网络流之最大流Dinic --- poj 1459
Description
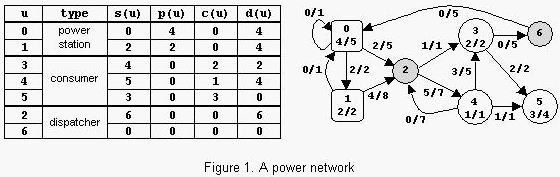
Input
Output
Sample Input
2 1 1 2 (0,1)20 (1,0)10 (0)15 (1)20
7 2 3 13 (0,0)1 (0,1)2 (0,2)5 (1,0)1 (1,2)8 (2,3)1 (2,4)7
(3,5)2 (3,6)5 (4,2)7 (4,3)5 (4,5)1 (6,0)5
(0)5 (1)2 (3)2 (4)1 (5)4
Sample Output
15
6
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = ;
const int MAXN = 1e9 + ; struct Edge {
int to;
int value;
int next;
}e[*N*N];
int head[N], cnt;
int deep[N];
int n, np, nc, m; void insert(int u, int v, int value) {
e[++cnt].to = v;
e[cnt].value = value;
e[cnt].next = head[u];
head[u] = cnt;
} void init() {
memset(head, -, sizeof(head));
cnt = -;
} bool BFS() {
memset(deep,-,sizeof(deep));
queue<int> Q;
deep[] = ;
Q.push();
while (!Q.empty()) {
int u = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int edge = head[u]; edge != -; edge = e[edge].next) {
int v = e[edge].to;
if (deep[v] == - && e[edge].value > ) {
deep[v] = deep[u] + ;
Q.push(v);
}
}
}
if (deep[n + ] == -) return false;
return true;
} int DFS(int u,int flow_pre) {
if (u == n + ) return flow_pre;
int flow = ;
for (int edge = head[u]; edge != -; edge = e[edge].next) {
int v = e[edge].to;
if (deep[v] != deep[u]+ || e[edge].value==) continue;
int _flow= DFS(v, min(flow_pre, e[edge].value));
flow_pre -= _flow;
flow += _flow;
e[edge].value -= _flow;
e[edge ^ ].value += _flow;
if (flow_pre == ) break;
}
if (flow == ) deep[u] = -;
return flow;
}
int GetMaxFlow() {
int ans = ;
while (BFS()) {
ans += DFS(,MAXN);
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
while (scanf("%d%d%d%d", &n, &np, &nc, &m) != EOF) {
init();
int u, v, z;
for (int i = ; i < m; i++) {
scanf(" (%d,%d)%d", &u, &v, &z);
insert(u+, v+, z);
insert(v+, u+, );
}
for (int i = ; i < np; i++) {
scanf(" (%d)%d", &u, &z);
insert(, u+, z);
insert(u+, , );
}
for (int i = ; i < nc; i++) {
scanf(" (%d)%d", &u, &z);
insert(u + , n + , z);
insert(n + , u + , );
}
printf("%d\n",GetMaxFlow());
}
}
网络流之最大流Dinic --- poj 1459的更多相关文章
- 网络流之最大流EK --- poj 1459
题目链接 本篇博客延续上篇博客(最大流Dinic算法)的内容,此次使用EK算法解决最大流问题. EK算法思想:在图中搜索一条从源点到汇点的扩展路,需要记录这条路径,将这条路径的最大可行流量 liu 增 ...
- 网络流之最大流Dinic算法模版
/* 网络流之最大流Dinic算法模版 */ #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #include <queue> using ...
- 我爱网络流之最大流Dinic
直接上大佬博客: Dinic算法详解及实现来自小菲进修中 Dinic算法(研究总结,网络流)来自SYCstudio 模板步骤: 第一步,先bfs把图划分成分成分层图网络 第二步,dfs多次找增广路 当 ...
- 网络流(最大流-Dinic算法)
摘自https://www.cnblogs.com/SYCstudio/p/7260613.html 网络流定义 在图论中,网络流(Network flow)是指在一个每条边都有容量(Capacity ...
- [Poj2112][USACO2003 US OPEN] Optimal Milking [网络流,最大流][Dinic+当前弧优化]
题意:有K个挤奶机编号1~K,有C只奶牛编号(K+1)~(C+K),每个挤奶机之多能挤M头牛,现在让奶牛走到挤奶机处,求奶牛所走的最长的一条边至少是多少. 题解:从起点向挤奶机连边,容量为M,从挤奶机 ...
- POJ 1459 Power Network / HIT 1228 Power Network / UVAlive 2760 Power Network / ZOJ 1734 Power Network / FZU 1161 (网络流,最大流)
POJ 1459 Power Network / HIT 1228 Power Network / UVAlive 2760 Power Network / ZOJ 1734 Power Networ ...
- POJ 2711 Leapin' Lizards / HDU 2732 Leapin' Lizards / BZOJ 1066 [SCOI2007]蜥蜴(网络流,最大流)
POJ 2711 Leapin' Lizards / HDU 2732 Leapin' Lizards / BZOJ 1066 [SCOI2007]蜥蜴(网络流,最大流) Description Yo ...
- POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory (网络流,最大流)
POJ 3436 ACM Computer Factory (网络流,最大流) Description As you know, all the computers used for ACM cont ...
- poj 1459 多源多汇点最大流
Sample Input 2 1 1 2 (0,1)20 (1,0)10 (0)15 (1)20 7 2 3 13 (0,0)1 (0,1)2 (0,2)5 (1,0)1 (1,2)8 (2,3)1 ...
随机推荐
- Pwnable-fd
打开Ubuntu输入ssh fd@pwnable.kr -p2222,连接之后输入密码guest 之后就是ls -l看看里面的文件和权限,fd.fd.c.flag 看看fd.c的源码 #include ...
- python 画小猪佩奇
转自:python画个小猪佩奇 # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """ Created on Mon May 20 11:36:03 2019 @auth ...
- ln -s 文件夹变成文件(txt) / linux 链接出错
问题: 平时没有注意过这这个问题,当我使用ln -s xxx yyy 将xxx 移动到yyy 路径时,文件夹就变成了txt文件, 解决: 找了半天,在stackoverflow上找到了答案,很简单, ...
- 10.python3实用编程技巧进阶(五)
5.1.如何派生内置不可变类型并修其改实例化行为 修改实例化行为 # 5.1.如何派生内置不可变类型并修其改实例化行为 #继承内置tuple, 并实现__new__,在其中修改实例化行为 class ...
- Fink| 实时热门商品
HotNItems 拓展需求:实时统计双十一下单量,实时统计成交额,实时查看锅炉温度变化曲线,每个5分钟看一下过去一个小时温度变化曲线, 涉及到的技术点:sliding window.Watermar ...
- Codeforces Round #573 (Div. 2) Tokitsukaze and Mahjong 水题
B. Tokitsukaze and Mahjong time limit per test1 second memory limit per test256 megabytes Tokitsukaz ...
- Note | MATLAB
目录 1. 读写文件 简单读写 将rgb保存为yuv文件 从yuv文件中读取Y通道 将TIFF图片拼接为yuv文件 2. 字符串操作 3. 画图 4. 词频统计 1. 读写文件 简单读写 fp = f ...
- Java实现字符串反转【Leetcode】
Write a function that reverses a string. The input string is given as an array of characters char[]. ...
- 一种单机支持 JavaWeb 容器万级并发的设想
当前的大部分 Java web 容器基于 Bio 线程模型,例如常见的 tomcat ,默认 200 线程,即 200 连接.由此带来的问题是,如果想提高并发,或者提高资源利用率,就得加大线程数. 如 ...
- LeetCode 622:设计循环队列 Design Circular Queue
LeetCode 622:设计循环队列 Design Circular Queue 首先来看看队列这种数据结构: 队列:先入先出的数据结构 在 FIFO 数据结构中,将首先处理添加到队列中的第一个元素 ...
