WGS84坐标和UTM坐标的转换
如题。做了一个Demo,主要是把最后面的参考资料1里面的脚本改成了C语言版本的.
代码:
#ifndef __COORCONV_H__
#define __COORCONV_H__ #include <cmath> double pi = 3.14159265358979; /* Ellipsoid model constants (actual values here are for WGS84) */
double sm_a = 6378137.0;
double sm_b = 6356752.314;
double sm_EccSquared = 6.69437999013e-03;
double UTMScaleFactor = 0.9996; typedef struct tagUTMCorr
{
double x;
double y;
}UTMCoor; typedef struct tagWGS84Corr
{
double lat;
double log;
}WGS84Corr;
/*
* DegToRad
*
* Converts degrees to radians.
*
*/
inline double DegToRad (double deg)
{
return (deg / 180.0 * pi);
} /*
* RadToDeg
*
* Converts radians to degrees.
*
*/
inline double RadToDeg (double rad)
{
return (rad / pi * 180.0);
} /*
* ArcLengthOfMeridian
*
* Computes the ellipsoidal distance from the equator to a point at a
* given latitude.
*
* Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J.,
* GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994.
*
* Inputs:
* phi - Latitude of the point, in radians.
*
* Globals:
* sm_a - Ellipsoid model major axis.
* sm_b - Ellipsoid model minor axis.
*
* Returns:
* The ellipsoidal distance of the point from the equator, in meters.
*
*/
double ArcLengthOfMeridian (double phi)
{
double alpha, beta, gamma, delta, epsilon, n;
double result; /* Precalculate n */
n = (sm_a - sm_b) / (sm_a + sm_b); /* Precalculate alpha */
alpha = ((sm_a + sm_b) / 2.0) * (1.0 + (pow(n, 2.0) / 4.0) + (pow(n, 4.0) / 64.0)); /* Precalculate beta */
beta = (-3.0 * n / 2.0) + (9.0 * pow(n, 3.0) / 16.0) + (-3.0 * pow(n, 5.0) / 32.0); /* Precalculate gamma */
gamma = (15.0 * pow(n, 2.0) / 16.0) + (-15.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 32.0); /* Precalculate delta */
delta = (-35.0 * pow(n, 3.0) / 48.0) + (105.0 * pow(n, 5.0) / 256.0); /* Precalculate epsilon */
epsilon = (315.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 512.0); /* Now calculate the sum of the series and return */
result = alpha * (phi + (beta * sin(2.0 * phi)) + (gamma * sin(4.0 * phi)) + (delta * sin(6.0 * phi)) + (epsilon * sin(8.0 * phi))); return result;
} /*
* UTMCentralMeridian
*
* Determines the central meridian for the given UTM zone.
*
* Inputs:
* zone - An integer value designating the UTM zone, range [1,60].
*
* Returns:
* The central meridian for the given UTM zone, in radians, or zero
* if the UTM zone parameter is outside the range [1,60].
* Range of the central meridian is the radian equivalent of [-177,+177].
*
*/
inline double UTMCentralMeridian (int zone)
{
return DegToRad(-183.0 + (zone * 6.0));
} /*
* FootpointLatitude
*
* Computes the footpoint latitude for use in converting transverse
* Mercator coordinates to ellipsoidal coordinates.
*
* Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J.,
* GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994.
*
* Inputs:
* y - The UTM northing coordinate, in meters.
*
* Returns:
* The footpoint latitude, in radians.
*
*/
double FootpointLatitude (double y)
{
double y_, alpha_, beta_, gamma_, delta_, epsilon_, n;
double result; /* Precalculate n (Eq. 10.18) */
n = (sm_a - sm_b) / (sm_a + sm_b); /* Precalculate alpha_ (Eq. 10.22) */
/* (Same as alpha in Eq. 10.17) */
alpha_ = ((sm_a + sm_b) / 2.0) * ( + (pow(n, 2.0) / ) + (pow(n, 4.0) / )); /* Precalculate y_ (Eq. 10.23) */
y_ = y / alpha_; /* Precalculate beta_ (Eq. 10.22) */
beta_ = (3.0 * n / 2.0) + (-27.0 * pow(n, 3.0) / 32.0) + (269.0 * pow(n, 5.0) / 512.0); /* Precalculate gamma_ (Eq. 10.22) */
gamma_ = (21.0 * pow(n, 2.0) / 16.0) + (-55.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 32.0); /* Precalculate delta_ (Eq. 10.22) */
delta_ = (151.0 * pow (n, 3.0) / 96.0) + (-417.0 * pow (n, 5.0) / 128.0); /* Precalculate epsilon_ (Eq. 10.22) */
epsilon_ = (1097.0 * pow(n, 4.0) / 512.0); /* Now calculate the sum of the series (Eq. 10.21) */
result = y_ + (beta_ * sin(2.0 * y_)) + (gamma_ * sin(4.0 * y_)) + (delta_ * sin(6.0 * y_)) + (epsilon_ * sin(8.0 * y_)); return result;
} /*
* MapLatLonToXY
*
* Converts a latitude/longitude pair to x and y coordinates in the
* Transverse Mercator projection. Note that Transverse Mercator is not
* the same as UTM; a scale factor is required to convert between them.
*
* Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J.,
* GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994.
*
* Inputs:
* phi - Latitude of the point, in radians.
* lambda - Longitude of the point, in radians.
* lambda0 - Longitude of the central meridian to be used, in radians.
*
* Outputs:
* xy - A 2-element array containing the x and y coordinates
* of the computed point.
*
* Returns:
* The function does not return a value.
*
*/
void MapLatLonToXY (double phi, double lambda, double lambda0, UTMCoor &xy)
{
double N, nu2, ep2, t, t2, l;
double l3coef, l4coef, l5coef, l6coef, l7coef, l8coef;
double tmp; /* Precalculate ep2 */
ep2 = (pow(sm_a, 2.0) - pow(sm_b, 2.0)) / pow(sm_b, 2.0); /* Precalculate nu2 */
nu2 = ep2 * pow(cos(phi), 2.0); /* Precalculate N */
N = pow(sm_a, 2.0) / (sm_b * sqrt( + nu2)); /* Precalculate t */
t = tan (phi);
t2 = t * t;
tmp = (t2 * t2 * t2) - pow (t, 6.0); /* Precalculate l */
l = lambda - lambda0; /* Precalculate coefficients for l**n in the equations below
so a normal human being can read the expressions for easting
and northing
-- l**1 and l**2 have coefficients of 1.0 */
l3coef = 1.0 - t2 + nu2; l4coef = 5.0 - t2 + * nu2 + 4.0 * (nu2 * nu2); l5coef = 5.0 - 18.0 * t2 + (t2 * t2) + 14.0 * nu2 - 58.0 * t2 * nu2; l6coef = 61.0 - 58.0 * t2 + (t2 * t2) + 270.0 * nu2 - 330.0 * t2 * nu2; l7coef = 61.0 - 479.0 * t2 + 179.0 * (t2 * t2) - (t2 * t2 * t2); l8coef = 1385.0 - 3111.0 * t2 + 543.0 * (t2 * t2) - (t2 * t2 * t2); /* Calculate easting (x) */
xy.x = N * cos (phi) * l + (N / 6.0 * pow(cos(phi), 3.0) * l3coef * pow(l, 3.0))
+ (N / 120.0 * pow(cos(phi), 5.0) * l5coef * pow(l, 5.0))
+ (N / 5040.0 * pow(cos (phi), 7.0) * l7coef * pow(l, 7.0)); /* Calculate northing (y) */
xy.y = ArcLengthOfMeridian (phi)
+ (t / 2.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 2.0) * pow(l, 2.0))
+ (t / 24.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 4.0) * l4coef * pow(l, 4.0))
+ (t / 720.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 6.0) * l6coef * pow(l, 6.0))
+ (t / 40320.0 * N * pow(cos(phi), 8.0) * l8coef * pow(l, 8.0));
} /*
* MapXYToLatLon
*
* Converts x and y coordinates in the Transverse Mercator projection to
* a latitude/longitude pair. Note that Transverse Mercator is not
* the same as UTM; a scale factor is required to convert between them.
*
* Reference: Hoffmann-Wellenhof, B., Lichtenegger, H., and Collins, J.,
* GPS: Theory and Practice, 3rd ed. New York: Springer-Verlag Wien, 1994.
*
* Inputs:
* x - The easting of the point, in meters.
* y - The northing of the point, in meters.
* lambda0 - Longitude of the central meridian to be used, in radians.
*
* Outputs:
* philambda - A 2-element containing the latitude and longitude
* in radians.
*
* Returns:
* The function does not return a value.
*
* Remarks:
* The local variables Nf, nuf2, tf, and tf2 serve the same purpose as
* N, nu2, t, and t2 in MapLatLonToXY, but they are computed with respect
* to the footpoint latitude phif.
*
* x1frac, x2frac, x2poly, x3poly, etc. are to enhance readability and
* to optimize computations.
*
*/
void MapXYToLatLon (double x, double y, double lambda0, WGS84Corr &philambda)
{
double phif, Nf, Nfpow, nuf2, ep2, tf, tf2, tf4, cf;
double x1frac, x2frac, x3frac, x4frac, x5frac, x6frac, x7frac, x8frac;
double x2poly, x3poly, x4poly, x5poly, x6poly, x7poly, x8poly; /* Get the value of phif, the footpoint latitude. */
phif = FootpointLatitude (y); /* Precalculate ep2 */
ep2 = (pow(sm_a, 2.0) - pow(sm_b, 2.0)) / pow(sm_b, 2.0); /* Precalculate cos (phif) */
cf = cos (phif); /* Precalculate nuf2 */
nuf2 = ep2 * pow (cf, 2.0); /* Precalculate Nf and initialize Nfpow */
Nf = pow(sm_a, 2.0) / (sm_b * sqrt( + nuf2));
Nfpow = Nf; /* Precalculate tf */
tf = tan (phif);
tf2 = tf * tf;
tf4 = tf2 * tf2; /* Precalculate fractional coefficients for x**n in the equations
below to simplify the expressions for latitude and longitude. */
x1frac = 1.0 / (Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**2) */
x2frac = tf / (2.0 * Nfpow); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**3) */
x3frac = 1.0 / (6.0 * Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**4) */
x4frac = tf / (24.0 * Nfpow); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**5) */
x5frac = 1.0 / (120.0 * Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**6) */
x6frac = tf / (720.0 * Nfpow); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**7) */
x7frac = 1.0 / (5040.0 * Nfpow * cf); Nfpow *= Nf; /* now equals Nf**8) */
x8frac = tf / (40320.0 * Nfpow); /* Precalculate polynomial coefficients for x**n.
-- x**1 does not have a polynomial coefficient. */
x2poly = -1.0 - nuf2; x3poly = -1.0 - * tf2 - nuf2; x4poly = 5.0 + 3.0 * tf2 + 6.0 * nuf2 - 6.0 * tf2 * nuf2 - 3.0 * (nuf2 *nuf2) - 9.0 * tf2 * (nuf2 * nuf2); x5poly = 5.0 + 28.0 * tf2 + 24.0 * tf4 + 6.0 * nuf2 + 8.0 * tf2 * nuf2; x6poly = -61.0 - 90.0 * tf2 - 45.0 * tf4 - 107.0 * nuf2 + 162.0 * tf2 * nuf2; x7poly = -61.0 - 662.0 * tf2 - 1320.0 * tf4 - 720.0 * (tf4 * tf2); x8poly = 1385.0 + 3633.0 * tf2 + 4095.0 * tf4 + * (tf4 * tf2); /* Calculate latitude */
philambda.lat = phif + x2frac * x2poly * (x * x) + x4frac * x4poly * pow(x, 4.0) + x6frac * x6poly * pow(x, 6.0) + x8frac * x8poly * pow(x, 8.0); /* Calculate longitude */
philambda.log = lambda0 + x1frac * x + x3frac * x3poly * pow(x, 3.0) + x5frac * x5poly * pow(x, 5.0) + x7frac * x7poly * pow(x, 7.0);
} /*
* LatLonToUTMXY
*
* Converts a latitude/longitude pair to x and y coordinates in the
* Universal Transverse Mercator projection.
*
* Inputs:
* lat - Latitude of the point, in radians.
* lon - Longitude of the point, in radians.
* zone - UTM zone to be used for calculating values for x and y.
* If zone is less than 1 or greater than 60, the routine
* will determine the appropriate zone from the value of lon.
*
* Outputs:
* xy - A 2-element array where the UTM x and y values will be stored.
*
* Returns:
* void
*
*/
void LatLonToUTMXY (double lat, double lon, int zone, UTMCoor &xy)
{
MapLatLonToXY (lat, lon, UTMCentralMeridian(zone), xy); /* Adjust easting and northing for UTM system. */
xy.x = xy.x * UTMScaleFactor + 500000.0;
xy.y = xy.y * UTMScaleFactor;
if (xy.y < 0.0)
xy.y += 10000000.0;
} /*
* UTMXYToLatLon
*
* Converts x and y coordinates in the Universal Transverse Mercator
* projection to a latitude/longitude pair.
*
* Inputs:
* x - The easting of the point, in meters.
* y - The northing of the point, in meters.
* zone - The UTM zone in which the point lies.
* southhemi - True if the point is in the southern hemisphere;
* false otherwise.
*
* Outputs:
* latlon - A 2-element array containing the latitude and
* longitude of the point, in radians.
*
* Returns:
* The function does not return a value.
*
*/
void UTMXYToLatLon (double x, double y, int zone, bool southhemi, WGS84Corr &latlon)
{
double cmeridian; x -= 500000.0;
x /= UTMScaleFactor; /* If in southern hemisphere, adjust y accordingly. */
if (southhemi)
y -= 10000000.0; y /= UTMScaleFactor; cmeridian = UTMCentralMeridian (zone);
MapXYToLatLon (x, y, cmeridian, latlon);
} #endif //__COORCONV_H__
然后用MFC写了一个类似的对话框程序:
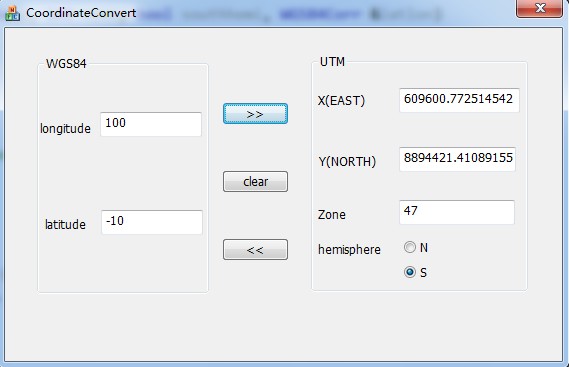
全部的源代码:
http://files.cnblogs.com/wb-DarkHorse/CoordinateConvert.rar
RERERENCE:
1 http://home.hiwaay.net/~taylorc/toolbox/geography/geoutm.html 网页版demo
2 http://www.mogoo.org/fang/?p=65 一位博客里面的,用Java写的
3 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universal_Transverse_Mercator_coordinate_system wiki的介绍,公式都写的很清楚,不多说
4 http://my.oschina.net/lidayong/blog/59869 一位博客里的,用c#写的
5 http://www.zhdzch.com/xxyd/chzs/200904/522.html 比较清楚的介绍,用VB写的
下面是国外的几篇资料:
http://www.movable-type.co.uk/scripts/latlong-vincenty-direct.html 根据经纬度求距离
http://www.ngs.noaa.gov/PUBS_LIB/inverse.pdf 对应上面链接的文章
http://trac.osgeo.org/proj/ 一个开源的地图投影库
WGS84坐标和UTM坐标的转换的更多相关文章
- 百度坐标(BD09)、国测局坐标(火星坐标,GCJ02)、和WGS84坐标系之间的转换(JS版代码)
/** * Created by Wandergis on 2015/7/8. * 提供了百度坐标(BD09).国测局坐标(火星坐标,GCJ02).和WGS84坐标系之间的转换 */ //定义一些常量 ...
- 转载: utm坐标和经纬度相互转换
原文地址: https://blog.csdn.net/hanshuobest/article/details/77752279 //经纬度转utm坐标 int convert_lonlat_utm( ...
- WGS84、Web墨卡托、火星坐标、百度坐标互转
转自:1.http://blog.csdn.net/wildboy2001/article/details/12031351 2.http://kongxz.com/2013/10/wgs-cgj/ ...
- WGS84、GCJ-02(火星坐标)、百度坐标,Web墨卡托坐标
GCJ-02坐标系统(火星坐标)简介:http://blog.csdn.net/giswens/article/details/8775121(存档:http://mapbd.com/cms/2012 ...
- 百度坐标(BD-09)、国测局坐标(火星坐标,GCJ-02)和WGS-84坐标互转
// 坐标转换 var coordTransform = (function () { // 一些常量 var PI = 3.1415926535897932384626; var X_PI = 3. ...
- 火星坐标、百度坐标、WGS84坐标转换代码(JS、python版)
火星坐标.百度坐标.WGS84坐标转换代码(JS.python版) 一.JS版本源码 github:https://github.com/wandergis/coordTransform /** * ...
- BD09坐标(百度坐标) WGS84(GPS坐标) GCJ02(国测局坐标) 的相互转换
BD09坐标(百度坐标) WGS84(GPS坐标) GCJ02(国测局坐标) 的相互转换 http://www.cnphp6.com/archives/24822 by root ⋅ Leave a ...
- 火星坐标、百度坐标、WGS84坐标转换代码(JS)
JS版本源码 /** * Created by Wandergis on 2015/7/8. * 提供了百度坐标(BD09).国测局坐标(火星坐标,GCJ02).和WGS84坐标系之间的转换 */ / ...
- wgs84 转百度经纬度坐标
/** * wgs84 转百度地图坐标 * @param $lng * @param $lat * @return array */ function toBaiduLocation($lng,$la ...
随机推荐
- NOI模拟赛Day5
T1 有and,xor,or三种操作,每个人手中一个数,求和左边进行某一种运算的最大值,当t==2时,还需要求最大值的个数. test1 20% n<=1000 O(n^2)暴力 test2 2 ...
- 对GitHub的认识
Github创建于2008年被市场研究公司Forrester称作开发者的Facebook .作为开源代码库以及版本控制系统,Github拥有140多万开发者用户.随着越来越多的应用程序转移到了云上,G ...
- Picture effect of JavaScript
每隔一定时间跟换图片Img = new Array("image/2.jpg","image/1.jpg","image/3.jpg",&q ...
- Jquery实现MD5加密
$.md5("你想要加密的字符串"); md5插件下载地址:http://xiazai.jb51.net/201003/yuanma/jquery_md5.rar <!DOC ...
- ambari无法登陆 设备空间不足
1.ambari无法登陆,Unable to connect to Ambari Server ? ——>原因:端口8080被spark占用.修改${SPARK_HOME}/sbin/start ...
- android-数据存储之手机内部file存储
一.基础概要 1.说明: 1>应用程序运行需要一些较大的数据或者图片可保存在手机内部 2>文件类型:任意 3>路径:/data/data/packageName/files/ 4&g ...
- Jquery广告浮动效果小案例
导入<script src="<%=path%>/html5/js/jquery.js"></script>文件 <SCRIPT type ...
- HDU 2577
How to Type Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Tota ...
- 网络地址转换NAT原理及其作用
1 概述 1.1 简介 NAT英文全称是“Network Address Translation”,中文意思是“网络地址转换”,它是一个IETF(Internet Engineering Task F ...
- [读书]10g/11g编程艺术深入体现结构学习笔记(持续更新...)
持续更新...) 第8章 1.在过程性循环中提交更新容易产生ora-01555:snapshot too old错误.P257 (这种情况我觉得应该是在高并发的情况下才会产生) 假设的一个场景是系统一 ...
