别
v-bind 缩写 : 动态地绑定一个或多个特性,或一个组件 prop 到表达式. 官网举例 <!-- 绑定一个属性 --> <img v-bind:src=" ...
- ASP.Net Jquery 随机验证码 文本框判断
// 登陆验证 $(function () { var chars = ['0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'a', 'B' ...
- 如何使用GUID硬盘分区格式安装新windows系统
全局唯一标识分区表(GUID Partition Table,缩写:GPT)是一个实体硬盘的分区结构.目前硬盘格式有两种,一种MBR,另一个就是GUID.一般电脑买过来是windows7以上,比如wi ...
- RSA加密&解密【Java&Scala】
一.简介 RSA加密算法是一种非对称加密算法.在公开密钥加密和电子商业中RSA被广泛使用. RSA公开密钥密码体制.所谓公开密钥密码体制就是使用不同的加密密钥与解密密钥,是一种“由已知加密密钥推导出解 ...
- PHP编程实现阳历转换为阴历的方法
php类: 2 /** 3 *PHP编程实现阳历转换为阴历的方法 4 *根据实际情况所需进行调用 5 * 6 / 7 10 <?php class Lunar { public $MIN_YEA ...
- PostgreSQL数据库安装
PostgreSQL数据库安装 postgresqllinux9.6.0 2018年01月31日 10时53分13秒 编译以及安装 源码编译 程序安装 数据库的启动和停止 启动数据库 关闭数据库 数据 ...
- Echo团队Alpha冲刺随笔 - 第八天
项目冲刺情况 进展 程序基本完成,根据实际,添加完善新接口 问题 根据功能对接出现的问题继续进行改进 心得 放假了放松下 今日会议内容 黄少勇 今日进展 测试小程序,添加异常和错误操作的处理 存在问题 ...
- php数组打乱顺序
shuffle() PHP shuffle() 函数随机排列数组单元的顺序(将数组打乱).本函数为数组中的单元赋予新的键名,这将删除原有的键名而不仅是重新排序. 语法: bool shuffle ( ...
- c# 3.0语言主要增强
1隐含类型的局部变量 var i=5; var h=23.56; var s="Cshap" var intarr=new[]{1,2,3}; var 为关键字,可以根据后边的初始 ...
