Hibernate--对象关系
在hibernate中,关联关系映射分为单向关联和双向关联。共有七种关系
hibernate在维护这几种关系的时候,要不通过连接表,要不通过外键的方式。
@Many To One
这是一种最常见的关系,hibernate是通过在many的一方加入one的一个主键作为外键的方式来管理关系的。
此时的多的一方和一的一方,需要各自管理,分别保存,也可以在many-to-one的配置中加入级联属性,则在保存多的一端的时候,会自动保存一的一端
先看配置文件版
package com.fuwh.model;
//one
public class Father { private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.model;
//Many
public class Child { private int id;
private String name;
//在many的一端中加入one作为一个属性变量
private Father father; public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public Father getFather() {
return father;
} public void setFather(Father father) {
this.father = father;
} }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Father" table="t_father">
<id name="id" column="fatherId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="fatherName"></property>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd">
<!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model">
<class name="Child" table="t_child">
<id name="id" column="childId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="childName"></property>
<!--
单向多(child)对一(father)的关系
会在多(child)的一方生成的表中添加一个外键,指向一(father)的主键
需要在多(child)的一方配置many-to-one
name:指定类中的Father对象变量
column:指定外键名字
cascade:表示级联操作,包含以下集中取值
none(默认),all,persist, merge, delete, save-update, evict, replicate,lock and refresh,delete-orphan ;
可以用逗号隔开,表示几个取值,all代表所有的
-->
<many-to-one name="father" column="father_Id" cascade="all"></many-to-one>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-configuration PUBLIC
"-//Hibernate/Hibernate Configuration DTD//EN"
"http://hibernate.sourceforge.net/hibernate-configuration-3.0.dtd"> <hibernate-configuration> <session-factory>
<!-- 数据库连接设置 -->
<property name="hibernate.connection.driver_class">com.mysql.jdbc.Driver</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.url">jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/hibernate</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.username">root</property>
<property name="hibernate.connection.password">mysqladmin</property>
<!--
指定方言,表明用的是哪种数据库,也可以不指定,hibernate默认会翻译成正确的数据库脚本
方言可以在 hibernate-release-xx.xx/project/etc/hibernate.properties 中查找
-->
<property name="hibernate.dialect">MySQL5</property>
<!-- 设定时候更新表结构,不存在或自动创建 -->
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto">update</property>
<!-- 配置 在后台打印出sql语句 -->
<property name="hibernate.show_sql">true</property>
<property name="hibernate.format_sql">true</property>
<!-- 引入实体类和表的映射文件 -->
<mapping resource="/com/fuwh/model/Father.hbm.xml"/>
<mapping resource="/com/fuwh/model/Child.hbm.xml"/> </session-factory> </hibernate-configuration>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
} }
执行空的测试语句,生成的sql文如下
Hibernate:
create table t_child (
childId integer not null auto_increment,
childName varchar(255),
father_Id integer,
primary key (childId)
)
Hibernate:
create table t_father (
fatherId integer not null auto_increment,
fatherName varchar(255),
primary key (fatherId)
)
Hibernate:
alter table t_child
add constraint FKg4qwua9ltkkkfik7fsvubyou7
foreign key (father_Id)
references t_father (fatherId)
操作表中的数据
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child;
import com.fuwh.model.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Father father=new Father();
father.setName("爸爸");
//因为在多的一断配置了级联属性为all,就表明把操作都交给了多的一端来维护关系,不需要保存father对象
//在保存child的时候,会自动保存father Child child1=new Child();
child1.setName("儿子1");
child1.setFather(father); Child child2=new Child();
child2.setName("儿子2");
child2.setFather(father); session.save(child1);
session.save(child2);
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close();
}
}
生成的sql文
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_father
(fatherName)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_child
(childName, father_Id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_child
(childName, father_Id)
values
(?, ?)


注解版
package com.fuwh.mto; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Father { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="fatherName")
private String name; public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.mto; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.ForeignKey;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Child { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="childName")
private String name; /**
* 定义多对一
* JoinCloumn中的name指定外键的列名,foreignkey中指定定义的外键的名字
* 这一列也可以不加,不加就是默认的设置
*/
@ManyToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name="father_id",foreignKey=@ForeignKey(name="FATHER_ID_FK"))
private Father father;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Father getFather() {
return father;
}
public void setFather(Father father) {
this.father = father;
} }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.mto.Child;
import com.fuwh.mto.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Father father=new Father();
father.setName("爸爸"); Child child1=new Child();
child1.setName("儿子一");
child1.setFather(father);
Child child2=new Child();
child2.setName("儿子二");
child2.setFather(father); session.save(child1);
session.save(child2); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
@One To Many单向
@One To Many关系把一个父节点和多个子节点联系起来,如果在子节点没有一个@Many To One和@One To Many相匹配的话,那就是一个单向的@One To Many,否则的话就是一个多向的@One To Many,并且可以在任意一边来维护关系。
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; public class Father { private int id;
private String name; private List<Child> children=new ArrayList<Child>(); public List<Child> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List<Child> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.model;
public class Child {
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model">
<class name="Child" table="t_child">
<id name="id" column="childId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="childName"></property>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Father" table="t_father">
<id name="id" column="fatherId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="fatherName"></property>
<set name="children" cascade="true">
<key column="father_Id"></key>
<one-to-many class="com.fuwh.model.Child"/>
</set>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
生成的sql文
Hibernate:
create table t_child (
childId integer not null auto_increment,
childName varchar(255),
father_Id integer,
primary key (childId)
)
Hibernate:
create table t_father (
fatherId integer not null auto_increment,
fatherName varchar(255),
primary key (fatherId)
)
Hibernate:
alter table t_child
add constraint FKev9uk6ojrjsv10ba9qoa4yhsy
foreign key (father_Id)
references t_father (fatherId)
注解版

package com.fuwh.otm; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Child { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="childName")
private String name; public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.otm; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Father { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="fatherName")
private String name; //orphanRemoval:表示在删除集合中的child的时候,也会删除child表中的相应纪录
@OneToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL,orphanRemoval=true)
private List<Child> children=new ArrayList<Child>(); public List<Child> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List<Child> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.otm.Child;
import com.fuwh.otm.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father();
father1.setName("爸爸1");
Father father2=new Father();
father2.setName("爸爸2");
Child child1=new Child();
child1.setName("儿子一");
Child child2=new Child();
child2.setName("儿子二"); father1.getChildren().add(child1);
father1.getChildren().add(child2); session.save(father1); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
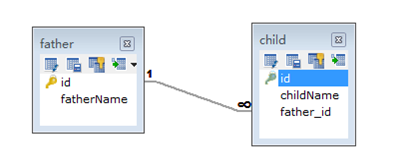
@One To Many双向
package com.fuwh.model;
public class Child {
private int id;
private String name;
private Father father;
public Father getFather() {
return father;
}
public void setFather(Father father) {
this.father = father;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set; public class Father { private int id;
private String name; private Set<Child> children=new HashSet<Child>(); public Set<Child> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(Set<Child> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Father" table="t_father">
<id name="id" column="fatherId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="fatherName"></property>
<set name="children">
<key column="father_Id"/>
<one-to-many class="com.fuwh.model.Child"/>
</set>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model">
<class name="Child" table="t_child">
<id name="id" column="childId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="childName"></property>
<many-to-one name="father" column="father_Id" cascade="all"></many-to-one>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child;
import com.fuwh.model.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Father father=new Father();
father.setName("爸爸");
Child child1=new Child();
child1.setName("儿子1");
Child child2=new Child();
child2.setName("儿子2"); child1.setFather(father);
child2.setFather(father); father.getChildren().add(child1);
father.getChildren().add(child2); session.save(child1);
session.save(child2); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
生成的sql
Hibernate:
select
father0_.fatherId as fatherId1_1_0_,
father0_.fatherName as fatherNa2_1_0_
from
t_father father0_
where
father0_.fatherId=?
Hibernate:
select
child0_.childId as childId1_0_0_,
child0_.childName as childNam2_0_0_,
child0_.father_Id as father_I3_0_0_
from
t_child child0_
where
child0_.childId=?
Hibernate:
select
children0_.father_Id as father_I3_0_0_,
children0_.childId as childId1_0_0_,
children0_.childId as childId1_0_1_,
children0_.childName as childNam2_0_1_,
children0_.father_Id as father_I3_0_1_
from
t_child children0_
where
children0_.father_Id=?
Hibernate:
update
t_child
set
childName=?,
father_Id=?
where
childId=?
Hibernate:
update
t_child
set
father_Id=?
where
childId=?
注解版
package com.fuwh.otmbi; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Father { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="fatherName")
private String name; /**
* orphanRemoval:表示在删除集合中的child的时候,也会删除child表中的相应纪录
* mappedBy/inverse:表示由另一方来维护关系
*
*/
@OneToMany(mappedBy="father",cascade=CascadeType.ALL,orphanRemoval=true) private List<Child> children=new ArrayList<Child>(); public List<Child> getChildren() {
return children;
}
public void setChildren(List<Child> children) {
this.children = children;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.otmbi; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Child { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="childName")
private String name; @ManyToOne
private Father father; public Father getFather() {
return father;
}
public void setFather(Father father) {
this.father = father;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.otmbi.Child;
import com.fuwh.otmbi.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father();
father1.setName("爸爸1");
Child child1=new Child();
child1.setName("儿子一");
child1.setFather(father1);
Child child2=new Child();
child2.setName("儿子二");
child2.setFather(father1); father1.getChildren().add(child1);
father1.getChildren().add(child2); session.save(father1);
session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
@One To One单向
单向的关系又可以分为基于主键的关联和基于外键的关联。
基于外键
package com.fuwh.model;
public class Wife {
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.fuwh.model;
public class Husband {
private int id;
private String name;
private Wife wife;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Wife getWife() {
return wife;
}
public void setWife(Wife wife) {
this.wife = wife;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife">
<id name="id" column="wifeId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="wifeName"></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model">
<class name="Husband" table="t_husband">
<id name="id" column="husbandId">
<!-- 主键生成策略为 外键 指向 wife-->
<generator class="foreign">
<param name="property">wife</param>
</generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="husbandName"></property>
<one-to-one name="wife" constrained="true"/>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child;
import com.fuwh.model.Father;
import com.fuwh.model.Husband;
import com.fuwh.model.Wife; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Husband husband=new Husband();
Wife wife=new Wife();
wife.setName("老婆"); husband.setName("老公");
husband.setWife(wife); session.save(wife);
session.save(husband); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
生成的sql文
Hibernate:
create table t_husband (
husbandId integer not null,
husbandName varchar(255),
primary key (husbandId)
)
Hibernate:
create table t_wife (
wifeId integer not null auto_increment,
wifeName varchar(255),
primary key (wifeId)
)
Hibernate:
alter table t_husband
add constraint FK2tae450lphjy8nciwyrxxlfkv
foreign key (husbandId)
references t_wife (wifeId)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_wife
(wifeName)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_husband
(husbandName, husbandId)
values
(?, ?)
在单向一对一中,hibernate默认是让client-side(上例的Husband)通过外键来管理关系的。
注解版

package com.fuwh.oto; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Father { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="fatherName")
private String name; public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.oto; import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Child { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="childName")
private String name; @OneToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name="father_id")
private Father father; public Father getFather() {
return father;
}
public void setFather(Father father) {
this.father = father;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.oto.Child;
import com.fuwh.oto.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father();
father1.setName("爸爸1");
Child child1=new Child();
child1.setName("儿子一");
child1.setFather(father1); session.save(child1); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
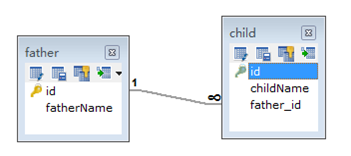
@One-To-One(双向)
package com.fuwh.model;
public class Wife {
private int id;
private String name;
private Husband husband;
public Husband getHusband() {
return husband;
}
public void setHusband(Husband husband) {
this.husband = husband;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife">
<id name="id" column="wifeId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="wifeName"></property>
<one-to-one name="husband"/> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
Hibernate:
create table t_husband (
husbandId integer not null,
husbandName varchar(255),
primary key (husbandId)
)
Hibernate:
create table t_wife (
wifeId integer not null auto_increment,
wifeName varchar(255),
primary key (wifeId)
)
Hibernate:
alter table t_husband
add constraint FK2tae450lphjy8nciwyrxxlfkv
foreign key (husbandId)
references t_wife (wifeId)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_wife
(wifeName)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_husband
(husbandName, husbandId)
values
(?, ?)
注解版
package com.fuwh.otobi; import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Father { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="fatherName")
private String name; @OneToOne(mappedBy="father",cascade=CascadeType.ALL,fetch=FetchType.LAZY)
private Child child; public Child getChild() {
return child;
}
public void setChild(Child child) {
this.child = child;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.otobi; import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.JoinColumn;
import javax.persistence.OneToOne; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity
public class Child { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id; @Column(name="childName")
private String name; @OneToOne(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
@JoinColumn(name="father_id")
private Father father; public Father getFather() {
return father;
}
public void setFather(Father father) {
this.father = father;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.otobi.Child;
import com.fuwh.otobi.Father; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Father father1=new Father();
father1.setName("爸爸1");
Child child1=new Child();
child1.setName("儿子一");
child1.setFather(father1); session.save(child1); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
@Many-To-Many(单向)
@Many-To-Many关系需要一个连接表来连接两张表。
package com.fuwh.model;
public class Wife {
private int id;
private String name;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set; public class Husband { private int id;
private String name;
private Set<Wife> wives=new HashSet<Wife>(); public Set<Wife> getWives() {
return wives;
} public void setWives(Set<Wife> wives) {
this.wives = wives;
} public int getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife">
<id name="id" column="wifeId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="wifeName"></property> </class> </hibernate-mapping>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model">
<class name="Husband" table="t_husband">
<id name="id" column="husbandId">
<generator class="native"/>
</id>
<property name="name" column="husbandName"></property>
<set name="wives" cascade="all">
<!-- key 指定连接表的主键列
many-to-many:中的列指定连接另一端的列,或对应的类
-->
<key column="husband_id"></key>
<many-to-many column="wife_id" class="com.fuwh.model.Wife"></many-to-many>
</set>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child;
import com.fuwh.model.Father;
import com.fuwh.model.Husband;
import com.fuwh.model.Wife; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Husband husband=new Husband();
husband.setName("老公"); Wife wife1=new Wife();
wife1.setName("老婆1");
Wife wife2=new Wife();
wife2.setName("老婆2"); husband.getWives().add(wife1);
husband.getWives().add(wife2);
// session.save(wife);
session.save(husband); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
注解
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="person")
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id;
@ManyToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
private List<Address> addresses=new ArrayList<Address>();
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public List<Address> getAddresses() {
return addresses;
}
public void setAddresses(List<Address> addresses) {
this.addresses = addresses;
} }
package com.fuwh.model; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="address")
public class Address { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id;
@Column(name="street")
private String street;
private String number;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
} }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Address;
import com.fuwh.model.Person; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Person person=new Person(); Address address1=new Address();
address1.setNumber("1001");
address1.setStreet("java路"); Address address2=new Address();
address2.setNumber("1002");
address2.setStreet("php路"); person.getAddresses().add(address1);
person.getAddresses().add(address2); session.save(person); session.flush();
//删除的时候会把所有的address的id的记录删除,在插入其他不用删除的
person.getAddresses().remove(address1); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
生成的SQL文
Hibernate:
create table address (
id integer not null auto_increment,
number varchar(255),
street varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table person (
id integer not null auto_increment,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table person_address (
person_id integer not null,
addresses_id integer not null
)
Hibernate:
alter table person_address
add constraint FKkvjdfs4jhjpxa6y3melormp0w
foreign key (addresses_id)
references address (id)
Hibernate:
alter table person_address
add constraint FKnndfs0btabect8upo03uwgfxt
foreign key (person_id)
references person (id)
Hibernate:
insert
into
person
values
( )
Hibernate:
insert
into
address
(number, street)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
address
(number, street)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
person_address
(person_id, addresses_id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
person_address
(person_id, addresses_id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
delete
from
person_address
where
person_id=?
Hibernate:
insert
into
person_address
(person_id, addresses_id)
values
(?, ?)
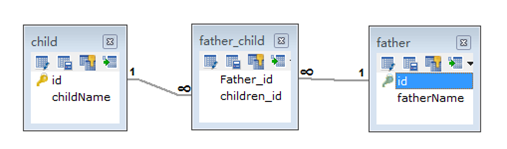
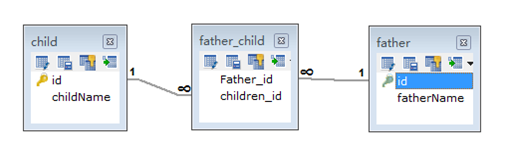
@Many-To-Many(双向)
package com.fuwh.model; import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Set; public class Wife { private int id;
private String name;
private Set<Husband> husbands=new HashSet<Husband>(); public Set<Husband> getHusbands() {
return husbands;
}
public void setHusbands(Set<Husband> husbands) {
this.husbands = husbands;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE hibernate-mapping PUBLIC "-//Hibernate/Hibernate Mapping DTD 3.0//EN" "http://www.hibernate.org/dtd/hibernate-mapping-3.0.dtd"> <!-- 这是实体类和表的映射关系的配置文件 -->
<hibernate-mapping package="com.fuwh.model"> <class name="Wife" table="t_wife">
<id name="id" column="wifeId">
<generator class="native"></generator>
</id>
<property name="name" column="wifeName"></property>
<!-- 这里必须参照Husband.hbm.xml文件中的连接表的配置,否则会默认生成两个连接表
也就是两个单向的多对多
-->
<set name="husbands" inverse="true" table="husband_wife">
<key column="wife_id"></key>
<many-to-many column="husband_id" class="com.fuwh.model.Husband" ></many-to-many>
</set>
</class> </hibernate-mapping>
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.model.Child;
import com.fuwh.model.Father;
import com.fuwh.model.Husband;
import com.fuwh.model.Wife; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Husband husband1=new Husband();
husband1.setName("老公1");
Husband husband2=new Husband();
husband2.setName("老公2"); Wife wife1=new Wife();
wife1.setName("老婆1");
Wife wife2=new Wife();
wife2.setName("老婆2"); husband1.getWives().add(wife1);
husband1.getWives().add(wife2);
wife1.getHusbands().add(husband1);
wife1.getHusbands().add(husband2); session.save(husband1);
session.save(husband2); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
生成的SQL文
Hibernate:
create table husband_wife (
husband_id integer not null,
wife_id integer not null,
primary key (husband_id, wife_id)
)
Hibernate:
create table t_husband (
husbandId integer not null auto_increment,
husbandName varchar(255),
primary key (husbandId)
)
Hibernate:
create table t_wife (
wifeId integer not null auto_increment,
wifeName varchar(255),
primary key (wifeId)
)
Hibernate:
alter table husband_wife
add constraint FK56txr9ocpn1k0eyc7ax1a2smw
foreign key (wife_id)
references t_wife (wifeId)
Hibernate:
alter table husband_wife
add constraint FKsiwjiutn6eoha0iv059pd75fc
foreign key (husband_id)
references t_husband (husbandId)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_husband
(husbandName)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_wife
(wifeName)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_husband
(husbandName)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
t_wife
(wifeName)
values
(?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
husband_wife
(husband_id, wife_id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
husband_wife
(husband_id, wife_id)
values
(?, ?)
注解
package com.fuwh.mtmbi; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.CascadeType;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="person")
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id;
@ManyToMany(cascade=CascadeType.ALL)
private List<Address> addresses=new ArrayList<Address>();
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public List<Address> getAddresses() {
return addresses;
}
public void setAddresses(List<Address> addresses) {
this.addresses = addresses;
} }
package com.fuwh.mtmbi; import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.ManyToMany; import org.hibernate.annotations.GenericGenerator; @Entity(name="address")
public class Address { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator="_native")
@GenericGenerator(name="_native",strategy="native")
private int id;
@Column(name="street")
private String street;
private String number;
@ManyToMany(mappedBy="address")
private List<Person> owners=new ArrayList<Person>(); public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStreet() {
return street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
} }
package com.fuwh.service; import org.hibernate.Session;
import org.hibernate.SessionFactory;
import org.hibernate.boot.MetadataSources;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistry;
import org.hibernate.boot.registry.StandardServiceRegistryBuilder;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test; import com.fuwh.mtmbi.Person;
import com.fuwh.mtmbi.Address; public class DoTest { //标准的sessionFactory取得方式
private SessionFactory sessionFactory; @Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
final StandardServiceRegistry registry=new StandardServiceRegistryBuilder().configure().build();
try {
sessionFactory=new MetadataSources(registry).buildMetadata().buildSessionFactory();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
e.printStackTrace();
StandardServiceRegistryBuilder.destroy(registry);
}
} @After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
if(sessionFactory != null){
sessionFactory.close();
}
} @Test
public void testAdd() {
Session session=sessionFactory.openSession();
session.beginTransaction(); Person person1=new Person();
Person person2=new Person();
Address address1=new Address();
address1.setNumber("101");
Address address2=new Address();
address2.setNumber("102");
person1.getAddresses().add(address1);
person1.getAddresses().add(address2); person2.getAddresses().add(address1);
session.save(person1);
session.save(person2); session.getTransaction().commit();
session.close(); }
}
生成的SQL文
Hibernate:
create table address (
id integer not null auto_increment,
number varchar(255),
street varchar(255),
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table person (
id integer not null auto_increment,
primary key (id)
)
Hibernate:
create table person_address (
owners_id integer not null,
addresses_id integer not null
)
Hibernate:
alter table person_address
add constraint FKkvjdfs4jhjpxa6y3melormp0w
foreign key (addresses_id)
references address (id)
Hibernate:
alter table person_address
add constraint FKpts56mn8uttsyi3b63b2cihvo
foreign key (owners_id)
references person (id)
Hibernate:
insert
into
person
values
( )
Hibernate:
insert
into
address
(number, street)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
address
(number, street)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
person
values
( )
Hibernate:
insert
into
person_address
(owners_id, addresses_id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
person_address
(owners_id, addresses_id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate:
insert
into
person_address
(owners_id, addresses_id)
values
(?, ?)
Hibernate--对象关系的更多相关文章
- hibernate对象关系实现(一)一对多
hibernate是对jdk一个封装工具,实现对象和数据库之间数据映射.使用时涉及到四个问题:a.对象之间的关系在类中的体现:b,对象关系对应的数据库中表之间体现:c.实现a,b在hibernate的 ...
- Hibernate 对象关系映射文件
简介: POJO 类和关系型数据库之间的映射可以用一个 XML 文档来定义 通过 POJO 类的数据库映射文件,Hibernate 可以理解持久化类和数据表之间的对应关系,也可以理解持久化类属性与数据 ...
- hibernate对象关系实现(二)一对一
双向一对一以部门和经理为例: a.部门和经理类中各自由对方的引用:(省略了get/set方法) b.数据库两种方式实现:一种(b.1)是外键映射,并将外键添加唯一约束(至于哪个对象的主键做外键,可随意 ...
- hibernate对象关系映射( 一对一,一对多,多对一,多对多的单向,双向映射 ——)
对象之间的关系: 关系映射之间的关系只的是对象之间的关系,并不指数据库表的关系(外键关系)这儿解决的问题是当对象之间的关系之一时,数据库表该如何映射,编程上如何对待. 一对一(主键关联,和单向的外键关 ...
- hibernate对象关系实现(三)多对多实现
单向n-n:(catogory-item)一个类别对应多个条目,一个条目对应多个类别 a.以类别类中有条目的集合的引用为例: b.数据库中的体现:建立一个新表,以类别和条目的主键关联的外键做新表的联合 ...
- hibernate对象关系实现(四)继承实现
继承实现方式分为三种:subclass; joined-subclass;union-subclass a.类中体现 b.库中体现分为三种: b.1:一种方式:人和学生公用一张表,添加一个辨别字段 ...
- hibernate对象关系映射的配置
一对一主键关联单双向 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE hibernate-m ...
- Hibernate -- 对象关系映射基础
- Hibernate(开放源代码的对象关系映射框架)
Hibernate是一个开放源代码的对象关系映射框架,它对JDBC进行了非常轻量级的对象封装,它将POJO与数据库表建立映射关系,是一个全自动的orm框架,hibernate可以自动生成SQL语句,自 ...
- hibernate(四)__由表逆向创建Domain对象和对象关系映射文件
之前我们是手写Domain对象和对象关系映射文件->然后生成数据库中的Table. 现在我们反过来先在数据库中建好Table->然后用工具生成Domain对象和对象关系映射文件. 步骤: ...
随机推荐
- [BZOJ 1190][HNOI2007]梦幻岛宝珠
1190: [HNOI2007]梦幻岛宝珠 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 1057 Solved: 611[Submit][Stat ...
- TOJ 1214: 数据结构练习题――线性表操作
描述 请你定义一个线性表,可以对表进行"在某个位置之前插入一个元素"."删除某个位置的元素"."清除所有元素"."获取某个位置的元 ...
- python+selenium:解决上传文件<input type='file'>标签属性被css的visibility隐藏导致无法定位元素的问题
要想上传文件,需要找到在HTML中<input type="file" />这个标签,有它就可以利用send_keys上传文件,不过这里的<input>元素 ...
- Beta冲刺链接总汇
Beta冲刺 咸鱼 Beta 冲刺day1 Beta 冲刺day2 Beta 冲刺day3 Beta 冲刺day4 Beta 冲刺day5 Beta 冲刺day6 Beta 冲刺day7 凡事预则立- ...
- C语言的第 次作业总结
PTA实验作业 第一题: 使用函数输出水仙花数 1.设计思路: 2.碰到的问题及解决方法: 实验中碰到的主要问题是:虽然知道如何求每一位的数但不知道如何输出m到n之间的水仙花数,我上面截图中的和瓮恺视 ...
- scrapy crawl rules设置
rules = [ Rule(SgmlLinkExtractor(allow=('/u012150179/article/details'), restrict_xpaths=('//li[@clas ...
- Network in Network
 论文要点: 用更有效的非线性函数逼近器(MLP,multilayer perceptron)代替 GLM 以增强局部模型的抽象能力.抽象能力指的模型中特征是对于同一概念的变体的不变形. 使用 gl ...
- 第一篇:Python入门
一.编程与编程语言 编程的目的: 计算机的发明,是为了用机器取代/解放人力,而编程的目的则是将人类的思想流程按照某种能够被计算机识别表达方式传递给计算机,从而达到让计算机能够像人脑/电脑一样自动执行的 ...
- 职场选择之大公司 VS 小公司
其实这是个非常难回答的问题,很多职场新人都会有类似的顾虑和疑问. 这个问题就好比业界比较容易引起争议的编程语言哪个是最好的一样.大公司还是小公司里面发展,只有身处其中才能体会,如人饮水,冷暖自知. 笔 ...
- php框架中的phalcon框架的安装,及初步认识,从表单提交简单的数据到数据库中
php框架中的phalcon框架的安装,及初步认识,从表单提交简单的数据到数据库中 1.phalcon框架的安装: phalcon框架在windows本地安装可以利用wamp软件,安装之后可以查看对应 ...
