The Runtime Interaction Model for Views-UI布局事件处理流程
The Runtime Interaction Model for Views
Any time a user interacts with your user interface, or any time your own code programmatically changes something, a complex sequence of events takes place inside of UIKit to handle that interaction. At specific points during that sequence, UIKit calls out to your view classes and gives them a chance to respond on behalf of your application. Understanding these callout points is important to understanding where your views fit into the system. Figure 1-7shows the basic sequence of events that starts with the user touching the screen and ends with the graphics system updating the screen content in response. The same sequence of events would also occur for any programmatically initiated actions.
Figure 1-7 UIKit interactions with your view objects 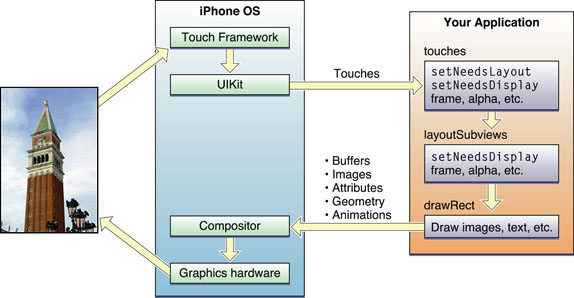
The following steps break the event sequence in Figure 1-7 down even further and explain what happens at each stage and how you might want your application to react in response.
The user touches the screen.
The hardware reports the touch event to the UIKit framework.
The UIKit framework packages the touch into a
UIEventobject and dispatches it to the appropriate view. (For a detailed explanation of how UIKit delivers events to your views, see Event Handling Guide for iOS.)The event-handling code of your view responds to the event. For example, your code might:
Change the properties (frame, bounds, alpha, and so on) of the view or its subviews.
Call the
setNeedsLayoutmethod to mark the view (or its subviews) as needing a layout update.Call the
setNeedsDisplayorsetNeedsDisplayInRect:method to mark the view (or its subviews) as needing to be redrawn.Notify a controller about changes to some piece of data.
Of course, it is up to you to decide which of these things the view should do and which methods it should call.
If the geometry of a view changed for any reason, UIKit updates its subviews according to the following rules:
If you have configured autoresizing rules for your views, UIKit adjusts each view according to those rules. For more information about how autoresizing rules work, see Handling Layout Changes Automatically Using Autoresizing Rules.
If the view implements the
layoutSubviewsmethod, UIKit calls it.You can override this method in your custom views and use it to adjust the position and size of any subviews. For example, a view that provides a large scrollable area would need to use several subviews as “tiles” rather than create one large view, which is not likely to fit in memory anyway. In its implementation of this method, the view would hide any subviews that are now offscreen or reposition them and use them to draw newly exposed content. As part of this process, the view’s layout code can also invalidate any views that need to be redrawn.
If any part of any view was marked as needing to be redrawn, UIKit asks the view to redraw itself.
For custom views that explicitly define a
drawRect:method, UIKit calls that method. Your implementation of this method should redraw the specified area of the view as quickly as possible and nothing else. Do not make additional layout changes at this point and do not make other changes to your application’s data model. The purpose of this method is to update the visual content of your view.Standard system views typically do not implement a
drawRect:method but instead manage their drawing at this time.Any updated views are composited with the rest of the application’s visible content and sent to the graphics hardware for display.
The graphics hardware transfers the rendered content to the screen.
https://developer.apple.com/library/content/documentation/WindowsViews/Conceptual/ViewPG_iPhoneOS/WindowsandViews/WindowsandViews.html#//apple_ref/doc/uid/TP40009503-CH2-SW5
The Runtime Interaction Model for Views-UI布局事件处理流程的更多相关文章
- iOS-屏幕适配-UI布局
iOS 屏幕适配:autoResizing autoLayout和sizeClass 一.图片解说 -------------------------------------------------- ...
- iOS开发~UI布局(三)深入理解autolayout
一.概要 通过对iOS8界面布局的学习和总结,发现autolayout才是主角,autolayout是iOS6引入的新特性,当时还粗浅的学习了下,可是没有真正应用到项目中.随着iOS设备尺寸逐渐碎片化 ...
- 移动UI布局设计原则(一)
学习笔记1 Learning notes one 移动UI布局设计的布局原则 Layout Principles of Mobile UI Layout Design 移动UI视觉交互设计法则 Des ...
- Duilib源码分析(五)UI布局—Layout与各子控件
接下来,继续分析duilib之UI布局Layout,目前提供的布局有:VerticalLayout.HorizontalLayout.TileLayout.TabLayout.ChildLayout分 ...
- iOS开发之遍历Model类的属性并完善使用Runtime给Model类赋值
在上篇博客<iOS开发之使用Runtime给Model类赋值>中介绍了如何使用运行时在实体类的基类中添加给实体类的属性赋值的方法,这个方法的前提是字典的Key必须和实体类的Property ...
- AppleWatch___学习笔记(二)UI布局和UI控件
1.UI布局 直接开发,你会发现Apple Watch并不支持AutoLayout,WatchKit里有个类叫做WKInterfaceGroup,乍一看像是UIView,但是这货其实是用来布局的.从 ...
- iOS开发~UI布局(二)storyboard中autolayout和size class的使用详解
一.概要:前一篇初步的描述了size class的概念,那么实际中如何使用呢,下面两个问题是我们一定会遇到的: 1.Xcode6中增加了size class,在storyboard中如何使用? 2.a ...
- iOS开发~UI布局(一)初探Size Class
随着iOS8系统的发布,一个全新的页面UI布局概念出现,这个新特性将颠覆包括iOS7及之前版本的UI布局方式,这个新特性就是Size Class.Size Class配合Auto Layout可以解决 ...
- WPF UI布局之概述
在线演示:http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XNzA5NDk2Mjcy.html 清晰版视频+代码下载:http://115.com/lb/5lbeer0m9lad 一.简单介 ...
随机推荐
- MAVEN项目模块化
maven的最大的特点之中的一个就是能够把项目模块化. 前面的一篇文章MAVEN创建并打包web项目已经创建了一个简单的webapp,注意这个webapp的打包方式是war. 假设如今又要划分出来一个 ...
- 图像处理之基础---用Shader实现的YUV到RGB转换:使用3重纹理实现 .
上一篇中,我是用一个RGB格式的纹理来存储每一帧的画面,其中纹理为m_FrameWidth * m_FrameHeight大小,这样,在内存中,就必须要先对YUV的数据进行排序,然后才能当做RGB的数 ...
- git 在一台机器上配置多个账户
前提: 必须知道怎样配置git账户,请參考git官方教程:https://help.github.com/articles/generating-ssh-keys 这个教程能教你怎样生成ssh-key ...
- (二)Java 简介
Java 简介 Java是由Sun Microsystems公司于1995年5月推出的Java面向对象程序设计语言和Java平台的总称.由James Gosling和同事们共同研发,并在1995年正式 ...
- 危险的kill
. ps -aux | grep -E "chk.*url.*py" | cut -c 10-15 | xargs kill -9 ps -x | grep -E "ch ...
- Dagger2----一个最简单的Dagger2依赖的实现
Dagger2是首个使用生成代码实现完整依赖注入的框架,极大降低了使用者的编码负担.Dagger2分析全部依赖并生成代码将这些依赖组织在一起,关于很多其它的Dagger2理论介绍请移步具体解释Dagg ...
- jquery uploadify在谷歌浏和火狐下无法上传的解决方案(.Net版)
在项目紧张的进行过程中,jquery uploadify上传不兼容的问题一直没有试着去解决,只幻想着用ie的人越来越多,怎么奈何firefox4刚推出,就有4000万的下载.......仰天长叹,记生 ...
- scapy基础-网络数据包结构
网络层次模型,数据包的组成是学习scapy的基础,下文主要关注模型中各个层次的用途,ethernet II和ip包数据结构. 1.五层模型简介 名称 作用 包含协议 应用层 面向程序对程序的传输 ...
- mybaties中,模糊查询的几种写法
模糊查询: 工作中用到,写三种用法吧,第四种为大小写匹配查询 1. sql中字符串拼接 SELECT * FROM tableName WHERE name LIKE CONCAT(CONCAT('% ...
- 4-2 买家类目-dao(下)
查询出来的对象ProductCategory就已经有updateTime和createTime了,然而你只是把对象的categoryType给修改了一下,修改之后就执行save方法保存了.所以它还是原 ...
